Abstract
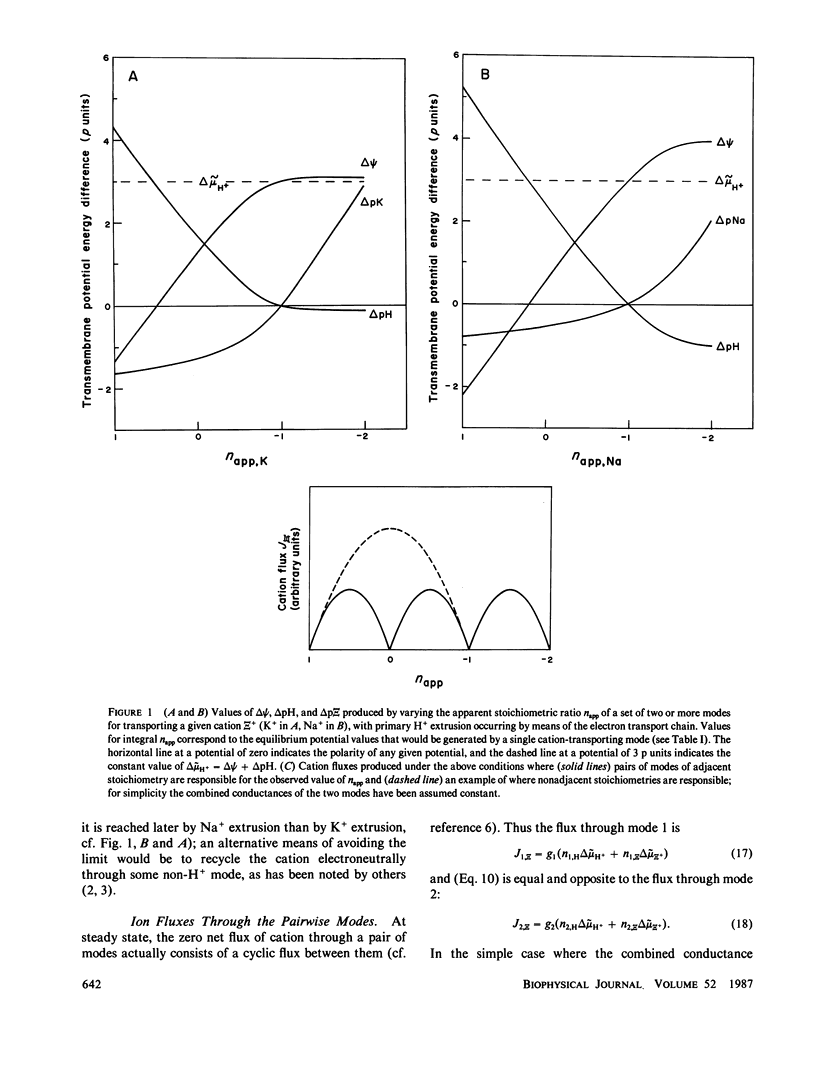
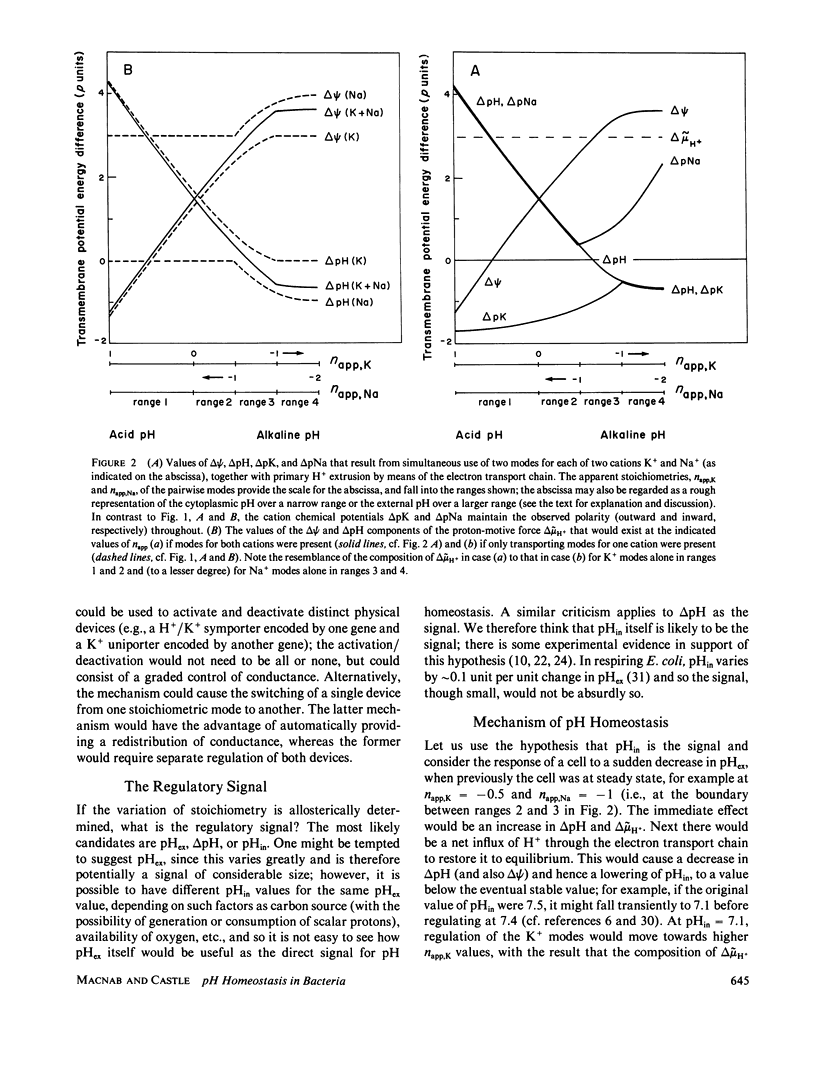
The composition of the proton-motive force of a hypothetical bacterial cell of wide pH tolerance is analyzed according to a model whereby the electron transport chain and various proton-linked sodium and potassium ion transporting modes are responsible for the development of the membrane potential and the chemical potentials of the three cations. Simultaneous use of two or more modes employing the same metal cation, but at a different stoichiometric ratio with respect to protons, produces nonintegral stoichiometry; the modes could represent either different devices or different states of a single device. Cycling of the cation, driven by proton-motive force, results. The relative conductances of the various modes are postulated to be pH-dependent. The pattern of potentials that results is qualitatively in accord with current knowledge and may reflect the mechanism of pH homeostasis in bacteria. The membrane potential is outwardly directed (positive inside) at extremely acid pH, becoming inwardly directed as the pH increases; the pH gradient across the membrane is large and inwardly directed (alkaline inside) at acid pH, becoming smaller and eventually inverting at alkaline pH values; the transmembrane potassium gradient is outwardly directed (high concentration inside) at all pH values; the transmembrane sodium gradient is inwardly directed at all pH values, following the pH gradient from acid through neutral pH, but then diverging at alkaline pH.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Kroll R. G. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH (pH1) in bacteria and its relationship to metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):70–72. doi: 10.1042/bst0110070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle A. M., Macnab R. M., Shulman R. G. Coupling between the sodium and proton gradients in respiring Escherichia coli cells measured by 23Na and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7797–7806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle A. M., Macnab R. M., Shulman R. G. Measurement of intracellular sodium concentration and sodium transport in Escherichia coli by 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3288–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Whitelaw V., Hesse J. A K+ transport ATPase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6666–6668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Characterization of the Na+/H+ antiporter of alkalophilic bacilli in vivo: delta psi-dependent 22Na+ efflux from whole cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1151-1157.