Abstract
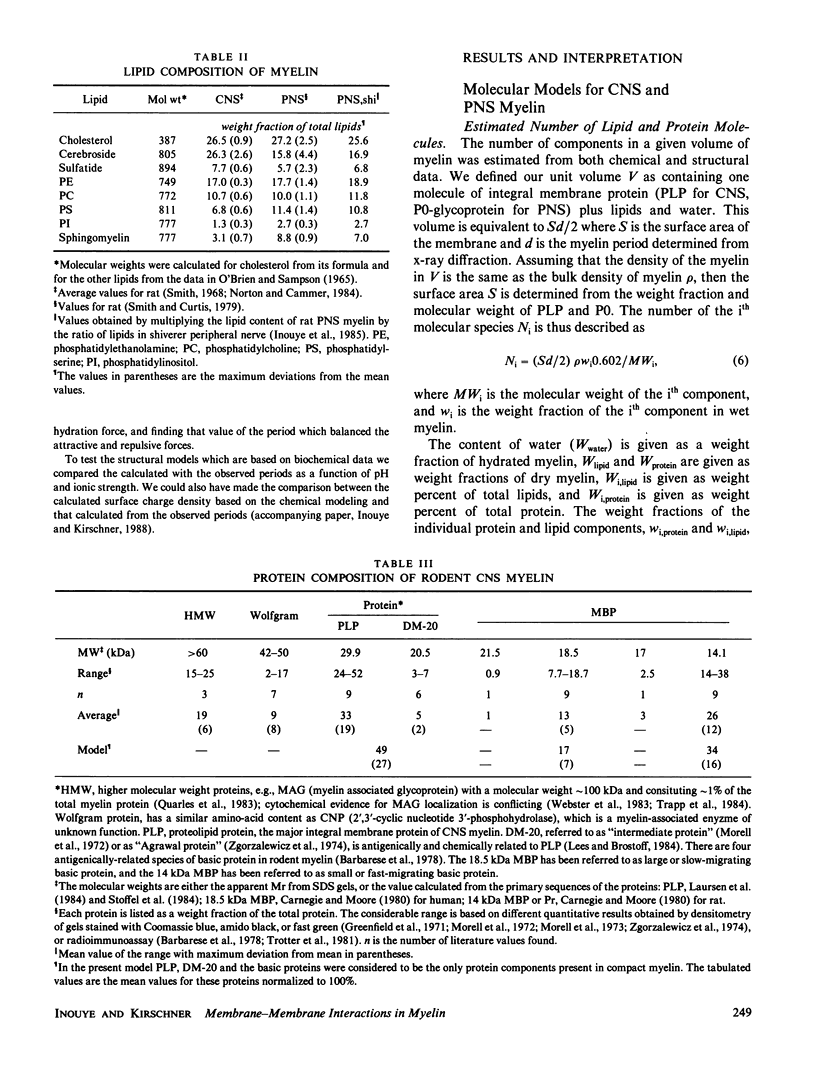
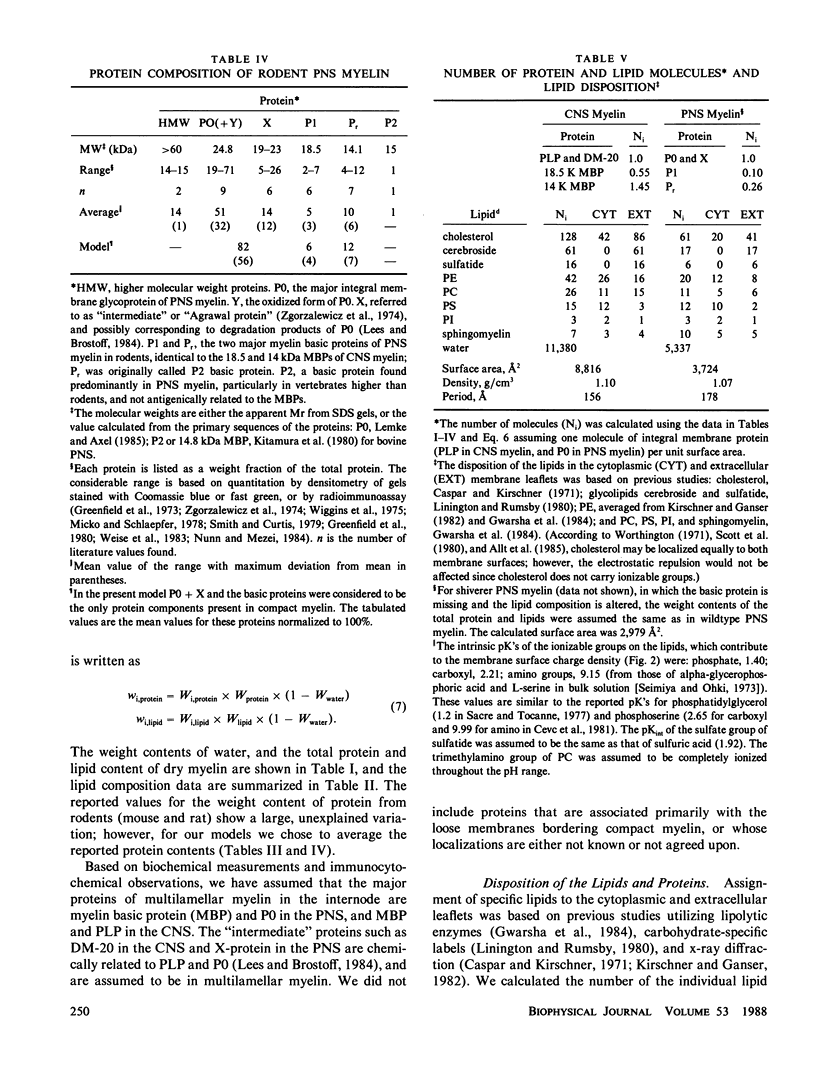
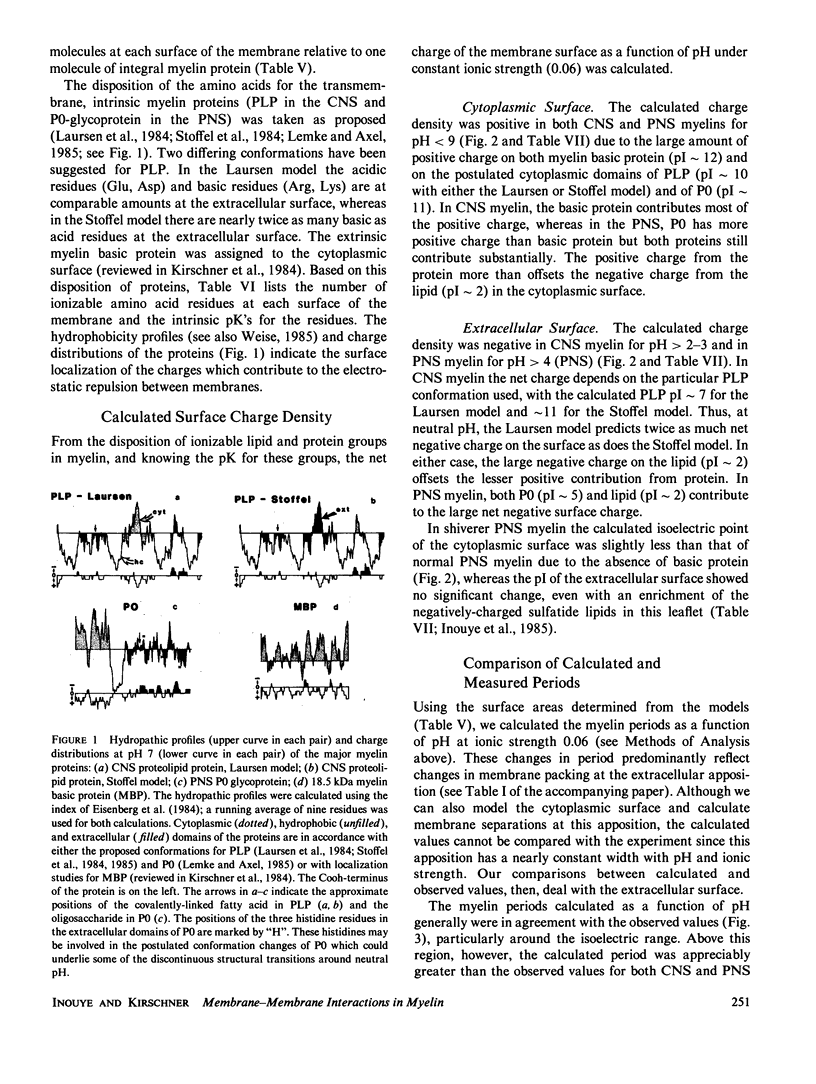
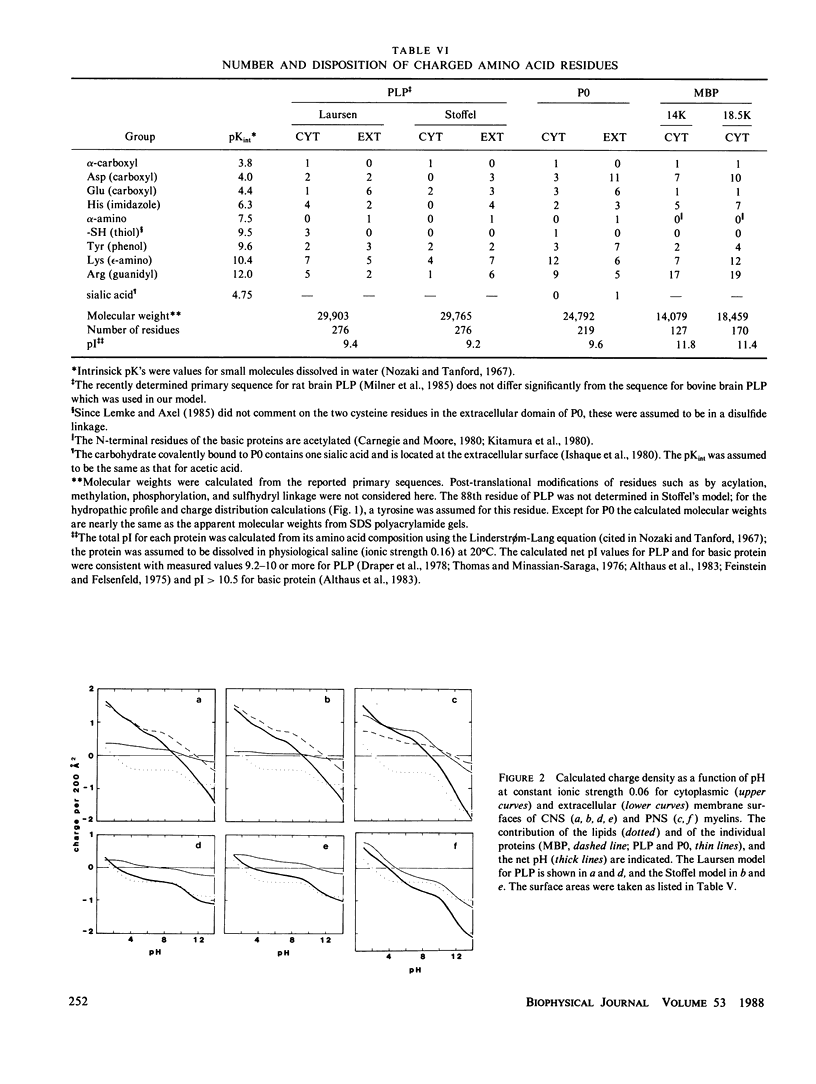
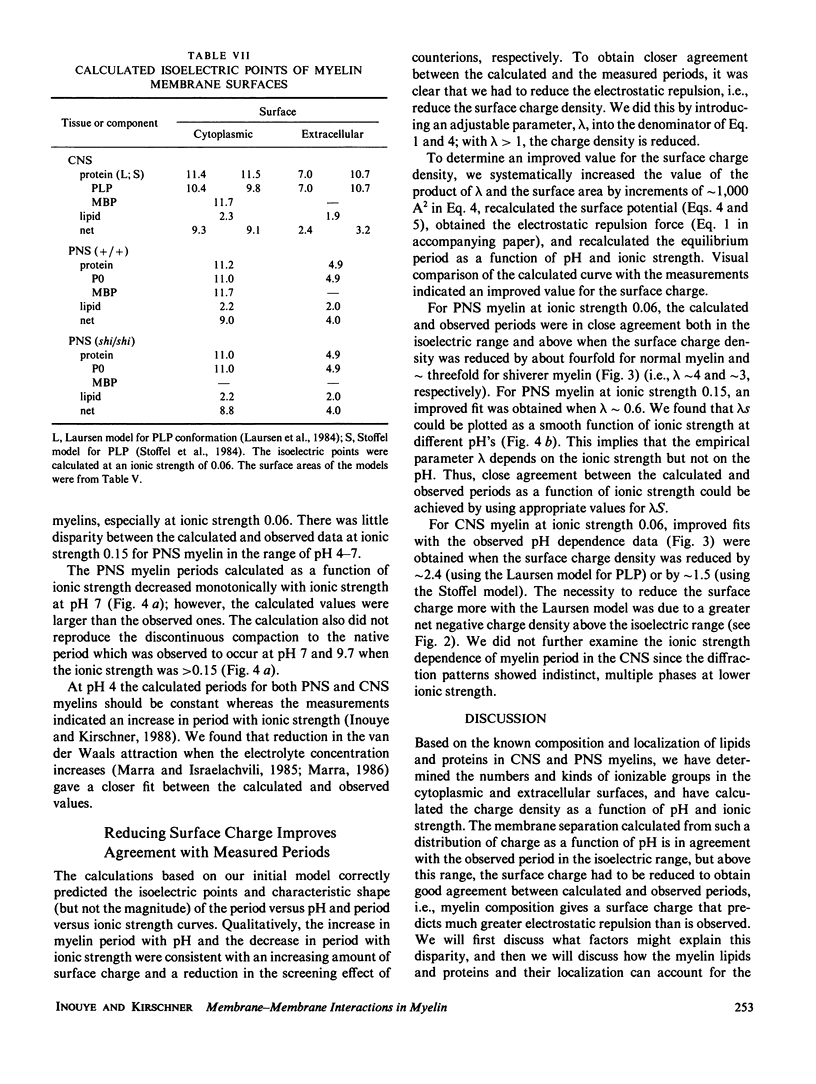
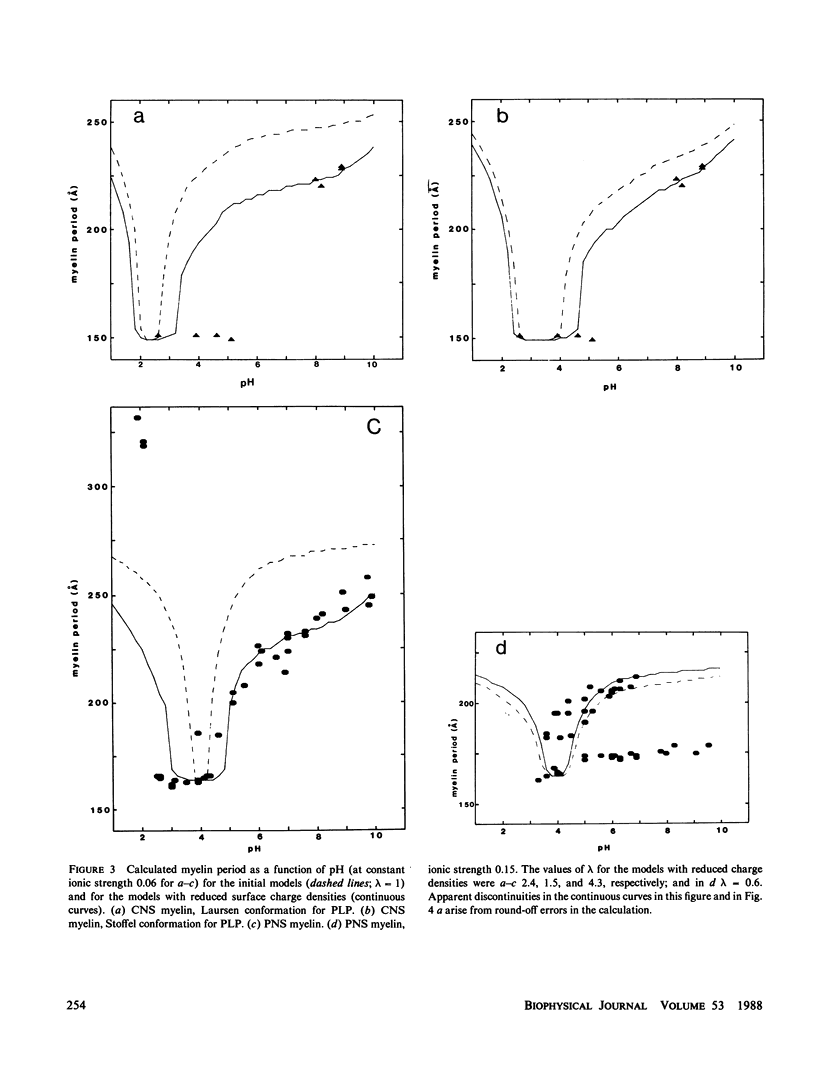
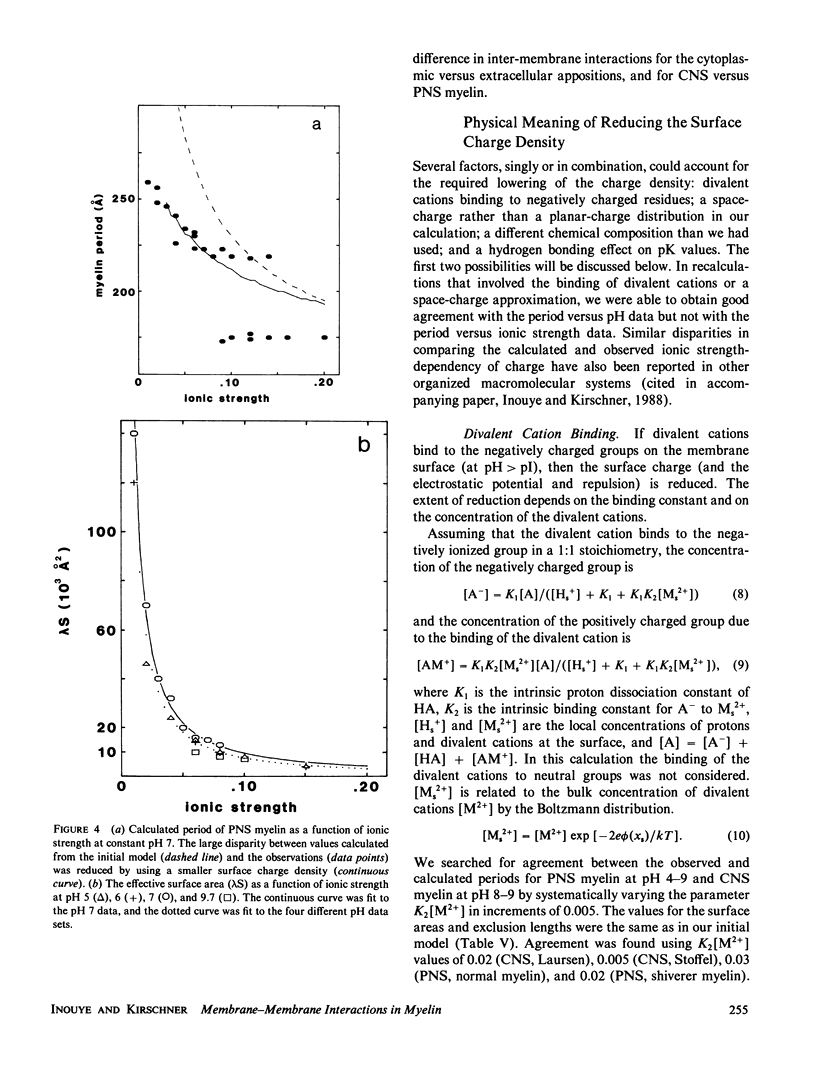
In our accompanying paper (Inouye and Kirschner, 1988) we calculated the surface charge density at the extracellular surfaces in peripheral and central nervous system (PNS; CNS) myelins from observations on the dependency of the width of the extracellular space on pH and ionic strength. Here, we have determined the surface charge density of the membrane surfaces in myelin from its chemical composition and the localization of some of its molecular components. We then analyzed the attractive and repulsive forces between the apposed surfaces and calculated equilibrium periods for comparison with the measured values. The biochemical model accounts for the observed isoelectric range of the myelin period and, with the surface charge reduced (possibly by divalent cation binding or a space charge approximation), the model also accounts for the dependency of period on pH above the isoelectric range. At the extracellular (and cytoplasmic) surfaces the contribution of lipid (with pI approximately 2) to the net surface charge is about the same in both PNS and CNS myelin, whereas the contribution of protein depends on which ones are exposed at the two surfaces. The protein conformation and localization modulate the surface charge of the lipid, resulting in positively-charged cytoplasmic surfaces (pI approximately 9) and negatively-charged extracellular surfaces (pI approximately 2-4). The net negative charge at the extracellular surface is due in CNS myelin to lipid, and in PNS myelin to both lipid and (PO) glycoprotein. The net positive charge at the cytoplasmic surface is due in CNS myelin mostly to basic protein, and in PNS myelin to PO glycoprotein and basic protein. The invariance of the cytoplasmic packing may be due to specific short-range interactions. Our models demonstrate how the particular myelin proteins and their localization and conformation can account for the differences in inter-membrane interactions in CNS and PNS myelins.