Abstract
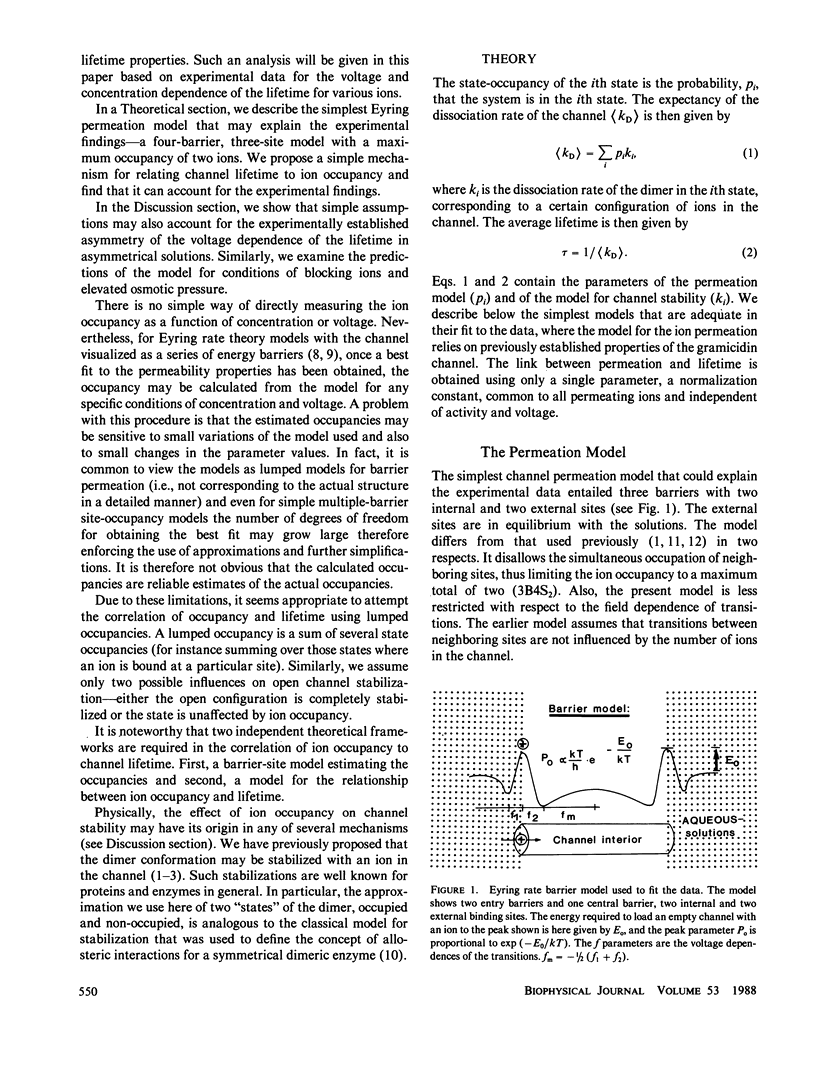
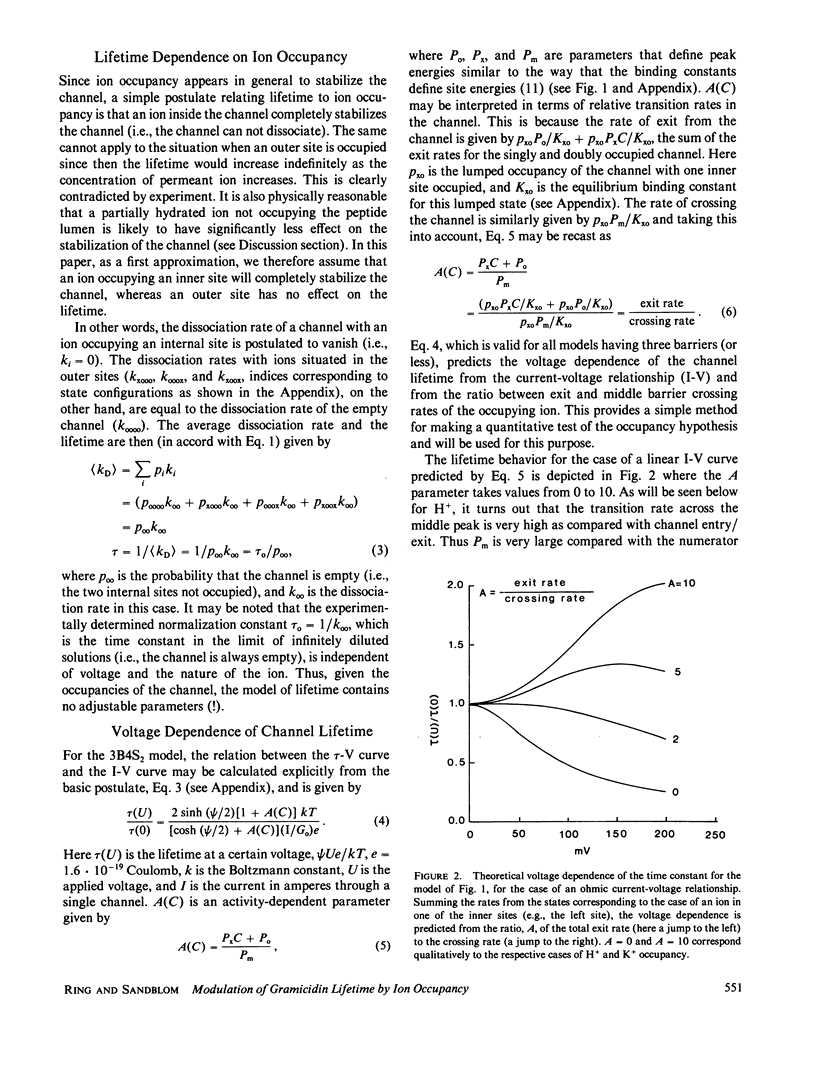
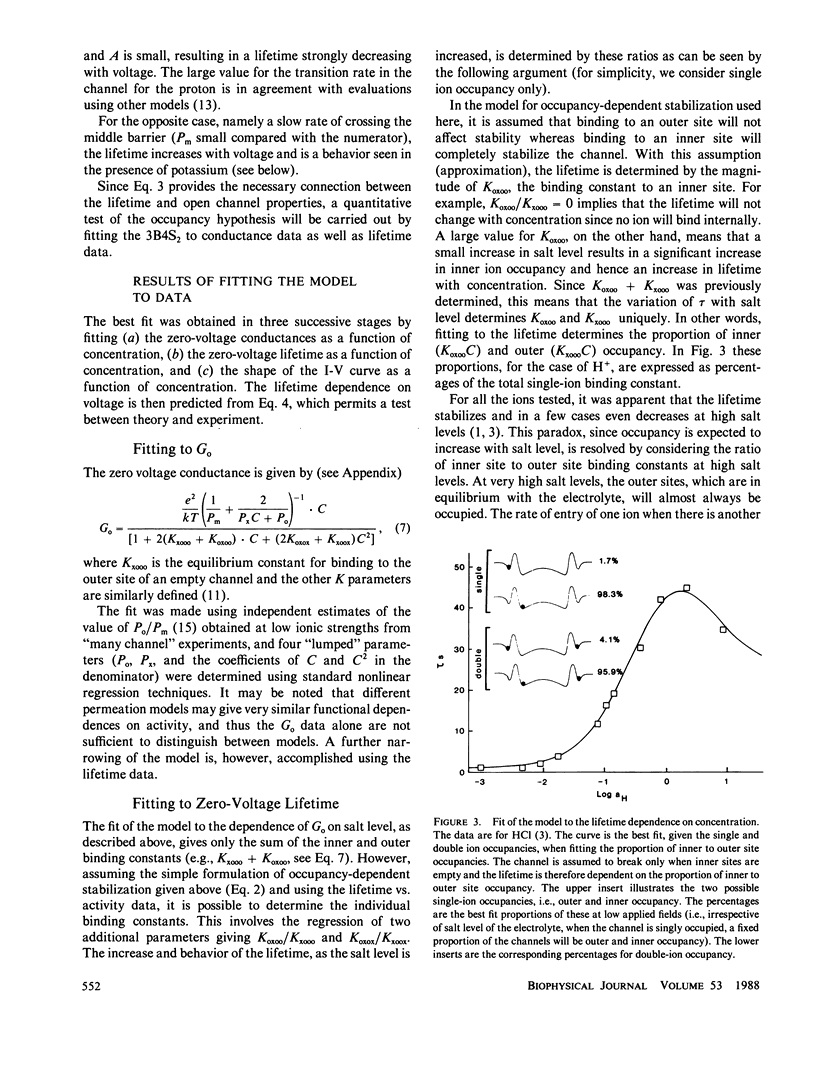
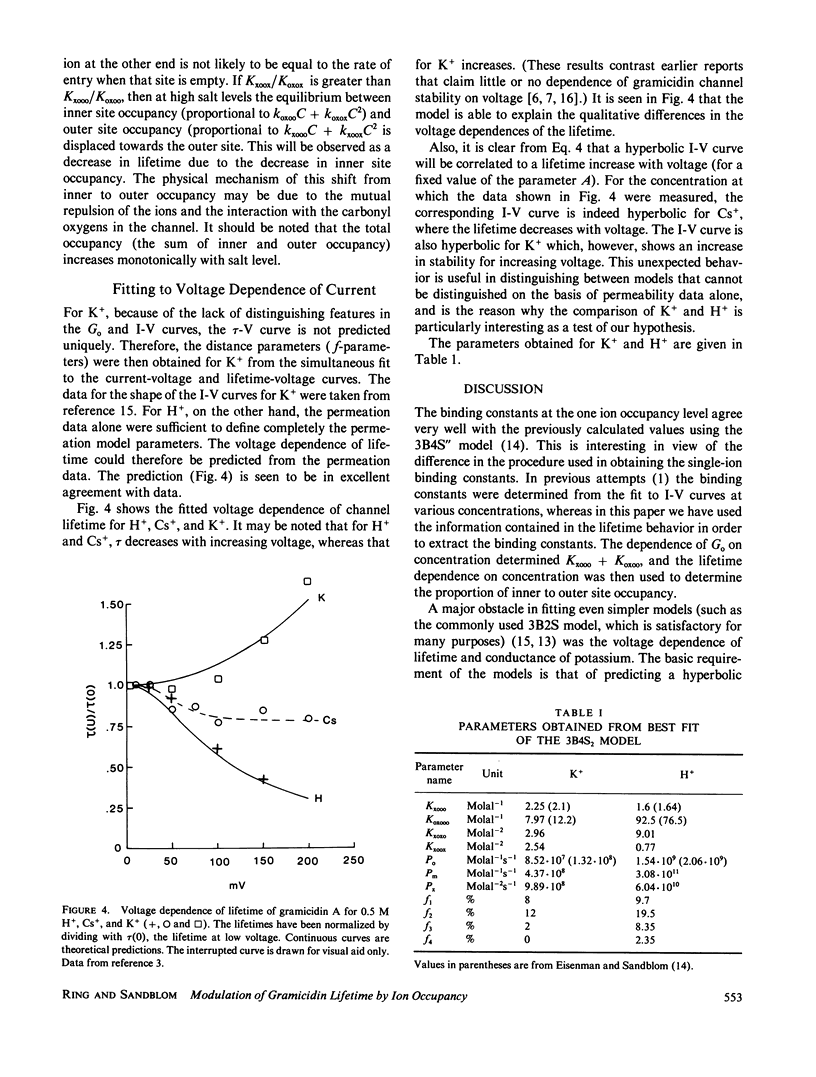
The hypothesis that the gramicidin A channel stability depends on the level of ion occupancy of the channel was used to derive a mathematical model relating channel lifetime to channel occupancy. Eyring barrier permeation models were examined for their ability to fit the zero-voltage conductance, current-voltage, as well as lifetime data. The simplest permeation model required to explain the major features of the experimental data consists of three barriers and four sites (3B4S) with a maximum of two ions occupying the channel. The average lifetime of the channel was calculated from the barrier model by assuming the closing rate constant to be proportional to the probability of the internal channel sites being empty. The link between permeation and lifetime has as its single parameter the experimentally determined averaged lifetime of gramicidin A channels in the limit of infinitely dilute solutions and has therefore no adjustable parameters. This simple assumption that one or more ions inside the channel completely stabilize the dimer conformation is successful in explaining the experimental data considering the fact that this model for stabilization is independent of ion species and configurational occupancy. The model is used to examine, by comparison with experimental data, the asymmetrical voltage dependence of the lifetime in asymmetrical solutions, the effects of blockers, and the effects of elevated osmotic pressure.
