Abstract
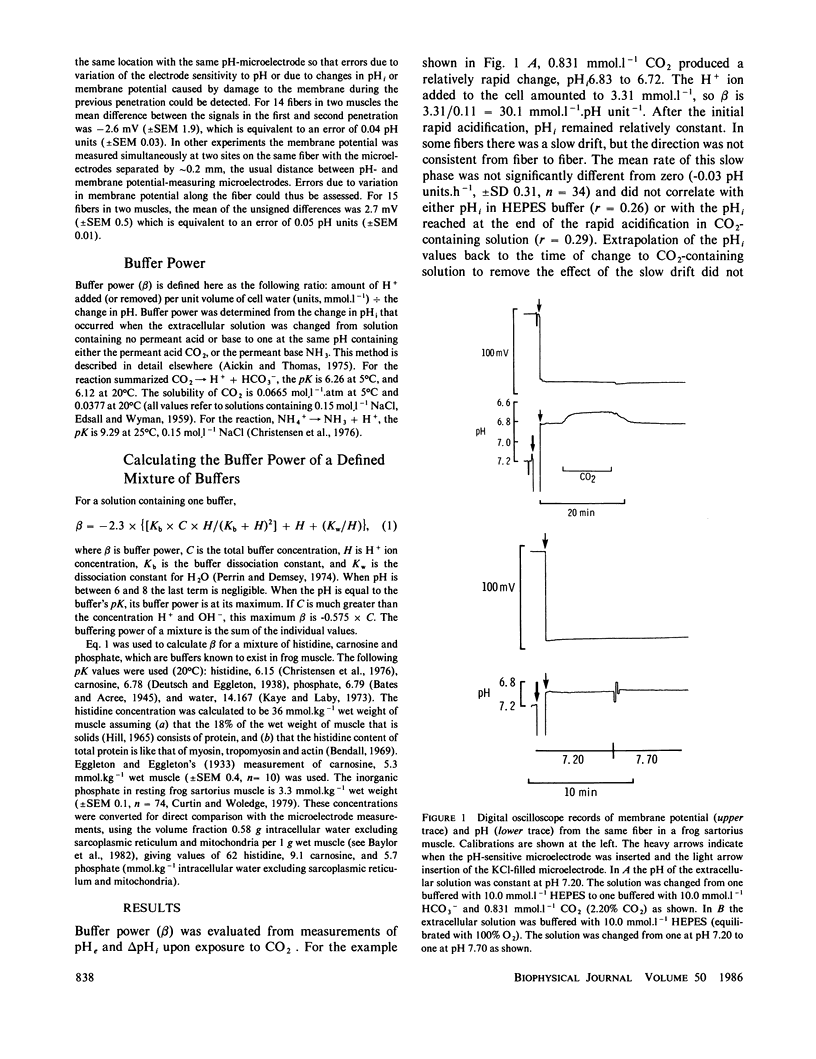
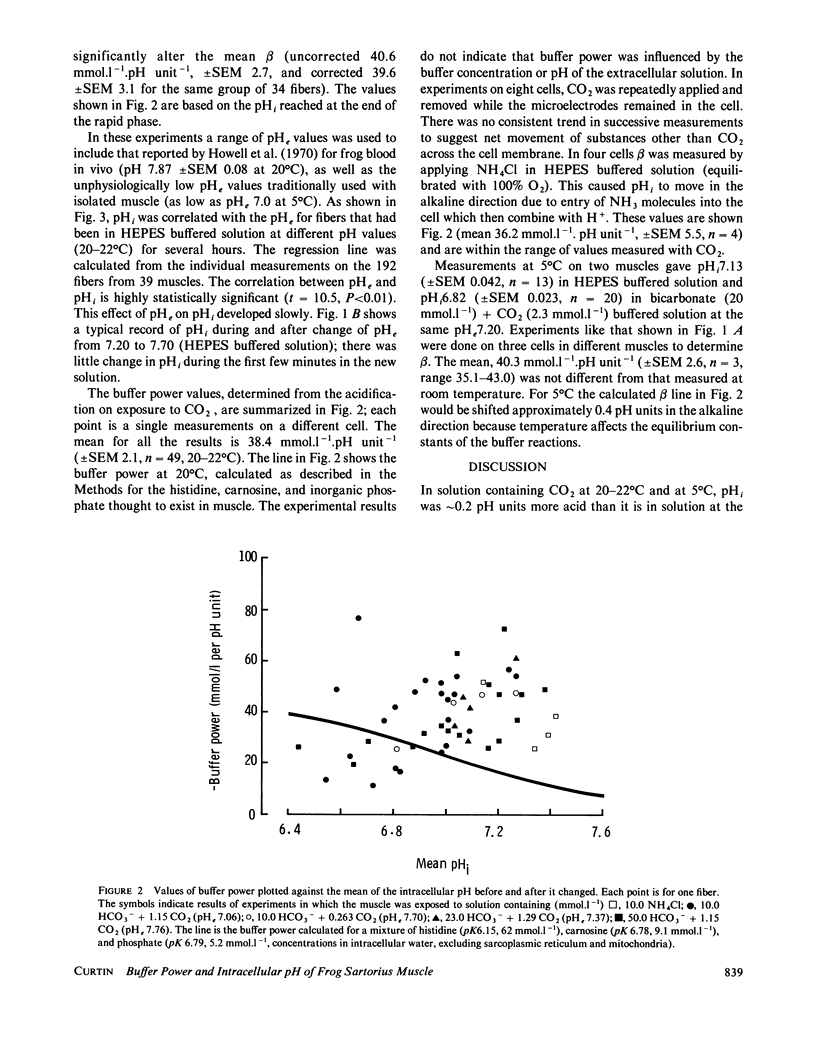
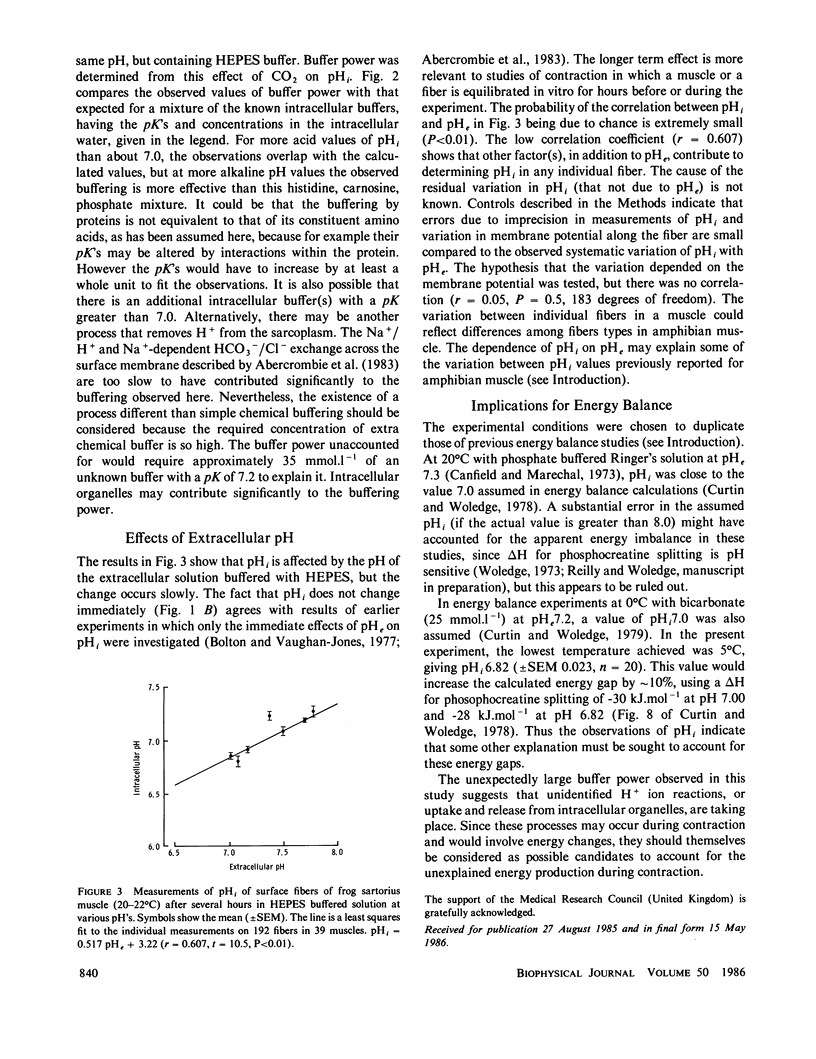
Intracellular pH (pHi) and buffer power of frog muscle were measured using pH-sensitive microelectrodes under conditions used previously in energy balance experiments because pH strongly influences the molar enthalpy change for phosphocreatine splitting, the major net reaction during brief contractions. The extracellular pH (pHe) of HEPES buffered Ringer's solution influenced pHi, but change in pHi developed slowly. Addition or removal of CO2 or NH3 from the extracellular solution caused a rapid change in pHi. The mean buffer power measured with CO2 was 38.4 mmol.l-1.pH unit-1 (+/- SEM 2.1, n = 49) and with NH3 was 36.2 (+/- SEM 5.5, n = 4) at 20-22 degrees C. At 5 degrees C, in experiments with CO2 the mean buffer power was 40.3 (+/- SEM 2.6, n = 3). For pHi values above approximately 7.0, the observed buffer power was greater than that expected from the values in the literature for the histidine content of intracellular proteins, carnosine and inorganic phosphate in the sarcoplasm. The measured pHi values were similar to those assumed in energy balance calculations, but the high measured buffer power suggests that other buffering reactions occur in addition to those included in energy balance calculations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie R. F., Putnam R. W., Roos A. The intracellular pH of frog skeletal muscle: its regulation in isotonic solutions. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:175–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Thomas R. C. Micro-electrode measurement of the internal pH of crab muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):803–815. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Optical measurements of intracellular pH and magnesium in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:105–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Continuous direct measurement of intracellular chloride and pH in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):801–833. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield P., Maréchal G. Equilibrium of nucleotides in frog sartorius muscle during an isometric tetanus at 20 degrees C. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):453–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. Chemical change and energy production during contraction of frog muscle: how are their time courses related? J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:353–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. Energy changes and muscular contraction. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jul;58(3):690–761. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.3.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch A., Eggleton P. The titration constants of anserine, carnosine and some related compounds. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):209–211. doi: 10.1042/bj0320209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell B. J., Baumgardner F. W., Bondi K., Rahn H. Acid-base balance in cold-blooded vertebrates as a function of body temperature. Am J Physiol. 1970 Feb;218(2):600–606. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.2.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Intracellular pH of snail neurones measured with a new pH-sensitive glass mirco-electrode. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):159–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


