Abstract
In the flow studies described in two previous papers (Tha, S. P., and H. L. Goldsmith, 1986, Biophys. J. 50:1109-1116; Tha, S. P., J. Shuster, and H. L. Goldsmith, 1986, Biophys. J. 50:1117-1126), hydrodynamic forces of the order of 10(-11) N (mu dyn) were applied to measure the force of separation of doublets of hardened, sphered human red blood cells cross-linked by anti-B antibody. The same cell preparation and hyperimmune antiserum has here been used to carry out experiments with micropipet aspiration techniques. One cell of a doublet was aspirated onto a holding pipet, and a second aspiration pipet was brought into proximity of the other cell so that the two pipets and the doublet were colinear. Suction was then raised until the two cells separated. Some doublets were assembled by aspiration of a singlet, bringing a second singlet into apposition with the first, and releasing it from the pipet which was then withdrawn. Cells could be repeatedly assembled and separated. At 3.56% vol/vol antiserum, the mean normal force of separation was 0.45 +/- 0.11 nN in phosphate-buffered saline suspensions containing 2.5 x 10(4) cells/microliter; at 1.22% vol/vol antiserum, the value was 0.22 +/- 0.11 nN. The above values of the force were approximately 2.5 x greater than those from the flow studies. The data could be fitted to a Poisson distribution with 0.05 nN as the force needed to break a single cross-bridge (c.f. 0.024 nN from the previous hydrodynamic data). The forces of separation of randomly assembled doublets were lower than those of preexisting doublets. Repeated assembly and separation of doublets showed that the cell surfaces are nonuniform in adhesion strength both over the local scale less than 0.25 micron2 and the cell population.
Full text
PDF
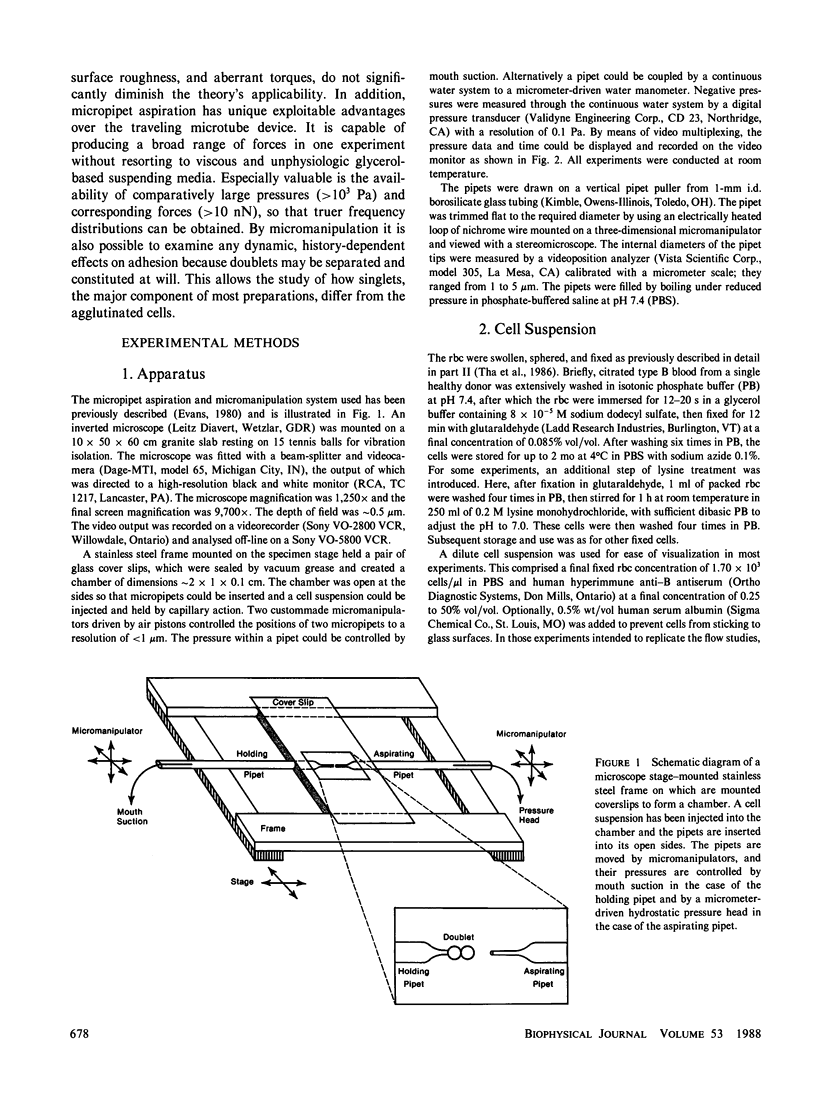









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. J. Purification and quantitation of glutaraldehyde and its effect on several enzyme activities in skeletal muscle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Aug;15(11):652–661. doi: 10.1177/15.11.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Estimate of the sticking probability for cells in uniform shear flow with adhesion caused by specific bonds. Cell Biophys. 1981 Sep;3(3):289–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02782629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum K., Evans E., Brooks D. E. Quantitation of surface affinities of red blood cells in dextran solutions and plasma. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3235–3239. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capo C., Garrouste F., Benoliel A. M., Bongrand P., Ryter A., Bell G. I. Concanavalin-A-mediated thymocyte agglutination: a model for a quantitative study of cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:21–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Rutishauser U., Millette C. F. Cell fractionation and arrangement on fibers, beads, and surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2153–2157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Minimum energy analysis of membrane deformation applied to pipet aspiration and surface adhesion of red blood cells. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):265–284. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85093-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Buxbaum K. Affinity of red blood cell membrane for particle surfaces measured by the extent of particle encapsulation. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84834-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Leung A. Adhesivity and rigidity of erythrocyte membrane in relation to wheat germ agglutinin binding. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1201–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer K., Stege N. On the pathogenesis of ABO erythroblastosis: demonstration of quantitative variations in the power of neonatal erythrocytes to combine with antibody, using the immuno-fluorescent technique. Vox Sang. 1967 Feb;12(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBURY C. L., MOORE D. H., NUNN L. A. REACTION OF 7S AND 19S COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE RABBIT ANTISERA WITH HUMAN GROUP A AND AB RED CELLS. Immunology. 1963 Sep;6:421–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Mechanism of protein stabilization by glycerol: preferential hydration in glycerol-water mixtures. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4667–4676. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Weed R. I., Reed C. F. Adhesion of human erythrocytes to glass: the nature of the interaction and the effect of serum and plasma. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Feb;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Blood group ABH and Ii antigens of human erythrocytes: chemistry, polymorphism, and their developmental change. Semin Hematol. 