Full text
PDF
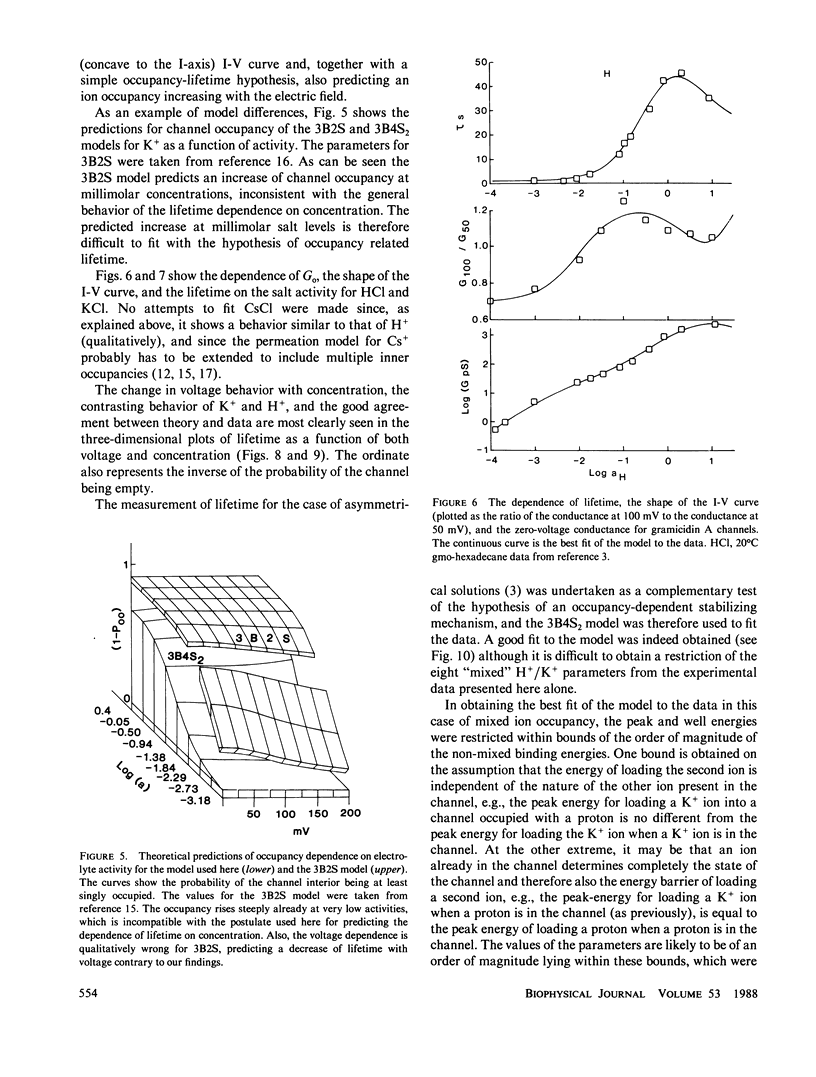
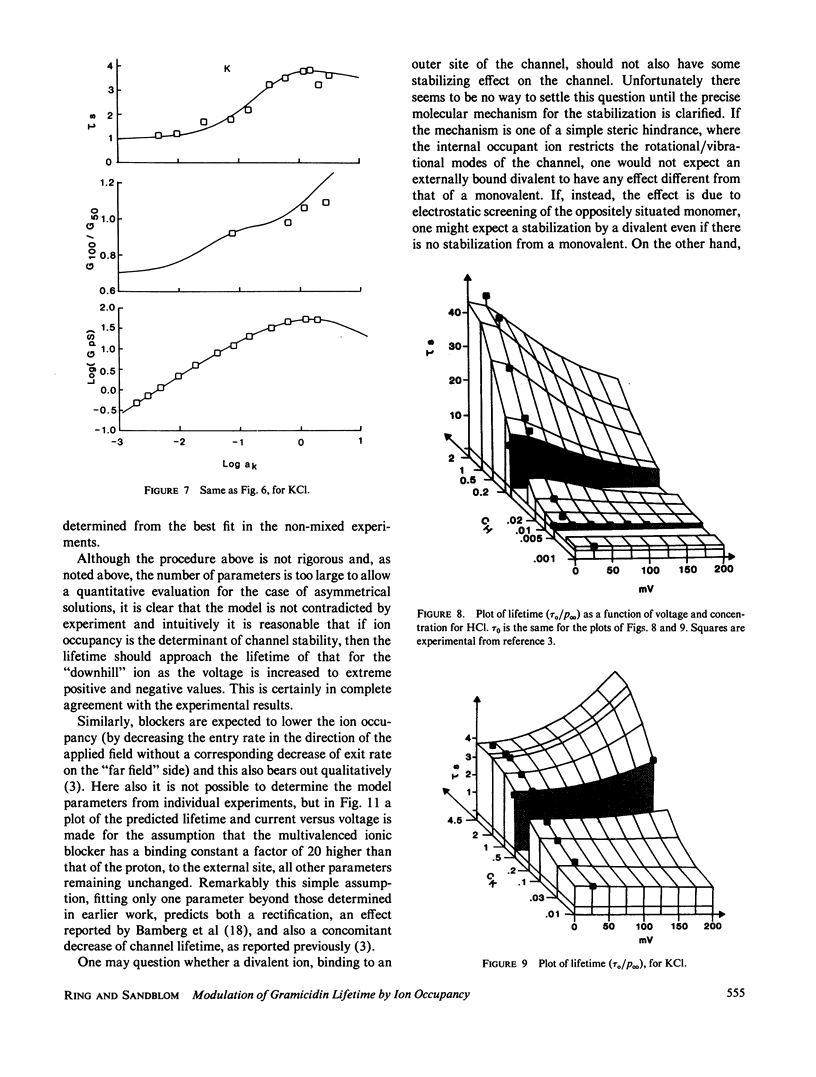
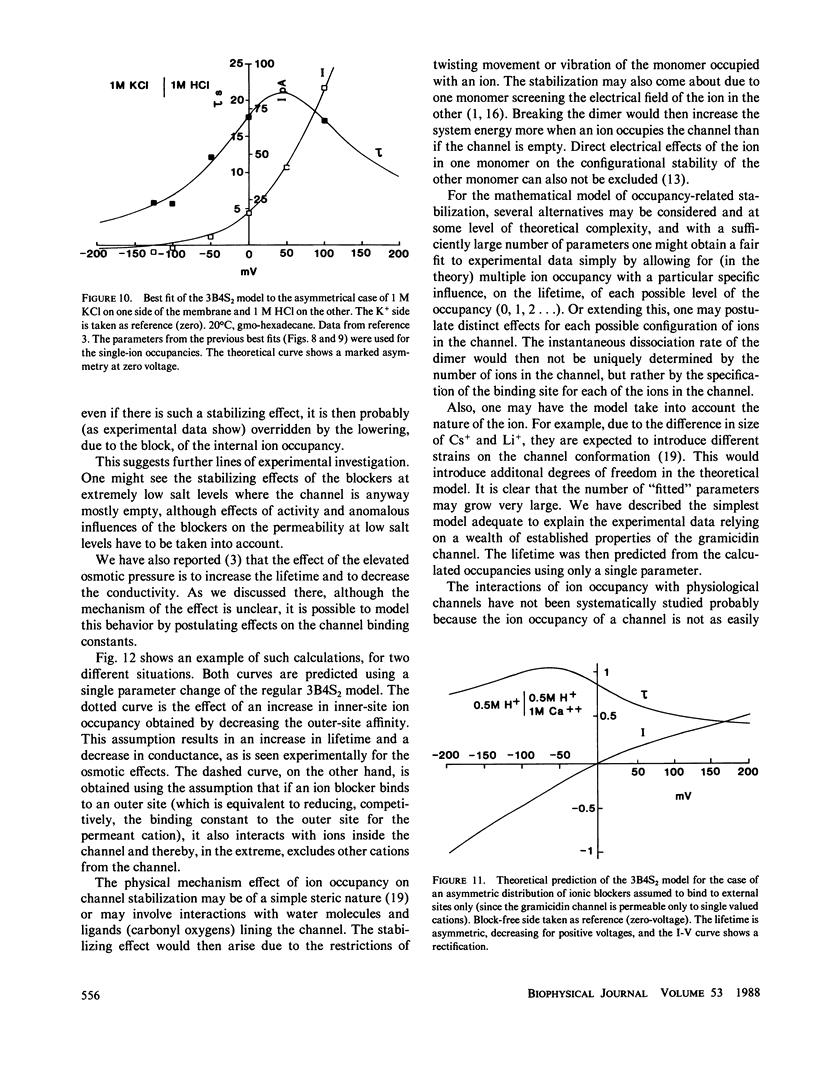
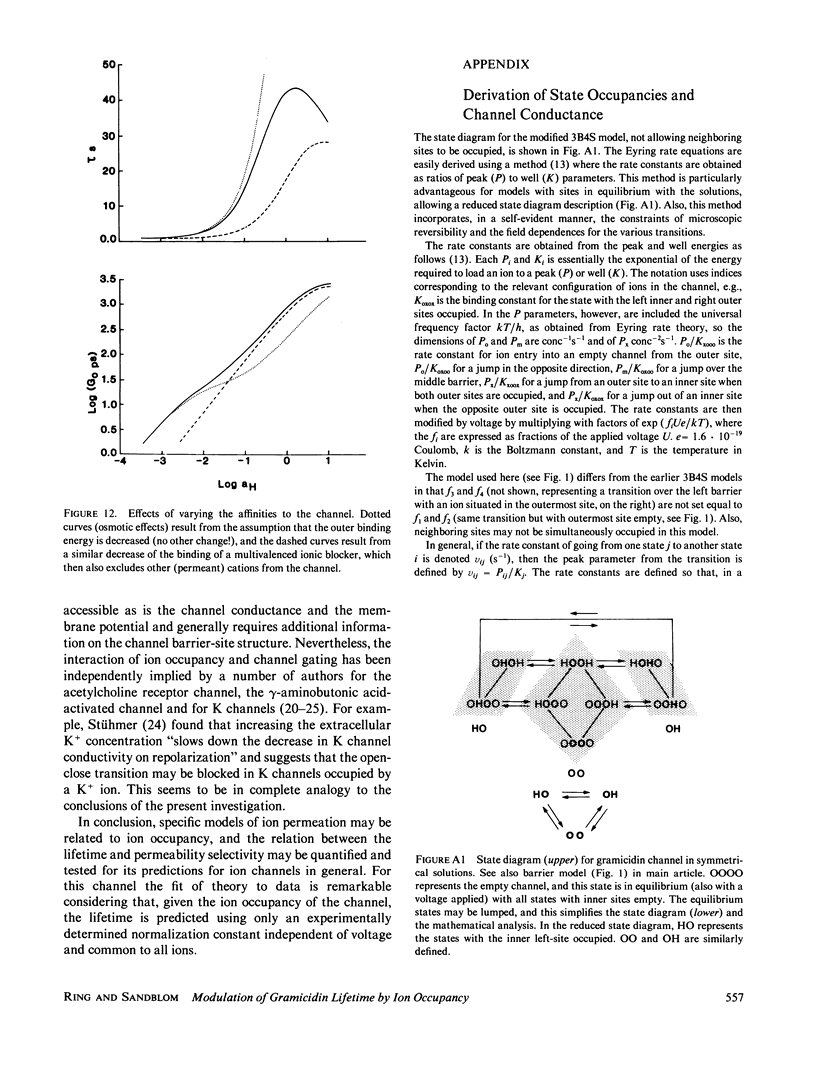


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Marty A., Neild T. O. Life time and elementary conductance of the channels mediating the excitatory effects of acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:177–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Läuger P. Channel formation kinetics of gramicidin A in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973;11(2):177–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01869820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Läuger P. Channel formation kinetics of gramicidin A in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973;11(2):177–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01869820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Bergman C. The steady-state potassium conductance of the Ranvier node at various external K-concentrations. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Aug 29;370(2):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00581693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Bamberg E. Influence of membrane thickness and ion concentration on the properties of the gramicidin a channel. Autocorrelation, spectral power density, relaxation and single-channel studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Elias S. R., Hautman J. M. Number of water molecules coupled to the transport of sodium, potassium and hydrogen ions via gramicidin, nonactin or valinomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):436–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchais D., Marty A. Interaction of permeant ions with channels activated by acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):9–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring A., Sandblom J. Evaluation of surface tension and ion occupancy effects on gramicidin A channel lifetime. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):541–548. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83134-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom J., Eisenman G., Neher E. Ionic selectivity, saturation and block in gramicidin A channels: I. Theory for the electrical properties of ion selective channels having two pairs of binding sites and multiple conductance states. J Membr Biol. 1977 Mar 23;31(4):383–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01869414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Jr, Armstrong C. M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):427–429. doi: 10.1038/291427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban B. W., Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion movements in gramicidin pores. An example of single-file transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):331–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Venkatachalam C. M., Spisni A., Läuger P., Khaled M. A. Rate theory calculation of gramicidin single-channel currents using NMR-derived rate constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2028–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden D., Hamill O. P., Gage P. W. Permeant cations alter endplate channel characteristics. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):711–713. doi: 10.1038/269711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


