Abstract
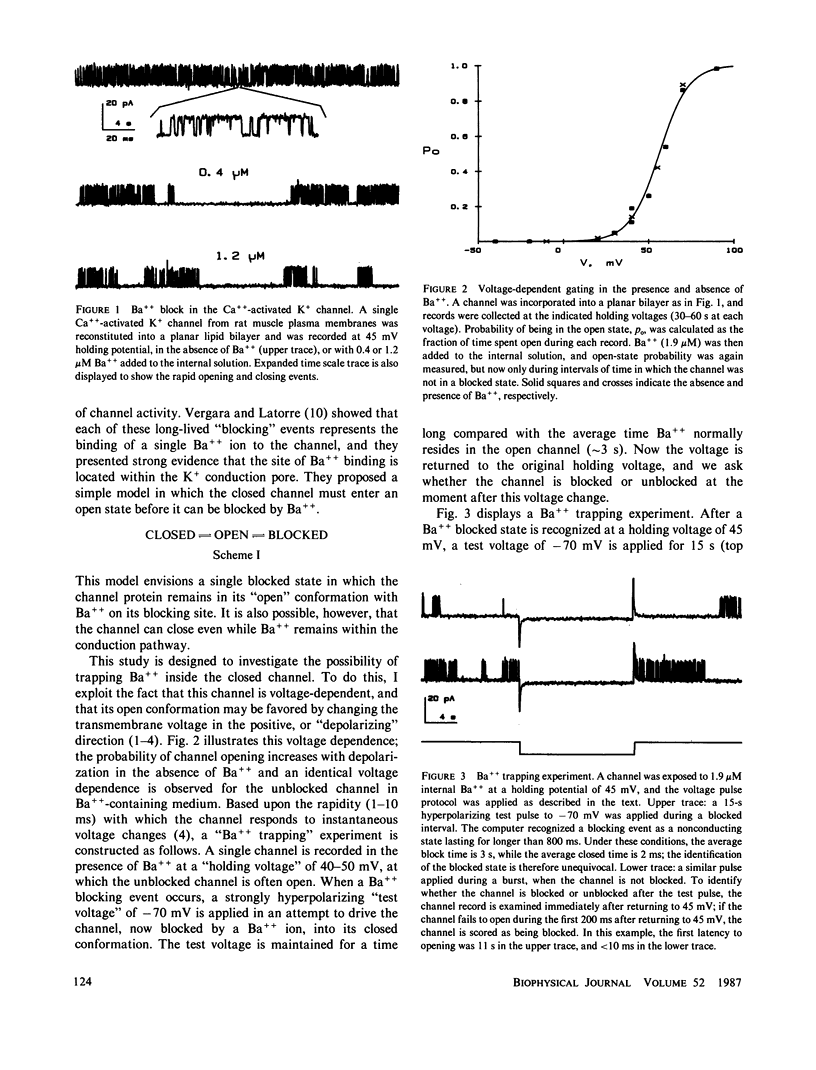
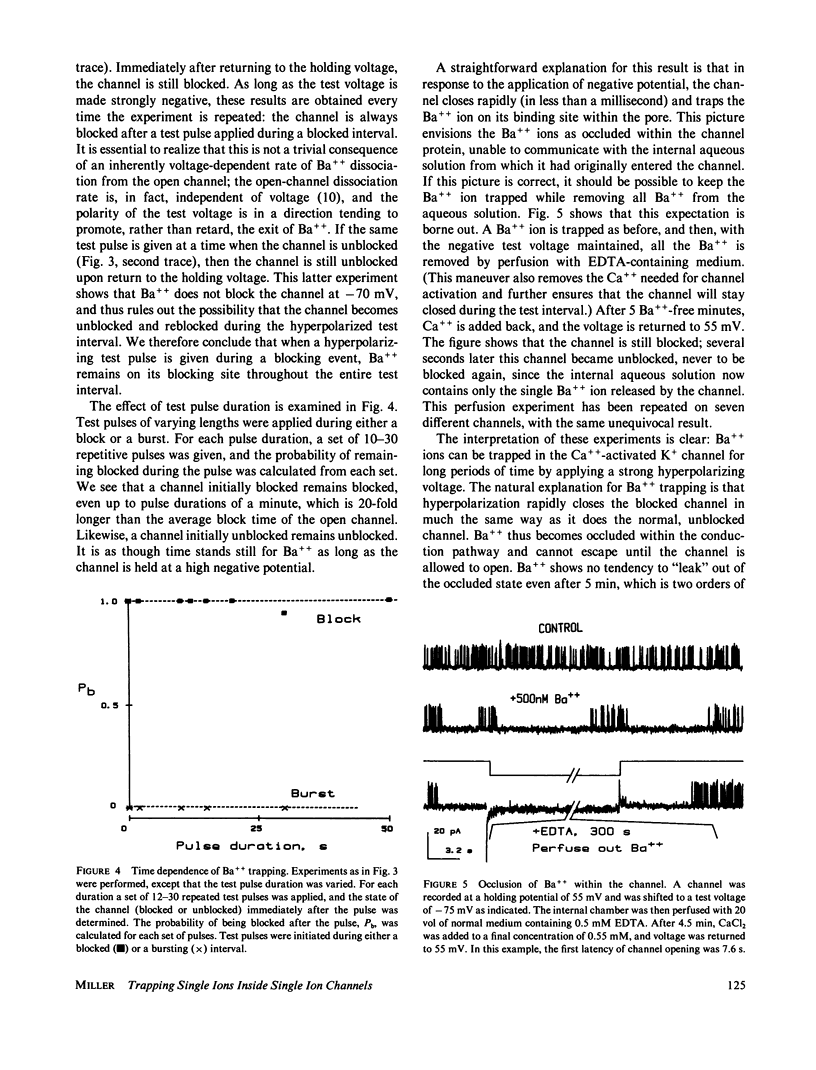
Single Ca++-activated K+ channels from rat muscle plasma membranes are inhibited by Ba++. A single Ba++ entering the channel's conduction pore induces a long-lived blocked state. This study employs Ba++ as a probe of the channel's conduction pathway to show that the channel can be forced to close with a single Ba++ ion inside the pore. A Ba++ ion inside the closed channel is trapped and cannot escape until the channel opens. The results demonstrate that in the channel's closed state, the cytoplasmic side of the conduction pore is obstructed to the passage of ions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Ionic pores, gates, and gating currents. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 May;7(2):179–210. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Taylor S. R. Interaction of barium ions with potassium channels in squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):473–488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85108-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S. Effects of barium on the potassium conductance of squid axon. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jun;75(6):727–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Latorre R., Miller C. Multi-ion conduction and selectivity in the high-conductance Ca++-activated K+ channel from skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83546-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Latorre R. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):543–568. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


