Abstract
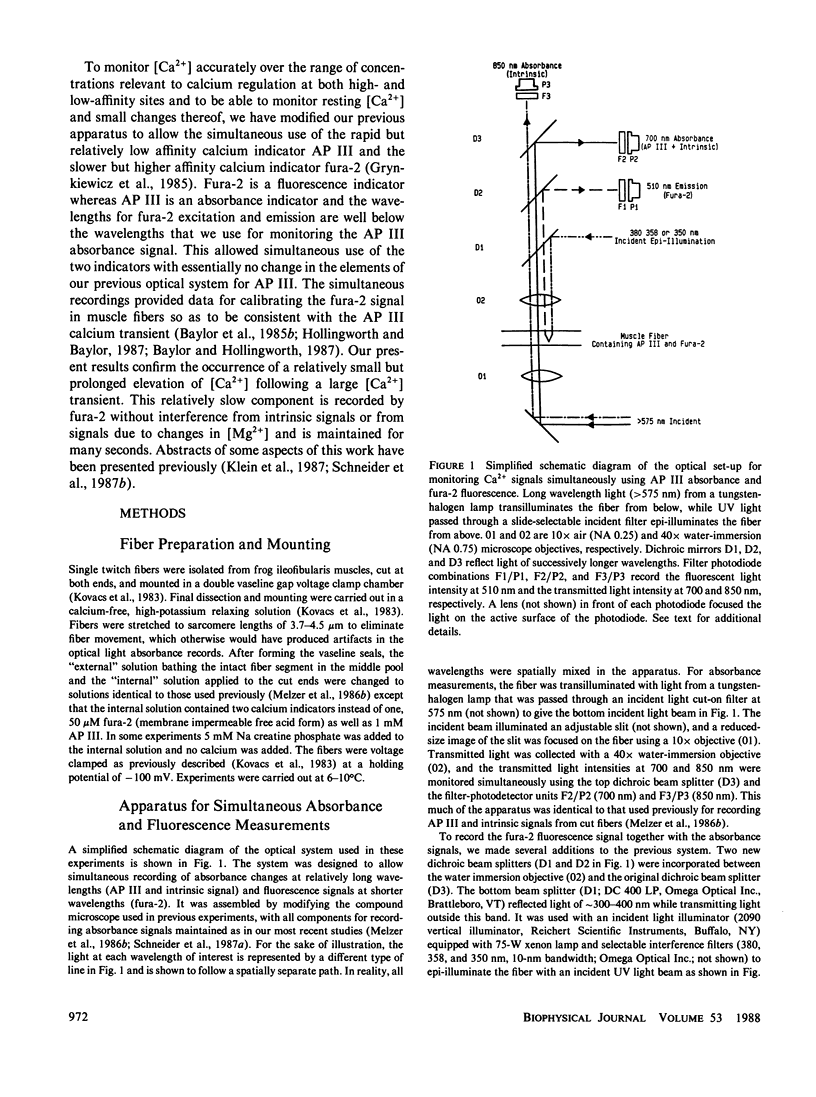
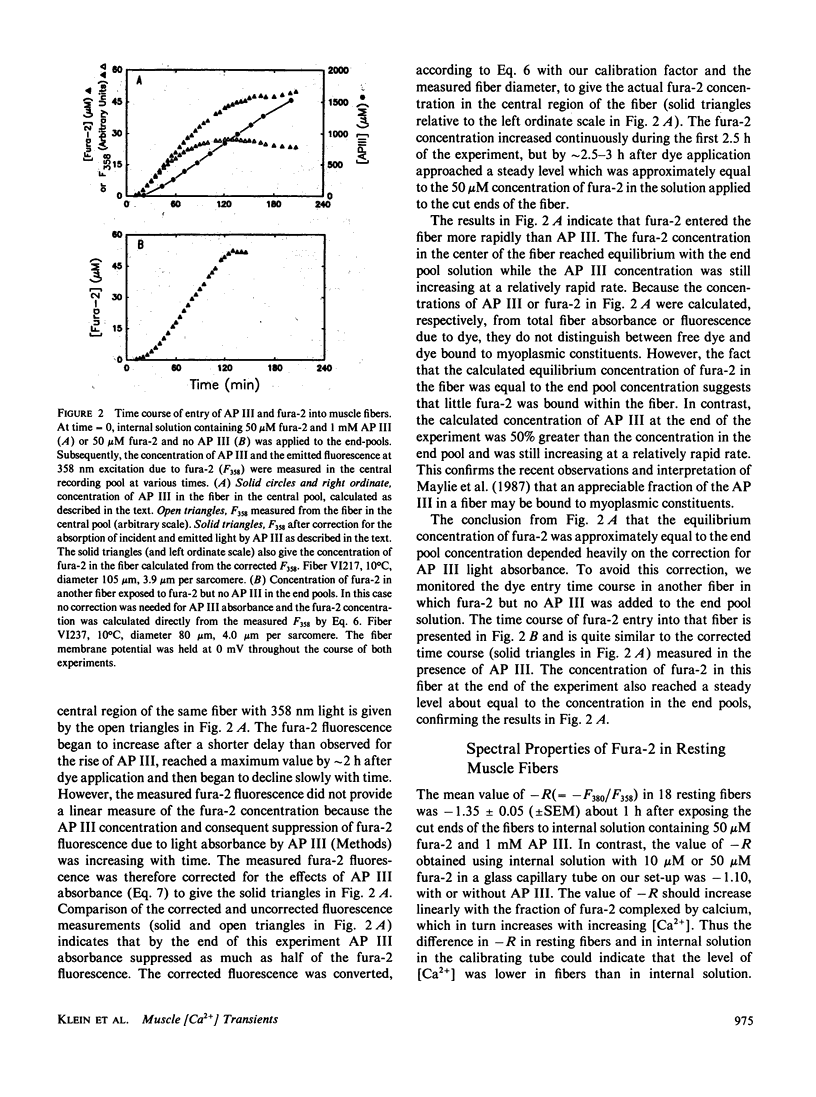
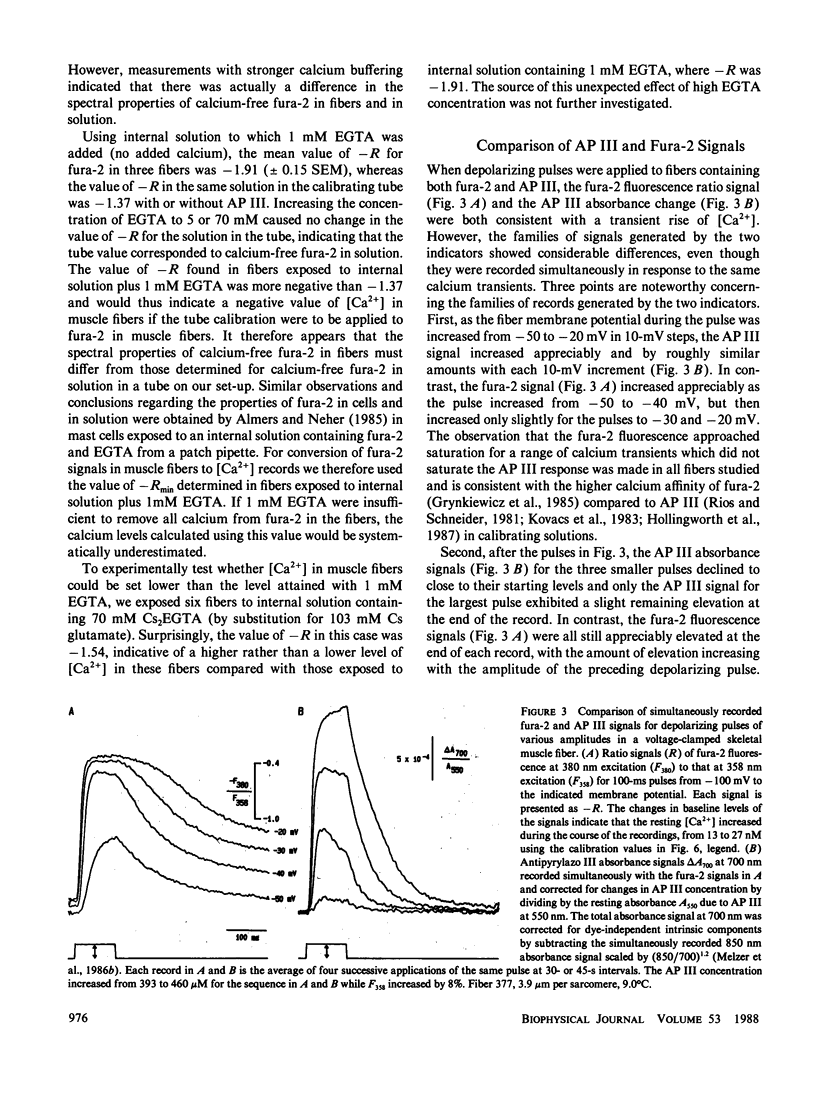
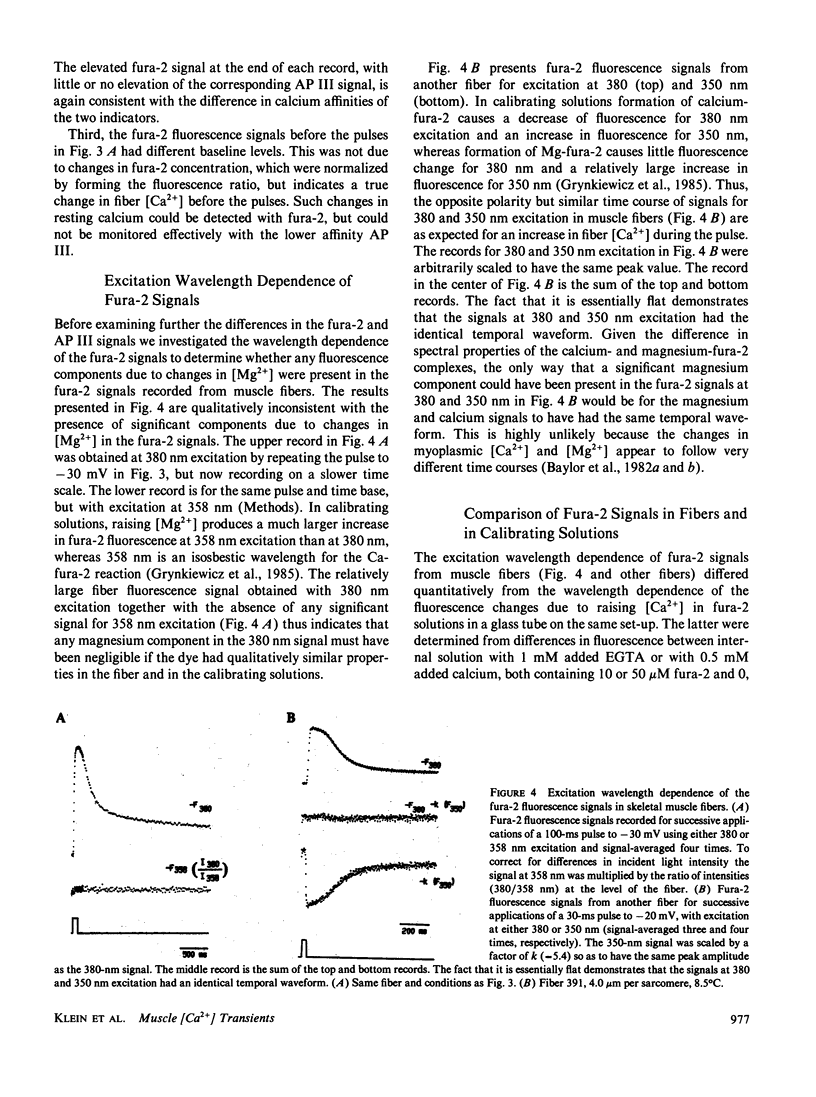
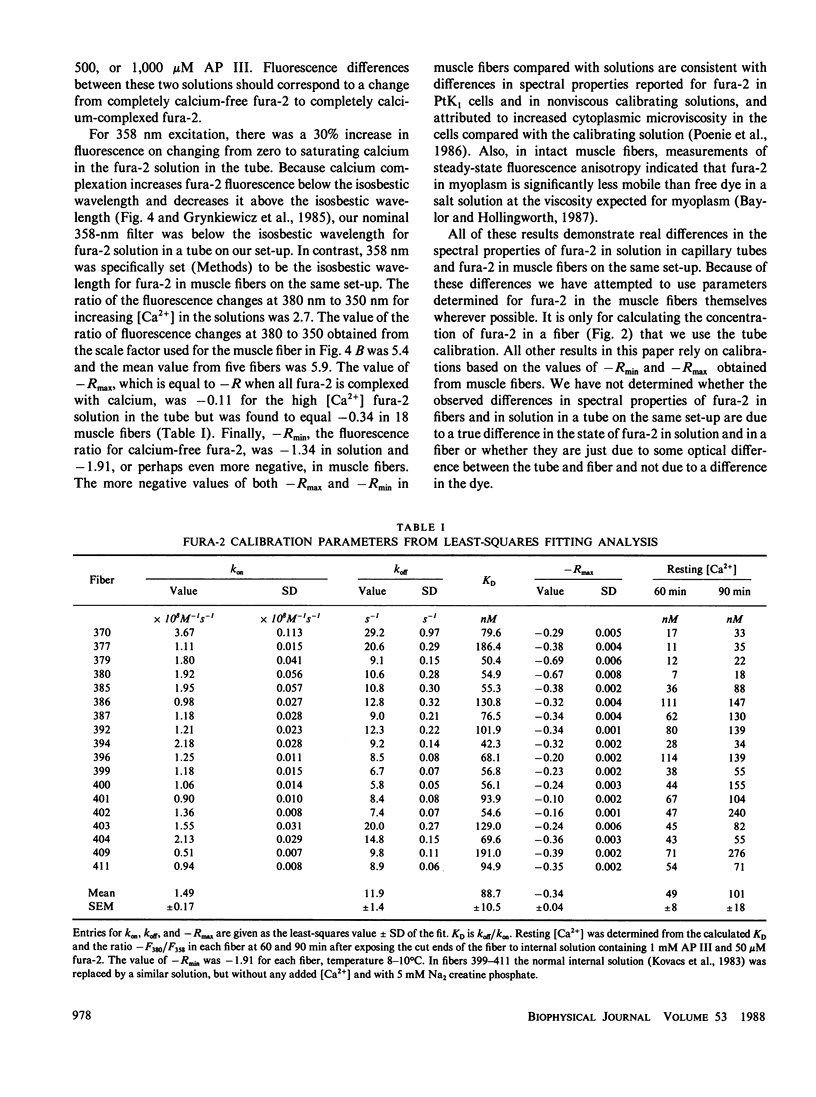
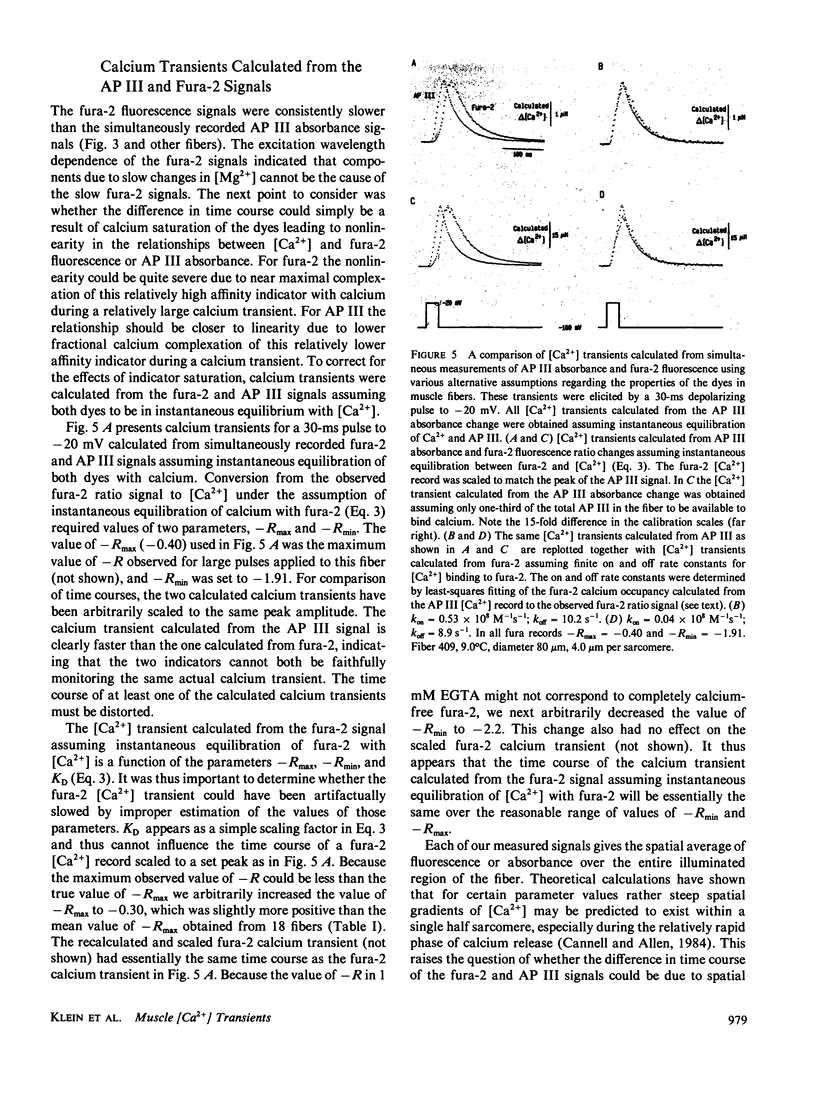
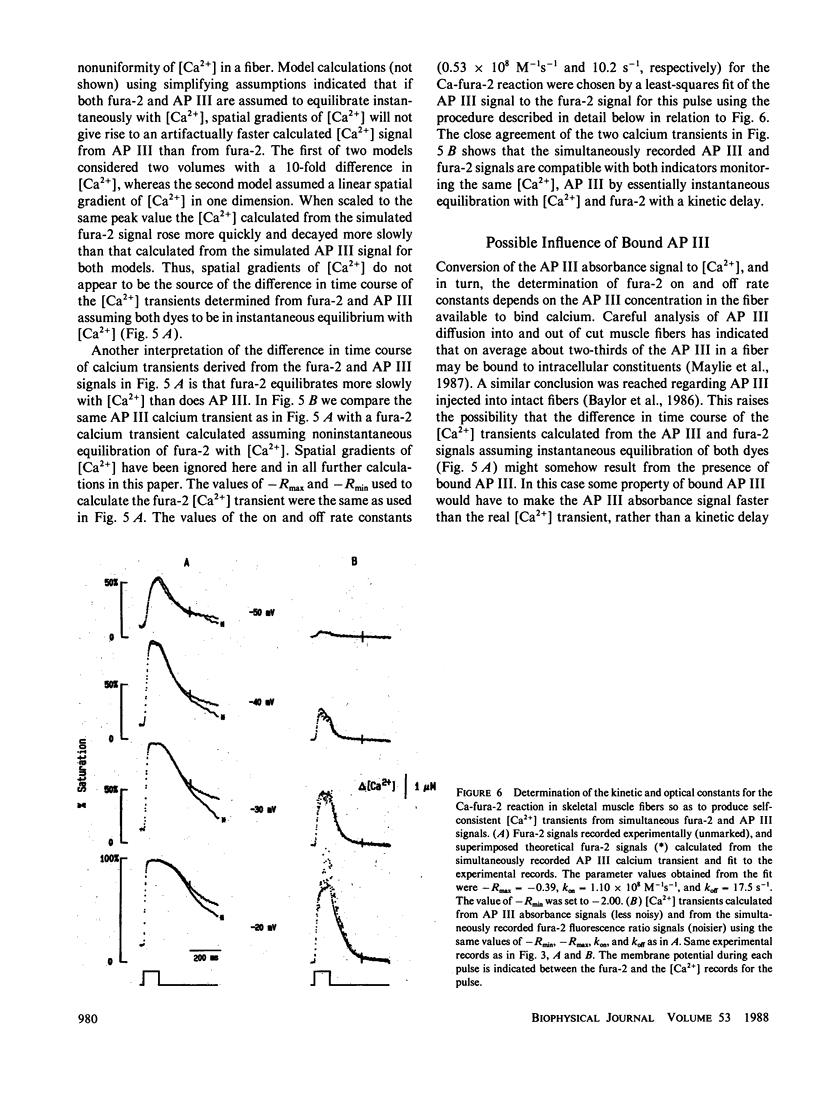
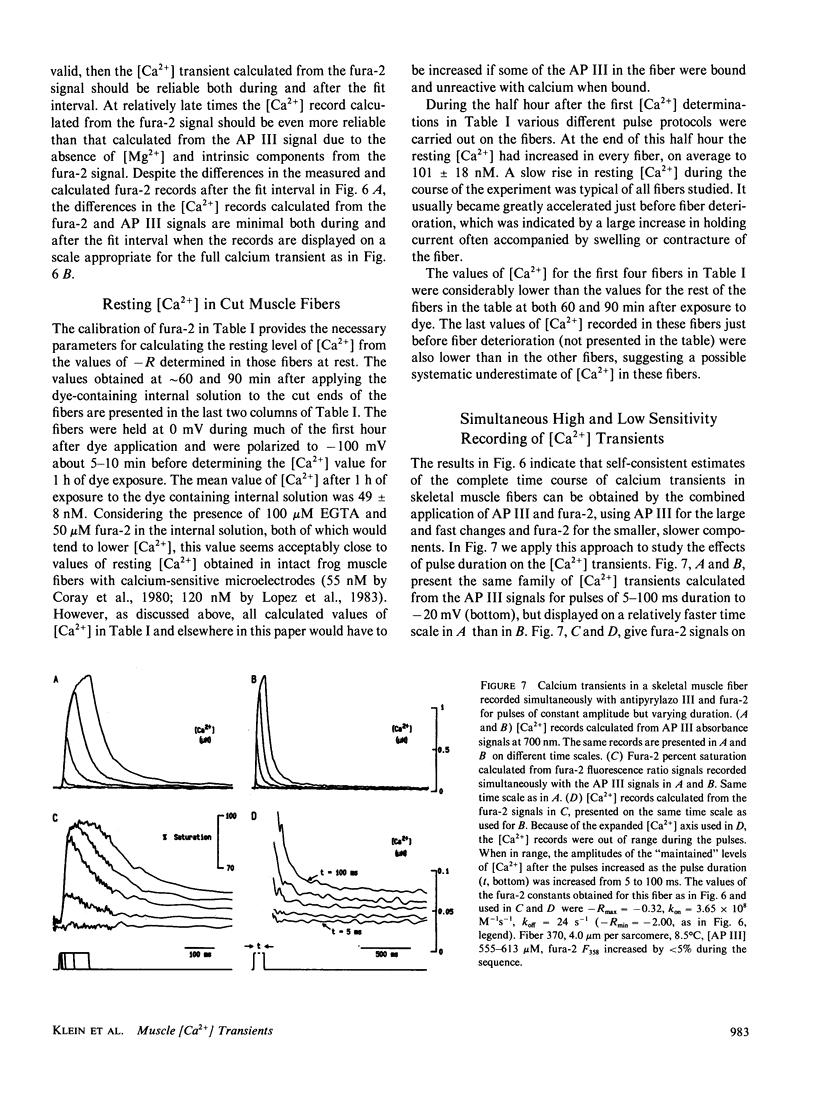
To monitor cytosolic [Ca2+] over a wide range of concentrations in functioning skeletal muscle cells, we have used simultaneously the rapid but relatively low affinity calcium indicator antipyrylazo III (AP III) and the slower but higher affinity indicator fura-2 in single frog twitch fibers cut at both ends and voltage clamped with a double vaseline gap system. When both dyes were added to the end pool solution the cytosolic fura-2 concentration reached a steady level equal to the end pool concentration within approximately 2.5 h, a time when the AP III concentration was still increasing. For depolarizing pulses of increasing amplitude, the