Abstract
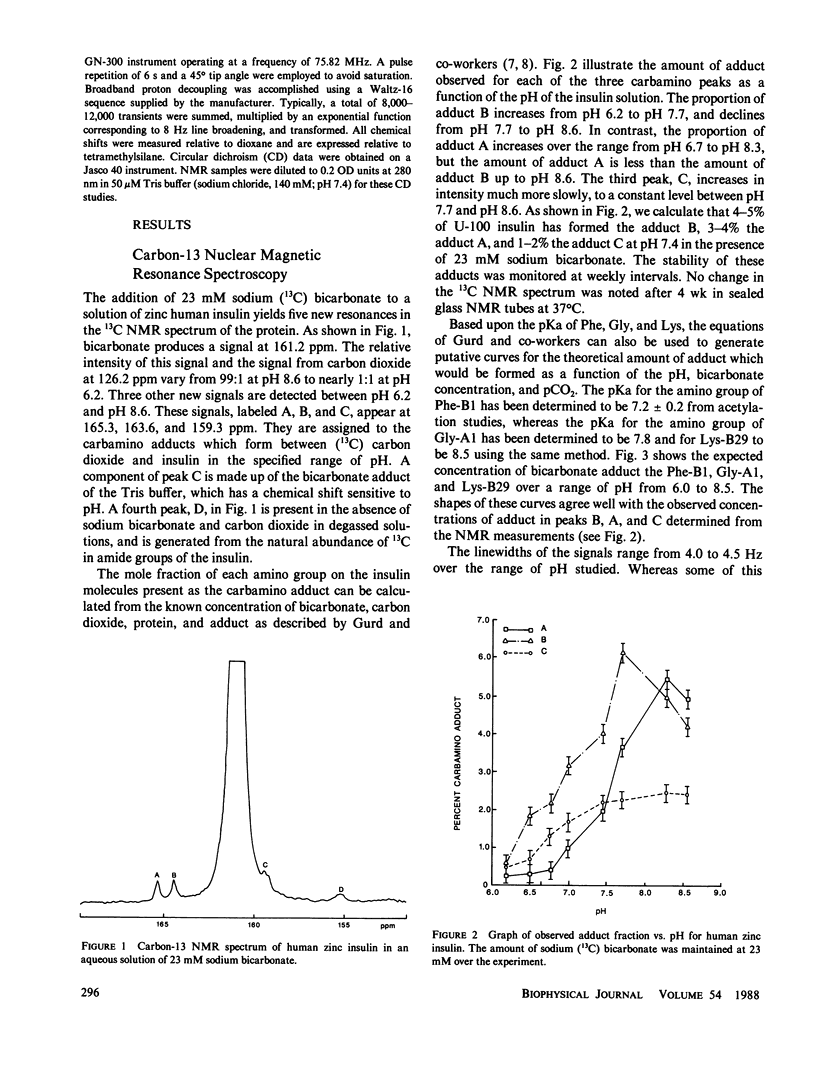
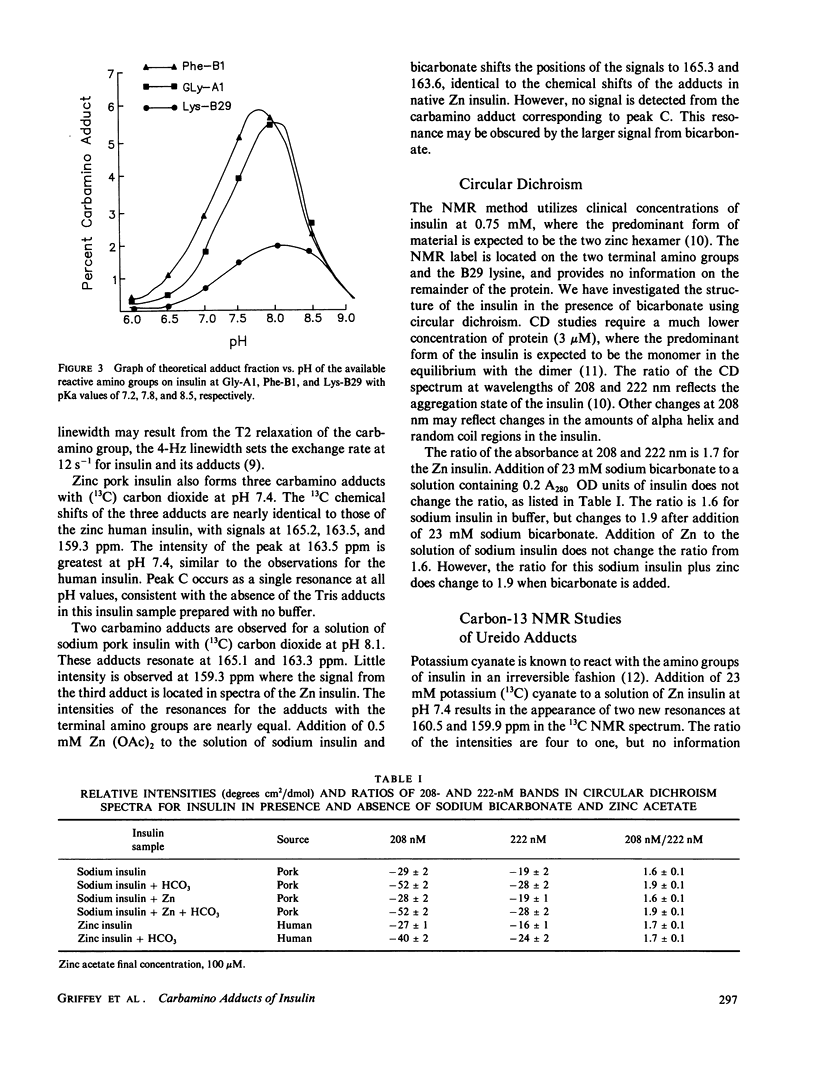
Carbon-13 (13C) nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is performed to characterize the formation of carbamino adducts between insulin and (13C) carbon dioxide over a range of pH values in the presence of a physiological concentration (23 mM) of sodium bicarbonate. The peaks from two of the carbamino adducts resonate at higher frequencies than the signal from bicarbonate, at 164.6 and 165.3 ppm, and are attributed to the adducts with the terminal amino groups of phenylalanine B1 and glycine A1. The intensities of these signals vary with the pH, with unique patterns. Over 6% of each terminal amino group exists as the carbamino adduct at the optimum pH values of 7.8 and 8.3. A unique third adduct resonates at 159.3 ppm, and is attributed to lysine B29. This adduct is present on 2% of the insulin molecules at pH 8.2, but has minimal intensity at pH 7.4. No signals from adducts are detected below pH 6.2, where the amino groups exist predominantly in the protonated form. Creation of the adducts is rapid and they are stable for over 4 wk at 37 degrees C. The narrow bandwidth of the resonance of the adduct (4.0-4.5 Hz) relative to the irreversible cyanate adduct is consistent with molecular forms of the carbamino adduct smaller than the 2-Zn-hexamer which is the preponderate form of clinically utilized U-100 insulin (i.e., 100 U/ml).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne M., Cecil R., Miller J. C. Some reactions of insulin at non-polar surfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):233–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C., Reynolds C. D. Structural relationships in the two-zinc insulin hexamer. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):469–479. doi: 10.1139/o79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. H., Veros A. J. Interaction of zinc with proinsulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90710-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay D. G., Loge O., Losert W., Shall S. Carbamyl- and methylthiocarbamylinsulins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 18;263(3):658–665. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay D. G., Shall S. The acetylation of insulin. