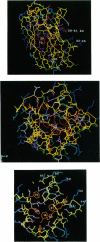
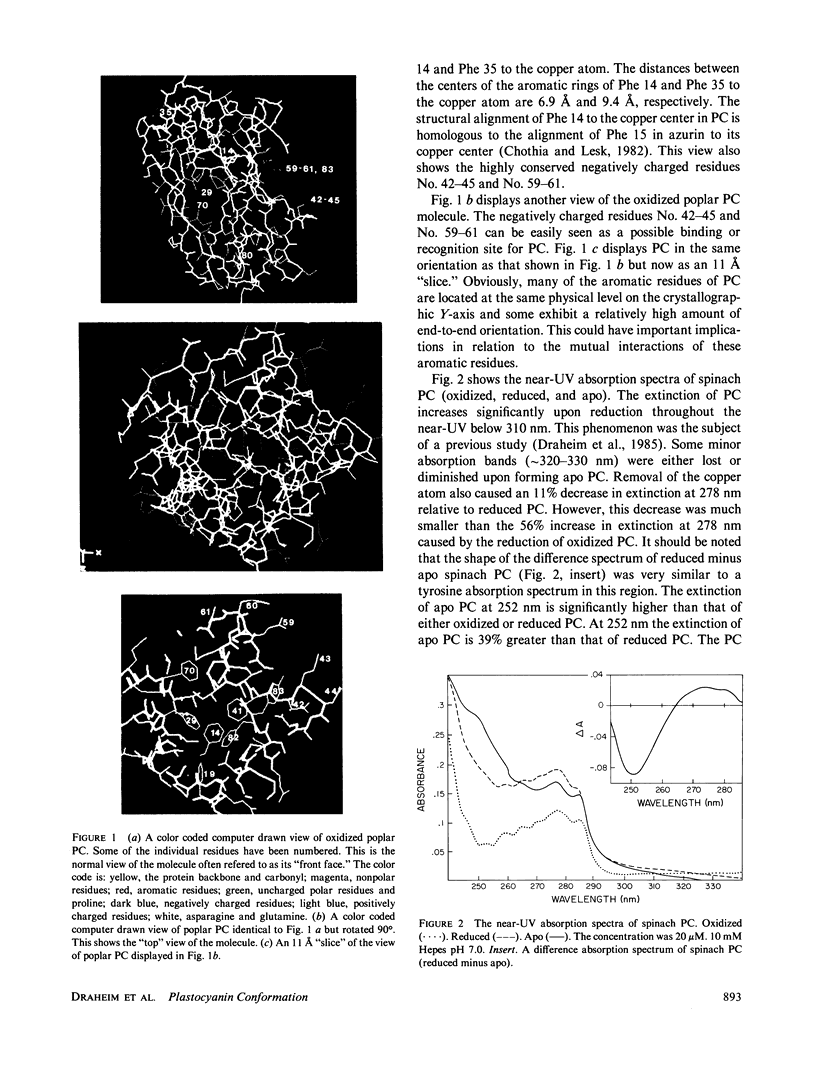
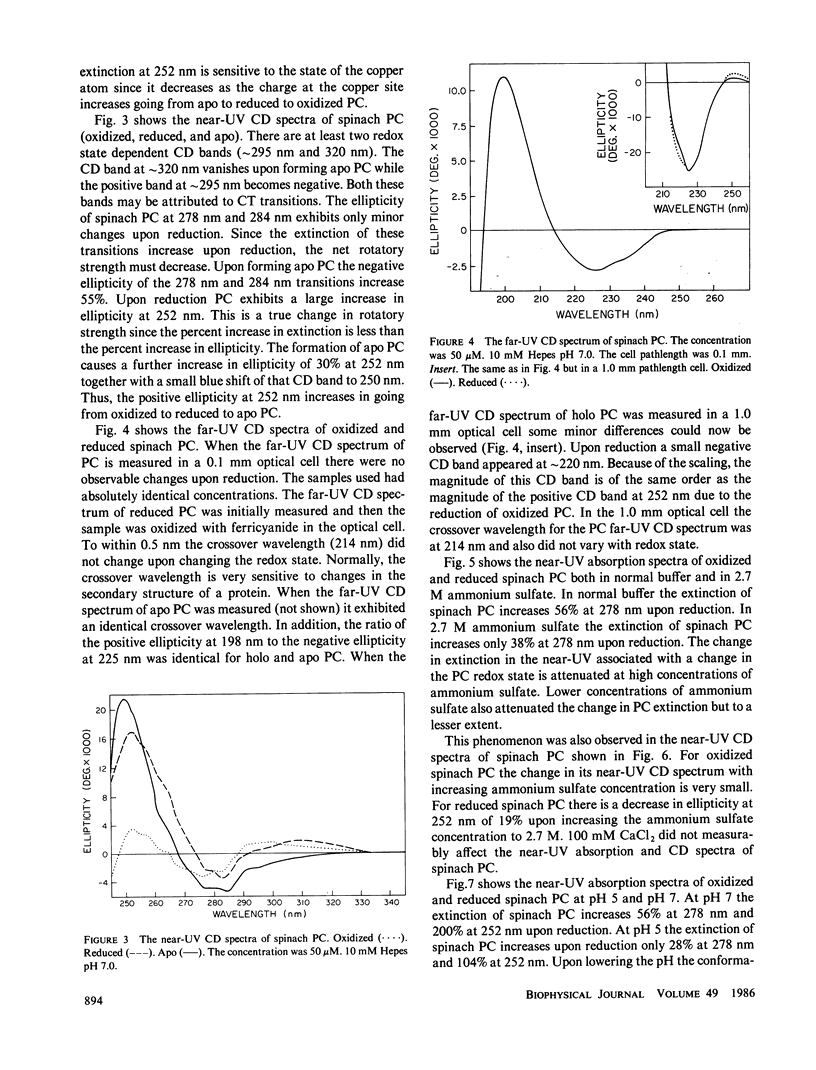
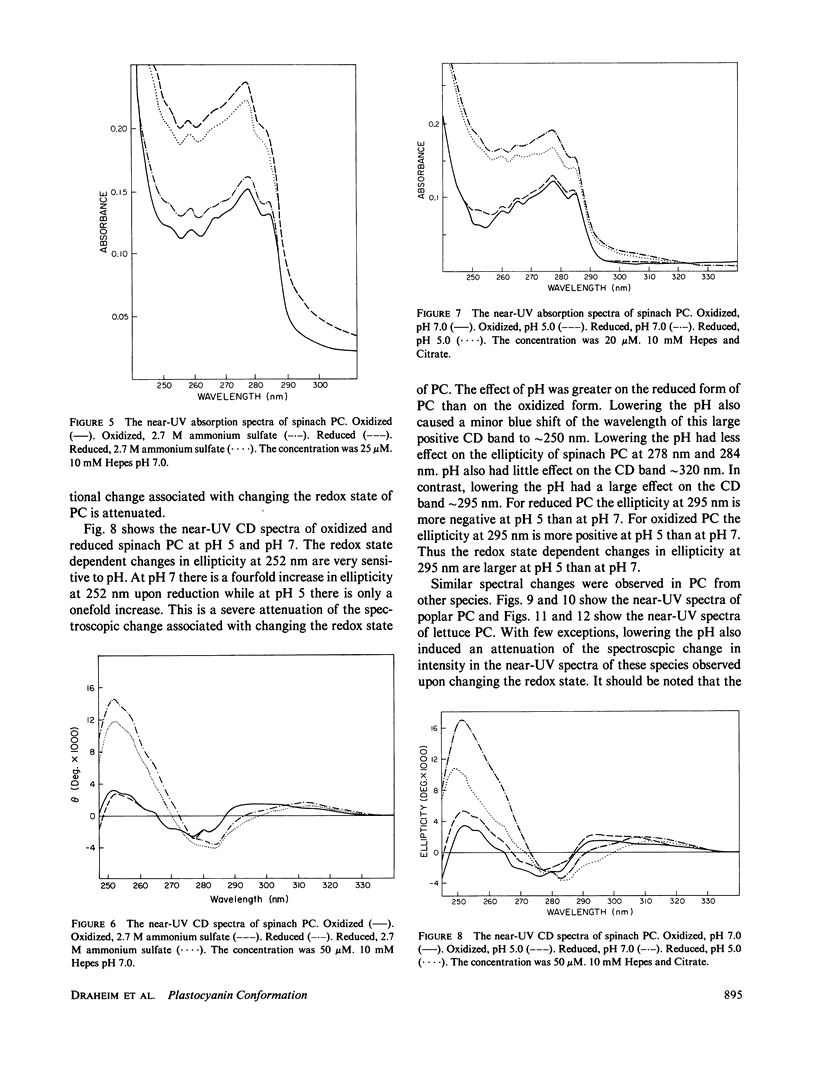
Abstract
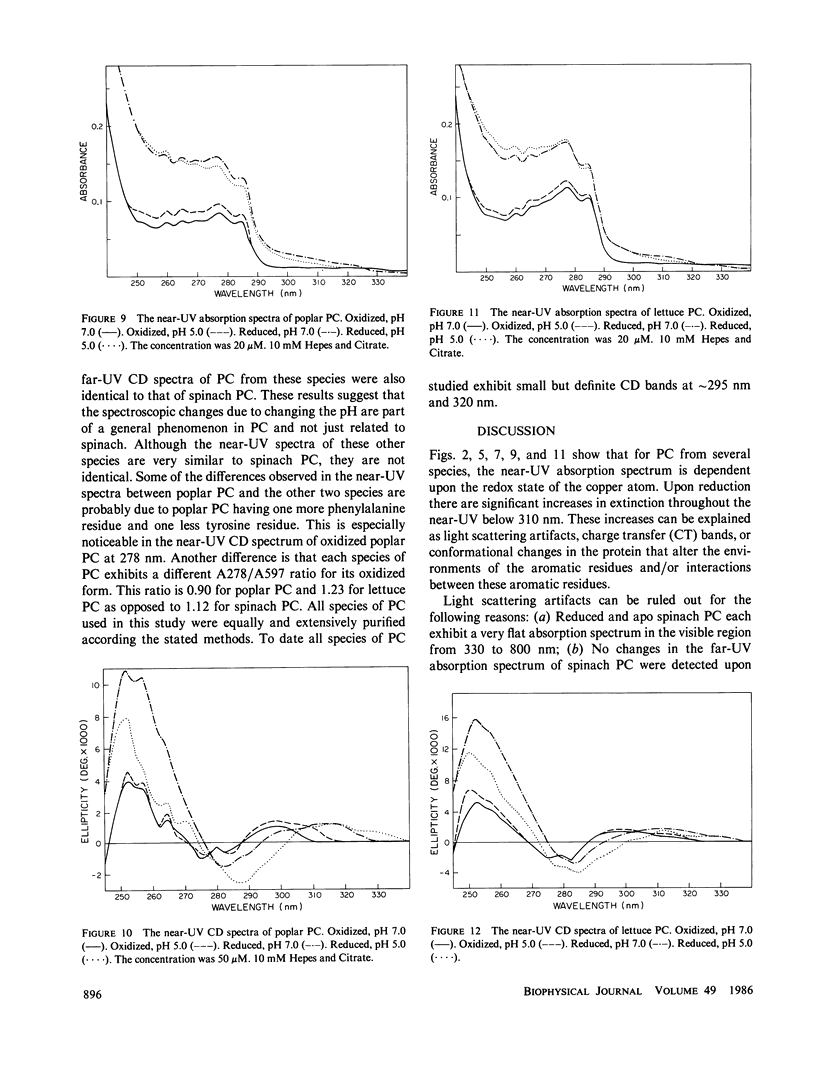
The near-ultraviolet absorption and circular dichroic spectra of plastocyanin are dependent upon the redox state, solution pH, and ammonium sulfate concentration. This dependency was observed in plastocyanin isolated from spinach, poplar, and lettuce. Removal of the copper atom also perturbed the near-ultraviolet spectra. Upon reduction there are increases in both extinction and ellipticity at 252 nm. Further increases at 252 nm were observed upon formation of apo plastocyanin eliminating charge transfer transitions as the cause. The spectral changes in the near-ultraviolet imply a flexible tertiary conformation for plastocyanin. There are at least two charge transfer transitions at approximately 295-340 nm. One of these transitions is sensitive to low pH's and is attributed to the His 87 copper ligand. The redox state dependent changes observed in the near-ultraviolet spectra of plastocyanin are attenuated either by decreasing the pH to 5 or by increasing the ammonium sulfate concentration to 2.7 M. This attenuation cannot be easily explained by simple charge screening. Hydrophobic interactions probably play an important role in this phenomenon. The pH and redox state dependent conformational changes may play an important role in regulating electron transport.