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Kakinuma Y. Primary and secondary transport of cations in bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;456:375–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb14888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A. Physiology of acidophilic and alkalophilic bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:173–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M., ENNIS H. L. ON THE ROLE OF INTRACELLULAR POTASSIUM IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 27;80:614–631. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., MacDonald R. E. Existence of electrogenic hydrogen ion/sodium ion antiport in Halobacterium halobium cell envelope vesicles. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4608–4614. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Silverman M. P. Gating effects in Halobacterium halobium membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4750–4755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels M., Bakker E. P. Generation of a large, protonophore-sensitive proton motive force and pH difference in the acidophilic bacteria Thermoplasma acidophilum and Bacillus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):231–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.231-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tokuda H., Unemoto T. K+/H+ antiporter functions as a regulator of cytoplasmic pH in a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto-Young D., Garcia M. L., Krulwich T. A. Reconstitution of a bacterial Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11393–11395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Macnab R. M., Alger J. R., Castle A. M. Effects of pH and repellent tactic stimuli on protein methylation levels in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):384–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.384-399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L. M., Bakker E. P., Booth I. R. Energy coupling to K+ uptake via the Trk system in Escherichia coli: the role of ATP. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):77–85. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Nakamura T., Unemoto T. Potassium ion is required for the generation of pH-dependent membrane potential and delta pH by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4198–4203. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. A respiration-dependent primary sodium extrusion system functioning at alkaline pH in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Hartmann R., Oesterhelt D. Potassium uniport and ATP synthesis in Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):169–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky E., Matin A. Cytoplasmic pH homeostasis in an acidophilic bacterium, Thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1352–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1352-1355.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


