Abstract
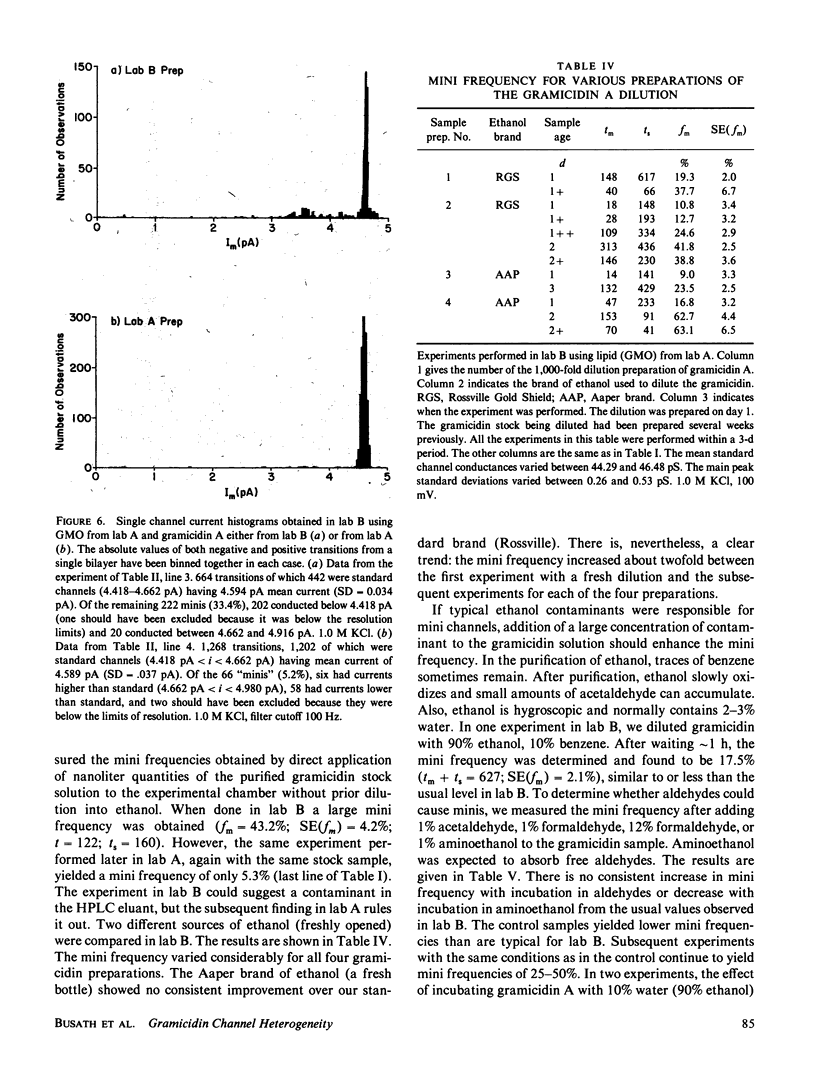
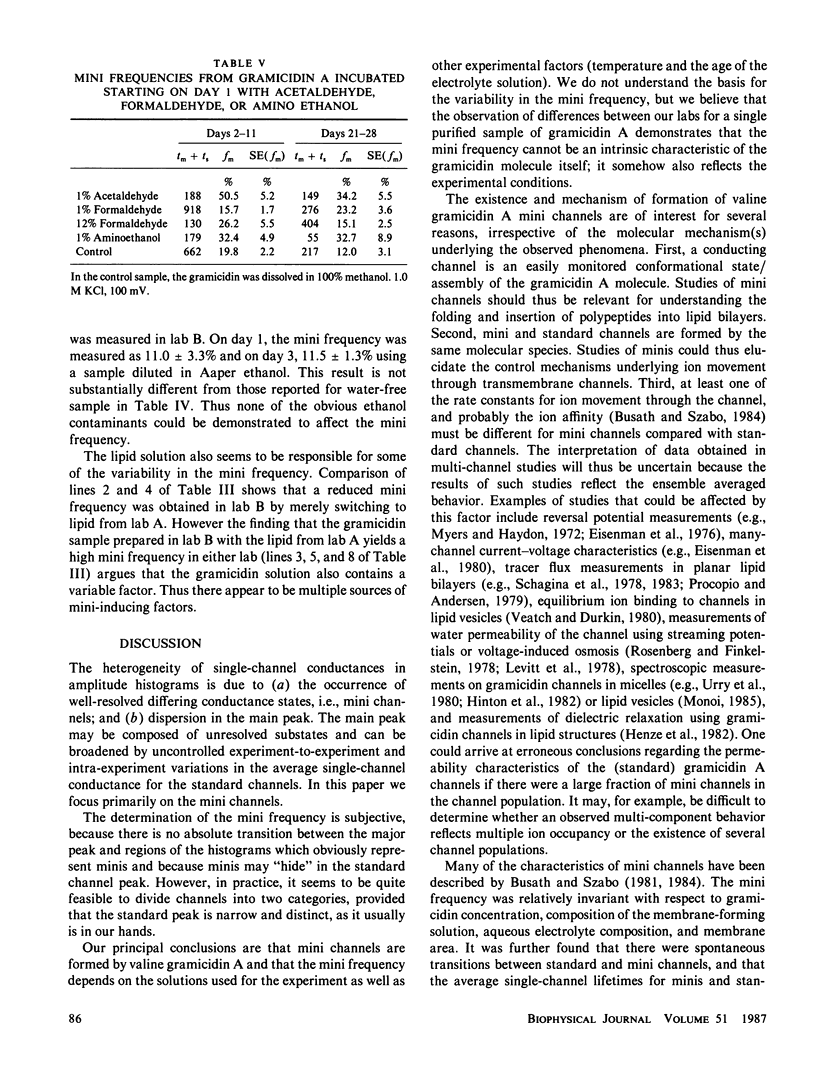
The relative frequency of low-conductance variants of gramicidin A channels in lipid bilayers was determined in parallel experiments in two different laboratories. A common gramicidin stock solution was tested in both labs and, initially, gave rise to significantly different proportions (9% v. 23%) of "mini" channels in the two labs. The lipid and gramicidin solutions were exchanged to identify the source of the difference: When using solutions prepared in lab A (Andersen), lab B (Busath) observed 9% minis, consistent with the original findings in lab A; when using the gramicidin solution prepared in lab B, lab A observed 18% minis, consistent with the original findings in lab B. The experimental apparatus and analysis techniques are therefore not the source of the discrepancy; rather, the difference appears to stem from some factor(s) related to the gramicidin, lipid, and electrolyte solutions. It appears that the mini frequency cannot reflect intrinsic characteristics of the channel-forming peptide, but rather must, at least in part, reflect environmental modulations of channel properties. This has implications for the interpretation of multi-channel experiments on gramicidin A.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Single-channel measurements at very high potentials. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):119–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84414-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen K. S., Vogelsang S. H. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of gramicidin, a polypeptide antibiotic. J Chromatogr. 1977 Oct 11;140(2):174–178. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)88411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Noda K., Gross E., Läuger P. Single-channel parameters of gramicidin A,B, and C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busath D., Szabo G. Atypical gramicidin a channels appear to have increased field strength at one binding site. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):85–87. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84118-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busath D., Szabo G. Gramicidin forms multi-state rectifying channels. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):371–373. doi: 10.1038/294371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Hägglund J., Sandblom J., Enos B. The current-voltage behavior of ion channels: important features of the energy profile of the gramicidin channel deduced from the conductance-voltage characteristic in the limit of low ion concentration. Ups J Med Sci. 1980;85(3):247–257. doi: 10.3109/03009738009179195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henze R., Neher E., Trapane T. L., Urry D. W. Dielectric relaxation studies of ionic processes in lysolecithin-packaged gramicidin channels. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(3):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01870890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. F., Young G., Millett F. S. Thallous ion interaction with gramicidin incorporated in micelles studied by thallium-205 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):651–654. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Elias S. R., Hautman J. M. Number of water molecules coupled to the transport of sodium, potassium and hydrogen ions via gramicidin, nonactin or valinomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):436–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazet J. L., Andersen O. S., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid sequences. A comparison of phenylalanine, tryptophane, and tyrosine substitutions at positions 1 and 11. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84153-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monoi H. Nuclear magnetic resonance of 23Na ions interacting with the gramicidin channel. Biophys J. 1985 Oct;48(4):643–662. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83820-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Veatch W. R., Stryer L. Transmembrane channel activity of gramicidin A analogs: effects of modification and deletion of the amino-terminal residue. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. U., Trapane T. L., Busath D., Szabo G., Urry D. W. Synthesis and characterization of 1-(13) C-D X Leu12, 14 gramicidin A. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Feb;19(2):162–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Finkelstein A. Interaction of ions and water in gramicidin A channels: streaming potentials across lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):327–340. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. W., Weiss L. B., Navetta F. I., Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Andersen O. S. Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid side chains. Effects of altering the polarity of the side chain at position 1 in gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):673–686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83694-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schagina L. V., Grinfeldt A. E., Lev A. A. Interaction of cation fluxes in gramicidin A channels in lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 May 18;273(5659):243–245. doi: 10.1038/273243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Alonso-Romanowski S., Venkatachalam C. M., Bradley R. J., Harris R. D. Temperature dependence of single channel currents and the peptide libration mechanism for ion transport through the gramicidin A transmembrane channel. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):205–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01868714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Alonso-Romanowski S., Venkatachalam C. M., Trapane T. L., Prasad K. U. The source of the dispersity of gramicidin A single-channel conductances. The L X Leu5-gramicidin A analog. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84019-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Trapane T. L., Romanowski S., Bradley R. J., Prasad K. U. Use of synthetic gramicidins in the determination of channel structure and mechanism. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1983 Jan;21(1):16–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1983.tb03073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Venkatachalam C. M., Spisni A., Läuger P., Khaled M. A. Rate theory calculation of gramicidin single-channel currents using NMR-derived rate constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2028–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Durkin J. T. Binding of thallium and other cations to the gramicidin A channel. Equilibrium dialysis study of gramicidin in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 15;143(4):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


