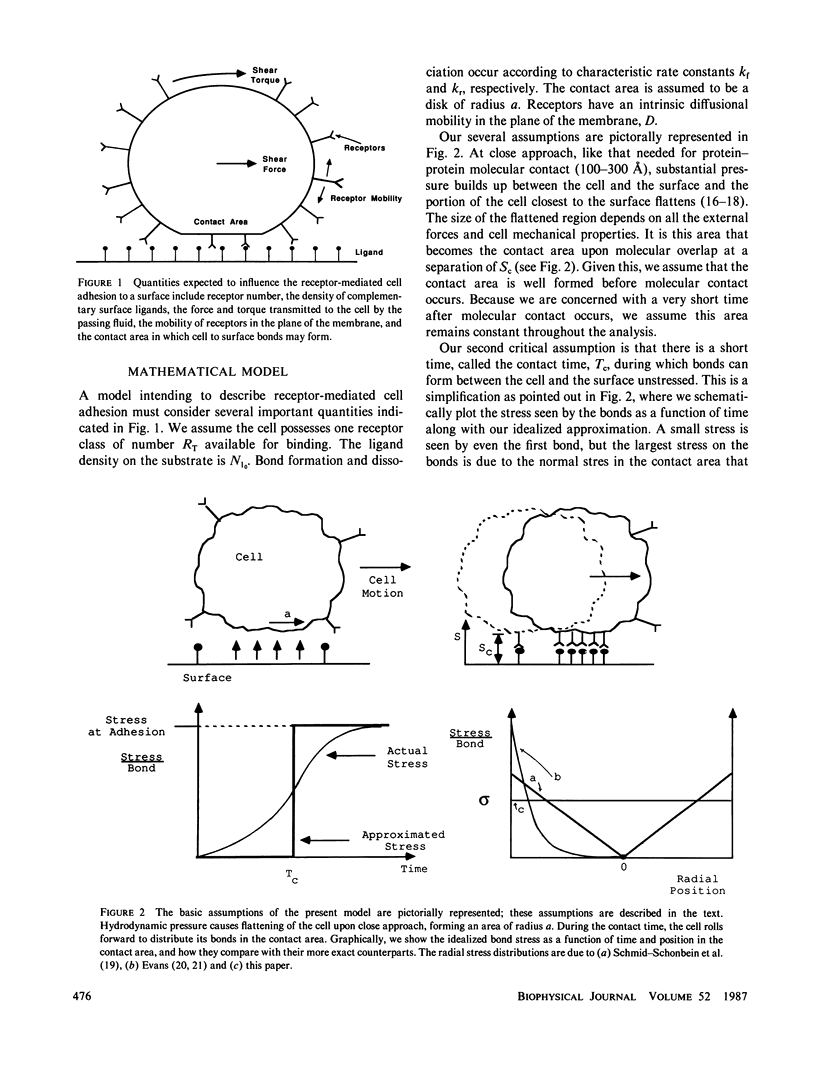
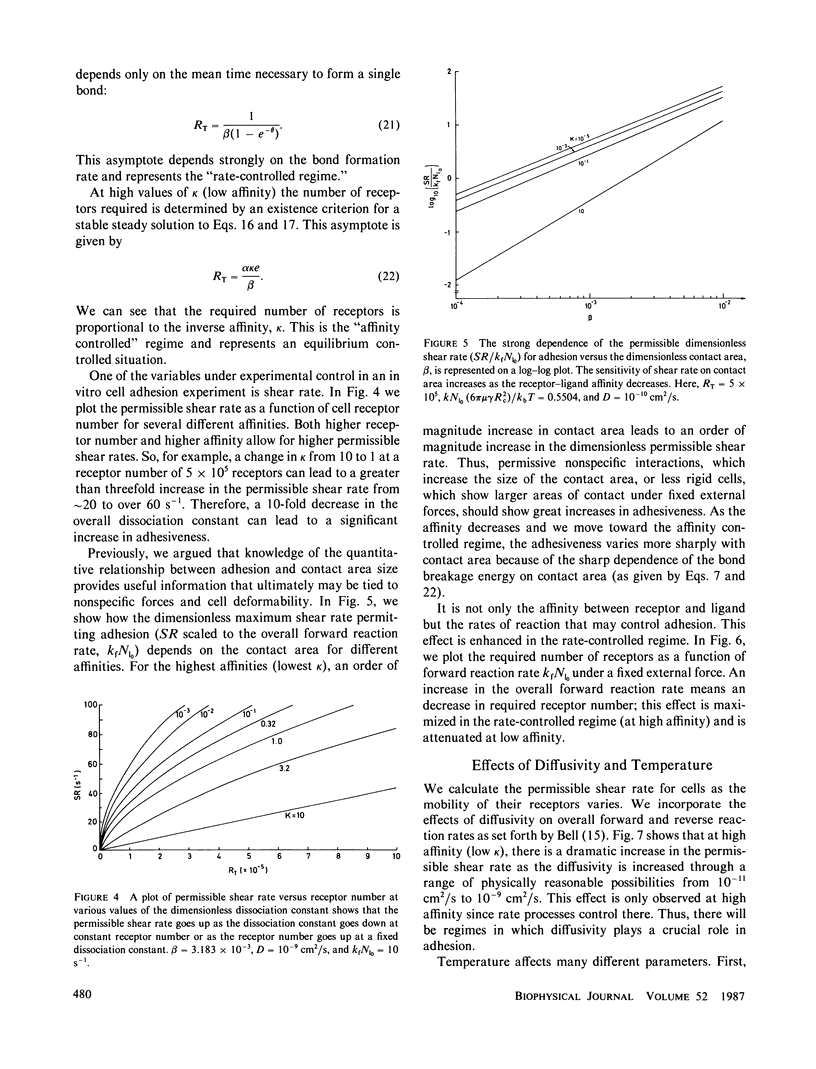
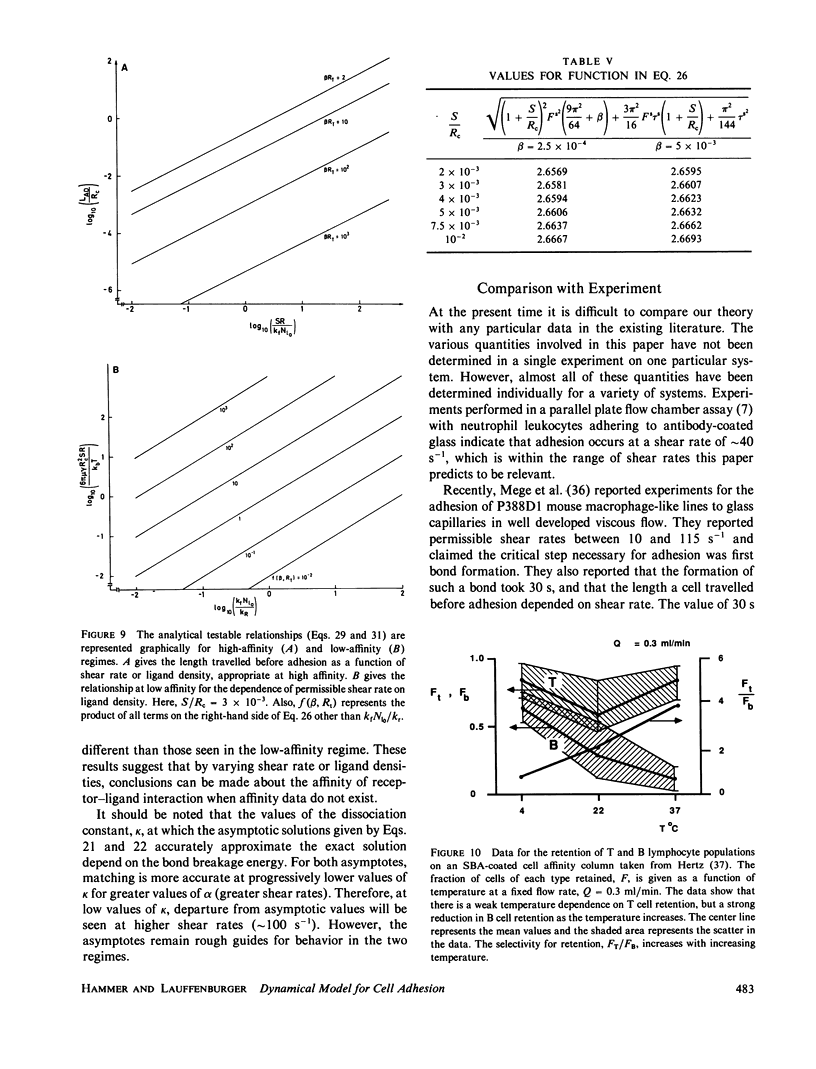
Abstract
We present a dynamical model for receptor-mediated adhesion of cells in a shear field of viscous fluid to surfaces coated with ligand molecules complementary to receptors in the cell membrane. We refer to this model as the "point attachment model" because it considers the contact area between the cell and the surface to be a small, homogeneous region that mediates the initial attachment of the cell to the surface. Using a phase plane analysis of a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations which govern the changes in free receptor density and bond density within the contact area with time, we can predict the conditions for which adhesion between the cell and the surface will take place. Whether adhesion occurs depends on values of dimensionless quantities that characterize the interaction of the cell and its receptors with the surface and its ligand, such as the bond formation rate, the receptor-ligand affinity, the fluid mechanical force, the receptor mobility, and the contact area. A key result is that there are two regimes in which different chemical and physical forces dominate: a rate-controlled high affinity regime and an affinity-controlled low-affinity regime. Many experimental observations can be explained by understanding which of these regimes is appropriate. We also provide simple approximate analytical solutions, relating adhesiveness to cell and surface properties as well as fluid forces, which allow convenient testing of model predictions by experiment.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton A., Born G. V. Quantitative investigations of the adhesiveness of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes to blood vessel walls. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):447–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Wight A., Webb W., Horwitz A. Influence of membrane lipids on acetylcholine receptor and lipid probe diffusion in cultured myotube membrane. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3604–3609. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran M. M., Allen D. M., Russell S. R., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Monthony J. F. Cell sorting using a universally applicable affinity chromatography matrix: solid-phase anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Dembo M., Bongrand P. Cell adhesion. Competition between nonspecific repulsion and specific bonding. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1051–1064. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84252-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Estimate of the sticking probability for cells in uniform shear flow with adhesion caused by specific bonds. Cell Biophys. 