1981 Jan;18(1):39–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. Theoretical and practical aspects of glutaraldehyde fixation. Histochem J. 1972 Jul;4(4):267–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01005005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE R. E., FELDMAN J. D. VISUALIZATION OF ANTIGENIC SITES OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES WITH FERRITIN-ANTIBODY CONJUGATES. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:396–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINTHAL C., DAVISON P. F. Degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid under hydrodynamic shearing forces. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:674–683. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Singer S. J. Alteration of the conformation of proteins in red blood cell membranes and in solution by fixatives used in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):117–121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura Y. Demonstration of ferritin-labelled antibodies bound to human erythrocytes fixed with glutaraldehyde. Vox Sang. 1972;22(6):549–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb04645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Hochmuth R. M., Spaeth E. E. Adhesion of red cells to foreign surfaces in the presence of flow. J Biomed Mater Res. 1974 Mar;8(2):119–136. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETHICA B. A. The physical chemistry of cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res. 1961;Suppl 8:123–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Richards F. M. Chemical cross-linking: reagents and problems in studies of membrane structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:523–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembaum A., Margel S., Levy J. Polyglutaraldehyde: a new reagent for coupling proteins to microspheres and for labeling cell-surface receptors. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(3-4):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockoff S. D., McIntire K. R., Ng A. K., Princler G. L., Herberman R. B., Larson J. N. Sensitive and convenient quantitation of antibody binding to cellular antigens using glutaraldehyde preserved cells. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(4):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Sachs L. Receptor mobility and the binding of cells to lectin-coated fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):76–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung K. L., Sung L. A., Crimmins M., Burakoff S. J., Chien S. Determination of junction avidity of cytolytic T cell and target cell. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1405–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3491426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. A., Kabat E. A., Chien S. Interaction energies in lectin-induced erythrocyte aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):652–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. A., Kabat E. A., Chien S. Interaction of lectins with membrane receptors on erythrocyte surfaces. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):646–651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tha S. P., Goldsmith H. L. Interaction forces between red cells agglutinated by antibody. I. Theoretical. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83555-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tha S. P., Shuster J., Goldsmith H. L. Interaction forces between red cells agglutinated by antibody. II. Measurement of hydrodynamic force of breakup. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1117–1126. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83556-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trommler A., Gingell D., Wolf H. Red blood cells experience electrostatic repulsion but make molecular adhesions with glass. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):835–841. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83842-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ewijk W., Coffman R. C., Weissman I. L. Immunoelectron microscopy of cell surface antigens: a quantitative analysis of antibody binding after different fixation protocols. Histochem J. 1980 May;12(3):349–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01006955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voak D., Williams M. A. An explanation of the failure of the direct antiglobulin test to detect erythrocyte sensitization in ABO haemolytic disease of the newborn and observations on pinocytosis of IgG anti-A antibodies by infant (cord) red cells. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jan;20(1):9–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Voak D. Studies with ferritin-labelled Dolichos biflorus lectin on the numbers and distribution of A sites on A 1 and A 2 erythrocytes, and on the nature of its specificity and enhancement by enzymes. Br J Haematol. 1972 Oct;23(4):427–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]