Abstract
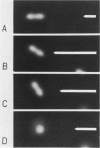
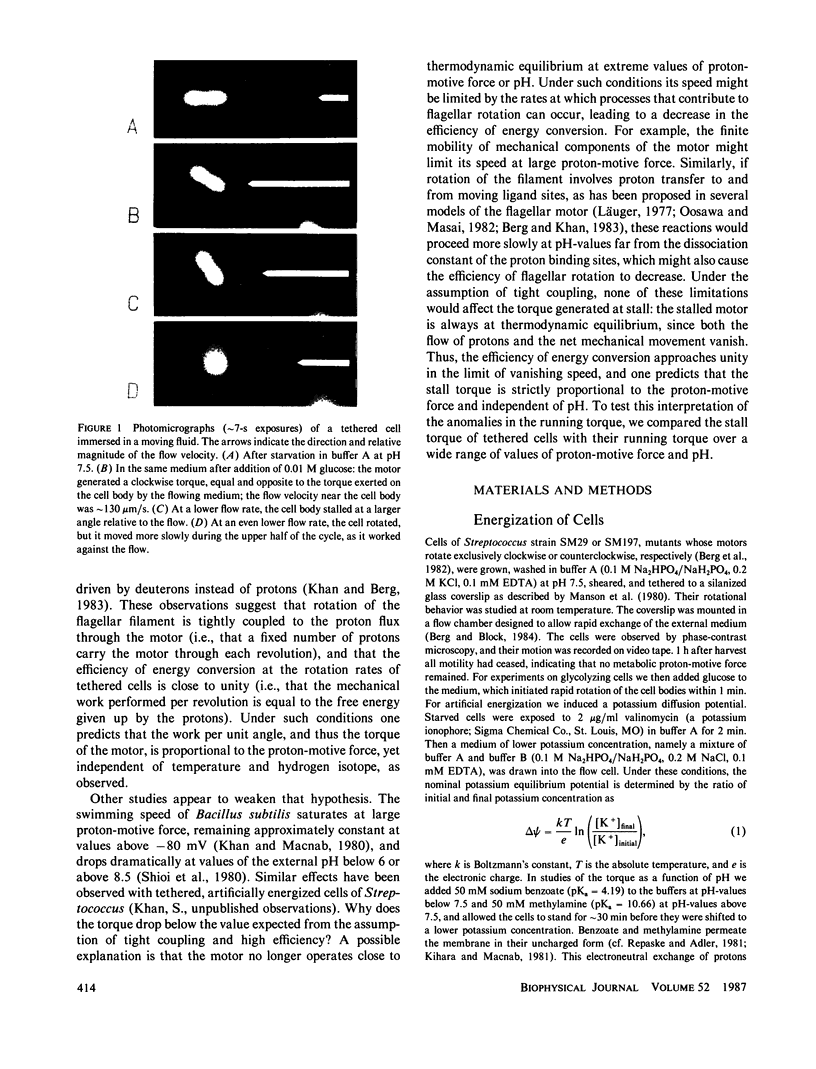
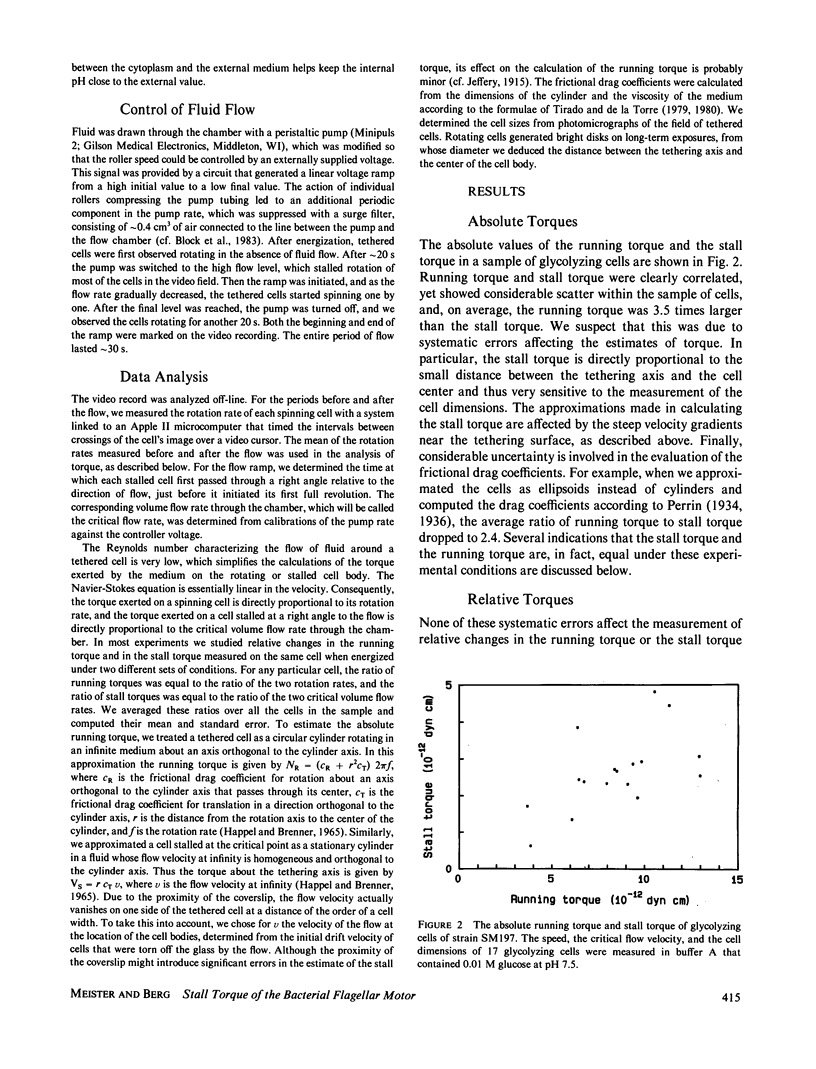
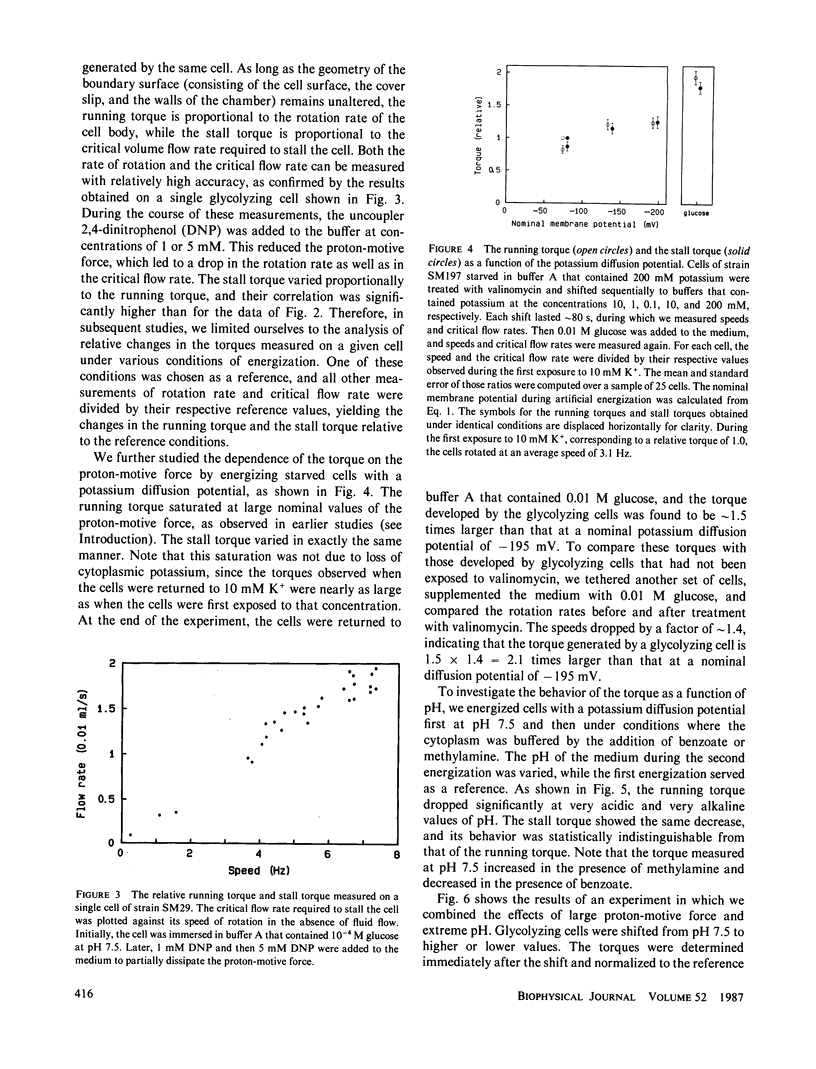
The bacterial flagellar motor couples the flow of protons across the cytoplasmic membrane to the rotation of a helical flagellar filament. Using tethered cells, we have measured the stall torque required to block this rotation and compared it with the torque of the running motor over a wide range of values of proton-motive force and pH. The stall torque and the running torque vary identically: both appear to saturate at large values of the proton-motive force and both decrease at low or high pH. This suggests that up to speeds of approximately 5 Hz the operation of the motor is not limited by the mobility of its internal components or the rates of proton transfer reactions coupled to flagellar rotation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Adaptation kinetics in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):312–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.312-323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. P., Berg H. C. Chemical modification of Streptococcus flagellar motors. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):832–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.832-843.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Imae Y. Na+-driven flagellar motors of an alkalophilic Bacillus strain YN-1. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10577–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Proton-coupled accumulation of galactoside in Streptococcus lactis 7962. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2866–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Berg H. C. Isotope and thermal effects in chemiosmotic coupling to the flagellar motor of Streptococcus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. Proton chemical potential, proton electrical potential and bacterial motility. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):599–614. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Meister M., Berg H. C. Constraints on flagellar rotation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):645–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport and rotation of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):360–362. doi: 10.1038/268360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P. M., Berg H. C. Energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Matsuura S., Imae Y. Quantitative measurements of proton motive force and motility in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):891–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.891-897.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]