1981 Sep;3(3):289–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02782629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Organ specificity of lymphocyte migration: mediation by highly selective lymphocyte interaction with organ-specific determinants on high endothelial venules. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):556–561. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capo C., Garrouste F., Benoliel A. M., Bongrand P., Ryter A., Bell G. I. Concanavalin-A-mediated thymocyte agglutination: a model for a quantitative study of cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:21–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin Y. H., Rasmussen R., Cakiroglu A. G., Woodruff J. J. Lymphocyte recognition of lymph node high endothelium. VI. Evidence of distinct structures mediating binding to high endothelial cells of lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2961–2965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor by hepatocytes in the perfused rat liver: ligand and receptor dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2148–2159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Detailed mechanics of membrane-membrane adhesion and separation. I. Continuum of molecular cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83770-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Detailed mechanics of membrane-membrane adhesion and separation. II. Discrete kinetically trapped molecular cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83771-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. M., Haest C. W., Stöhr-Liesen M., Schmid-Schönbein H., Skalak R. The stress-free shape of the red blood cell membrane. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):409–422. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84859-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester J. V., Lackie J. M. Adhesion of neutrophil leucocytes under conditions of flow. J Cell Sci. 1984 Aug;70:93–110. doi: 10.1242/jcs.70.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith H. L., Spain S. Margination of leukocytes in blood flow through small tubes. Microvasc Res. 1984 Mar;27(2):204–222. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(84)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., O'Dell D., August J. T. Lateral diffusion of an 80,000-dalton glycoprotein in the plasma membrane of murine fibroblasts: relationships to cell structure and function. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1624–1633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juckett D. A., Hultquist D. E. Chromatography of erythroblasts on immobilized transferrin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Jan;172(1):79–83. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Wigzell H., Holmquist G., Ersson B., Carlsson P. Selective affinity fractionation of murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). Unique lectin specific binding of the CTL associated surface glycoprotein, T 145. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):473–484. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege J. L., Capo C., Benoliel A. M., Bongrand P. Determination of binding strength and kinetics of binding initiation. A model study made on the adhesive properties of P388D1 macrophage-like cells. Cell Biophys. 1986 Apr;8(2):141–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02788478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H. Internalization and degradation of macrophage Fc receptors bound to polyvalent immune complexes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Cancer metastasis. Organ colonization and the cell-surface properties of malignant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 21;695(2):113–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecht I., Lancet D. Kinetics of antibody-hapten interactions. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1977;24:306–338. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81117-3_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky J. J., Patterson R. Binding constants of IgE receptors on human blood basophils for IgE. Immunology. 1986 Jun;58(2):257–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Sachs L. Receptor mobility and the binding of cells to lectin-coated fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):76–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schoenbein G. W., Fung Y. C., Zweifach B. W. Vascular endothelium-leukocyte interaction; sticking shear force in venules. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):173–184. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Sung K. L., Tözeren H., Skalak R., Chien S. Passive mechanical properties of human leukocytes. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):243–256. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84726-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Mahendroo P. P. Affinity chromatography of cells and cell membranes. J Chromatogr. 1980 Nov 7;184(4):471–499. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H., Andersson B. Cell separation on antigen-coated columns. Elimination of high rate antibody-forming cells and immunological memory cells. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):23–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Lackie J. M., Forrester J. V., Dunn G. A. Chemokinetic accumulation of human neutrophils on immune complex-coated substrata: analysis at a boundary. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1761–1768. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarda P. R., Chien S., Skalak R. Elastic deformations of red blood cells. J Biomech. 1977;10(4):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(77)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Sullivan S. J., Lauffenburger D. A. Kinetic analysis of chemotactic peptide receptor modulation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):34–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


