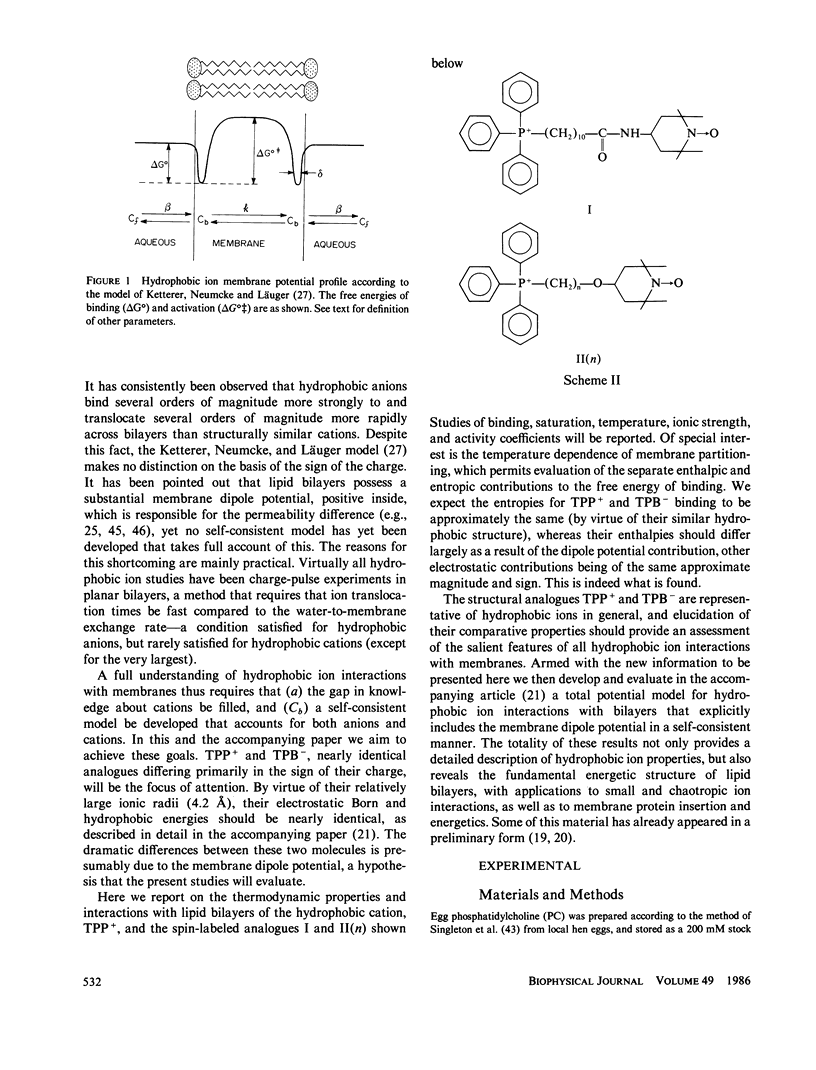
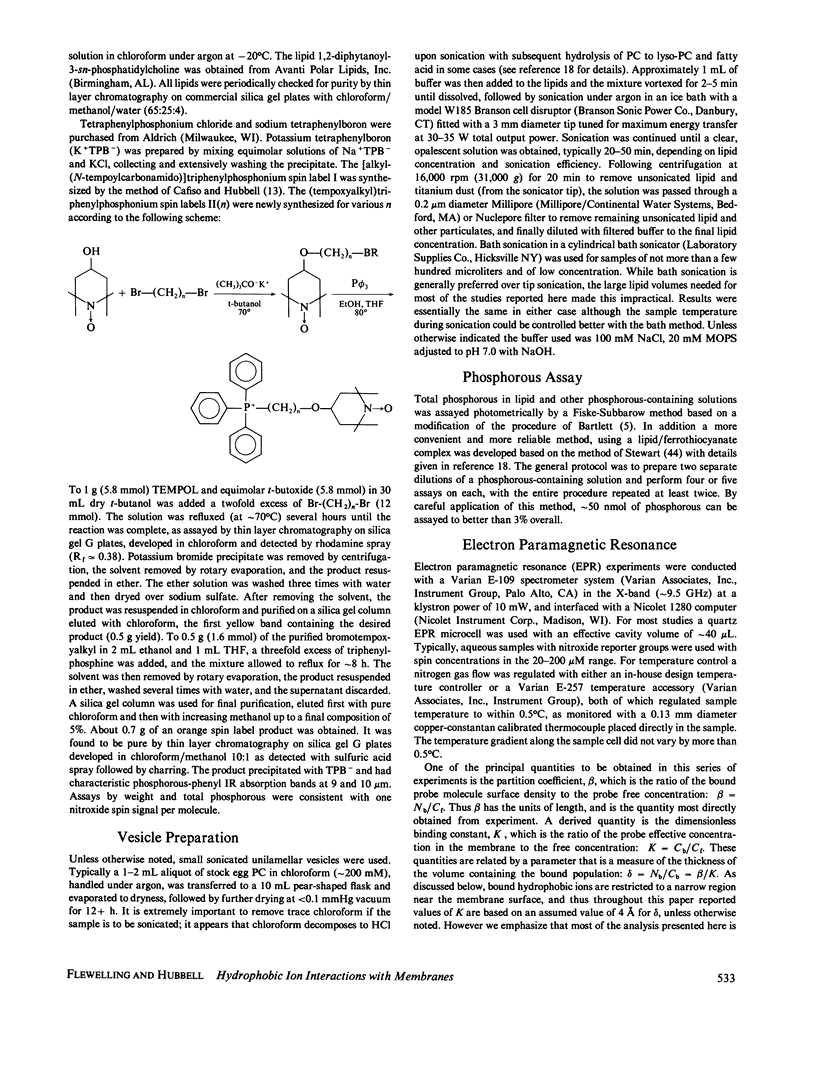
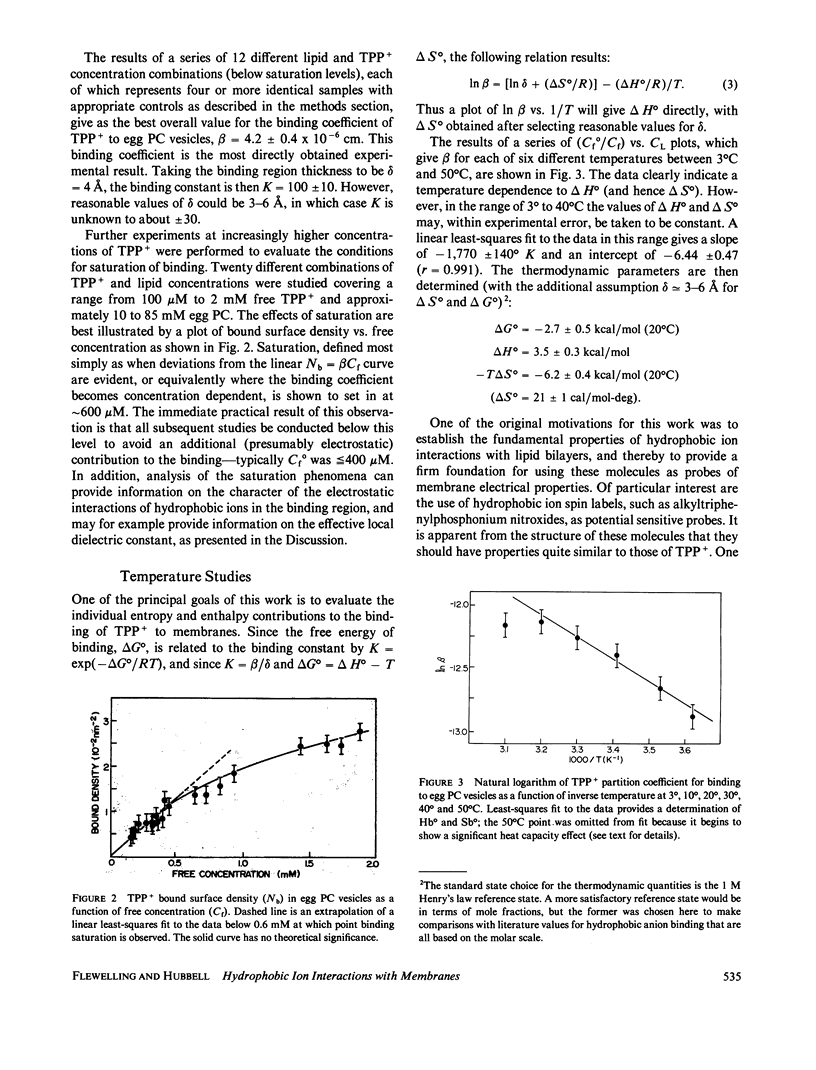
Abstract
The thermodynamic properties for the interaction of the hydrophobic ion tetraphenylphosphonium (TPP+) with egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles were studied in detail by equilibrium dialysis and spin label techniques. A partition coefficient of beta = 4.2 + 0.4 x 10(-6) cm (K congruent to 100) was determined. Electrostatic saturation sets in at approximately 600 microM (about one absorbed TPP+ molecule per 100 lipids), and is not screened by salt. The temperature dependence of binding was determined, which reveals that the binding is entropy-driven with a positive (repulsive) enthalpy of binding, a result to be compared with hydrophobic anions in which the binding enthalpy is negative. The membrane dipole potential may be responsible for this binding difference. Activity coefficients are determined and shown to be significantly different from those of most common salts, an important result that should be considered in all hydrophobic ion studies. Comparison of the TPP+ results with those of its anionic structural analogue, tetraphenylboron (TPB-), permits a general analysis of hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. A theoretical model consistent with the entire set of data is developed in an accompanying article.
Full text
PDF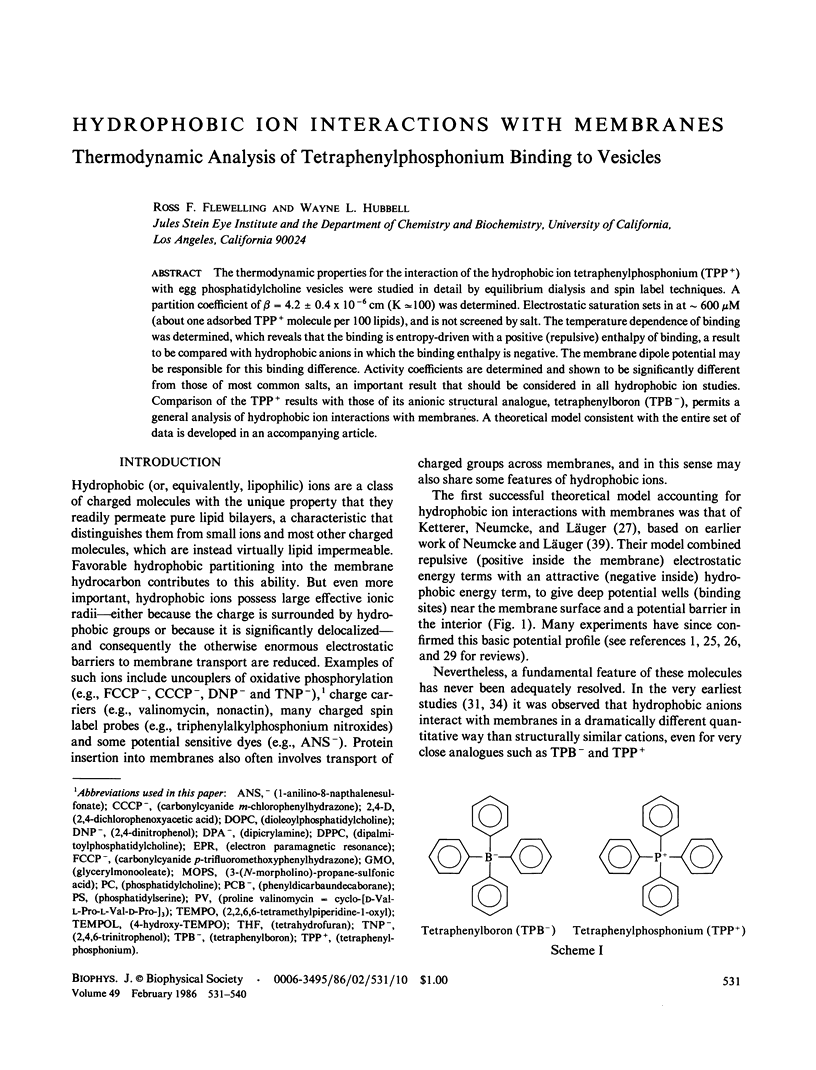





