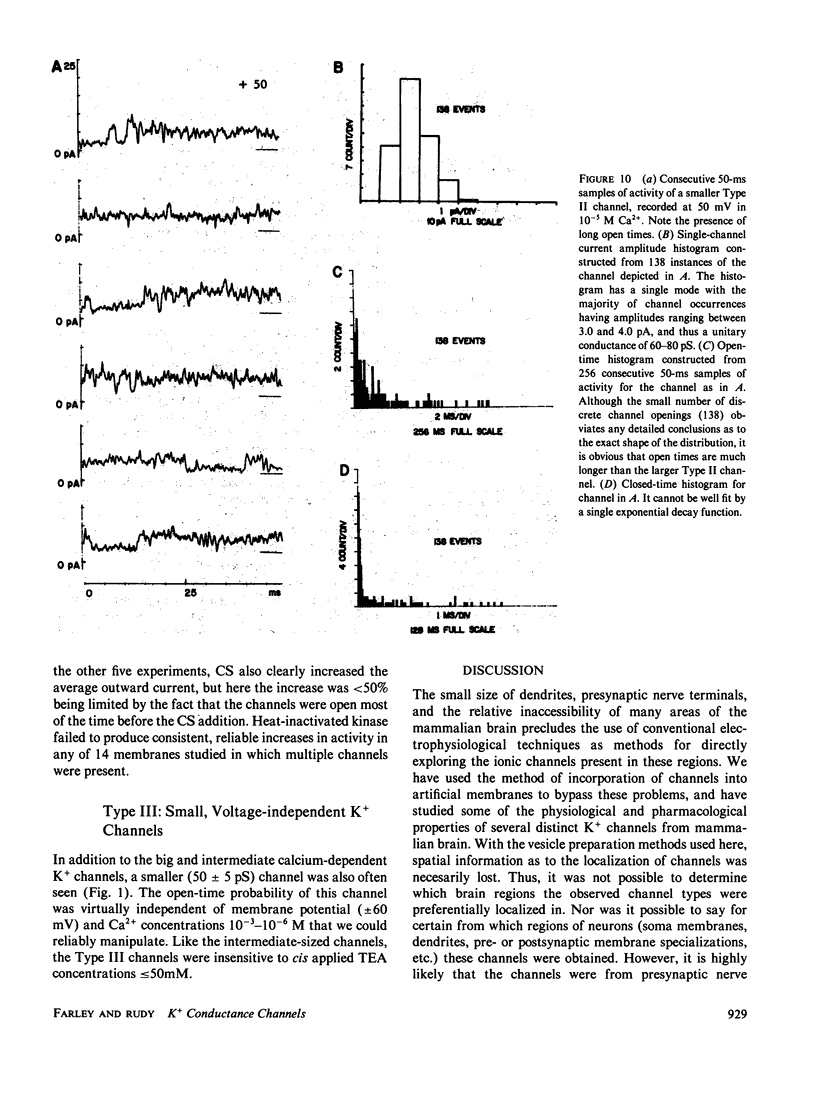
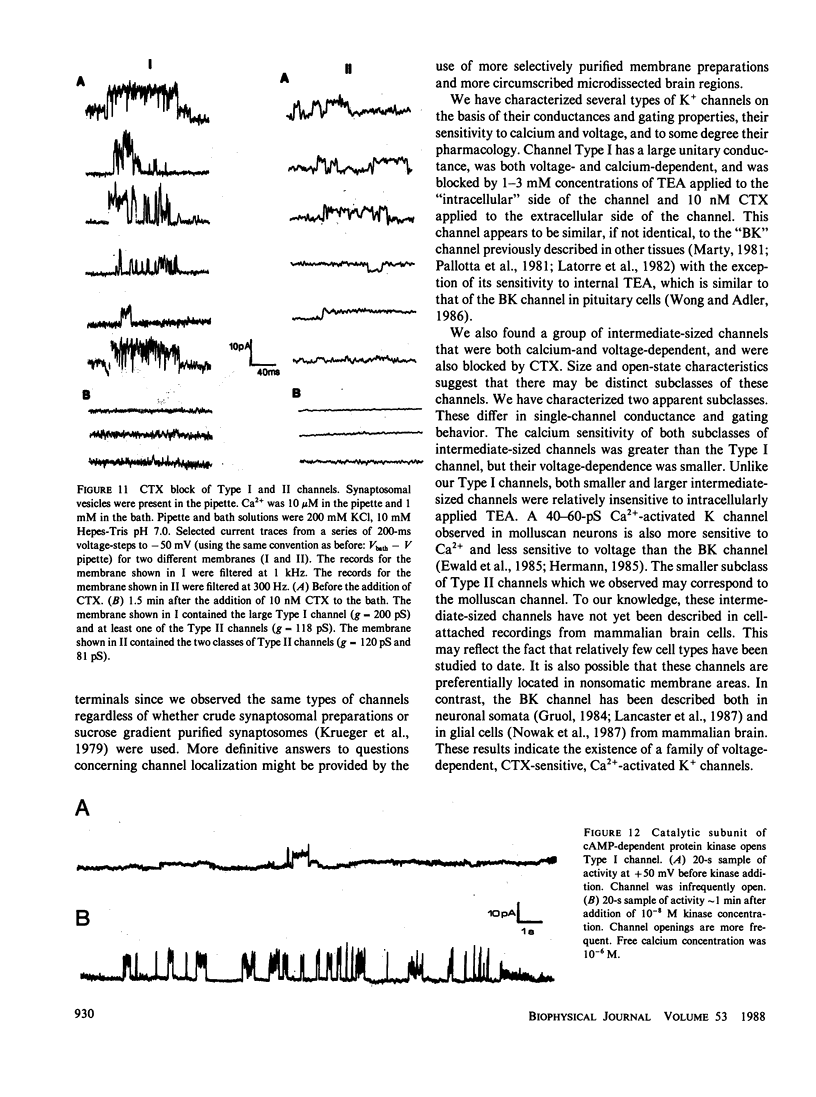
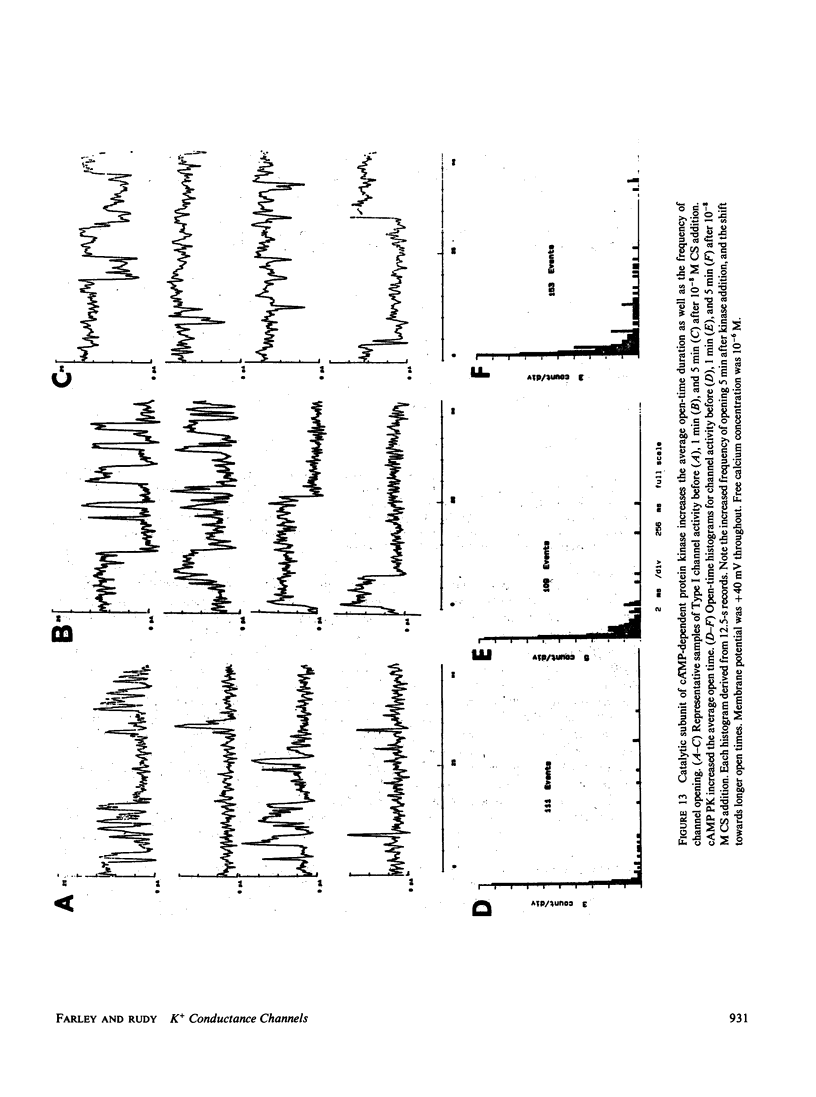
Abstract
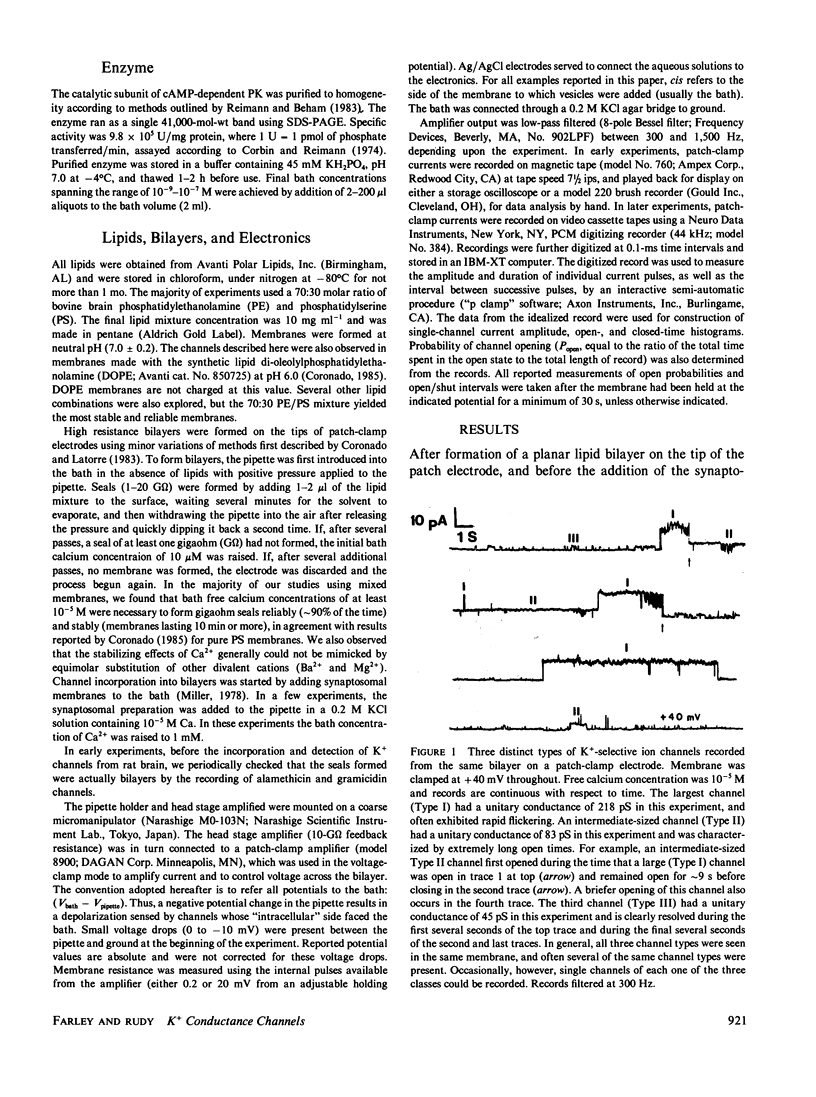
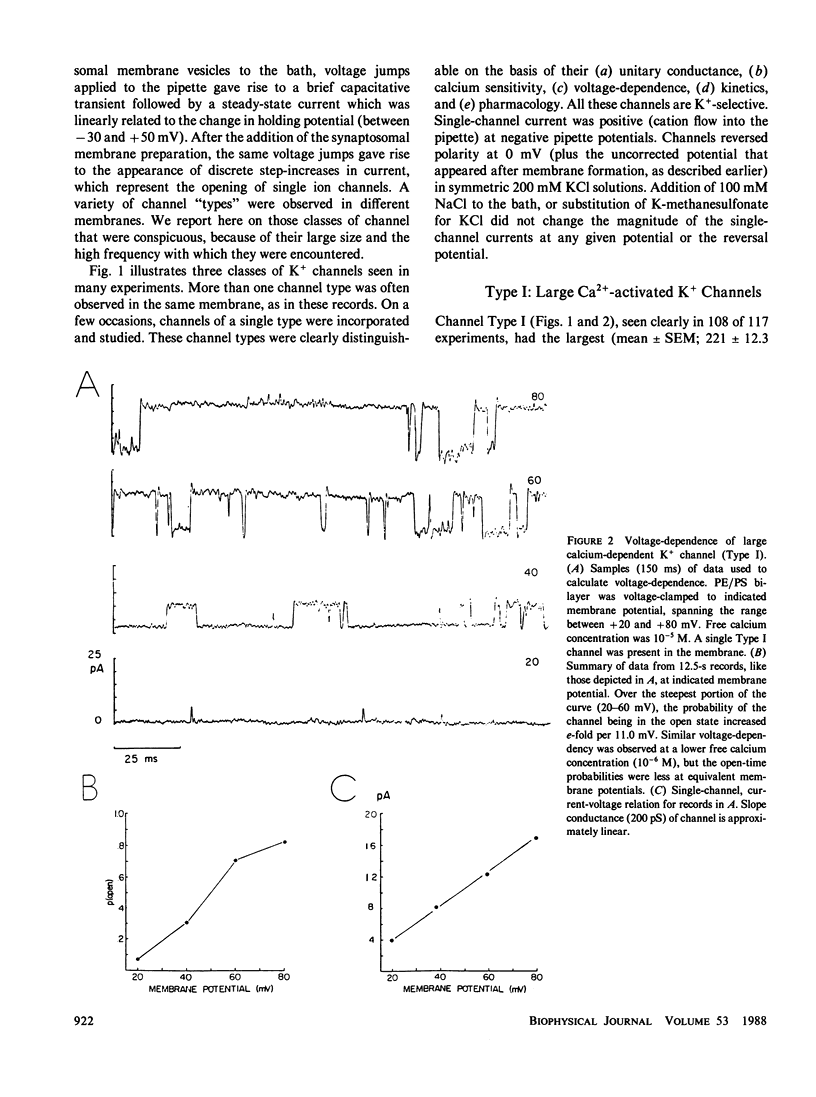
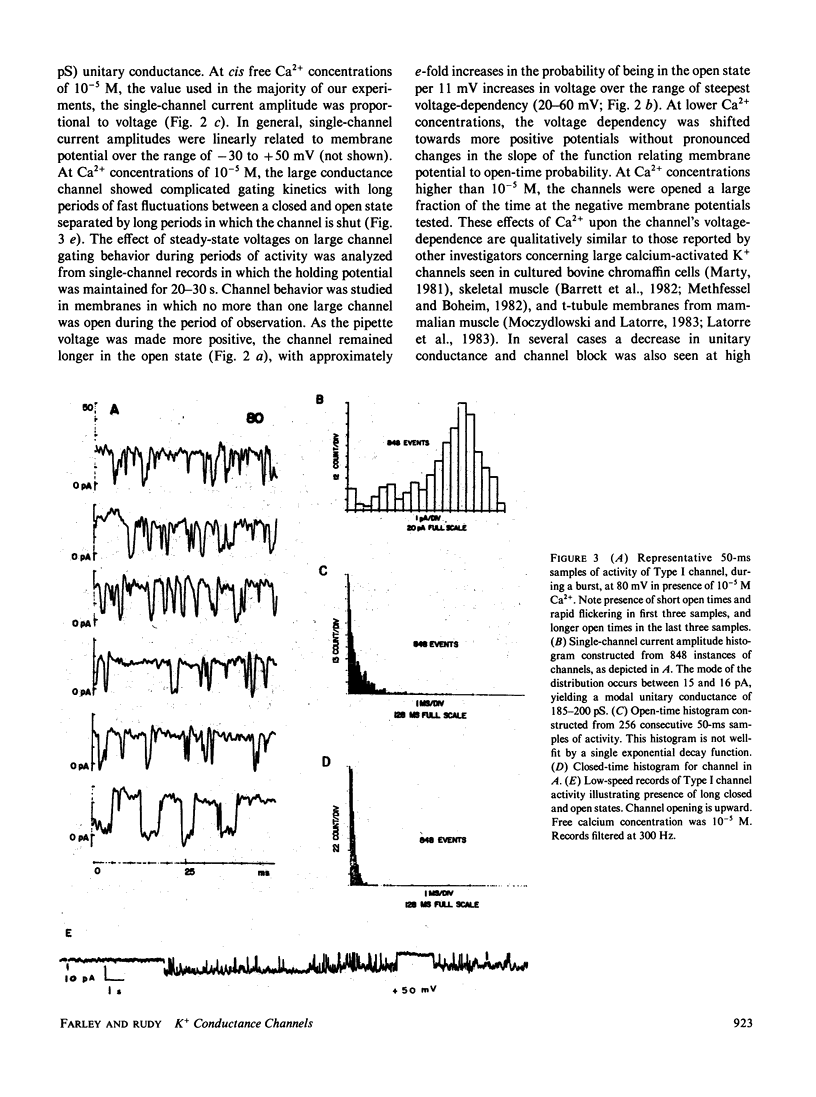
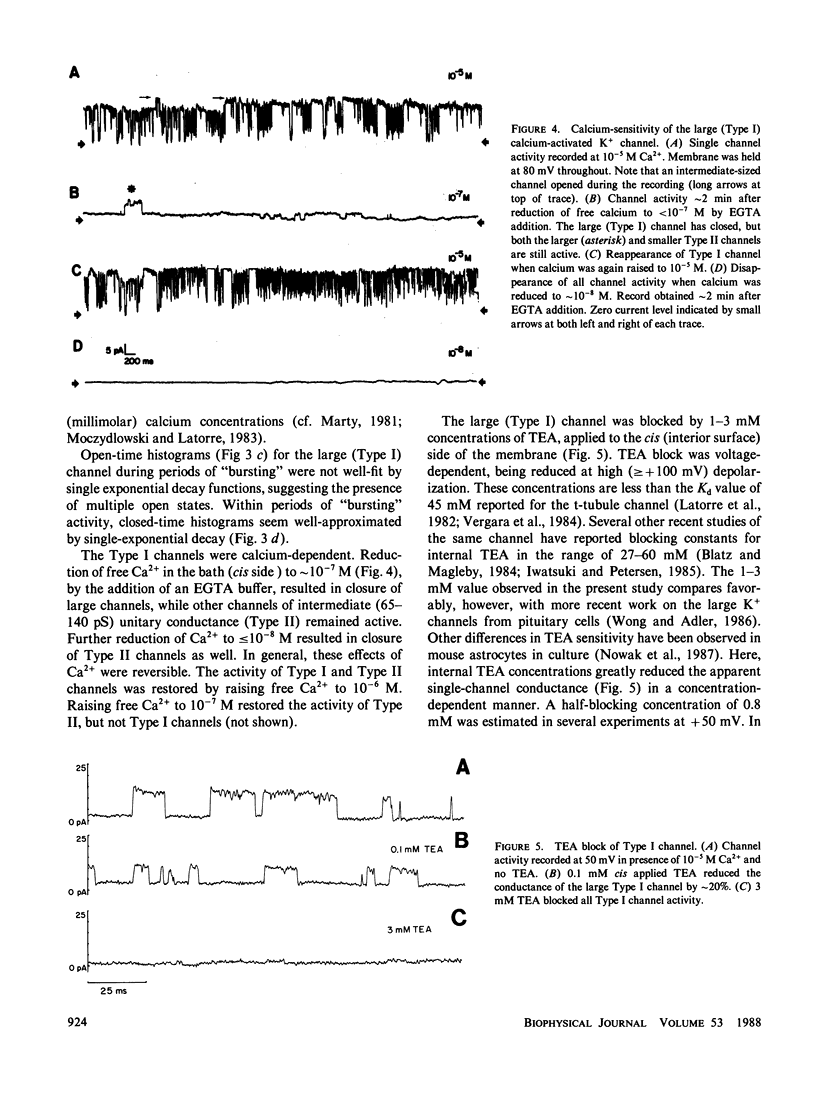
K+-selective ion channels from a mammalian brain synaptosomal membrane preparation were inserted into planar phospholipid bilayers on the tips of patch-clamp pipettes, and single-channel currents were measured. Multiple distinct classes of K+ channels were observed. We have characterized and described the properties of several types of voltage-dependent, Ca2+-activated K+ channels of large single-channel conductance (greater than 50 pS in symmetrical KCl solutions). One class of channels (Type I) has a 200-250-pS single-channel conductance. It is activated by internal calcium concentrations greater than 10(-7) M, and its probability of opening is increased by membrane depolarization. This channel is blocked by 1-3 mM internal concentrations of tetraethylammonium (TEA). These channels are similar to the BK channel described in a variety of tissues. A second novel group of voltage-dependent, Ca2+-activated K+ channels was also studied. These channels were more sensitive to internal calcium, but less sensitive to voltage than the large (Type I) channel. These channels were minimally affected by internal TEA concentrations of 10 mM, but were blocked by a 50 mM concentration. In