Abstract
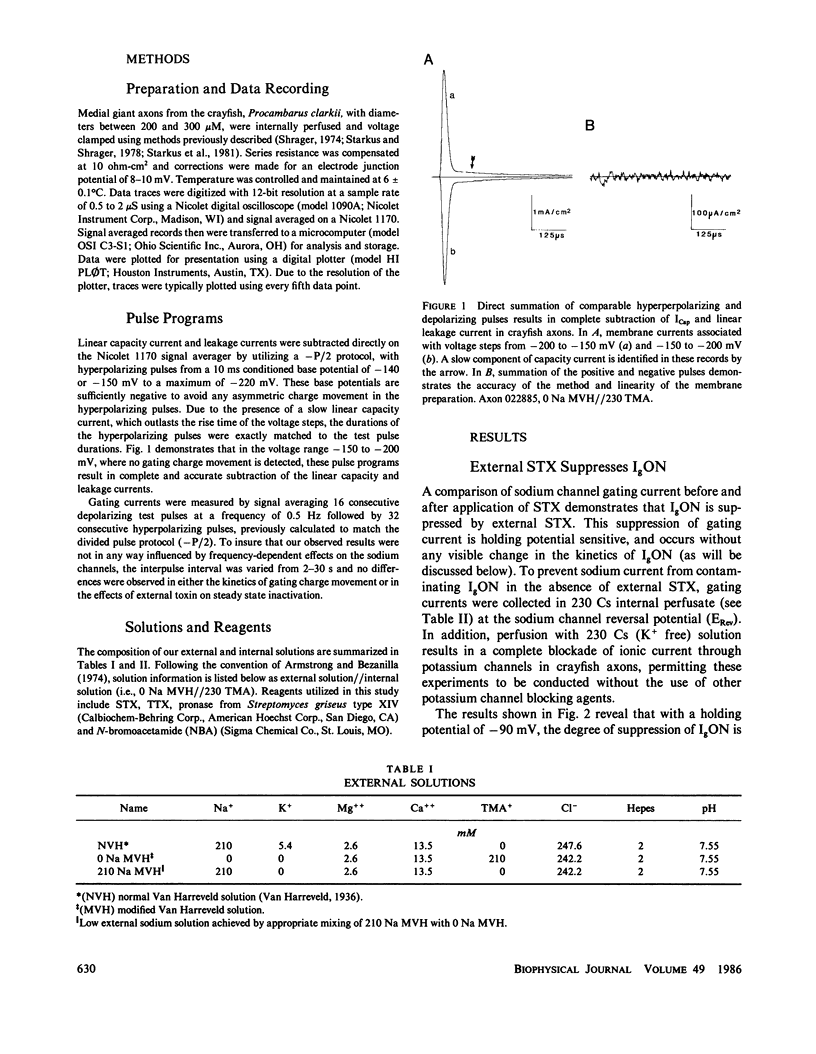
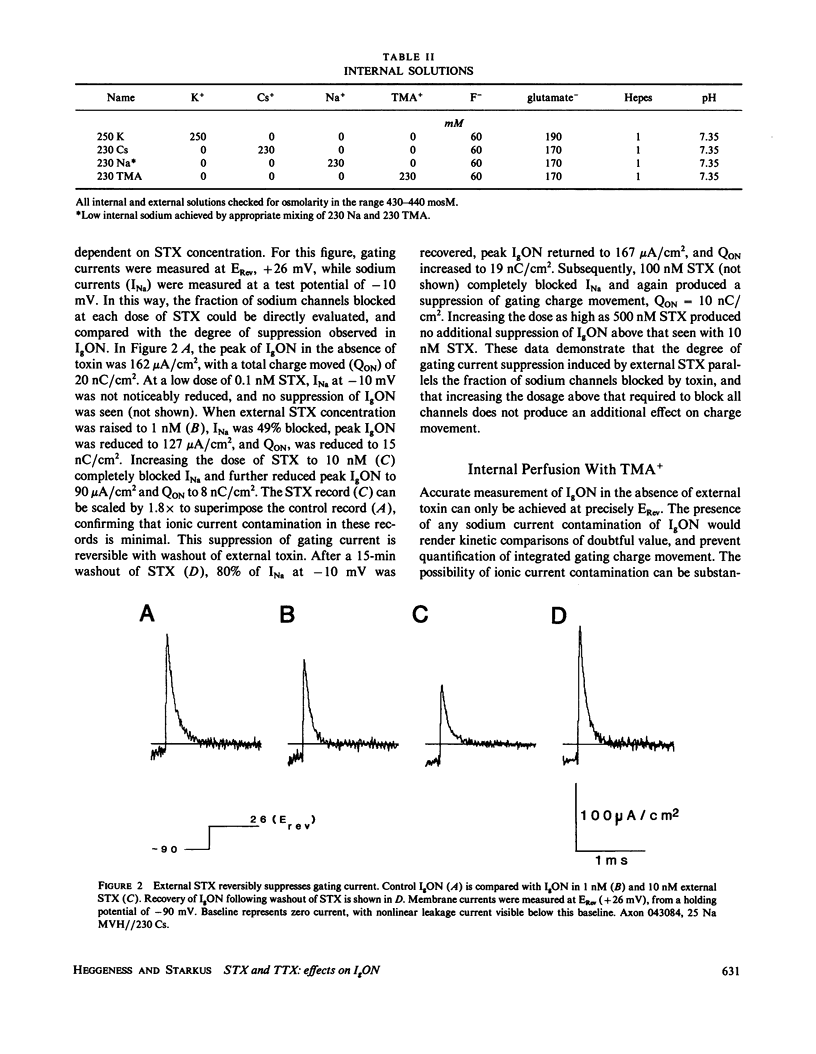
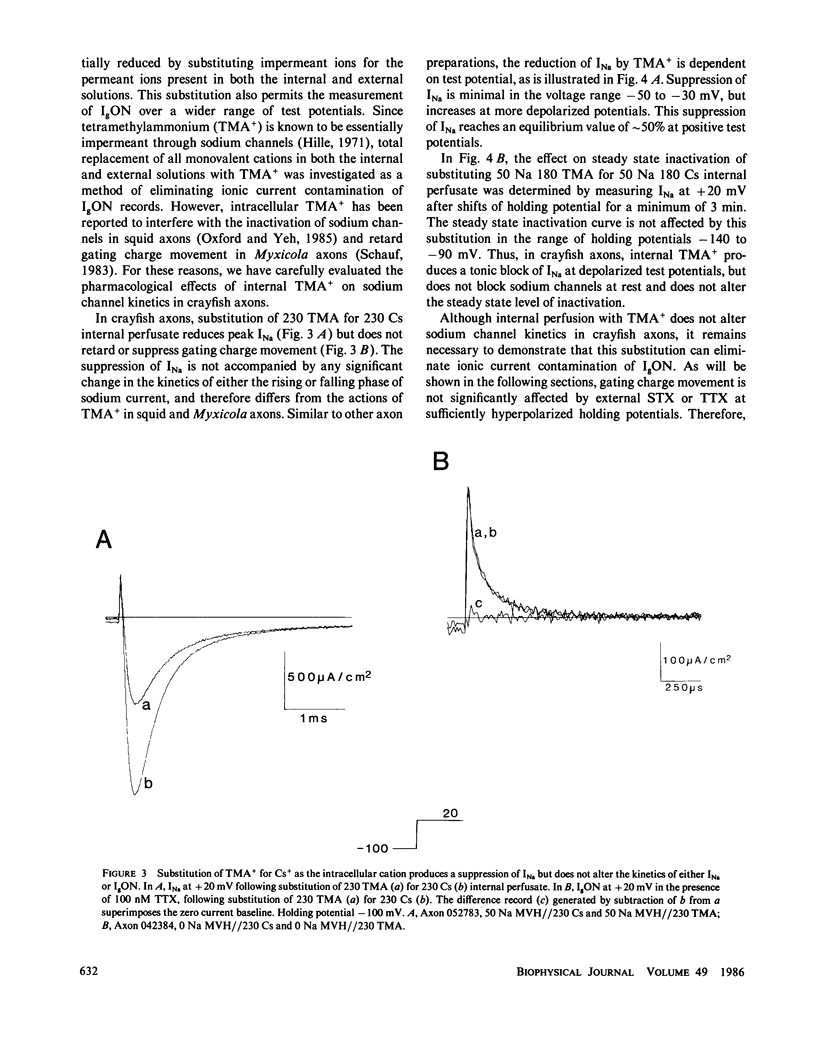
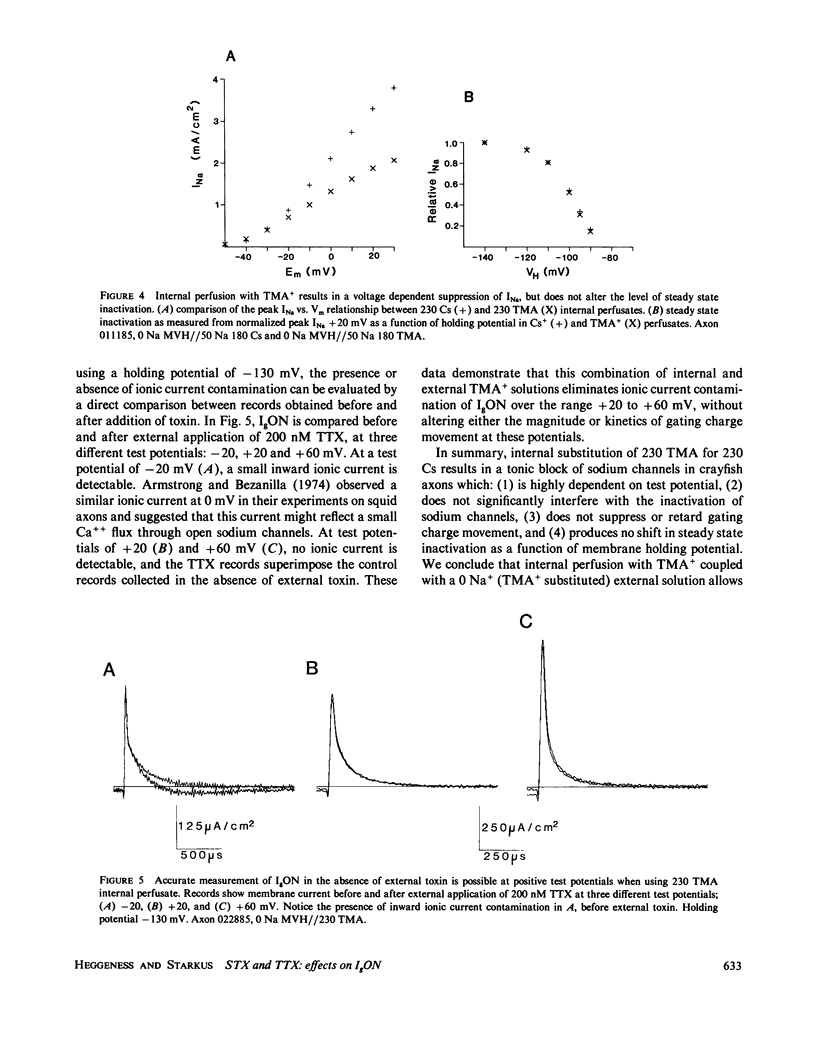
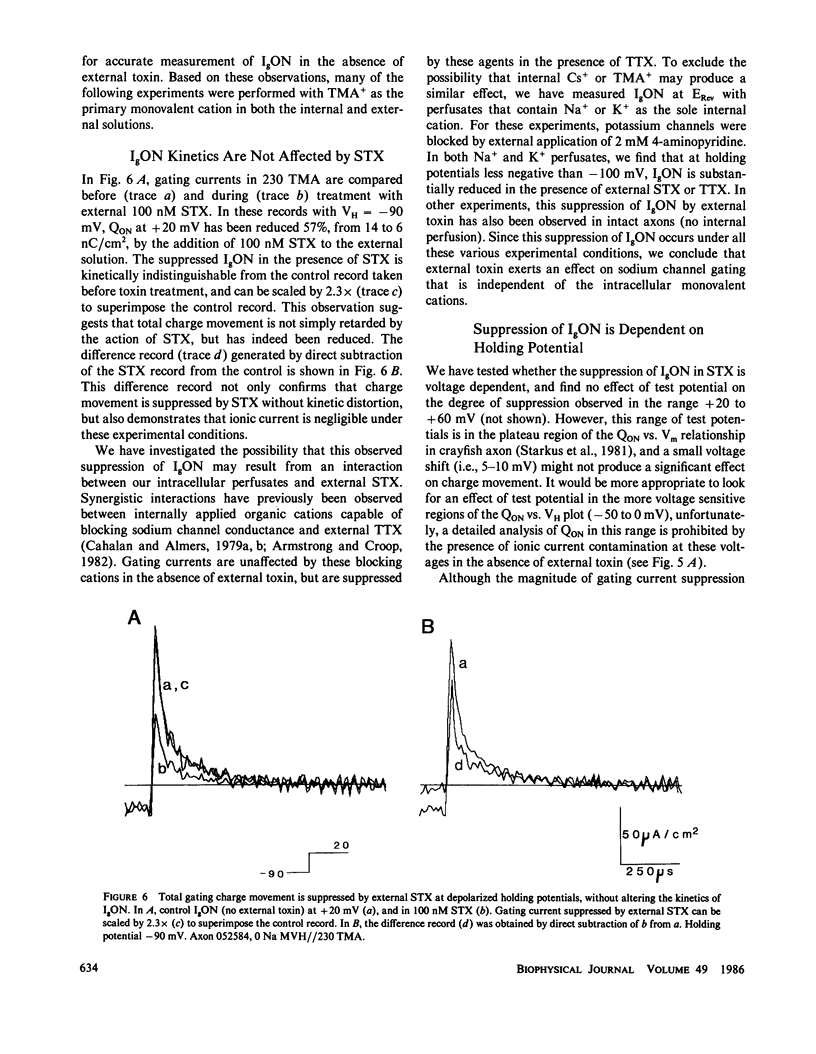
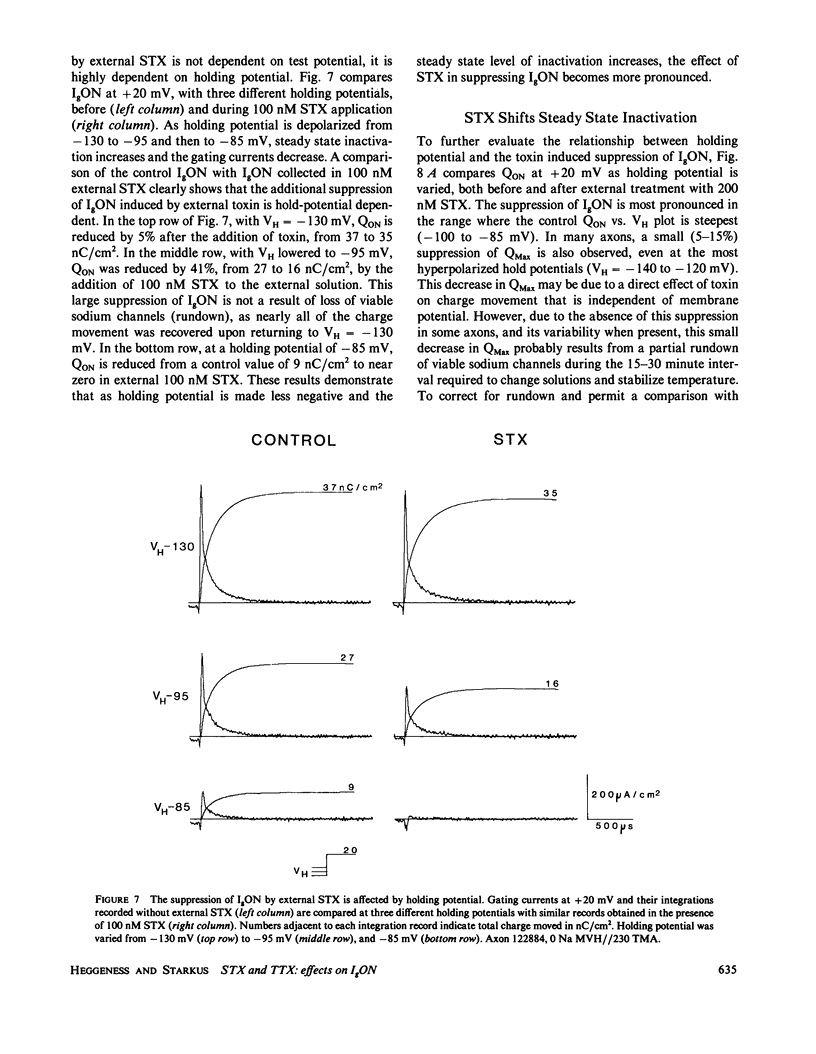
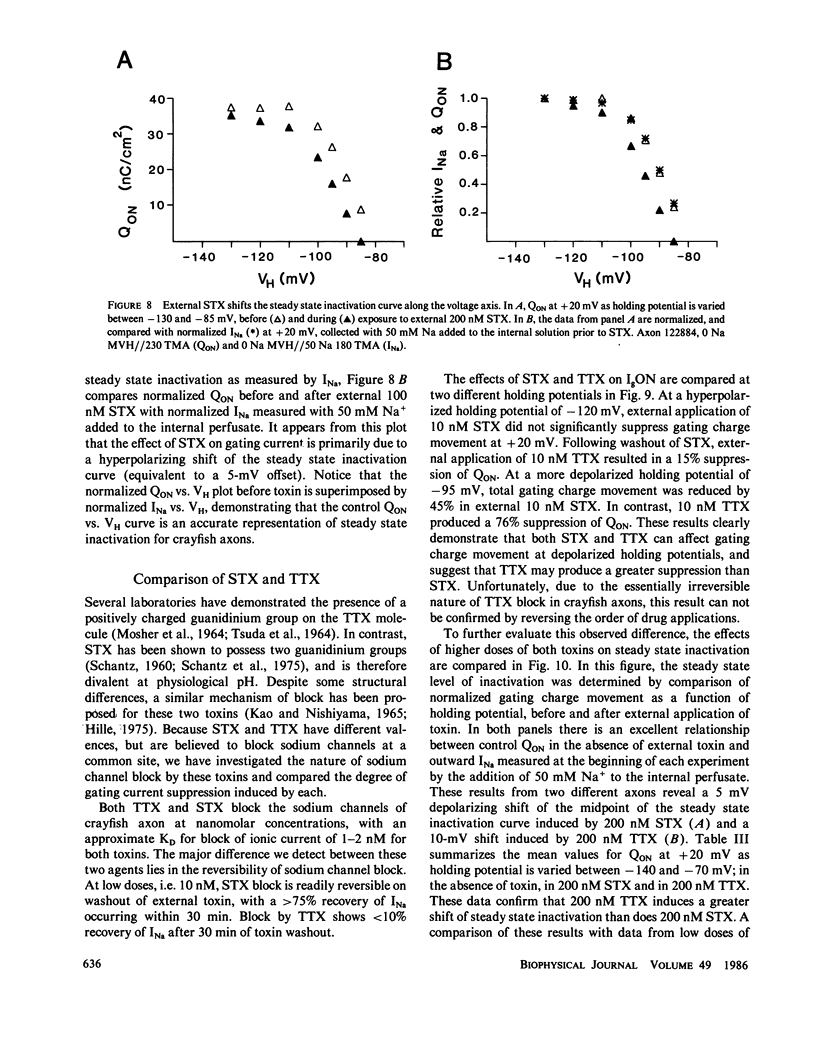
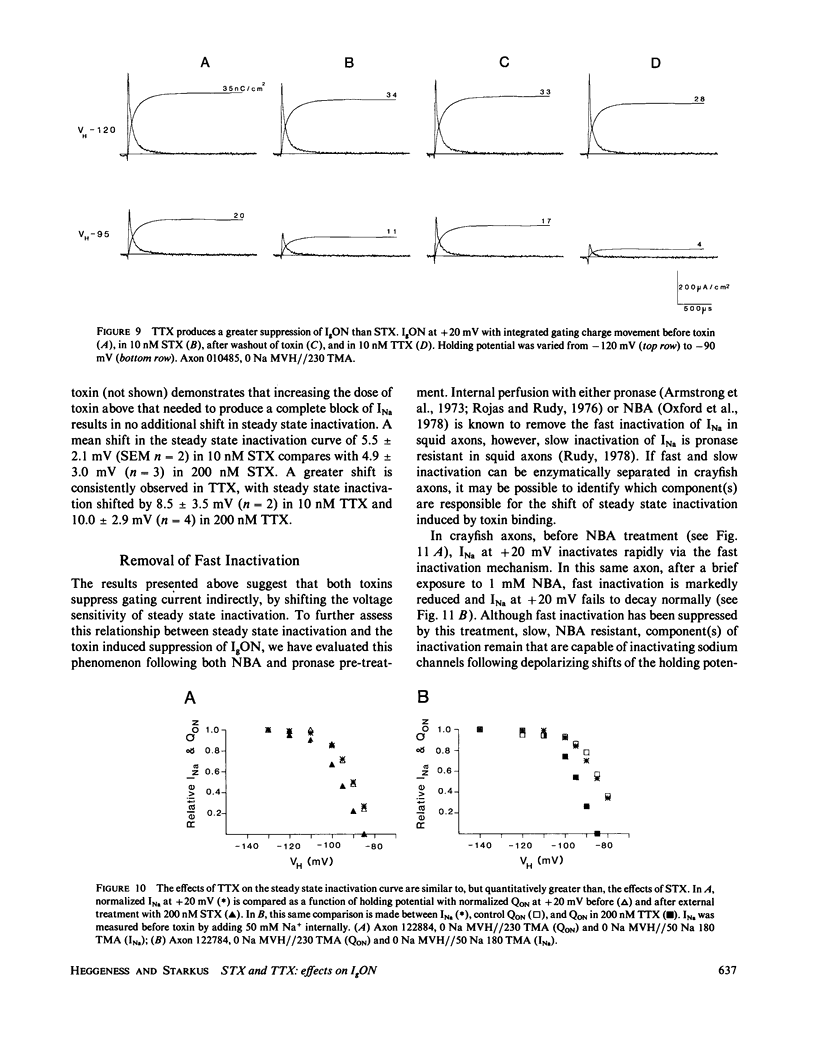
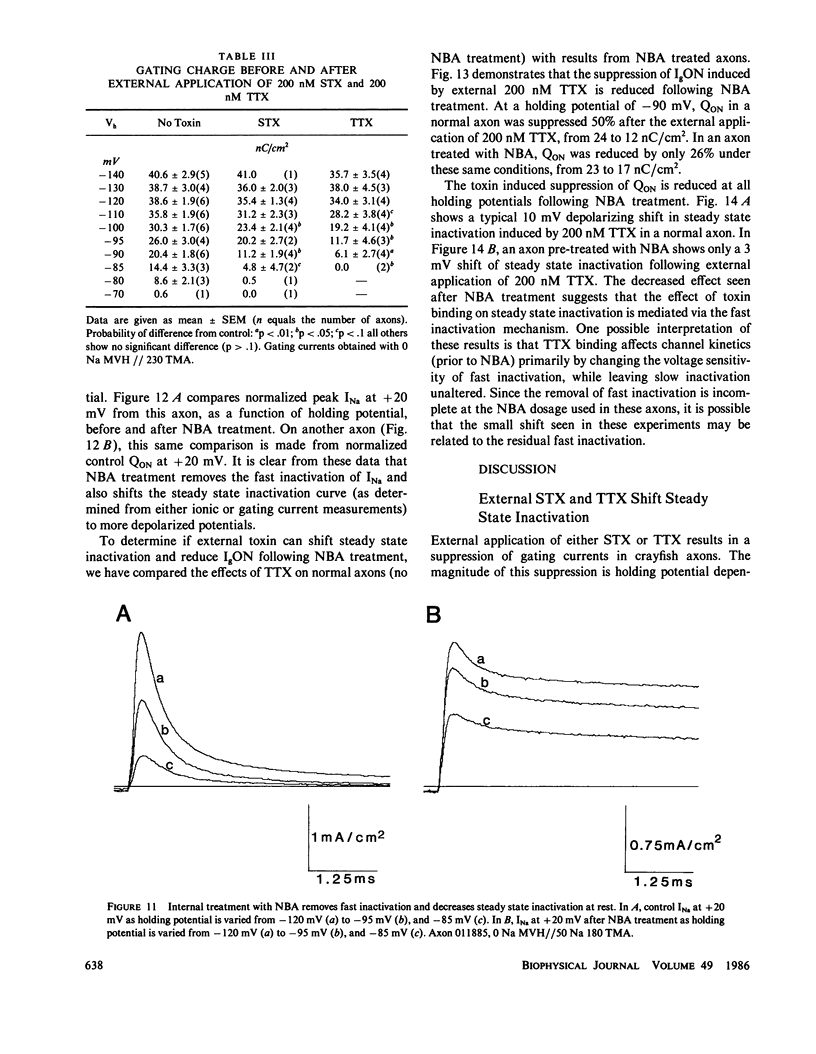
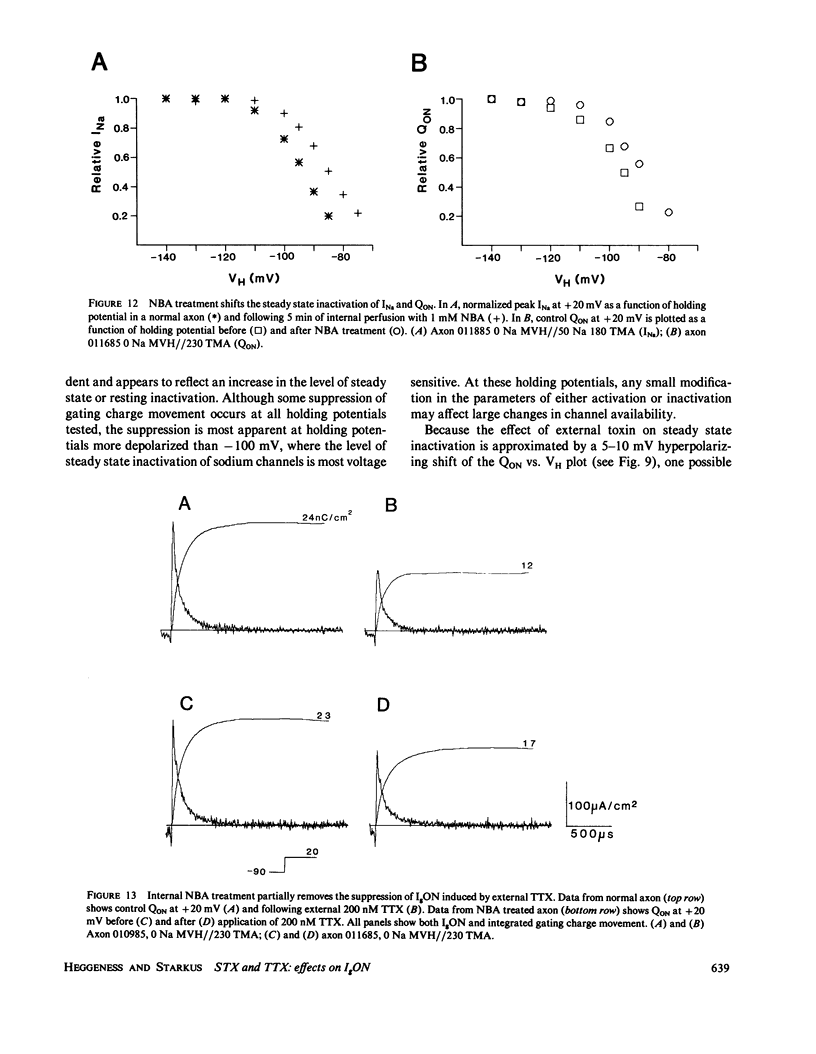
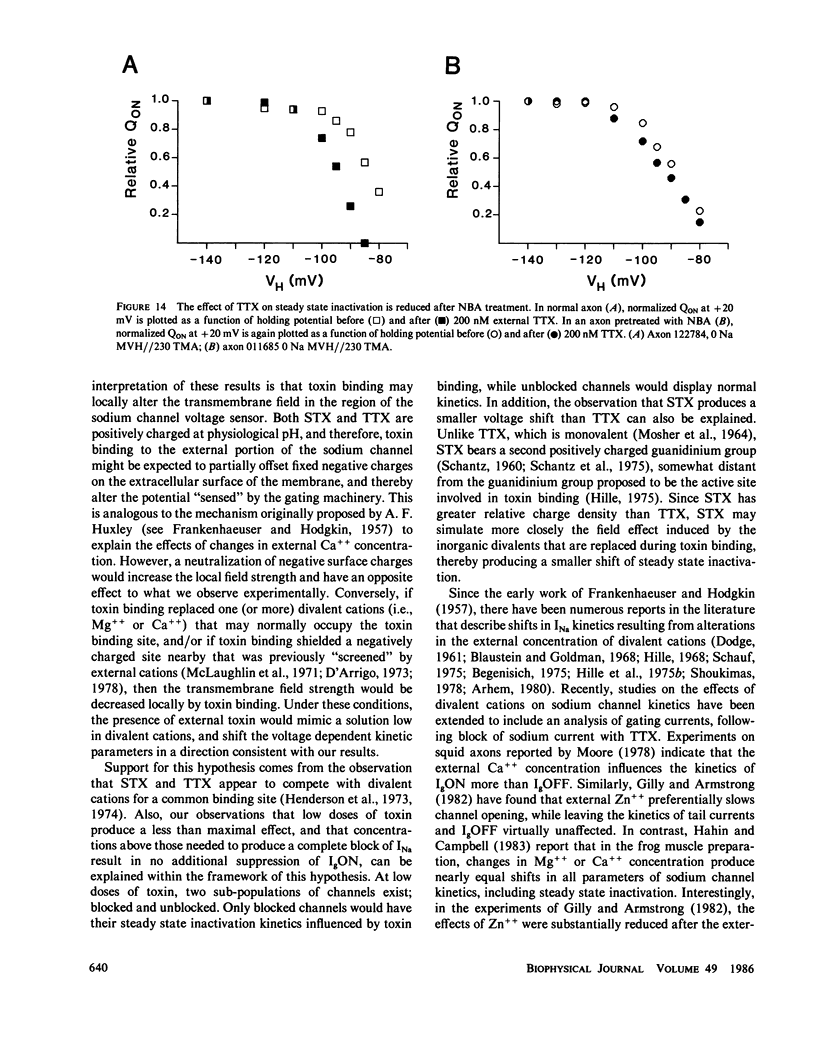
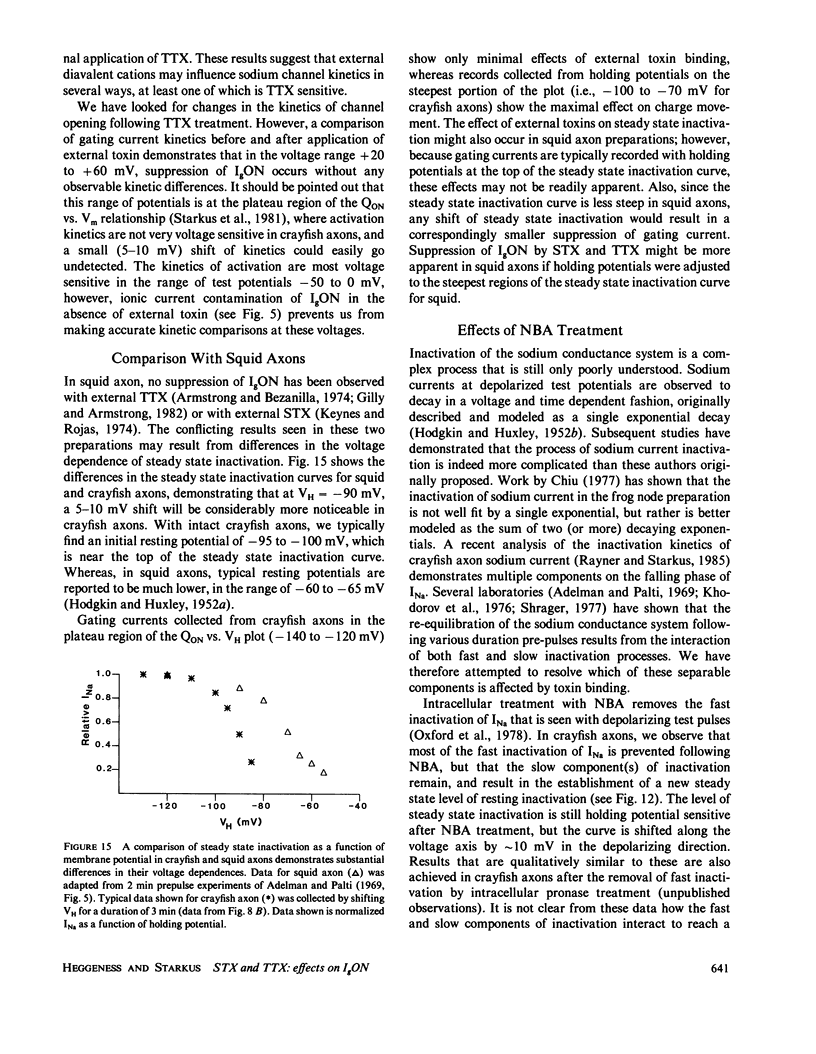
The effects of extracellular saxitoxin (STX) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) on gating current (IgON) were studied in voltage clamped crayfish giant axons. At a holding potential (VH) of -90 mV, integrated gating charge (QON) was found to be 56% suppressed when 200 nM STX was added to the external solution, and 75% suppressed following the addition of 200 nM TTX. These concentrations of toxin are sufficiently high to block greater than 99% of sodium channels. A smaller suppression of IgON was observed when 1 nM STX was used (KD = 1-2 nM STX). The suppression of IgON by external toxin was found to be hold potential dependent, with only minimal suppression observed