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Feldberg S., Nakadomari H., Levy S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):35–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Fuchs M. Potential energy barriers to ion transport within lipid bilayers. Studies with tetraphenylborate. Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):795–830. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85856-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Cros D. Influence of sterols on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Gisin B. F. Influence of membrane structure on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jun 9;40(4):293–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01874161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Läuger P., Janko K. Transport kinetics of hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Charge-pulse relaxation studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):701–720. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Läuger P. Transport kinetics of dipicrylamine through lipid bilayer membranes. Effects of membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 14;468(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock W., Stark G., Jordan P. C. A laser-temperature-jump method for the study of the rate of transfer of hydrophobic ions and carriers across the interface of thin lipid membranes. Biophys Chem. 1981 Aug;13(4):329–348. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)85007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner L. J. Blocking phenomena and charge transport through membranes. Biophysik. 1970;6(3):241–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01189085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner L. J. The interaction of hydrophobic ions with lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1975;22(2):125–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01868167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. EPR determination of membrane potentials. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:217–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Electrogenic H+/OH- movement across phospholipid vesicles measured by spin-labeled hydrophobic ions. Biophys J. 1983 Oct;44(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84276-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Light-induced interfacial potentials in photoreceptor membranes. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):243–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85092-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Hladky S. B. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: a critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1972 May;5(2):187–282. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Läuger P. Electrical noise from lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of hydrophobic ions. J Membr Biol. 1977 Dec 15;37(3-4):321–345. doi: 10.1007/BF01940938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blanc O. H., Jr Tetraphenylborate conductance through lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):350–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Topaly V. P. Selective transport of ions through bimolecular phospholipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P., Benz R., Stark G., Bamberg E., Jordan P. C., Fahr A., Brock W. Relaxation studies of ion transport systems in lipid bilayer membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Nov;14(4):513–598. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000247x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Membrane surface potential measurements with amphiphilic spin labels. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:515–526. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnik E., Latorre R., Hall J. E., Tosteson D. C. Phloretin-induced changes in ion transport across lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):243–257. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Läuger P. Nonlinear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. II. Integration of the generalized Nernst-Planck equations. Biophys J. 1969 Sep;9(9):1160–1170. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86443-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. C. Colorimetric determination of phospholipids with ammonium ferrothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G. Dual mechanism for the action of cholesterol on membrane permeability. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):47–49. doi: 10.1038/252047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Eisenman G., McLaughlin S. G., Krasne S. Ionic probes of membrane structures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:273–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Hladky S. B. Ion repulsion within membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84489-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Bruner L. J. Lipid-dependent and phloretin-induced modifications of dipicrylamine adsorption by bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):268–270. doi: 10.1038/272268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


