Abstract
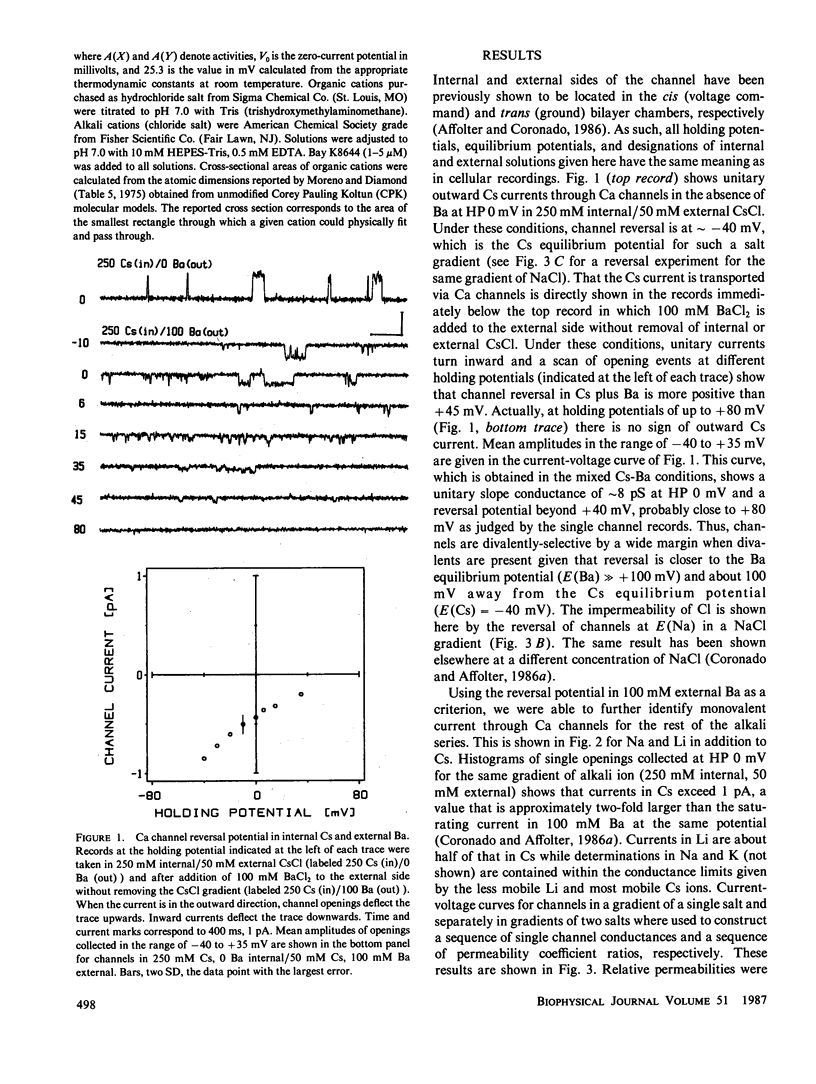
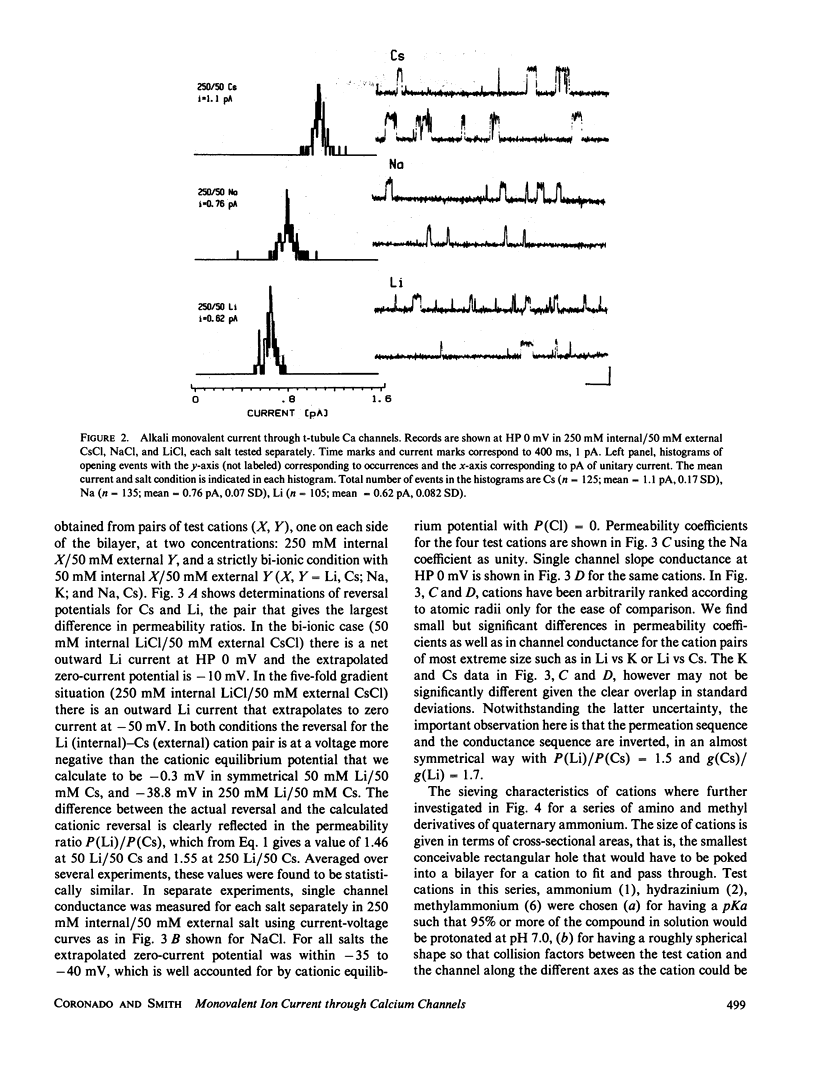
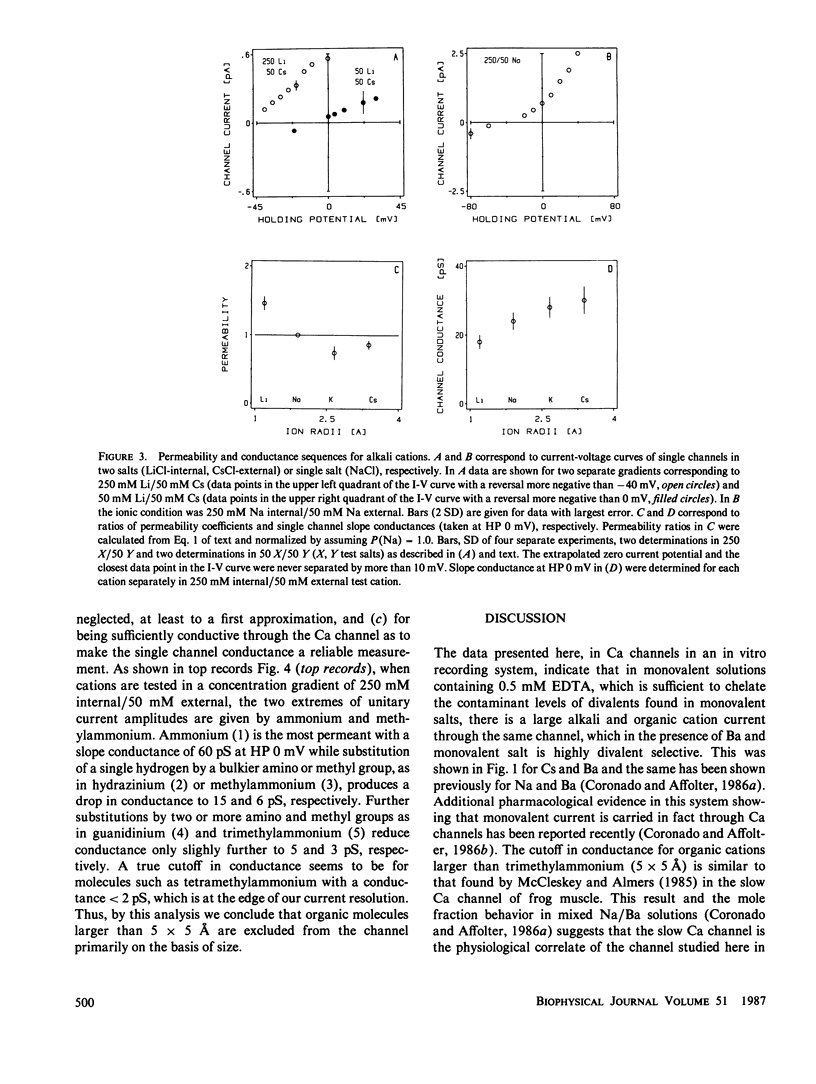
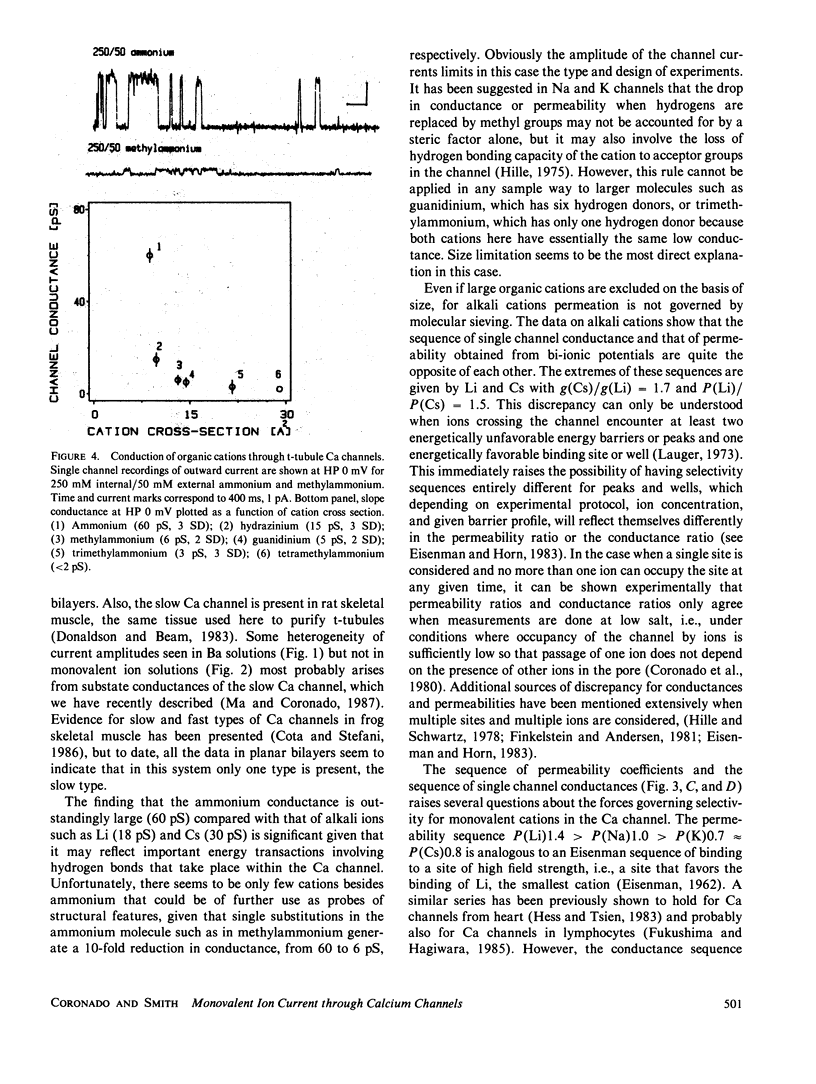
Akali monovalents, Li, Na, K, Cs, and organic monovalents of molecular cross section less than 20 A2, ammonium, methylammonium, hydrazinium, guanidinium, are shown to have a measurable conductance through Ca channels of muscle transverse tubules reconstituted into planar bilayers. For the alkali series, single channel conductances follow the sequence Cs approximately equal to K greater than Na greater than Li with a conductance ratio [g(Cs)/g(Li)] = 1.7. For permeability ratios, the sequence is Li greater than Na greater than K approximately equal to Cs with [P(Li)/P(Cs)] = 1.5. Monovalent current is only unmasked when Ba ions are not present. In mixtures of Cs and Ba, single channel current reverses close to the Ba equilibrium potential and more than 100 mV away from the Cs equilibrium potential. A cutoff in conduction is found for organic cations larger than trimethylammonium; this suggests an apparent pore aperture of about 5 X 5 A. Even in such a large pore, the fact that the alkali cation permeability sequence and conductance sequence are inverted rules out molecular sieving as the mechanism of selection among monovalents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Agonists Bay-K8644 and CGP-28392 open calcium channels reconstituted