Abstract
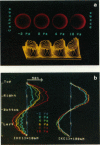
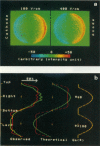
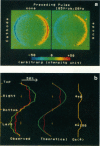
Controlled permeability can be conferred to cell membranes by exposing cells to a microsecond electric pulse of sufficient intensity (electroporation). By constructing a fluorescence microimaging system with a submicrosecond time resolution we have been able to resolve temporally and spatially the events in a single cell under a microsecond electric pulse. An enormous membrane conductance, corresponding to a loss of 0.01-0.1% of the membrane area, was observed in those membrane regions where the transmembrane potential induced by the electric pulse exceeded a critical value. The conductance decreased to a low level in a submillisecond after the pulse, leaving a moderately electroporated cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ehrenberg B., Farkas D. L., Fluhler E. N., Lojewska Z., Loew L. M. Membrane potential induced by external electric field pulses can be followed with a potentiometric dye. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):833–837. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83410-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Hildesheim R., Farber I. C., Anglister L. Improved fluorescent probes for the measurement of rapid changes in membrane potential. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84520-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D., Loew L. M., Webb W. W. Optical imaging of cell membrane potential changes induced by applied electric fields. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83467-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Formation and resealing of pores of controlled sizes in human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):438–441. doi: 10.1038/268438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):479–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced pore formation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 1;471(2):227–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y. Voltage modulation of membrane permeability and energy utilization in cells. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):487–505. doi: 10.1007/BF01120693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U. Electric field-mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):227–277. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]