Abstract
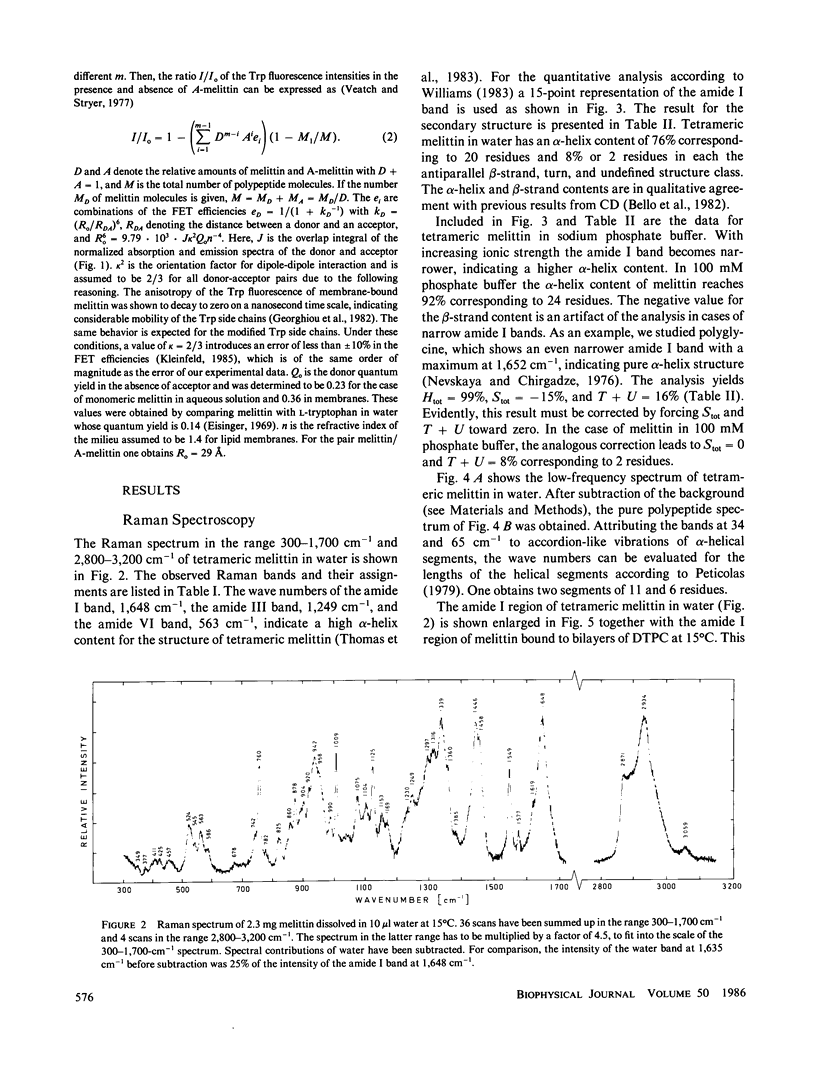
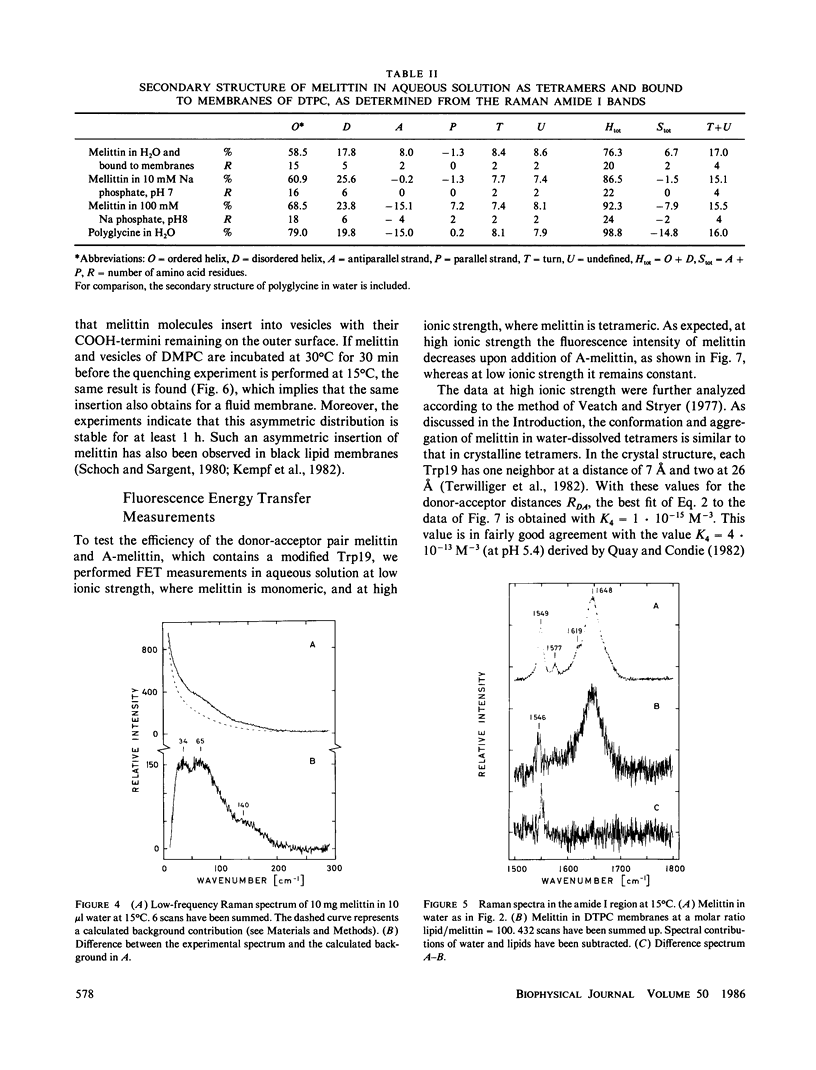
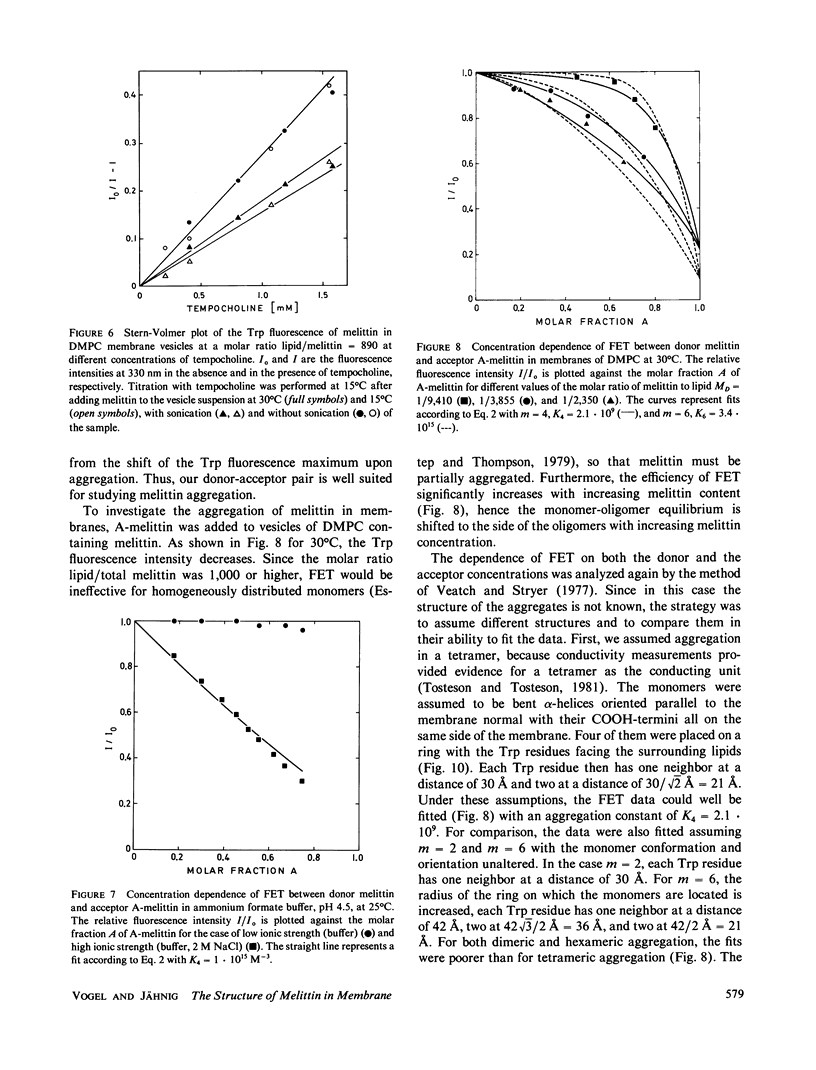
The conformation of the polypeptide melittin in lipid membranes as determined by Raman spectroscopy is a bent alpha-helix formed by the mainly hydrophobic residues 1-21, and a nonhelical COOH-terminal segment of the hydrophilic residues 22-26. Fluorescence quenching experiments on residue Trp19 reveal that all COOH-termini are located on that side of a vesicular membrane to which melittin was added. By means of fluorescence energy transfer between unmodified and modified Trp19 residues, melittin is shown to aggregate in membranes predominantly in the form of tetramers. These and previous results on the location and orientation of melittin permit the development of a model for the structure of melittin tetramers in membranes. The hydrophilic sides of four bilayer-spanning helices face each other to form a hydrophilic pore through the membrane.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bello J., Bello H. R., Granados E. Conformation and aggregation of melittin: dependence on pH and concentration. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):461–465. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Braun W., Kumar A., Wüthrich K. High resolution nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the conformation and orientation of melittin bound to a lipid-water interface. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):319–328. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84680-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier D., Pézolet M. Raman spectroscopic study of the interaction of poly-L-lysine with dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Oct;46(4):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84047-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. R., Drake A. F., Helliwell J., Hider R. C. The interaction of bee melittin with lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 16;510(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Musso G. F., Lieber M., Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Kinetics and mechanism of hemolysis induced by melittin and by a synthetic melittin analogue. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):329–338. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84681-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. F., Hider R. C. The structure of melittin in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 7;555(2):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):371–374. doi: 10.1038/299371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J. A variable temperature, U.V. luminescence spectrograph for small samples. Photochem Photobiol. 1969 Mar;9(3):247–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1969.tb07289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep T. N., Thompson T. E. Energy transfer in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1979 May;26(2):195–207. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85244-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. O., Jr, Richards F. M. A voltage-gated ion channel model inferred from the crystal structure of alamethicin at 1.5-A resolution. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):325–330. doi: 10.1038/300325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georghiou S., Thompson M., Mukhopadhyay A. K. Melittin-phospholipid interaction studied by employing the single tryptophan residue as an intrinsic fluorescent probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90355-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Jentsch J. Sequenzanalyse des Melittins aus den tryptischen und peptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Kowallek H. Modifikationen der Aminogruppen und des Tryptophans im Melittin als Mittel zur Erkennung von Struktur-Wirkungs-Beziehungen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Jul;351(7):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Methfessel C., Wilmsen H. U., Katz E., Jung G., Boheim G. Melittin and a chemically modified trichotoxin form alamethicin-type multi-state pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 5;727(1):108–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Khader F., Tatham A. S. Lytic activity of monomeric and oligomeric melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb;728(2):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90473-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N., Van Renswoude J., Pincus M., Blumenthal R. Voltage-dependent trans-bilayer orientation of melittin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2469–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Kochoumian L., Joslyn A. Melittin-specific monoclonal and polyclonal IgE and IgG1 antibodies from mice. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2668–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld A. M. Tryptophan imaging of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1874–1882. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöppel E., Eisenberg D., Wickner W. Interactions of melittin, a preprotein model, with detergents. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4177–4181. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavialle F., Adams R. G., Levin I. W. Infrared spectroscopic study of the secondary structure of melittin in water, 2-chloroethanol, and phospholipid bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Knowles P. F. Evidence for phase boundary lipid. Permeability of Tempo-choline into dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles at the phase transition. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3570–3578. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevskaya N. A., Chirgadze Y. N. Infrared spectra and resonance interactions of amide-I and II vibration of alpha-helix. Biopolymers. 1976 Apr;15(4):637–648. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Klausner R. D., Scheraga H. A. Calculation of the three-dimensional structure of the membrane-bound portion of melittin from its amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5107–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quay S. C., Condie C. C. Conformational studies of aqueous melittin: thermodynamic parameters of the monomer-tetramer self-association reaction. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):695–700. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch P., Sargent D. F. Quantitative analysis of the binding of melittin to planar lipid bilayers allowing for the discrete-charge effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):234–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom R., Crifo C., Viti V., Guidoni L., Podo F. Variations in circular dichroism and proton-NMR relaxation properties of melittin upon interaction with phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom R., Podo F., Crifo C., Berthet C., Zulauf M., Zaccai G. Structural aspects of the interaction of bee venom peptide melittin with phospholipids. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):391–396. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. C., Dufourcq J., de Bony J., Faucon J. F., Lussan C. Conformational change and self association of monomeric melittin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Weissman L., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin's lytic and surface activities. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):353–361. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84683-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Prescott B., Day L. A. Structure similarity, difference and variability in the filamentous viruses fd, If1, IKe, Pf1 and Xf. Investigation by laser Raman spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):321–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. Activation and inactivation of melittin channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):112–114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84130-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. The sting. Melittin forms channels in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84719-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran C. D., Beddard G. S. Studies of the fluorescence from tryptophan in melittin. Eur Biophys J. 1985;13(1):59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00266310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Stryer L. The dimeric nature of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: conductance and fluorescence energy transfer studies of hybrid channels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. Incorporation of melittin into phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Study of binding and conformational changes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 2;134(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80545-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F., Hoffmann V., Stümpel J. The orientation of melittin in lipid membranes. A polarized infrared spectroscopy study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. W., Dunker A. K. Determination of the secondary structure of proteins from the amide I band of the laser Raman spectrum. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):783–813. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. W. Estimation of protein secondary structure from the laser Raman amide I spectrum. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):581–603. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]