Abstract
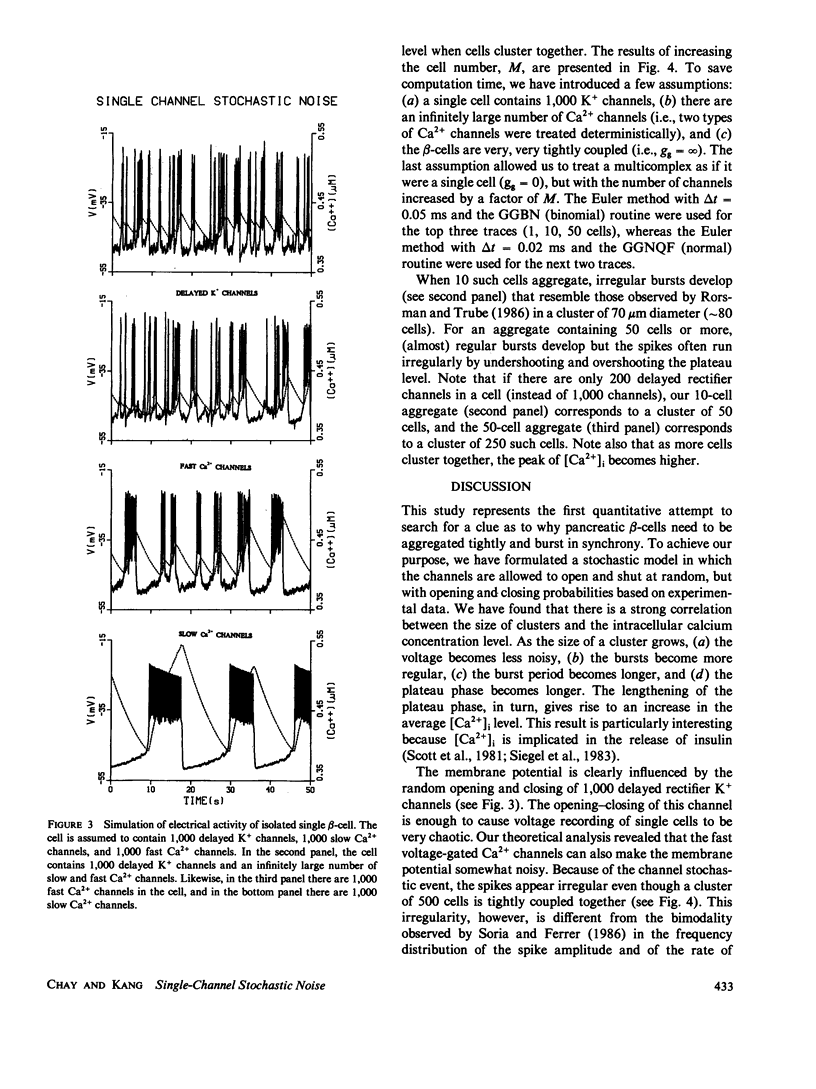
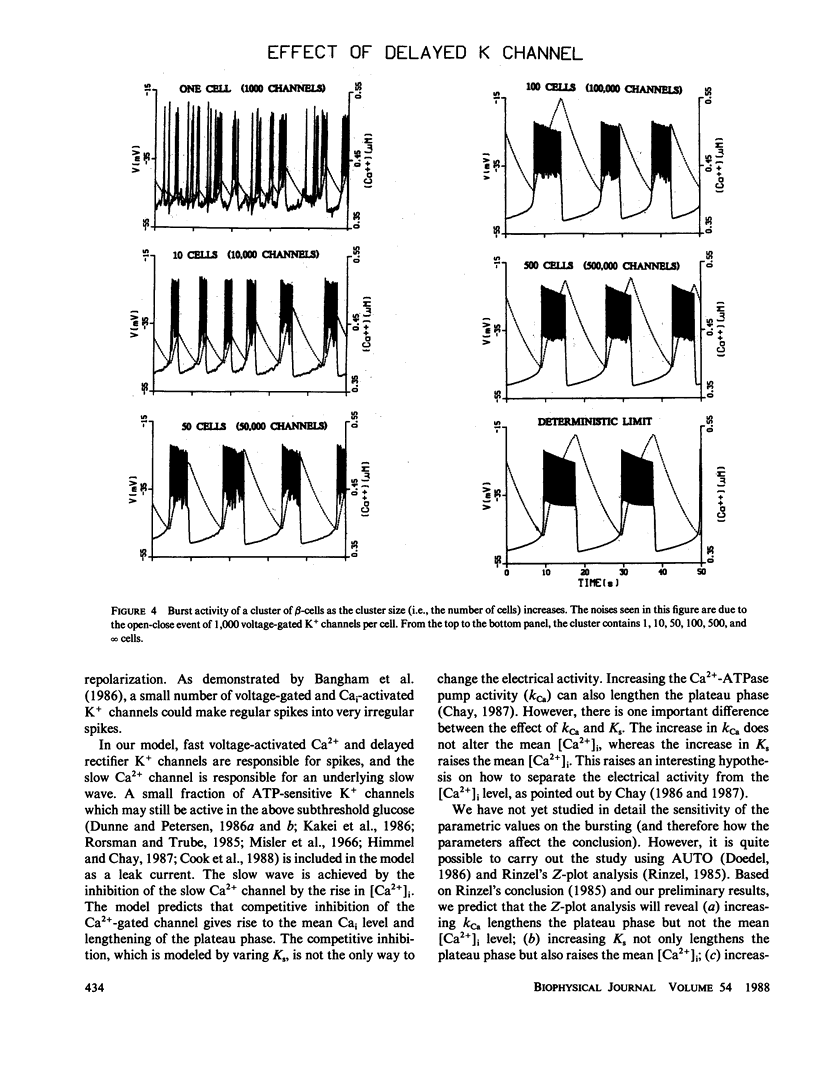
To study why pancreatic beta-cells prefer to burst as a multi-cellular complex, we have formulated a stochastic model for bursting clusters of excitable cells. Our model incorporated a delayed rectifier K+ channel, a fast voltage-gated Ca2+ channel, and a slow Cai-blockable Ca2+ channel. The fraction of ATP-sensitive K+ channels that may still be active in the bursting regime was included in the model as a leak current. We then developed an efficient method for simulating an ionic current component of an excitable cell that contains several thousands of channels opening simultaneously under unclamped voltage. Single channel open-close stochastic events were incorporated into the model by use of binomially distributed random numbers. Our simulations revealed that in an isolated beta-cell [Ca2+]i oscillates with a small amplitude about a low [Ca2+]i. However, in a large cluster of tightly coupled cells, stable bursts develop, and [Ca2+]i oscillates with a larger amplitude about a higher [Ca2+]i. This may explain why single beta-cells do not burst and also do not release insulin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham J. A., Smith P. A., Croghan P. C. Modelling the beta-cell electrical activity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;211:265–278. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5314-0_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Keizer J. Minimal model for membrane oscillations in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biophys J. 1983 May;42(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84384-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. On the effect of the intracellular calcium-sensitive K+ channel in the bursting pancreatic beta-cell. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):765–777. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83517-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. The effect of inactivation of calcium channels by intracellular Ca2+ ions in the bursting pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Biophys. 1987 Dec;11:77–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02797114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L. Electrical pacemaker mechanisms of pancreatic islet cells. Fed Proc. 1984 Jun;43(9):2368–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Ikeuchi M., Fujimoto W. Y. Lowering of pHi inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):269–271. doi: 10.1038/311269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Satin L. S., Ashford M. L., Hales C. N. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Spare-channel hypothesis. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):495–498. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. GTP and GDP activation of K+ channels that can be inhibited by ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):564–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00657518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Intracellular ADP activates K+ channels that are inhibited by ATP in an insulin-secreting cell line. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddlestone G. T., Beigelman P. M. Pancreatic beta-cell electrical activity: the role of anions and the control of pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C188–C197. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddlestone G. T., Gonçalves A., Bangham J. A., Rojas E. Electrical coupling between cells in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01871095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. Voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmel D. M., Chay T. R. Theoretical studies on the electrical activity of pancreatic beta-cells as a function of glucose. Biophys J. 1987 Jan;51(1):89–107. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83314-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Kelly R. P., Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The ATP-sensitivity of K+ channels in rat pancreatic B-cells is modulated by ADP. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Zucker R. S. Calcium-induced inactivation of calcium current causes the inter-burst hyperpolarization of Aplysia bursting neurones. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:131–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Atwater I., Gonçalves A., Bangham A., Orci L., Rojas E. The topography of electrical synchrony among beta-cells in the mouse islet of Langerhans. Q J Exp Physiol. 1984 Oct;69(4):719–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S. Role of pH as a transduction device in triggering electrical and secretory responses in islet B cells. Fed Proc. 1984 Jun;43(9):2379–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Calcium action potentials and potassium permeability activation in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):C124–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.239.3.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Evidence for two calcium currents in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):401–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00587719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Voltage-gated Ca2+ current in pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Aug;404(4):385–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00585354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. M., Atwater I., Rojas E. A method for the simultaneous measurement of insulin release and B cell membrane potential in single mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1981 Nov;21(5):470–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00257788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Janjic D., Ribes G., Sharp G. W. Involvement of Ca2+ in the impaired glucose-induced insulin release from islets cultured at low glucose. Diabetes. 1983 Nov;32(11):993–1000. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.11.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria B., Ferrer R. Graded spike electrogenesis in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;211:235–246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5314-0_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]