Abstract
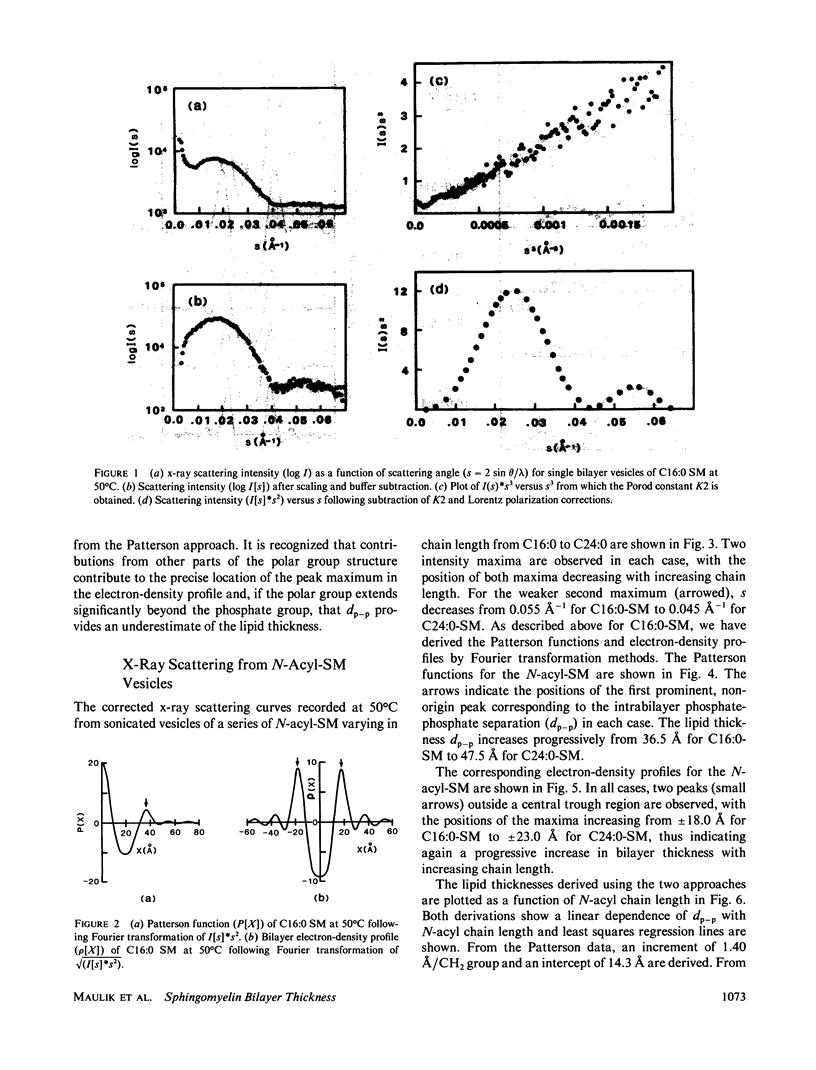
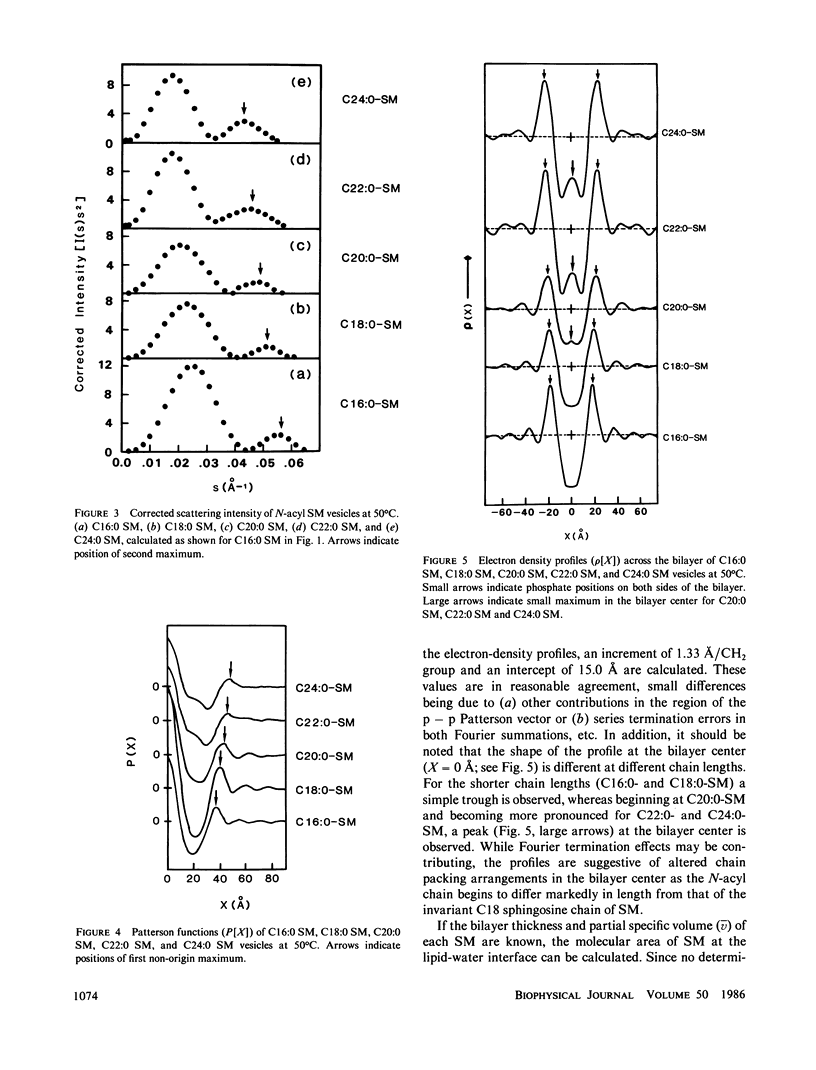
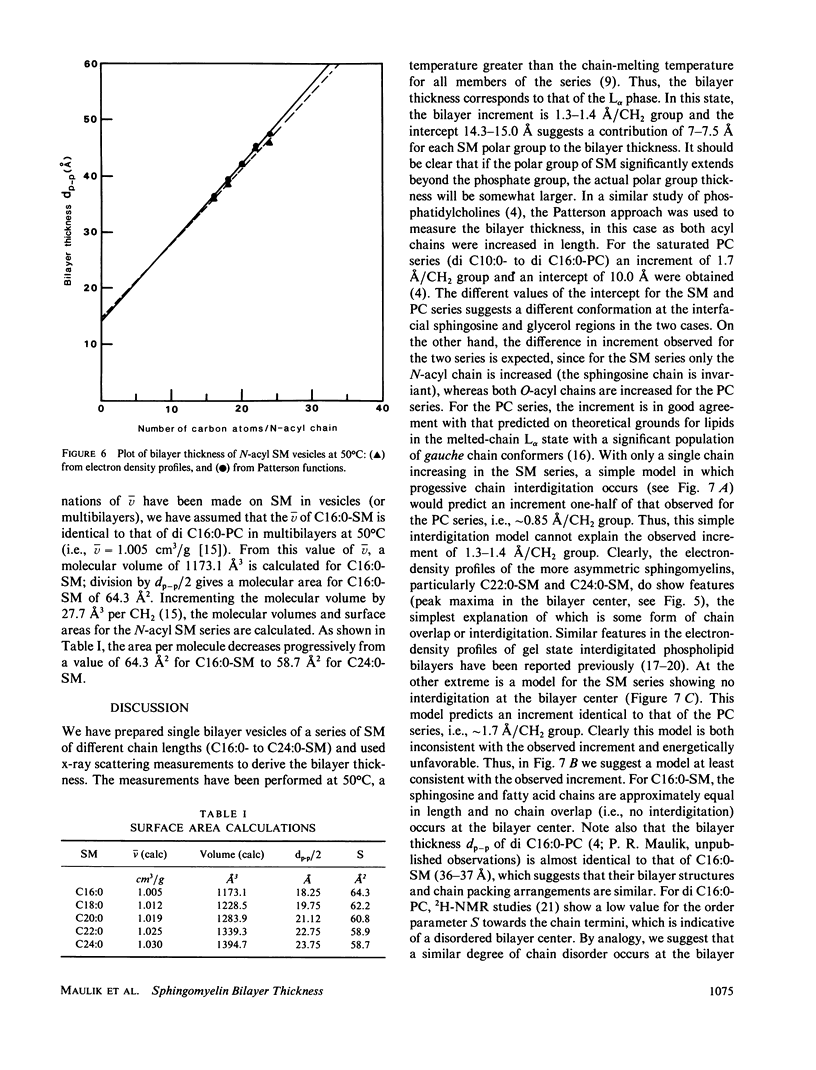
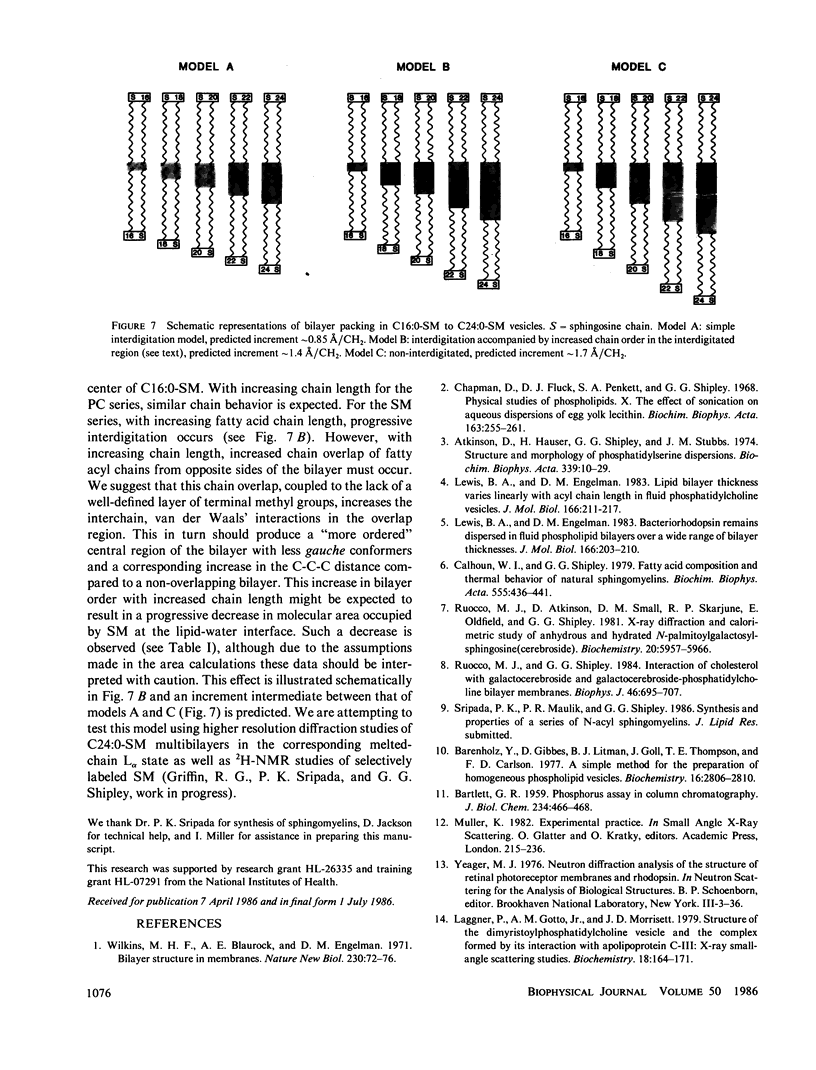
A series of N-acyl sphingomyelins (C16:0, C18:0, C20:0, C22:0, and C24:0) have been synthesized and single bilayer vesicles formed by sonication and ultracentrifugation. X-ray scattering data have been collected from the sphingomyelin vesicles at 50 degrees C in the melted-chain state. The x-ray scattering data have been transformed to the corresponding Patterson functions and Fourier electron density profiles; analysis of these functions has provided the intrabilayer phosphate-phosphate separation dp-p, a measure of the lipid bilayer thickness. The bilayer thickness increases linearly with increasing chain length (increment 1.3-1.4 A) and the intercept, 14.3-15.0 A, suggests a contribution of 7.0-7.5 A for each phosphorylcholine group to the bilayer thickness. The electron-density profiles have features suggestive of chain interdigitation when the length of the N-acyl chain (C20:0, C22:0, and C24:0) exceeds significantly the length of the invariant sphingosine chain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson D., Hauser H., Shipley G. G., Stubbs J. M. Structure and morphology of phosphatidylserine dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):10–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenholz