Abstract
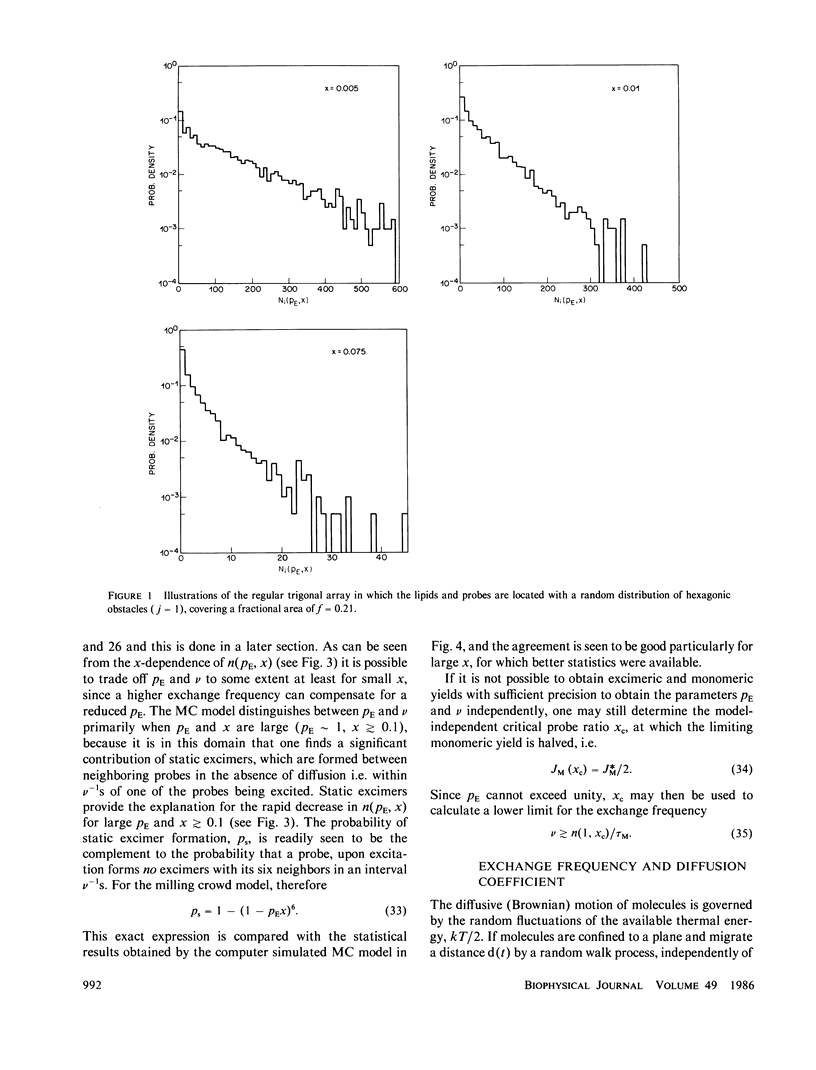
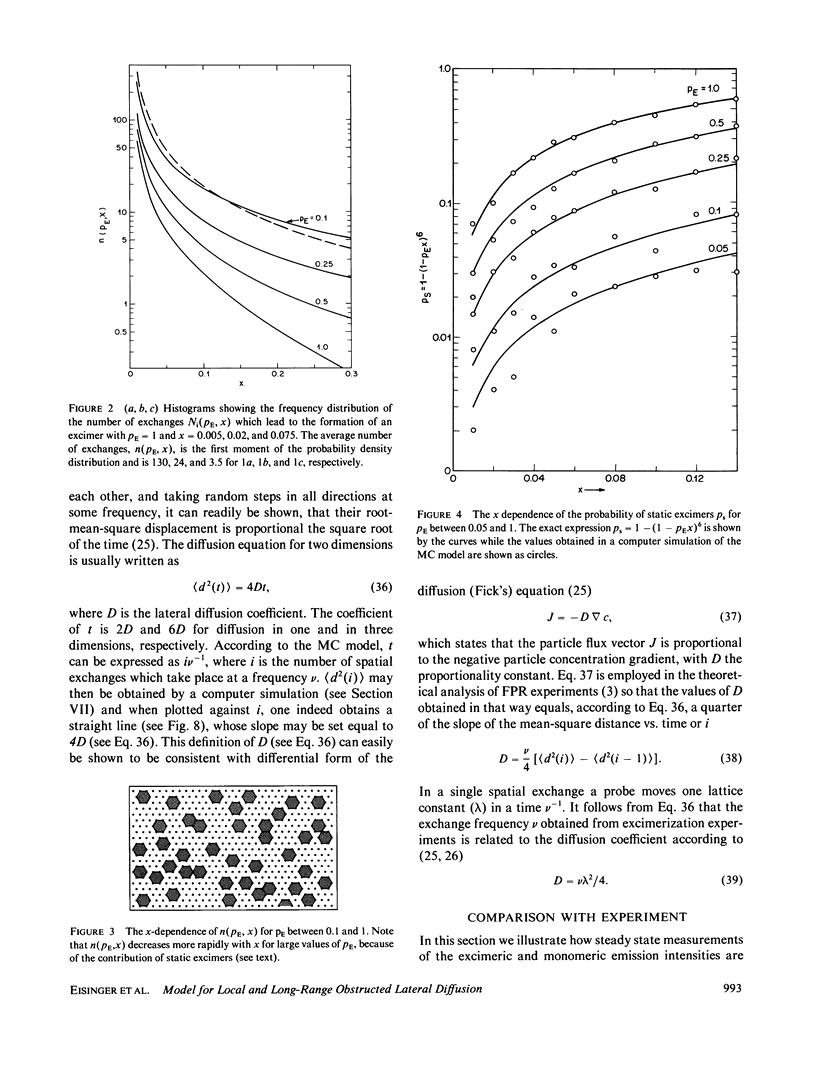
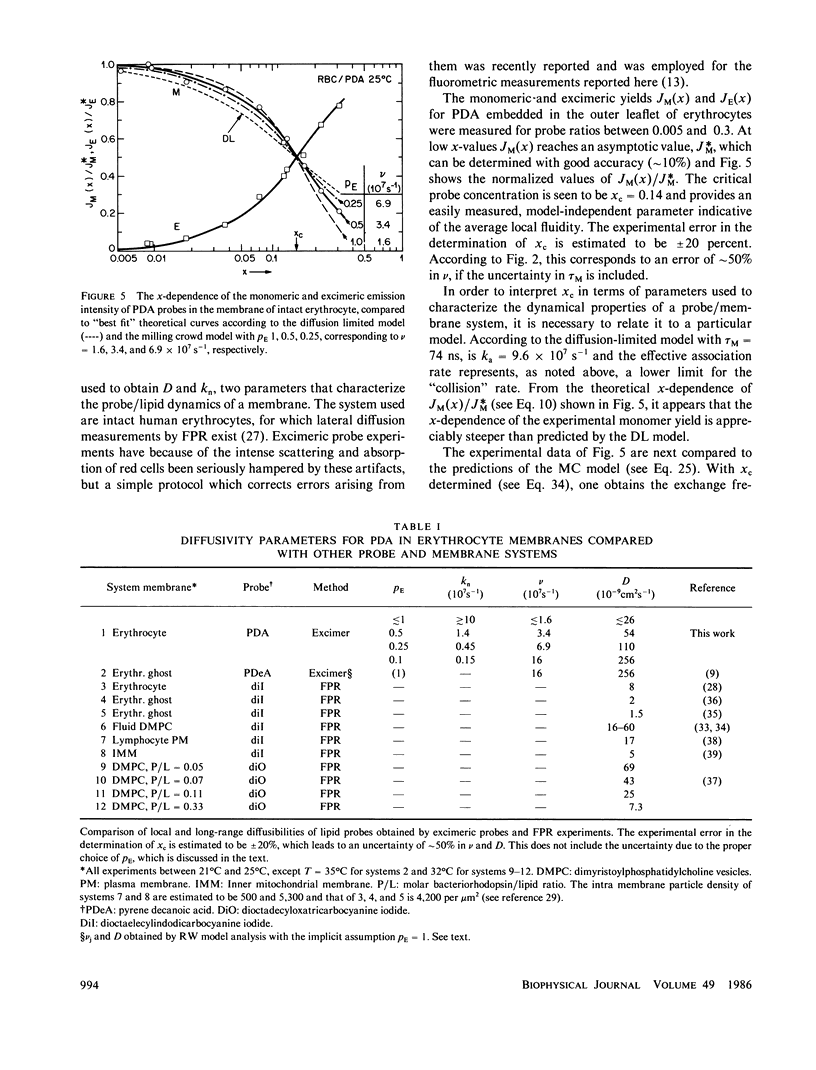
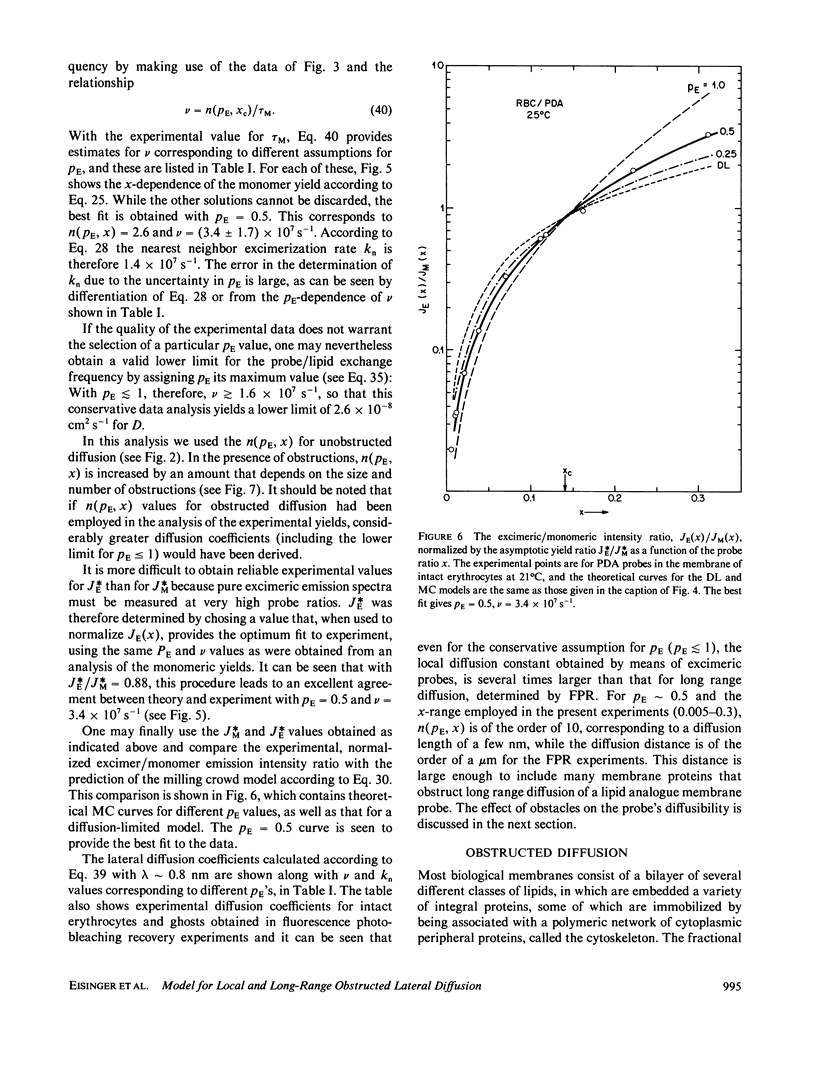
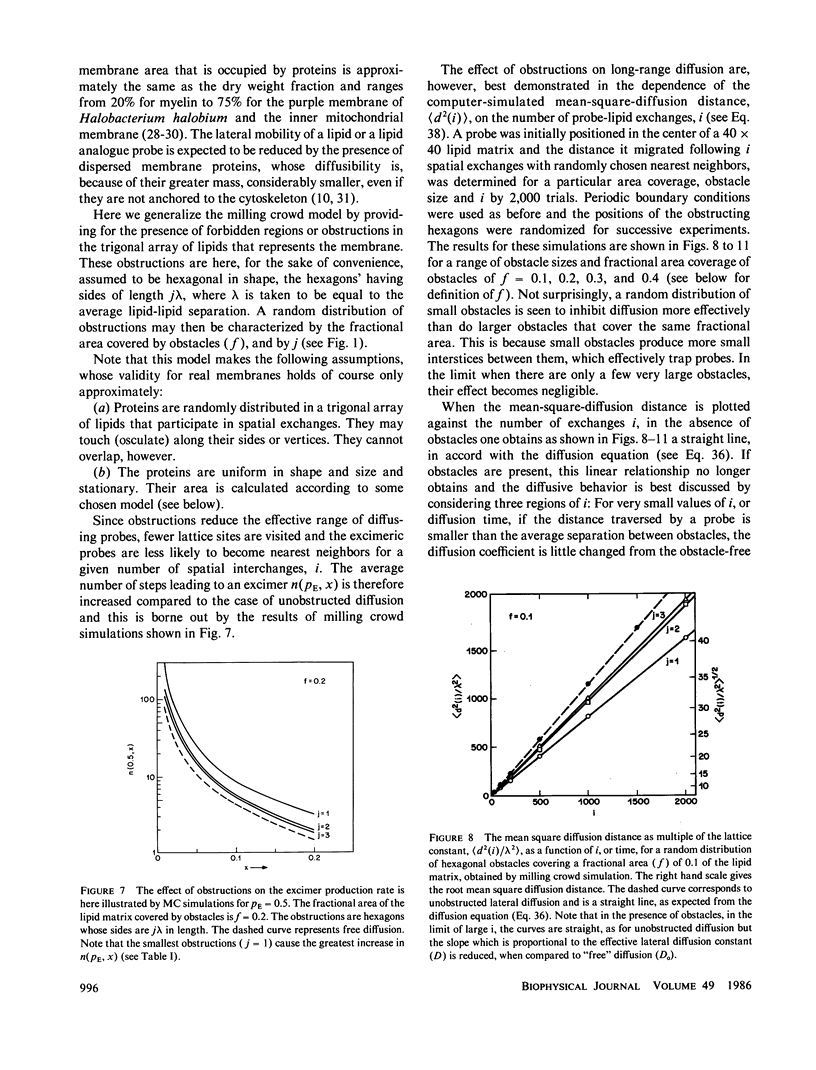
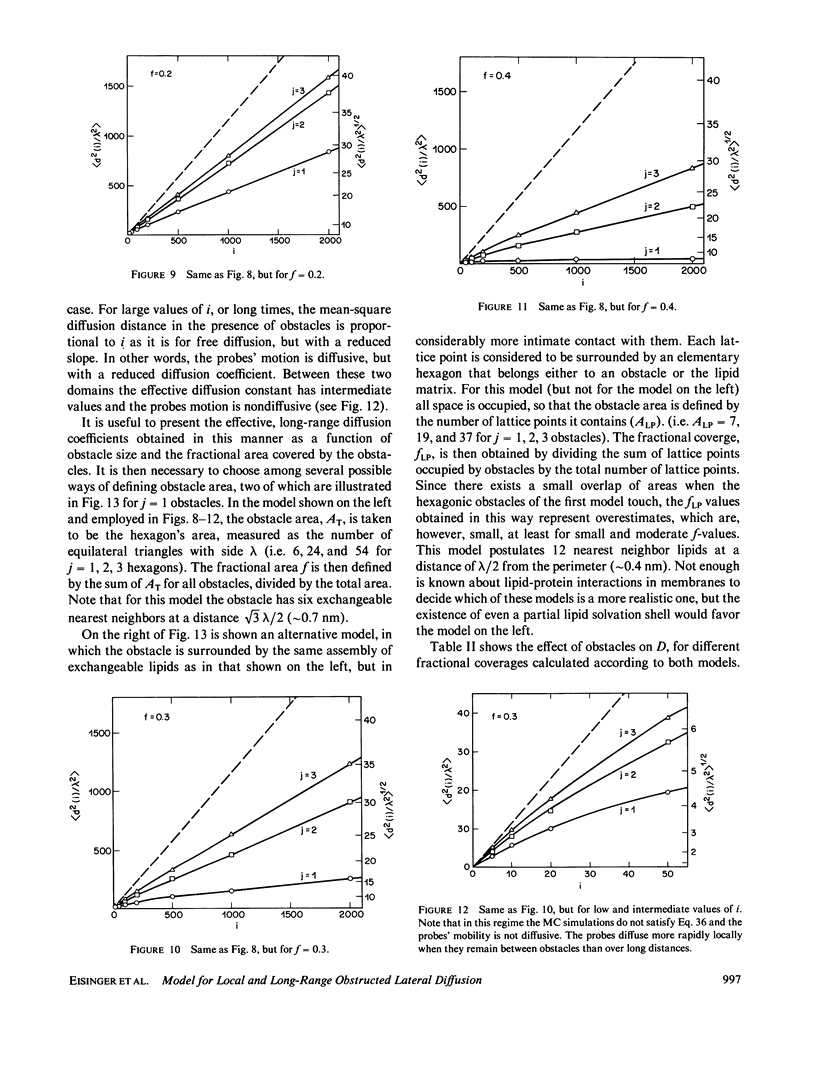
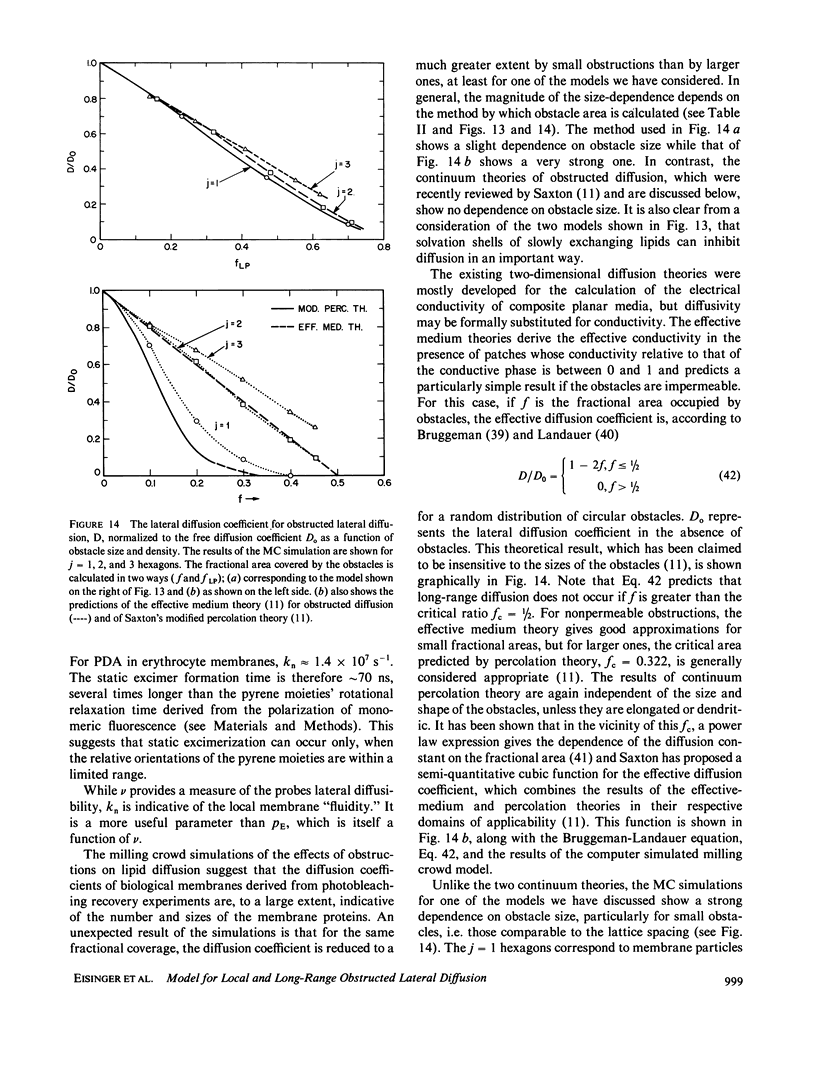
A new model for lateral diffusion, the milling crowd model (MC), is proposed and is used to derive the dependence of the monomeric and excimeric fluorescence yields of excimeric membrane probes on their concentration. According to the MC model, probes migrate by performing spatial exchanges with a randomly chosen nearest neighbor (lipid or probe). Only nearest neighbor probes, one of which is in the excited state, may form an excimer. The exchange frequency, and hence the local lateral diffusion coefficient, may then be determined from experiment with the aid of computer simulation of the excimer formation kinetics. The same model is also used to study the long-range lateral diffusion coefficient of probes in the presence of obstacles (e.g., membrane proteins). The dependence of the monomeric and excimeric fluorescence yields of 1-pyrene-dodecanoic acid probes on their concentration in the membranes of intact erythrocytes