Abstract
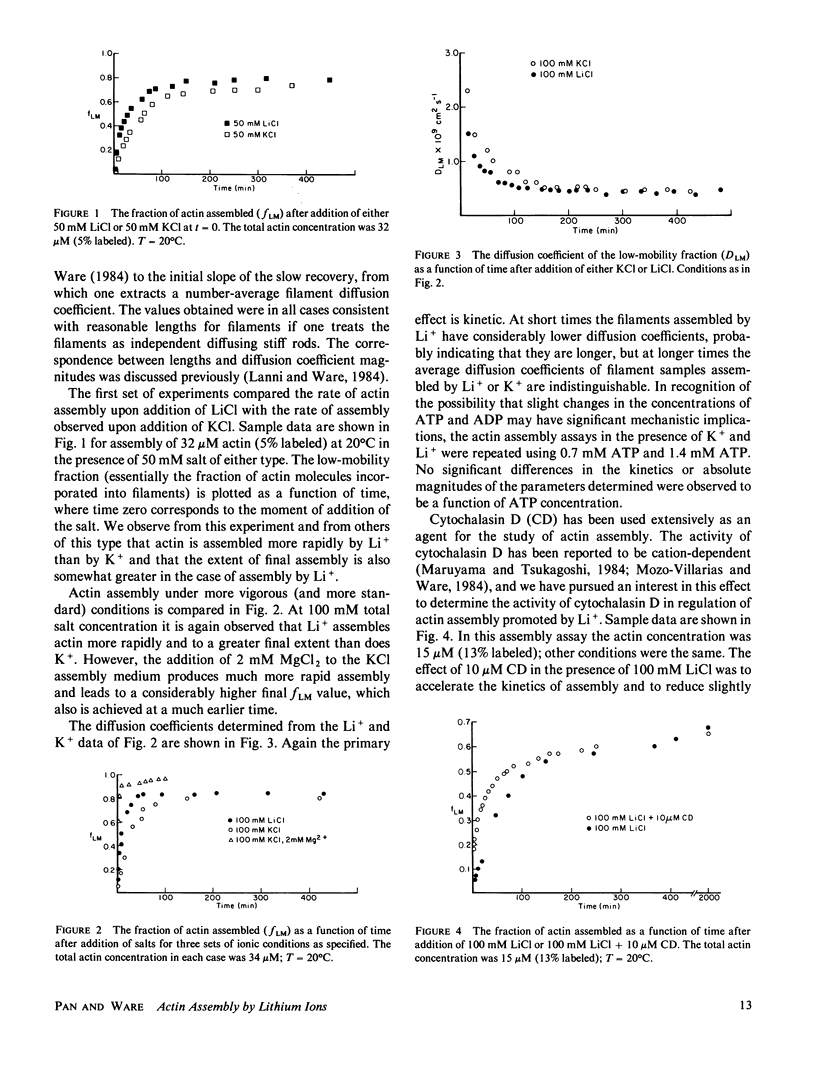
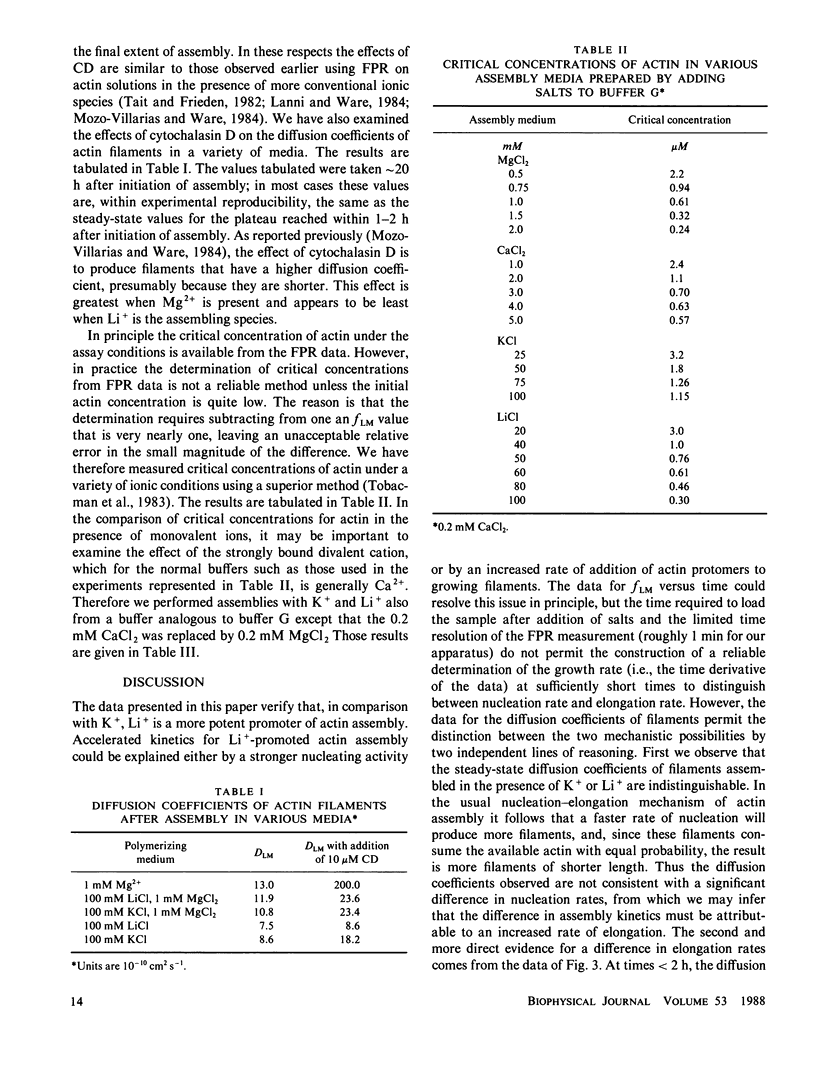
The ability of Li+ to promote the assembly of actin has been compared with the more common cations used in actin assembly assays, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. The principal assay of actin assembly utilized was fluorescence photobleaching recovery (FPR), from which it is possible to determine the fraction of actin protomers incorporated into filaments and the average diffusion coefficients of the filaments. In addition, critical concentrations of actin over a range of concentrations of all of these cations have been determined using an assay that involves sonication and dilution of assembled actin filaments containing trace amounts of pyrene-labeled actin. The results demonstrate that Li+ is a more potent promoter of actin assembly than is K+. The more rapid assembly of actin in the presence of Li+ is attributable to an increased rate of filament elongation. Filaments assembled in equivalent concentrations of Li+ or K+ have the same diffusion coefficients, and thus presumably the same average lengths. The critical concentration of actin is about three times less in the presence of Li+ than in the presence of an equal concentration of K+. Cytochalasin D accelerates the rate of Li+-promoted actin assembly and reduces slightly the total fraction of actin assembly. However, cytochalasin D causes less shortening of filaments in the presence of Li+ than in the presence of K+ or Mg2+. By the criteria of assembly kinetics and critical concentration, Li+ is much less potent as a promoter of actin assembly than either Mg2+ or Ca2+. These results are discussed in terms of the role of electrostatic forces in the actin assembly mechanism and in terms of possible relationships to therapeutic and toxicity mechanisms for Li+.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya B., Wolff J. Stabilization of microtubules by lithium ion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 22;73(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90719-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Stossel T. P. Interactions of actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein of chronic myelogenous leukemia leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):964–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI108373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. On the mechanism of actin monomer-polymer subunit exchange at steady state. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5013–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. Fluorescence measurements of the binding of cations to high-affinity and low-affinity sites on ATP-G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10778–10784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. The effects of Mg2+ at the high-affinity and low-affinity sites on the polymerization of actin and associated ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10785–10792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Mallakh R. S. Treatment of acute lithium toxicity. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1984 Feb;26(1):31–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias E., Boyer J. L. Chlorpromazine and its metabolites alter polymerization and gelation of actin. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1404–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.574316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Actin and tubulin polymerization: the use of kinetic methods to determine mechanism. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:189–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C., Lieberman D., Gilbert H. R. A fluorescent probe for conformational changes in skeletal muscle G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):8991–8993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. The Mg2+-induced conformational change in rabbit skeletal muscle G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershman L. C., Selden L. A., Estes J. E. High affinity binding of divalent cation to actin monomer is much stronger than previously reported. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Fluorimetry study of N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide-labelled F-actin. Local structural change of actin protomer both on polymerization and on binding of heavy meromyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni F., Taylor D. L., Ware B. R. Fluorescence photobleaching recovery in solutions of labeled actin. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84794-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni F., Ware B. R. Detection and characterization of actin monomers, oligomers, and filaments in solution by measurement of fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Biophys J. 1984 Jul;46(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84002-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSII A., MOLINO C. M., GERGELY J. THE BINDING OF DIVALENT CATIONS TO ACTIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1057–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Tsukagoshi K. Effects of KCl, MgCl2, and CaCl2 concentrations on the monomer-polymer equilibrium of actin in the presence and absence of cytochalasin D. J Biochem. 1984 Sep;96(3):605–611. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozo-Villarías A., Ware B. R. Distinctions between mechanisms of cytochalasin D activity for Mg2+- and K+-induced actin assembly. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5549–5554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Mechanism of K+-induced actin assembly. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):648–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):164–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouayrenc J. F., Travers F. The first step in the polymerisation of actin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sashidharan S. P. The relationship between serum lithium levels and clinical response. Ther Drug Monit. 1982;4(3):249–264. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198208000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Chaponnier C., Ezzell R. M., Hartwig J. H., Janmey P. A., Kwiatkowski D. J., Lind S. E., Smith D. B., Southwick F. S., Yin H. L. Nonmuscle actin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka-Gołaszewska H., Pròchniewicz E., Drabikowski W. Interaction of actin with divalent cations. 2. Characterization of protein-metal complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Frieden C. Polymerization and gelation of actin studied by fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3666–3674. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobacman L. S., Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. Effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on the pre-steady state kinetics of actin polymerization and on the concentration of F-actin at steady state. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8806–8812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L., Taylor D. L. Preparation and characterization of a new molecular cytochemical probe: 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein-labeled actin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Nov;28(11):1198–1206. doi: 10.1177/28.11.6107318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