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):737–745. doi: 10.1042/bj1210737a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lougheed W. D., Fischer U., Perlman K., Albisser A. M. A physiological solvent for crystalline insulin. Diabetologia. 1981;20(1):51–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00253817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matwiyoff N. A., Needham T. E. Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy of red blood cell suspensions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 4;49(5):1158–1164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90590-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Matthew J. B., Gurd F. R. Measurement of CO2 binding: the 13C NMR method. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:496–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocker Y., Biswas S. B. Conformational dynamics of insulin in solution. Circular dichroic studies. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):5043–5049. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocker Y., Biswas S. B. Self-association of insulin and the role of hydrophobic bonding: a thermodynamic model of insulin dimerization. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4354–4361. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothgeb T. M., England R. D., Jones B. N., Gurd R. S. Physical characterization of S-methylglucagon and quantitation of carbamino adduct formation. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4564–4571. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffer M. G., Kaplan H. Unusual chemical properties of the amino groups of insulin: implications for structure-function relationship. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):489–496. doi: 10.1139/o79-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAUGH D. F. Protein-protein interactions. Adv Protein Chem. 1954;9:325–437. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittebort R. J., Hayes D. F., Rothgeb T. M., Gurd R. S. The quantitation of carbamino adduct formation of angiotensin II and bradykinin. Biophys J. 1978 Dec;24(3):765–778. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85419-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