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allt G., Blanchard C. E., MacKenzie M. L., Sikri K. Distribution of filipin-sterol complexes in the myelinated nerve fiber. J Ultrastruct Res. 1985 May;91(2):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(85)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Carson J. H., Braun P. E. Accumulation of the four myelin basic proteins in mouse brain during development. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):779–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Kirschner D. A. Myelin membrane structure at 10 A resolution. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 12;231(19):46–52. doi: 10.1038/newbio231046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevc G., Watts A., Marsh D. Titration of the phase transition of phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Effects of pH, surface electrostatics, ion binding, and head-group hydration. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4955–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Bramhall J. Permeability of lipid bilayers to water and ionic solutes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Jun-Jul;40(2-4):167–188. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermietzel R., Thürauf N., Schünke D. Cytochemical demonstration of negative surface charges in central myelin. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper M., Lees M. B., Chan D. S. Isoelectric focusing of proteolipid. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B. The role of water in the structure of peripheral nerve myelin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Jan 25;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Felsenfeld H. Reactions of fluorescent probes with normal and chemically modified myelin basic protein and proteolipid. Comparisons with myelin. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3049–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Brostoff S. W., Hogan E. L. Characterization of the basic proteins from rodent peripheral nervous system myelin. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):453–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Brostoff S., Eylar E. H., Morell P. Protein composition of myelin of the peripheral nervous system. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):1207–1216. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Norton W. T., Morell P. Quaking mouse: isolation and characterization of myelin protein. J Neurochem. 1971 Nov;18(11):2119–2128. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb05070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton/hydroxide conductance through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(1):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01870737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Ganser A. L., Kirschner D. A. Shiverer and normal peripheral myelin compared: basic protein localization, membrane interactions, and lipid composition. J Neurochem. 1985 Dec;45(6):1911–1922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb10551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Kirschner D. A. Effects of ZnCl2 on membrane interactions in myelin of normal and shiverer mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque A., Roomi M. W., Szymanska I., Kowalski S., Eylar E. H. The PO glycoprotein of peripheral nerve myelin. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):913–921. doi: 10.1139/o80-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Caspar D. L. Myelin structure transformed by dimethylsulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3513–3517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Ganser A. L. Myelin labeled with mercuric chloride. Asymmetric localization of phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):635–658. