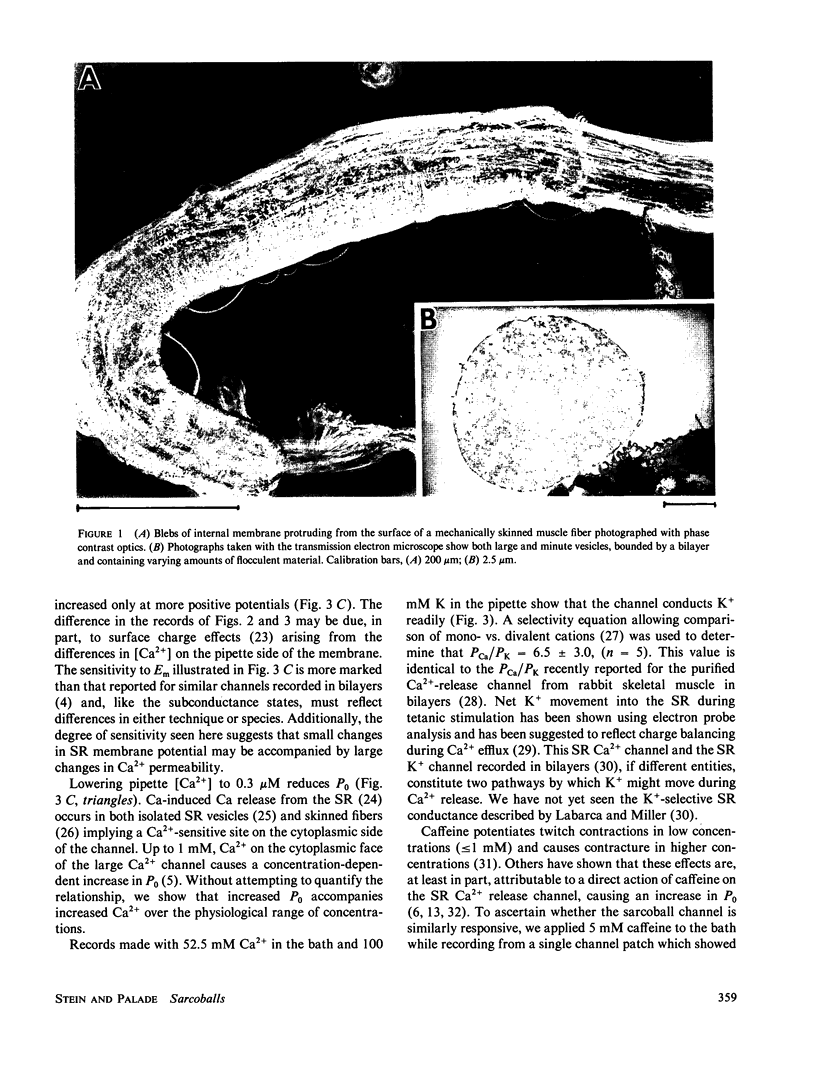
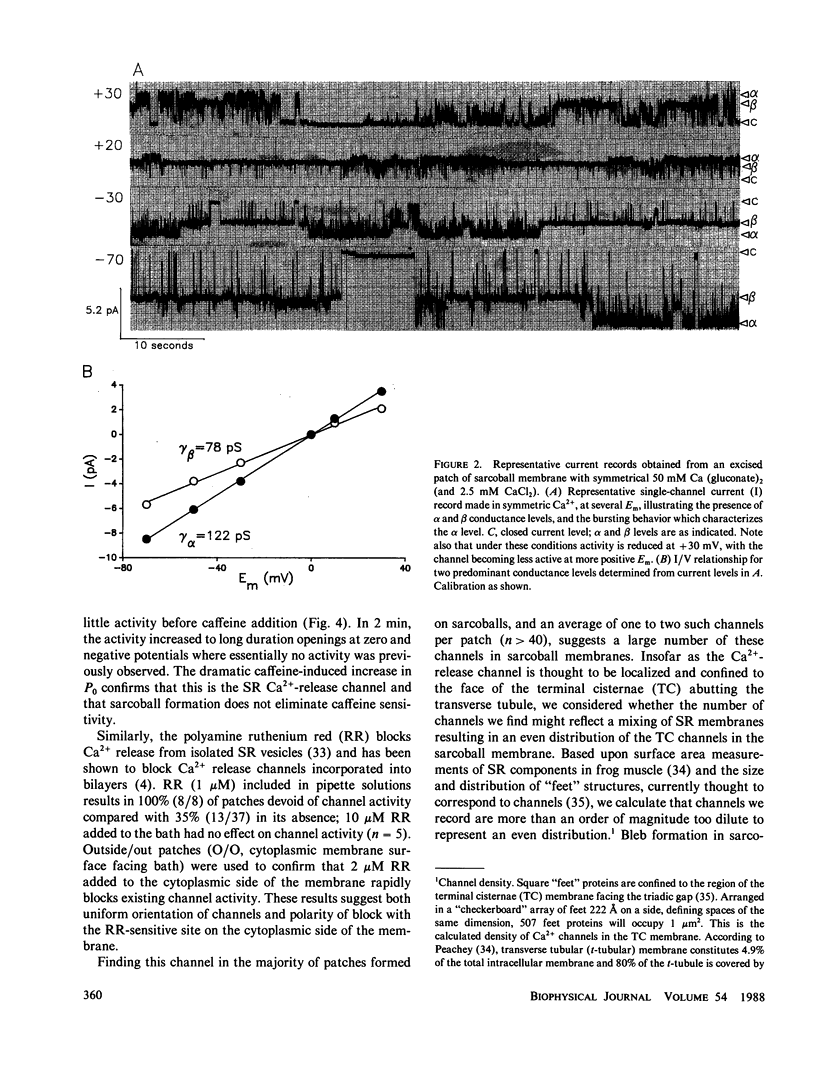
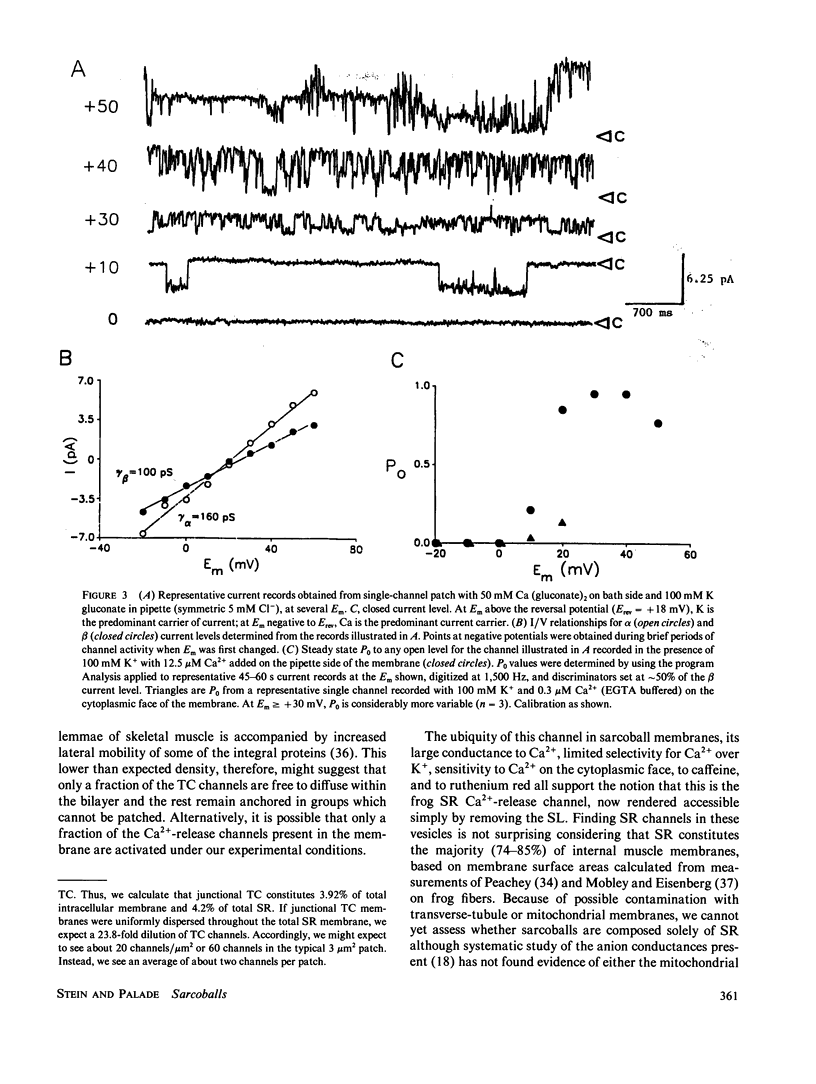
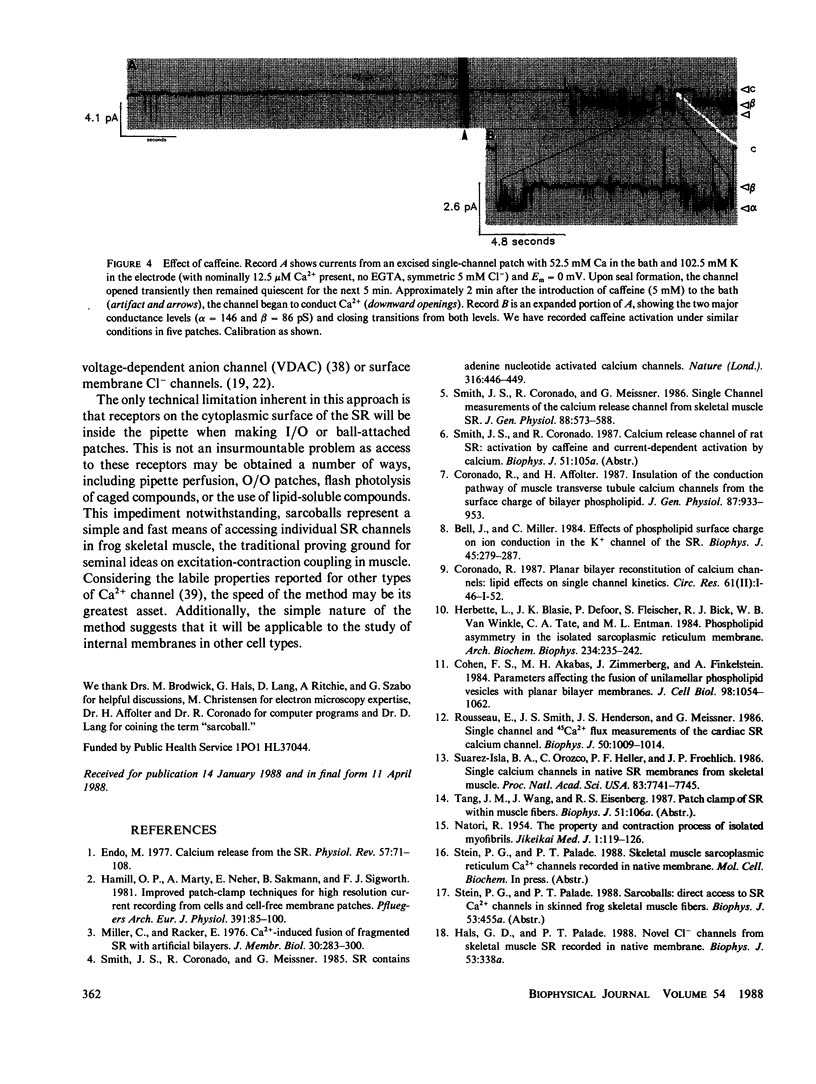
Abstract
In skeletal muscle, twitch contraction is caused by the rapid release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) (Endo, M. 1977. Physiol. Rev. 57:71-108) via Ca2+ conducting channels in the SR membrane (Smith, J. S., R. Coronado, and G. Meissner, 1985. Nature (Lond.). 316:446-449; Suarez-Isla, B. A., G. Orozco, P. F. Heller, and J. P. Froehlich. 1986. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83:7741-7745). To facilitate study of these and other intracellular channels, we have developed a method which allows direct patch-clamp recording of currents through SR channels in native membrane. The Ca2+-release channel studied using this method exhibits two predominant conductance levels (80-100 pS and 120-160 pS), conducts Ca2+ preferentially over K+ (PCa/Pk = 6.5), is highly voltage sensitive, blocked on one side by ruthenium red (1 microM), and displays enhanced activity in the presence of caffeine (5 mM). Studied in skinned fibers, this channel appears fundamentally similar to homologous channels from isolated rabbit SR incorporated into bilayers, with some distinct differences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. E., Miller C. Effects of phospholipid surface charge on ion conduction in the K+ channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):279–287. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84154-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. S., Akabas M. H., Zimmerberg J., Finkelstein A. Parameters affecting the fusion of unilamellar phospholipid vesicles with planar bilayer membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Affolter H. Insulation of the conduction pathway of muscle transverse tubule calcium channels from the surface charge of bilayer phospholipid. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):933–953. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):247–289. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., Blasie J. K., Defoor P., Fleischer S., Bick R. J., Van Winkle W. B., Tate C. A., Entman M. L. Phospholipid asymmetry in the isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Oct;234(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. M., Repke D. I., Fudyma G., Shigekawa M. Control of calcium efflux from sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles by external calcium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4210–4214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P. P., Miller C. A K+-selective, three-state channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog leg muscle. J Membr Biol. 1981;61(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01870750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. High selectivity of calcium channels in single dialysed heart cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:253–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1976;30(3):283–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01869673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto H., Racker E. Mechanism of calcium release from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Eisenberg B. R. Sizes of components in frog skeletal muscle measured by methods of stereology. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):31–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Stevens C. F., Tsien R. W., Yellen G. Properties of single calcium channels in cardiac cell culture. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):501–504. doi: 10.1038/297501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Henderson J. S., Meissner G. Single channel and 45Ca2+ flux measurements of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83543-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Seiler S., Chu A., Fleischer S. Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):875–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Colombini M., Finkelstein A. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 28;30(2):99–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01869662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Gonzalez-Serratos H. G., Shuman H., McClellan G., Somlyo A. P. Calcium release and ionic changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of tetanized muscle: an electron-probe study. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):577–594. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Orozco C., Heller P. F., Froehlich J. P. Single calcium channels in native sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7741–7745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanifuji M., Sokabe M., Kasai M. An anion channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum incorporated into planar lipid bilayers: single-channel behavior and conductance properties. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):103–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01871230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Wu E. S., Webb W. W. Enhanced molecular diffusibility in muscle membrane blebs: release of lateral constraints. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):207–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]