Y., Gibbes D., Litman B. J., Goll J., Thompson T. E., Carlson R. D. A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2806–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun W. I., Shipley G. G. Fatty acid composition and thermal behavior of natural sphingomyelins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 23;555(3):436–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Fluck D. J., Penkett S. A., Shipley G. G. Physical studies of phospholipids. X. The effect of sonication of aqueous dispersions of egg yolk lecithin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laggner P., Gotto A. M., Jr, Morrisett J. D. Structure of the dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicle and the complex formed by its interaction with apolipoprotein C-III: X-ray small-angle scattering studies. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):164–171. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer thickness varies linearly with acyl chain length in fluid phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Chain ordering in liquid crystals. II. Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 29;367(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattai J., Shipley G. G. The kinetics of formation and structure of the low-temperature phase of 1-stearoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 24;859(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranck J. L., Keira T., Luzzati V. A novel packing of the hydrocarbon chains in lipids. The low temperature phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl-glycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Atkinson D., Small D. M., Skarjune R. P., Oldfield E., Shipley G. G. X-ray diffraction and calorimetric study of anhydrous and hydrated N-palmitoylgalactosylsphingosine (cerebroside). Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5957–5966. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Shipley G. G. Interaction of cholesterol with galactocerebroside and galactocerebroside-phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):695–707. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84068-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrallach E. N., Dijkman R., de Haas G. H., Shipley G. G. Structure and thermotropic properties of 1,3-dipalmitoyl-glycero-2-phosphocholine. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):155–174. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. H., Blaurock A. E., Engelman D. M. Bilayer structure in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):72–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio230072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


