Abstract
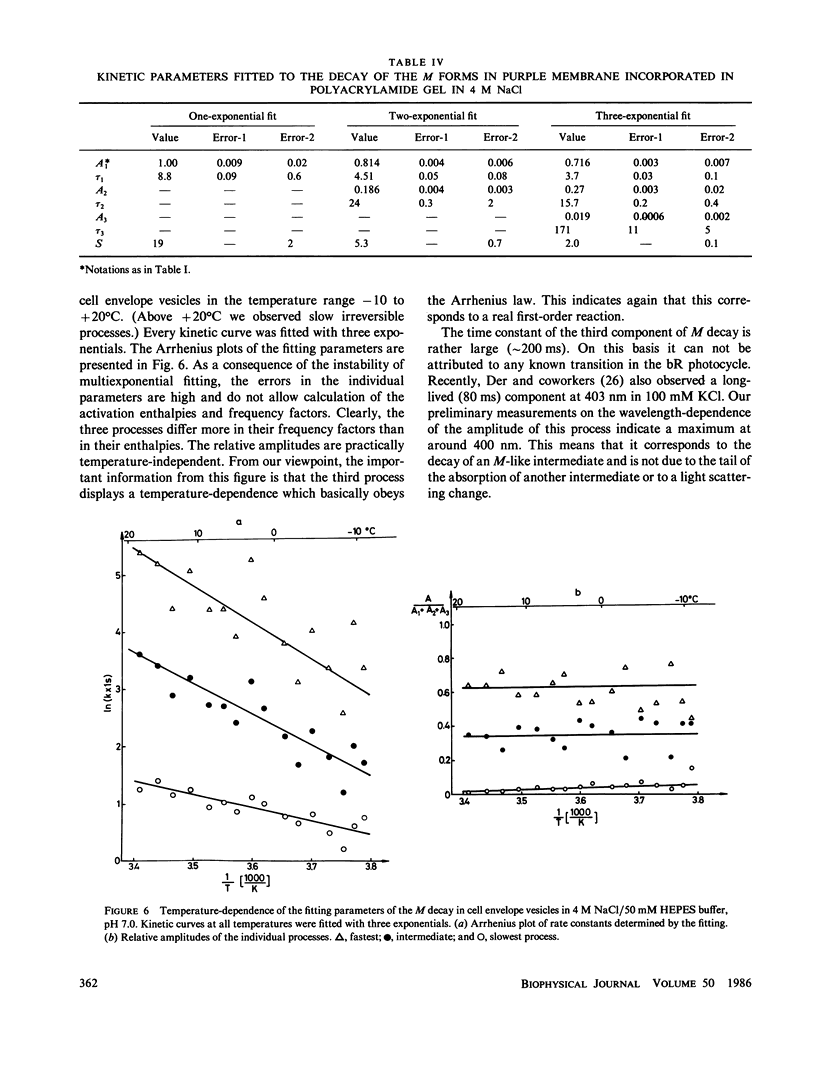
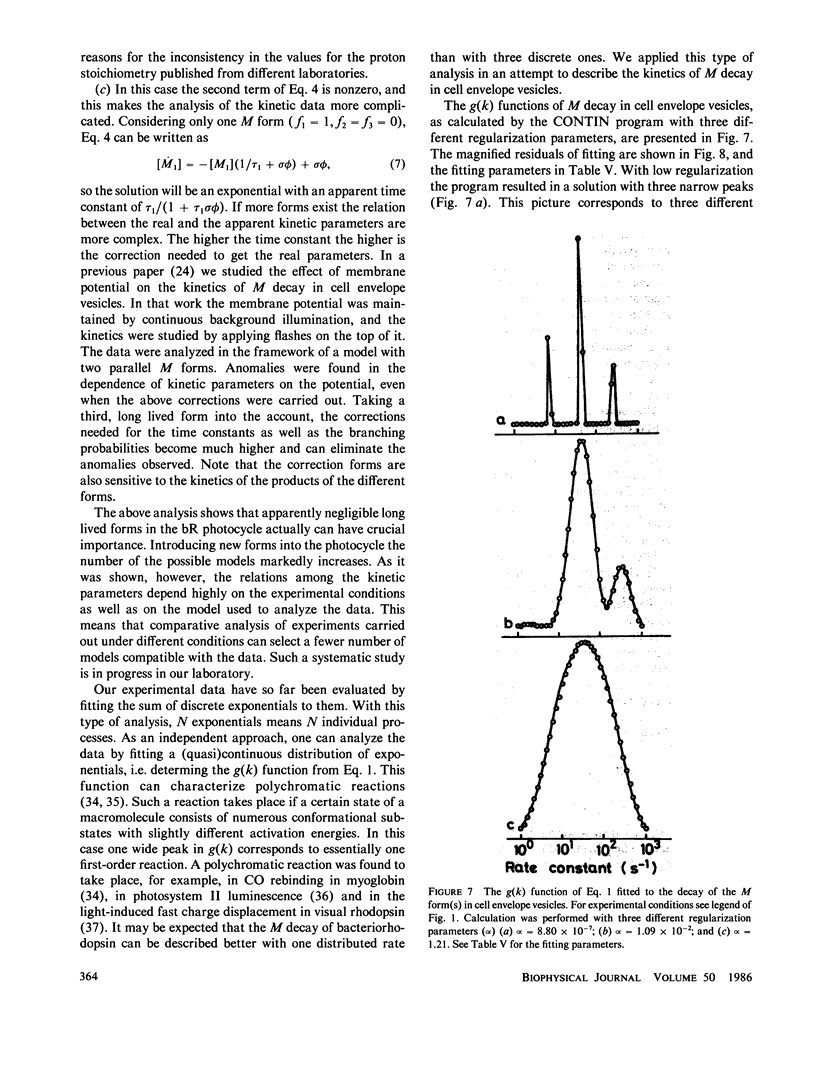
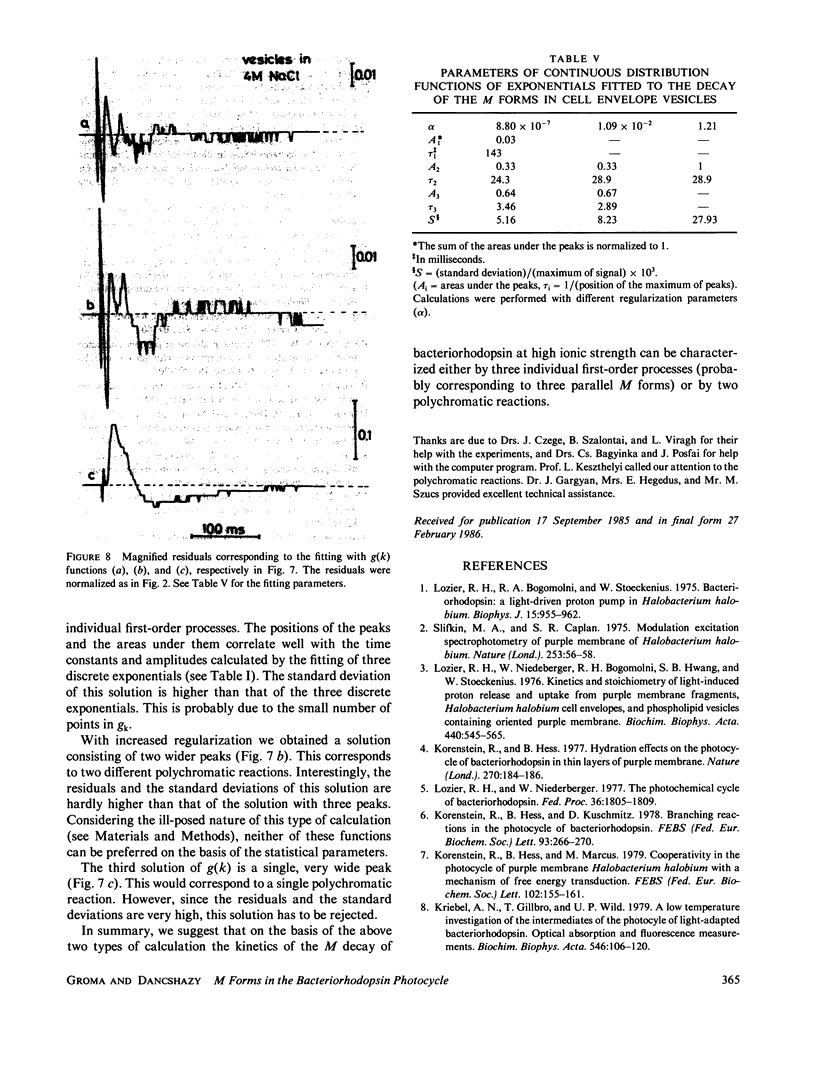
On capturing a quantum of light, the bacteriorhodopsin of Halobacterium halobium undergoes a photocycle involving different intermediates. The exact scheme of the photocycle and especially the number of M intermediates are subjects of debate. For a quantitative analysis of many effects connected with the photocycle, e.g. the effect of the membrane potential on the kinetics of M decay (Groma et al., 1984. Biophys. J. 45:985-992), a knowledge of the exact photocycle is needed. In the present work sophisticated measurements were made on the decay kinetics of the M forms in cell envelope vesicles, purple membrane suspension and purple membrane fragments incorporated in polyacrylamide gel. The experimental data were analyzed by fitting one, two, and three discrete exponentials. Three different real components were found in the M decay of cell envelope vesicles in 4 M NaCl. All of them exhibited a temperature-dependence obeying the Arrhenius law. Two real components were found for the purple membrane in suspension and in gel in NaCl-free medium. The