this class of channels we found a wide range of relatively large unitary channel conductances (65-140 pS). Within this group we have characterized two types (75-80 pS and 120-125 pS) that also differ in gating kinetics. The various types of voltage-dependent, Ca2+-activated K+ channels described here were blocked by charybdotoxin added to the external side of the channel. The activity of these channels was increased by exposure to nanomolar concentrations of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. These results indicate that voltage-dependent, charybdotoxin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channels comprise a class of related, but distinguishable channel types. Although the Ca2+-activated (Type I and II) K+ channels can be distinguished by their single-channel properties, both could contribute to the voltage-dependent Ca2+-activated macroscopic K+ current (IC) that has been observed in several neuronal somata preparations, as well as in other cells. Some of the properties reported here may serve to distinguish which type contributes in each case. A third class of smaller (40-50 pS) channels was also studied. These channels were independent of calcium over the concentration range examined (10(-7)-10(-3) M), and were also independent of voltage over the range of pipette potentials of -60 to +60 mV. Type III channels were unaffected by internal TEA concentrations <50 mM. Our results also indicate that the study of K+ channels in lipid bilayers may allow the identification and characterization of novel K+ channels from brain regions otherwise inaccessible to conventional recording techniques.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Galvan M. Voltage-dependent currents of vertebrate neurons and their role in membrane excitability. Adv Neurol. 1986;44:137–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartschat D. K., Blaustein M. P. Calcium-activated potassium channels in isolated presynaptic nerve terminals from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:441–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartschat D. K., Blaustein M. P. Potassium channels in isolated presynaptic nerve terminals from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:419–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Ion conductance and selectivity of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jul;84(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Reimann E. M. Assay of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R. Effect of divalent cations on the assembly of neutral and charged phospholipid bilayers in patch-recording pipettes. Biophys J. 1985 Jun;47(6):851–857. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83990-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Latorre R. Phospholipid bilayers made from monolayers on patch-clamp pipettes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84343-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M. Potassium currents in the frog node of Ranvier. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1983;42(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald D. A., Williams A., Levitan I. B. Modulation of single Ca2+-dependent K+-channel activity by protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):503–506. doi: 10.1038/315503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Auerbach S. Protein kinase C activation induces conductance changes in Hermissenda photoreceptors like those seen in associative learning. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):220–223. doi: 10.1038/319220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruol D. L. Single channel analysis of voltage-sensitive k channels in cultured purkinje neurons. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):53–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84105-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grygorczyk R., Schwarz W., Passow H. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human red cells. Comparison of single-channel currents with ion fluxes. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):693–698. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84211-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Action of tetraethylammonium on calcium-activated potassium channels in pig pancreatic acinar cells studied by patch-clamp single-channel and whole-cell current recording. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF01870780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjevic K., Van Meter W. G. Cyclic nucleotides in spinal cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;54(3):416–421. doi: 10.1139/y76-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Ratzlaff R. W., Strichartz G. R., Blaustein M. P. Saxitoxin binding to synaptosomes, membranes, and solubilized binding sites from rat brain. J Membr Biol. 1979 Nov 30;50(3-4):287–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01868894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Adams P. R. Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Moczydlowski E. Properties of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in a reconstituted system. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):343–357. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski M. Apamin, a neurotoxin specific for one class of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E., Marty A. Single channel activity associated with the calcium dependent outward current in Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Mar;389(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00584792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate mediates beta-receptor actions of noradrenaline in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:245–259. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Boheim G. The gating of single calcium-dependent potassium channels is described by an activation/blockade mechanism. Biophys Struct Mech. 1982;9(1):35–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00536014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):511–542. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Ascher P., Berwald-Netter Y. Ionic channels in mouse astrocytes in culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Beham R. A. Catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:51–55. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé R., Simoneau C., Monette R., Roy G. Single-channel analysis of the potassium permeability in HeLa cancer cells: evidence for a calcium-activated potassium channel of small unitary conductance. J Membr Biol. 1986;92(3):269–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01869395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Conduction, Blockade and Gating in a Ca -activated K Channel Incorporated into Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84114-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Adler M. Tetraethylammonium blockade of calcium-activated potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00585303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Peyer J. E., Cachelin A. B., Levitan I. B., Reuter H. Ca2+ -activated K+ conductance in internally perfused snail neurons is enhanced by protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4207–4211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


