Abstract
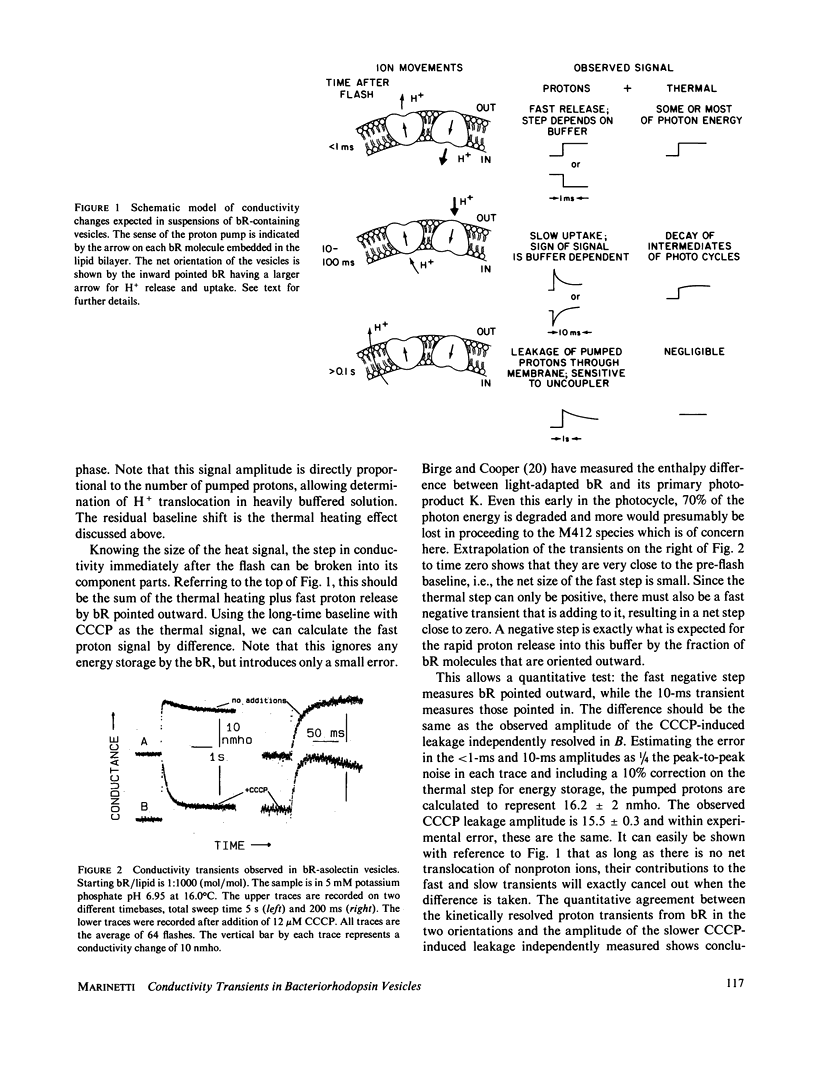
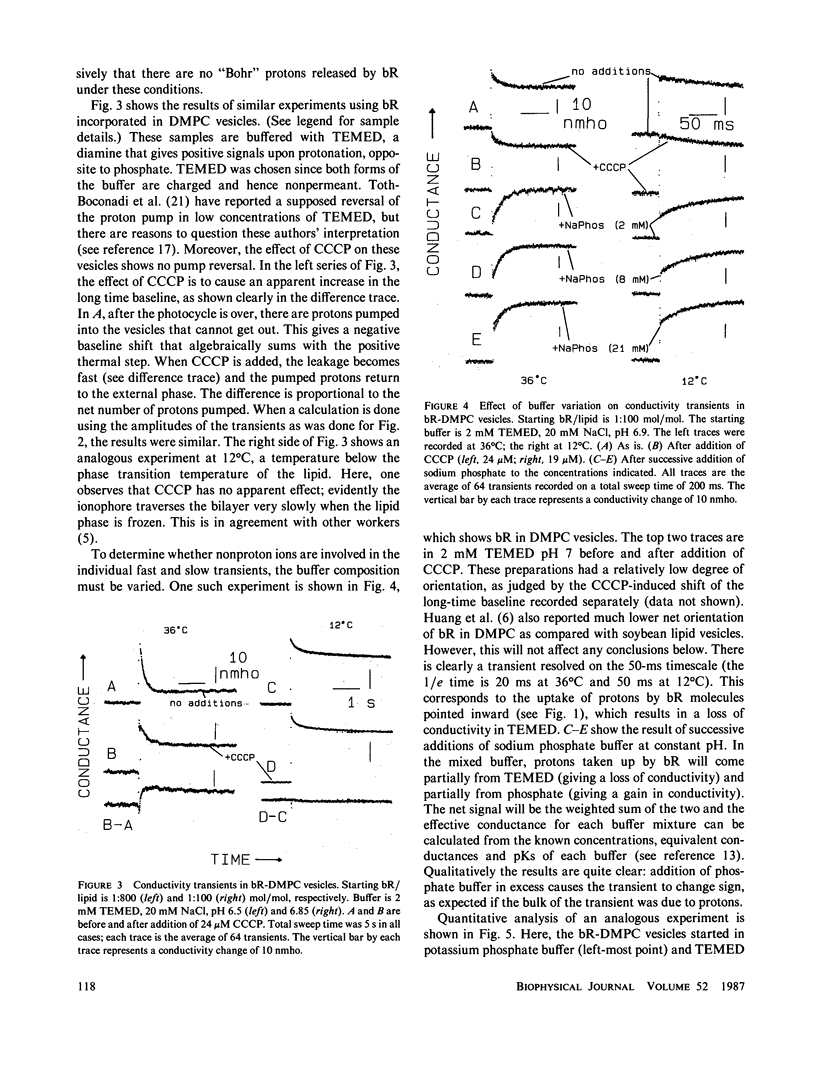
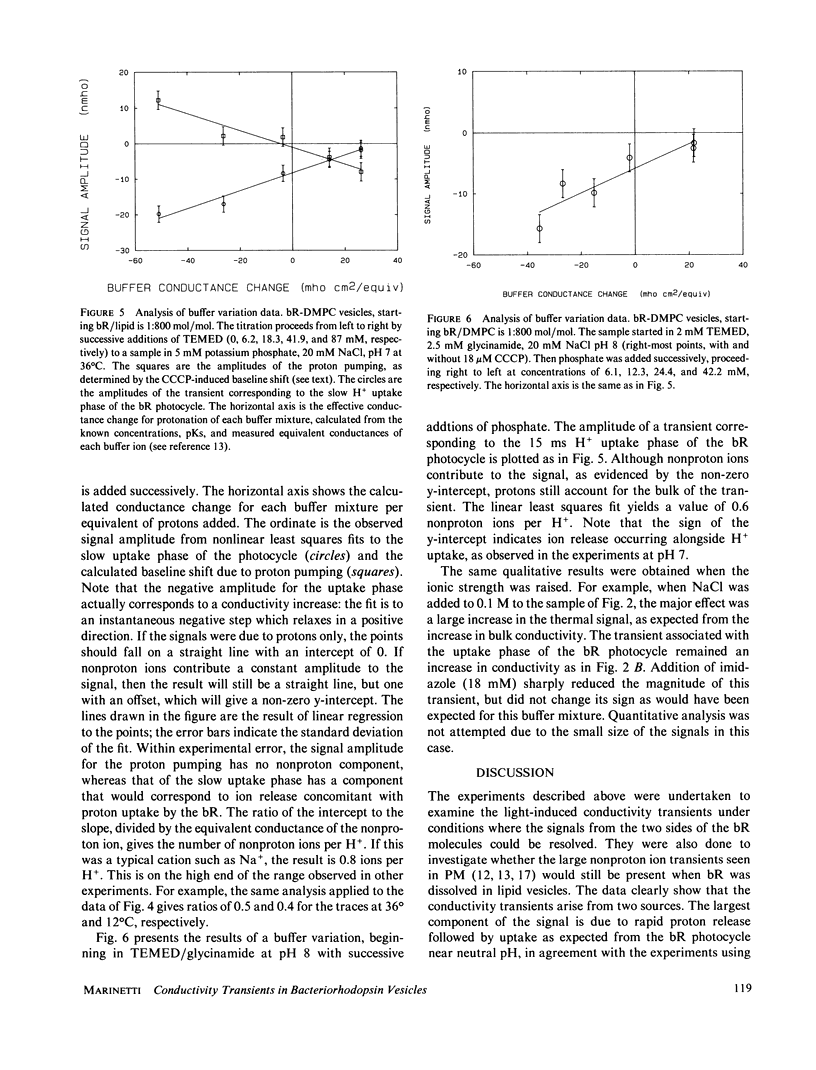
Light-induced conductivity transients have been observed in preparations of bacteriorhodopsin (bR) in phospholipid vesicles at high lipid/protein molar ratios. Under these conditions, bR is known to be dissolved as monomers in the lipid bilayer. The conductivity transients are due mostly to proton movements, including a trans-membrane component. Kinetic resolution of the conductance change due to proton ionophore-induced leakage through the vesicle membrane provides a novel method to quantitate the number of protons pumped, even in heavily buffered solutions. Some of the transient signal seen on the timescale of the bR photocycle is due to nonproton ions but is smaller than that observed in native purple membranes at pH 7 in low salt. Furthermore, when the pH is raised to 8, the very large transient nonproton ion release seen in purple membranes is not seen in the vesicles. This correlates well with previous results (Marinetti, T., and D. Mauzerall, 1986, Biophys. J., 50:405-415), in which the nonproton ion movements observed with native purple membranes were abolished by solubilization in Triton X-100. Thus, the nonproton ion release appears to be a property of bR in the native aggregated state.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birge R. R., Cooper T. M. Energy storage in the primary step of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84369-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadio R., Stoeckenius W. Effect of protein-protein interaction on light adaptation of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3374–3381. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U. Temperature-dependent aggregation of bacteriorhodopsin in dipalmitoyl- and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Bacteriorhodopsin monomers pump protons. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Formation and properties of bacteriorhodopsin monomers in the non-ionic detergents octyl-beta-D-glucoside and Triton X-100. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 15;96(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G., Crofts A. R. The quantum efficiency of proton pumping by the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85091-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Bayley H., Khorana H. G. Delipidation of bacteriorhodopsin and reconstitution with exogenous phospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T. Abrupt onset of large scale nonproton ion release in purple membranes caused by increasing pH or ionic strength. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):875–881. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83415-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T., Mauzerall D. Absolute quantum yields and proof of proton and nonproton transient release and uptake in photoexcited bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):178–180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T., Mauzerall D. Large transient nonproton ion movements in purple membrane suspensions are abolished by solubilization in Triton X-100. Biophys J. 1986 Sep;50(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83476-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Rayfield G. W. Order of proton uptake and release by bacteriorhodopsin at low pH. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):563–566. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83666-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. Flash-induced volume changes of bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments and their relationship to proton movements and absorbance transients. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. The quantum yield of flash-induced proton release by bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1979 Feb;25(2 Pt 1):341–353. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(79)85296-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Violand B., O'Neal S., Alfonzo M., Telford J. Reconstitution, a way of biochemical research; some new approaches to membrane-bound enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Dec;198(2):470–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Okazaki H., Tu S., Hutchinson H. Proton movement in reconstituted purple membrane of halobacteria: effects of pH and ionic composition of the medium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):464–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90545-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


