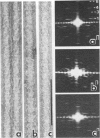
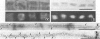Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cowgill R. W. Proteolysis of paramyosin from Mercenaria mercenaria and properties of its most stable segment. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):503–509. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. An electron microscopic and optical diffraction analysis of the structure of Limulus telson muscle thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):443–451. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Kensler R. W., Reedy M. C., Hofmann W., King H. A. Structure and paramyosin content of tarantula thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):186–195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Kensler R. W. Structure of short thick filaments from Limulus muscle. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of Limulus myosin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9274–9278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]