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Suzuki M., Suzuki A., Uyemura K. The complete amino acid sequence of the P2 protein in bovine peripheral nerve myelin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 16;115(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80719-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A., Samiullah M., Lees M. B. The structure of bovine brain myelin proteolipid and its organization in myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G., Axel R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA encoding the major structural protein of peripheral myelin. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Rumsby M. G. Accessibility of galactosyl ceramides to probe reagents in central nervous system myelin. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):983–992. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Waehneldt T. V., Neuhoff V. The lipid composition of light and heavy myelin subfractions isolated from rabbit sciatic nerve. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Nov;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra J., Israelachvili J. Direct measurements of forces between phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4608–4618. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Waehneldt T. V., Webster H. D., Bény M., Fagg G. E. Distribution of PNS myelin proteins and membrane enzymes in fractions isolated by continuous gradient zonal centrifugation. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 6;170(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90945-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Mulrine N., Gresalfi T., Vaio G., McLaughlin A. Adsorption of divalent cations to bilayer membranes containing phosphatidylserine. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):445–473. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micko S., Schlaepfer W. W. Protein composition of axons and myelin from rat and human peripheral nerves. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1041–1049. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Lai C., Nave K. A., Lenoir D., Ogata J., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequences of two mRNAs for rat brain myelin proteolipid protein. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell P., Greenfield S., Costantino-Ceccarini E., Wisniewski H. Changes in the protein composition of mouse brain myelin during development. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2545–2554. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell P., Lipkind R., Greenfield S. Protein composition of myelin from brain and spinal cord of several species. Brain Res. 1973 Aug 30;58(2):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscarello M. A., Chia L. S., Leighton D., Absolom D. Size and surface charge properties of myelin vesicles from normal and diseased (multiple sclerosis) brain. J Neurochem. 1985 Aug;45(2):415–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninham B. W., Parsegian V. A. Electrostatic potential between surfaces bearing ionizable groups in ionic equilibrium with physiologic saline solution. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jun;31(3):405–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. J., Mezei C. Solid-phase immunoassay of PO glycoprotein of peripheral nerve myelin. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):158–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Sampson E. L. Lipid composition of the normal human brain: gray matter, white matter, and myelin. J Lipid Res. 1965 Oct;6(4):537–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima H., Ohki S. Donnan potential and surface potential of a charged membrane. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):673–678. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83963-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A. Possible modulation of reactions on the cell surface by changes in electrostatic potential that accompany cell contact. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;238:362–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb26804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett S. M., Rumsby M. G. Development and application of a method to assay calcium and magnesium in isolated myelin-sheath preparations [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1429–1431. doi: 10.1042/bst0051429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Barbarash G. R., Figlewicz D. A., McIntyre L. J. Purification and partial characterization of the myelin-associated glycoprotein from adult rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 4;757(1):140–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:277–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacré M. M., Tocanne J. F. Importance of glycerol and fatty acid residues on the ionic properties of phosphatidylglycerols at the air-water interface. Chem Phys Lipids. 1977 Apr;18(3-4):334–354. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(77)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S. C., Bruckdorfer K. R., Worcester D. L. The symmetrical distribution of cholesterol across the myelin membrane bilayer determined by deuterium labelling in vivo and neutron diffraction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Dec;8(6):717–717. doi: 10.1042/bst0080717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seimiya T., Ohki S. Ionic structure of phospholipid membranes, and binding of calcium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 29;298(3):546–561. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Curtis B. M. Frog sciatic nerve myelin: a chemical characterization. J Neurochem. 1979 Aug;33(2):447–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E. The turnover of myelin in the adult rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Giersiefen H., Hillen H., Schroeder W., Tunggal B. Amino-acid sequence of human and bovine brain myelin proteolipid protein (lipophilin) is completely conserved. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Jul;366(7):627–635. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Hillen H., Giersiefen H. Structure and molecular arrangement of proteolipid protein of central nervous system myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5012–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Quarles R. H., Suzuki K. Immunocytochemical studies of quaking mice support a role for the myelin-associated glycoprotein in forming and maintaining the periaxonal space and periaxonal cytoplasmic collar of myelinating Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):594–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. L., Lieberman L., Margolis F. L., Agrawal H. C. Radioimmunoassay for central nervous system myelin-specific proteolipid protein. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1256–1262. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waehneldt T. V. Density and protein profiles of myelin from two regions of young and adult rat CNS. Brain Res Bull. 1978 Jan-Feb;3(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(78)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster H. D., Palkovits C. G., Stoner G. L., Favilla J. T., Frail D. E., Braun P. E. Myelin-associated glycoprotein: electron microscopic immunocytochemical localization in compact developing and adult central nervous system myelin. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1469–1479. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise M. J., Greenfield S., Brostoff S. W., Hogan E. L. Protein composition of PNS myelin: developmental comparison of control and quaking mice. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):448–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise M. J. Hydrophobic regions in myelin proteins characterized through analysis of "hydropathic" profiles. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):163–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Benjamins J. A., Morell P. Appearance of myelin proteins in rat sciatic nerve during development. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgorzalewicz B., Neuhoff V., Waehneldt T. V. Rat myelin proteins. Compositional changes in various regions of the nervous system during ontogenetic development. Neurobiology. 1974;4(5):265–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