at the most hyperpolarized hold potentials, -140 to -120 mV. The maximal effect of these toxins on IgON was observed at hold potentials where the QON vs. VH plot was found to be steepest, -100 to -80 mV. The suppression of IgON induced by TTX is partially relieved following the removal of fast inactivation by intracellular treatment with N-bromoacetamide (NBA). The effect of STX and TTX on IgON is equivalent to a hyperpolarizing shift in the steady state inactivation curve, with 200 nM STX and 200 nM TTX inducing shifts of 4.9 +/- 1.7 mV and 10.0 +/- 2.1 mV, respectively. Our results are consistent with a model where the binding of toxin displaces a divalent cation from a negatively charged site near the external opening of the sodium channel, thereby producing a voltage offset sensed by the channel gating apparatus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The effects of external potassium and long duration voltage conditioning on the amplitude of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):589–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of some heavy metal ions on the ionic currents of myelinated fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:219–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Croop R. S. Simulation of Na channel inactivation by thiazine dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):641–662. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T. Magnitude and location of surface charges on Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):47–65. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldman D. E. The action of certain polyvalent cations on the voltage-clamped lobster axon. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Mar;51(3):279–291. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Block of sodium conductance and gating current in squid giant axons poisoned with quaternary strychnine. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85202-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Interactions between quaternary lidocaine, the sodium channel gates, and tetrodotoxin. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85201-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., Bean B. P., Colatsky T. J., Tsien R. W. Tetrodotoxin block of sodium channels in rabbit Purkinje fibers. Interactions between toxin binding and channel gating. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Oct;78(4):383–411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arrigo J. S. Possible screening of surface charges on crayfish axons by polyvalent metal ions. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):117–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arrigo J. S. Screening of membrane surface charges by divalent cations: an atomic representation. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):C109–C117. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.3.C109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Slowing of sodium channel opening kinetics in squid axon by extracellular zinc. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):935–964. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahin R., Campbell D. T. Simple shifts in the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating caused by divalent cations. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Dec;82(6):785–805. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.6.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. Evidence that tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin act at a metal cation binding site in the sodium channels of nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3936–3940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):783–804. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. The effect of surface charge on the nerve membrane on the action of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin in frog myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):34P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The receptor for tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. A structural hypothesis. Biophys J. 1975 Jun;15(6):615–619. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85842-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y., Nishiyama A. Actions of saxitoxin on peripheral neuromuscular systems. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(1):50–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E. Kinetics and steady-state properties of the charged system controlling sodium conductance in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):393–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G. Divalent ions and the surface potential of charged phospholipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):667–687. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Narahashi T. Tetrodotoxin's highly selective blockage of an ionic channel. Fed Proc. 1967 Nov-Dec;26(6):1655–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Removal of sodium channel inactivation in squid giant axons by n-bromoacetamide. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Mar;71(3):227–247. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Yeh J. Z. Interactions of monovalent cations with sodium channels in squid axon. I. Modification of physiological inactivation gating. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):583–602. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Rudy B. Destruction of the sodium conductance inactivation by a specific protease in perfused nerve fibres from Loligo. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):501–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANTZ E. J. Biochemical studies on paralytic shellfish poisons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 17;90:843–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb26427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Ghazarossian V. E., Schnoes H. K., Strong F. M., Springer J. P., Pezzanite J. O., Clardy J. Letter: The structure of saxitoxin. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Mar 5;97(5):1238–1238. doi: 10.1021/ja00838a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Tetramethylammonium ions alter sodium-channel gating in Myxicola. Biophys J. 1983 Mar;41(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84437-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. The interactions of calcium with mpyxicola giant axons and a description in terms of a simple surface charge model. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;248(3):613–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoukimas J. J. Effect of calcium upon sodium inactivation in the giant axon of Loligo pealei. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jan 18;38(3):271–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01871926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Ionic conductance changes in voltage clamped crayfish axons at low pH. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):666–690. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Slow sodium inactivation in nerve after exposure to sulhydryl blocking reagents. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):183–202. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Fellmeth B. D., Rayner M. D. Gating currents in th intact crayfish giant axon. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):521–533. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84807-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Heggeness S. T., Rayner M. D. Kinetic analysis of sodium channel block by internal methylene blue in pronased crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):205–218. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84014-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Shrager P. Modification of slow sodium inactivation in nerve after internal perfusion with trypsin. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C238–C244. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUDA K., TACHIKAWA R., SAKAI K., TAMURA C., AMAKASU O., KAWAMURA M., IKUMA S. ON THE STRUCTURE OF TETRODOTOXIN. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1964 May;12:642–645. doi: 10.1248/cpb.12.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