fura-2 fluorescence signal approached saturation when the simultaneously recorded AP III absorbance change was far from saturation. Comparison of simultaneously recorded fura-2 and AP III signals indicated that the mean values of the on and off rate constants for calcium binding to fura-2 in 18 muscle fibers were 1.49 x 10(8) M-1 s-1 and 11.9 s-1, respectively (mean KD = 89 nM), if all AP III in the fiber is assumed to behave as in calibrating solution and to be in instantaneous equilibrium with [Ca2+]. [Ca2+] transients calculated from the fura-2 signals using these rate constants were consistent with the [Ca2+] transients calculated from the AP III signals. Resting [Ca2+] or small changes in [Ca2+] which could not be reliably monitored with AP III could be monitored with fura-2 with little or no interference from changes in [Mg2+] or from intrinsic signals. The fura-2 signal was also less sensitive to movement artifacts than the AP III signal. After a [Ca2+] transient the fura-2 signal demonstrated a relatively small elevation of [Ca2+] that was maintained for many seconds.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abstracts of the International symposium on localization and movement of cytoplasmic calcium in living muscle. Tokyo, May 18-20, 1987. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Oct;8(5):461–472. doi: 10.1007/BF01578435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abstracts of the International symposium on localization and movement of cytoplasmic calcium in living muscle. Tokyo, May 18-20, 1987. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Oct;8(5):461–472. doi: 10.1007/BF01578435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Optical measurements of intracellular pH and magnesium in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:105–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Use of metallochromic dyes to measure changes in myoplasmic calcium during activity