third phase appeared when the gel was soaked in 4 M NaCl. As an independent means of analysis, a continuous distribution of exponentials was also fitted to the M decay kinetics in cell envelope vesicles. This calculation also resulted in three processes with distinct rates or alternatively two processes with distributed rates.
Full text
PDF
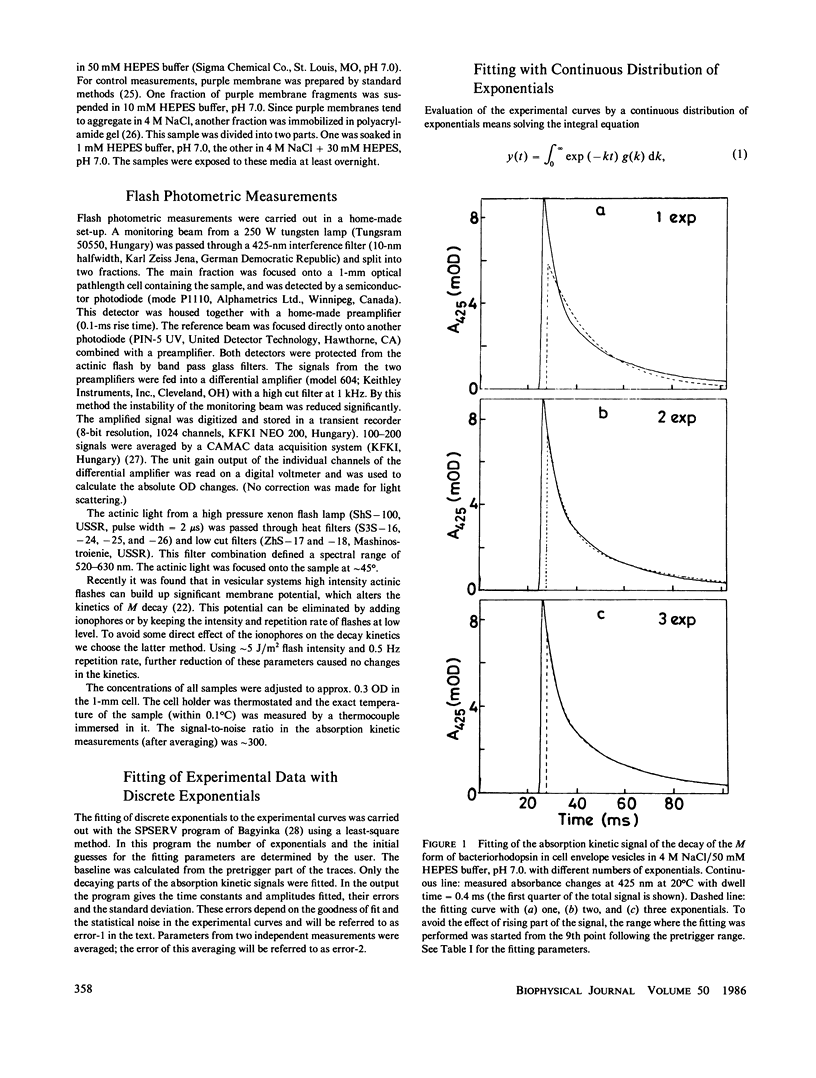
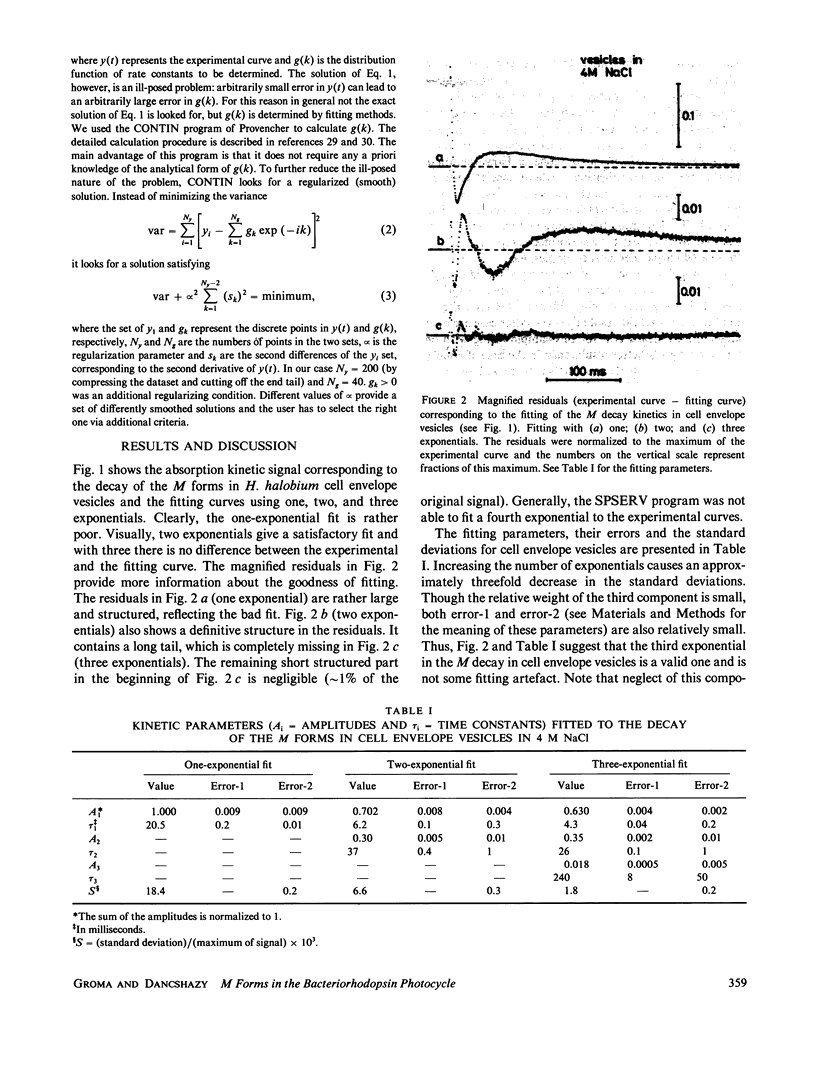
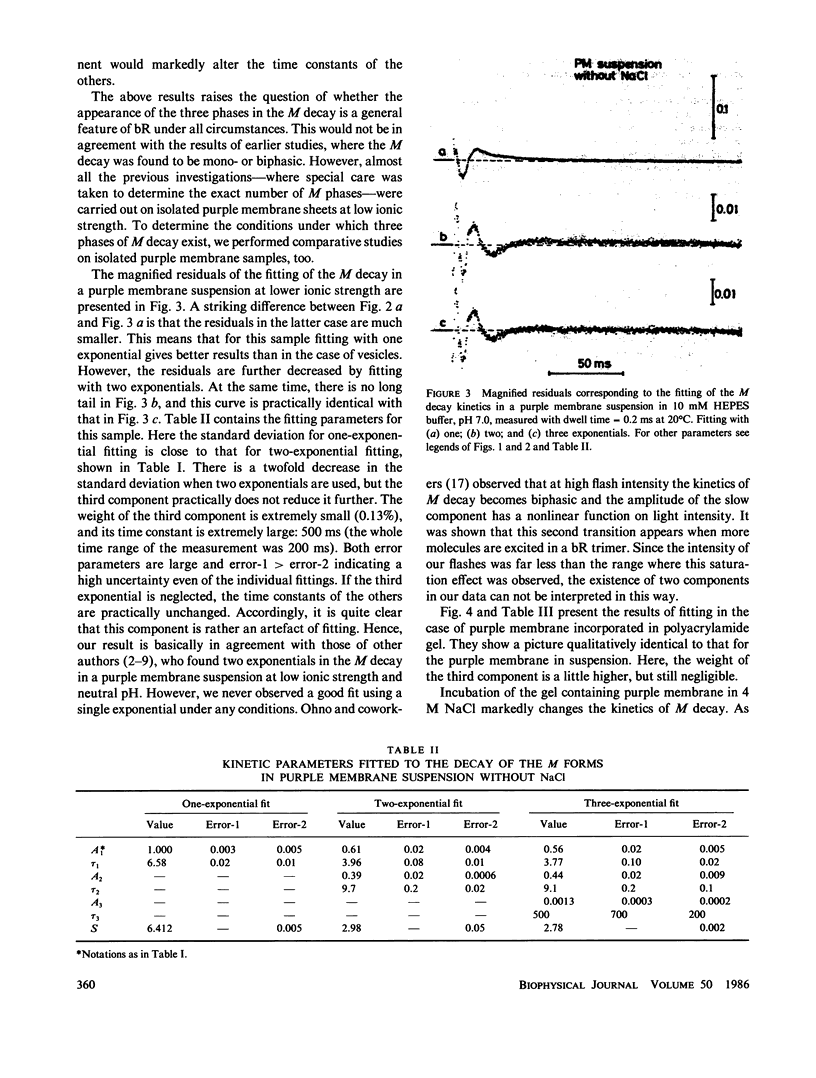
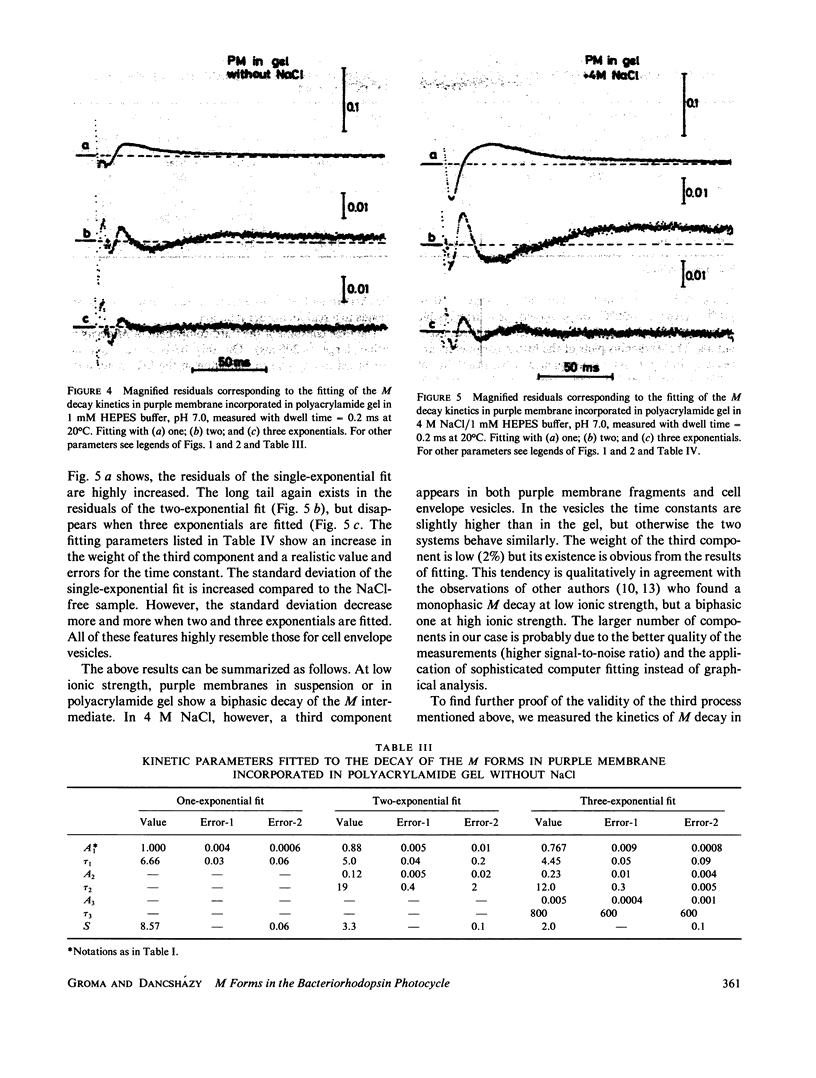


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin R. H., Beeson K. W., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Gunsalus I. C. Dynamics of ligand binding to myoglobin. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5355–5373. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Chen J. G., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. Cation binding by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):396–400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H., Pande C., Callender R. H., Ebrey T. G. A detailed resonance Raman study of the M412 intermediate in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Photochem Photobiol. 