from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83789-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Sidedness of reconstituted calcium channels from muscle transverse tubules as determined by D600 and D890 blockade. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):767–771. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83703-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Chase P. B., Stimers J. R. Permeation and interaction of divalent cations in calcium channels of snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):491–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Affolter H. Insulation of the conduction pathway of muscle transverse tubule calcium channels from the surface charge of bilayer phospholipid. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):933–953. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Rosenberg R. L., Miller C. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Oct;76(4):425–446. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cota G., Stefani E. A fast-activated inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog (Rana montezume). J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:151–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson P. L., Beam K. G. Calcium currents in a fast-twitch skeletal muscle of the rat. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):449–468. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENMAN G. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys J. 1962 Mar;2(2 Pt 2):259–323. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86959-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Horn R. Ionic selectivity revisited: the role of kinetic and equilibrium processes in ion permeation through channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(3):197–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01870364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity of Na and K channels of nerve membranes. Membranes. 1975;3:255–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Almers W. The Ca channel in skeletal muscle is a large pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7149–7153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C., Vergara C., Ikemoto N. Immunological and biochemical properties of transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8140–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto D., Washio H. Permeation of sodium through calcium channels of an insect muscle membrane. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;57(2):220–222. doi: 10.1139/y79-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S. Permeation of divalent and monovalent cations through the ovarian oocyte membrane of the mouse. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:631–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