in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:139–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S., Hui C. S., Quinta-Ferreira M. E. Properties of the metallochromic dyes Arsenazo III, Antipyrylazo III and Azo1 in frog skeletal muscle fibres at rest. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:89–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B. Effect of tetanus duration on the free calcium during the relaxation of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V., HOWARTH J. V. The effect of potassium on the resting metabolism of the frog's sartorius. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Aug 24;147(926):21–43. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Aldrich R. W., Baylor S. M. In vitro calibration of the equilibrium reactions of the metallochromic indicator dye antipyrylazo III with calcium. Biophys J. 1987 Mar;51(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83360-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Maylie J., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Intrinsic optical and passive electrical properties of cut frog twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):1–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schneider M. F. Increased optical transparency associated with excitation--contraction coupling in voltage-clamped cut skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):556–560. doi: 10.1038/265556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Huxley H. E., Faruqi A. R., Hendrix J. Structural changes during activation of frog muscle studied by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):325–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López J. R., Alamo L., Caputo C., DiPolo R., Vergara S. Determination of ionic calcium in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84316-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):83–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. A general procedure for determining the rate of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):849–863. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83413-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Time course of calcium release and removal in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):637–641. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84203-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. The removal of myoplasmic free calcium following calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:261–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:481–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Stoichiometry of the reactions of calcium with the metallochromic indicator dyes antipyrylazo III and arsenazo III. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):607–621. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84755-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Brinley F. J., Jr, Dubyak G. Antipyrylazo III, a "middle range" Ca2+ metallochromic indicator. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1378–1386. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Depletion of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum during calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:167–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. G., Solandt D. Y. The relation of contracture to the increment in the resting heat production of muscle under the influence of potassium. J Physiol. 1938 Sep 16;93(4):305–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowdowne K. W. Subcontracture depolarizations increase sarcoplasmic ionized calcium in frog skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C520–C526. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solandt D. Y. The effect of potassium on the excitability and resting metabolism of frog's muscle. J Physiol. 1936 Feb 8;86(2):162–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



