Abstract
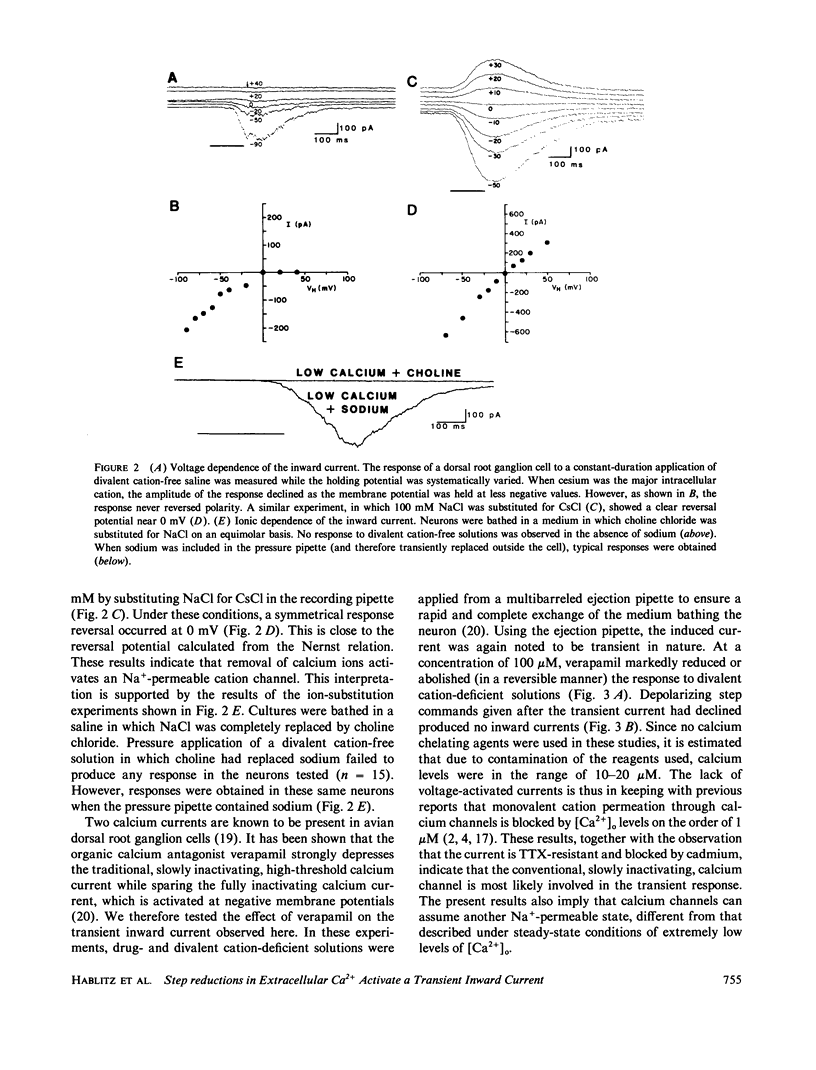
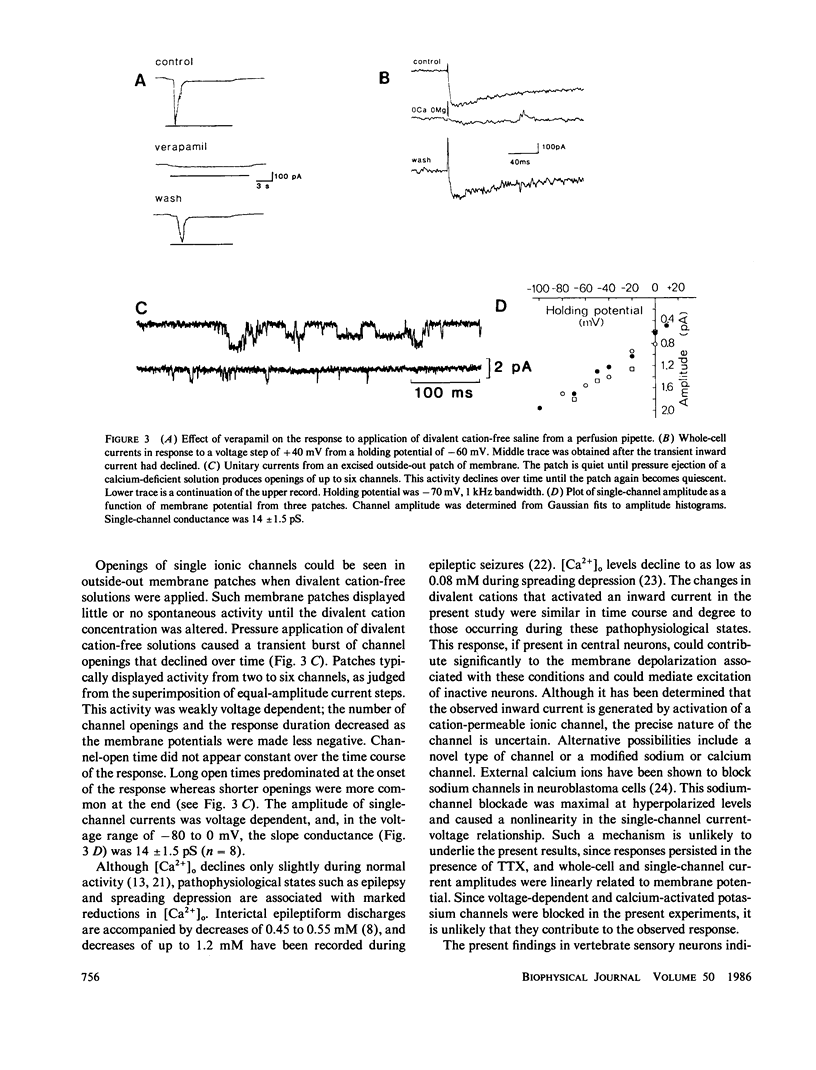
We investigated whether transient step reductions in divalent cations would produce detectable changes in neuronal excitability similar to those reported in the total absence of divalent cations. Using cultured chick dorsal root ganglion cells as a model system, our results indicate that a step reduction in divalent cations induces a transient inward current. This response is mediated by a tetrodotoxin-resistant, Na+-permeable, cation channel that is blocked by cadmium. This, and our observation that the response is abolished by verapamil, suggests that the current passes through calcium channels. This transient inward current was estimated to be activated by decreases in extracellular calcium ([Ca2+]o) as small as 0.5-0.8 mM and thus represents a different response from the one previously observed when steady-state [Ca2+]o levels were reduced to micromolar levels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W., Palade P. T. A non-selective cation conductance in frog muscle membrane blocked by micromolar external calcium ions. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Thoenen H. Sensory neurons in culture: changing requirements for survival factors during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1199–1203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boll W., Lux H. D. Action of organic antagonists on neuronal calcium currents. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 23;56(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Camerer H., Kunze D. L., Lux H. D. Similarity of unitary Ca2+ currents in three different species. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):156–158. doi: 10.1038/299156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. J., Zeuthen T. Extracellular ion concentrations during spreading depression and ischemia in the rat brain cortex. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Louvel J. Changes in [Ca2+]o and [K+]o during repetitive electrical stimulation and during pentetrazol induced seizure activity in the sensorimotor cortex of cats. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Sep;398(4):310–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00657240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Lux H. D., Gutnick M. J. Extracellular free calcium and potassium during paroxsmal activity in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Mar 30;27(3-4):237–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00235500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Hablitz J. J., Wilson W. A. Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):391–393. doi: 10.1038/286391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. High selectivity of calcium channels in single dialysed heart cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:253–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Brown A. M. Single channel studies on inactivation of calcium currents. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):432–434. doi: 10.1126/science.6330896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C., ten Bruggencate G., Stöckle H., Steinberg R. Calcium and potassium changes in extracellular microenvironment of cat cerebellar cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jul;41(4):1026–1039. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.4.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumain R., Kurcewicz I., Louvel J. Fast extracellular calcium transients: involvement in epileptic processes. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.6623068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumain R., Menini C., Heinemann U., Louvel J., Silva-Barrat C. Chemical synaptic transmission is not necessary for epileptic seizures to persist in the baboon Papio papio. Exp Neurol. 1985 Jul;89(1):250–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G. G. Stimulus-evoked and seizure-related responses of extracellular calcium activity in spinal cord compared to those in cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Oct;44(4):617–632. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C. E., Wallis D. I. Generation of an unusual depolarizing response in rabbit primary afferent neurones in the absence of divalent cations. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:49–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto D., Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. Voltage-dependent calcium block of normal and tetramethrin-modified single sodium channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):337–344. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84159-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