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkey K. O., Gross E. L. Effect of carboxyl group modification on redox properties and electron donation capability of spinach plastocyanin. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5495–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Evolution of proteins formed by beta-sheets. I. Plastocyanin and azurin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson D. J., Hayes M. T., Wright P. E. NMR study of the interaction of plastocyanin with chromium(II) analogues of inorganic electron transfer reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 10;591(1):162–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. J., San Pietro A. Preparation and characterization of a chemically modified plastocyanin. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draheim J. E., Anderson G. P., Pan R. L., Rellick L. M., Duane J. W., Gross E. L. Conformational changes in plastocyanin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Feb 15;237(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farver O., Shahak Y., Pecht I. Electron uptake and delivery sites on plastocyanin in its reactions with the photosynthetic electron transport system. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1885–1890. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Clingeleffer D. J., Guss J. M., Rogers S. J., Freeman H. C. The crystal structure of poplar apoplastocyanin at 1.8-A resolution. The geometry of the copper-binding site is created by the polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2822–2825. doi: 10.2210/pdb2pcy/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E. L., Anderson G. P., Ketchner S. L., Draheim J. E. Plastocyanin conformation. The effect of nitrotyrosine modification and pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 7;808(3):437–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss J. M., Freeman H. C. Structure of oxidized poplar plastocyanin at 1.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 15;169(2):521–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Ishikawa H., Niwa S., Itoh S. Electron transfer between plastocyanin and P700 in highly-purified photosystem I reaction center complex. Effects of pH, cations, and subunit peptide composition. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):1901–1911. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka K., Takabe T. Importance of local positive charges on cytochrome f for electron transfer to plastocyanin and potassium ferricyanide. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1813–1821. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]