was measured and compared with the prediction of the MC model. The analysis yields an excimer formation rate for nearest neighbor molecules of approximately 1 X 10(7) s-1 and an exchange frequency of approximately greater than 2 X 10(7) s-1, corresponding to a local diffusion coefficient of greater than 3 X 10(-8) cm2 s-1. This value is several times larger than the long-range diffusion coefficient for a similar system measured in fluorescence photobleaching recovery experiments. The difference is explained by the fact that long-range diffusion is obstructed by dispersed membrane proteins and is therefore greatly reduced when compared to free diffusion. The dependence of the diffusion coefficient on the fractional area covered by obstacles and on their size is derived from MC simulations and is compared to those of other theories lateral diffusibility.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. A., Webb W. W. Lipid diffusibility in the intact erythrocyte membrane. Biophys J. 1983 Jun;42(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84397-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Influence of increased membrane cholesterol on membrane fluidity and cell function in human red blood cells. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):413–430. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derzko Z., Jacobson K. Comparative lateral diffusion of fluorescent lipid analogues in phospholipid multibilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6050–6057. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in spin-labeled phosphatidylcholine multilayers. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4475–4481. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragsten P., Henkart P., Blumenthal R., Weinstein J., Schlessinger J. Lateral diffusion of surface immunoglobulin, Thy-1 antigen, and a lipid probe in lymphocyte plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5163–5167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Flores J., Bookchin R. M. The cytosol-membrane interface of normal and sickle erythrocytes. Effect of hemoglobin deoxygenation and sickling. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7169–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Flores J. Cytosol-membrane interface of human erythrocytes. A resonance energy transfer study. Biophys J. 1983 Mar;41(3):367–379. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84448-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Flores J. Fluorometry of turbid and absorbant samples and the membrane fluidity of intact erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83761-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. F., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion in phospholipid bilayer membranes and multilamellar liquid crystals. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3046–3053. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Lee K. J., Huestis W. H. Membrane bilayer balance and erythrocyte shape: a quantitative assessment. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2849–2857. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Hartmann W. Excimer-forming lipids in membrane research. Chem Phys Lipids. 1980 Oct;27(3):199–219. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(80)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Hartmann W., Theilen U., Sackmann E. On two-dimensional passive random walk in lipid bilayers and fluid pathways in biomembranes. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jul 31;48(3):215–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01872892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Luisetti J. Lateral and transversal diffusion and phase transitions in erythrocyte membranes. An excimer fluorescence study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 15;596(1):108–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes: use of pyrene excimers as optical probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S., Wu E. S., Hoechli L., Hoechli M., Jacobson K., Sowers A. E., Hackenbrock C. R. Relationship between lateral diffusion, collision frequency, and electron transfer of mitochondrial inner membrane oxidation-reduction components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W. Interactions between membrane skeleton proteins and the intrinsic domain of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec;694(4):331–352. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. Lateral diffusion in membranes. Cell Motil. 1983;3(5-6):367–373. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitza H. G., Sackmann E. Local measurement of lateral motion in erythrocyte membranes by photobleaching technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;595(1):56–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisetti J., Möhwald H., Galla H. J. Monitoring the location profile of fluorophores in phosphatidylcholine bilayers by the use or paramagnetic quenching. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 19;552(3):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Cherry R. J. Lateral and rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid bilayers: experimental test of the Saffman-Delbrück equations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Effects of impermeable patches on diffusion in a cell membrane. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84504-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Wu E. S., Meers P. R., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion of gramicidin C in phospholipid multibilayers. Effects of cholesterol and high gramicidin concentration. Biophys J. 1982 Nov;40(2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84467-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Axelrod D. Reduced lateral mobility of a fluorescent lipid probe in cholesterol-depleted erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb W. W., Barak L. S., Tank D. W., Wu E. S. Molecular mobility on the cell surface. Biochem Soc Symp. 1981;(46):191–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