1985 Apr;41(4):467–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1985.tb03513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dér A., Hargittai P., Simon J. Time-resolved photoelectric and absorption signals from oriented purple membranes immobilized in gel. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 Mar;10(5-6):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton M. E., Greenwood C. Evidence for a model of regeneration of a protonated species, bR, from a phototransient, M, in the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium halobium [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):1075–1077. doi: 10.1042/bst0071075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Bakker E. P., Korenstein R., Caplan S. R. Bacteriorhodopsin: biphasic kinetics of phototransients and of light-induced proton transfer by sub-bacterial Halobacterium halobium particles and by reconstituted liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 1;71(2):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80938-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillbro T. Flash kinetic study of the last steps in the photoinduced reaction cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 11;504(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G., Crofts A. R. The quantum efficiency of proton pumping by the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85091-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groma G. I., Helgerson S. L., Wolber P. K., Beece D., Dancsházy Z., Keszthelyi L., Stoeckenius W. Coupling between the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle and the protonmotive force in Halobacterium halobium cell envelope vesicles. II. Quantitation and preliminary modeling of the M----bR reactions. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):985–992. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84243-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamoto J. H., Dupuis P., El-Sayed M. A. On the protein (tyrosine)-chromophore (protonated Schiff base) coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Ikegami A., Stoeckenius W. Salt and pH-dependent changes of the purple membrane absorption spectrum. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Nov;40(5):641–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb05353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B. Hydration effects on the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin in thin layers of purple membrane. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):184–186. doi: 10.1038/270184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B., Kuschmitz D. Branching reactions in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel A. N., Gillbro T., Wild U. P. A low temperature investigation of the intermediates of the photocycle of light-adapted bacteriorhodopsin. Optical absorption and fluorescence measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 11;546(1):106–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuschmitz D., Hess B. On the ratio of the proton and photochemical cycles in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5950–5957. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Packer L. Nonionic detergent effects on spectroscopic characteristics and the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin in purple membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. A correlation between proton pumping and the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7079–7082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W. The photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1805–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Parodi L. A., Lozier R. H. Procedure for testing kinetic models of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):161–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84543-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. Flash-induced volume changes of bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments and their relationship to proton movements and absorbance transients. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi L. A., Lozier R. H., Bhattacharjee S. M., Nagle J. F. Testing kinetic models for the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle--II. Inclusion of an O to M backreaction. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Oct;40(4):501–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb04624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M. A., Caplan S. R. Modulation excitation spectro-photometry of purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Jan 3;253(5486):56–58. doi: 10.1038/253056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



