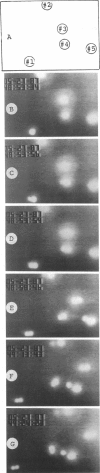
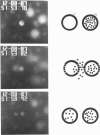
Abstract
The mechanism of membrane fusion was studied by using human erythrocyte ghosts held in close contact by alternating current-induced dielectrophoresis and inducing fusion with a single electric field pulse. Individual fusion events were followed visually using either 1,1'-dihexadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindo carbocyanine perchlorate as a membrane-mixing label or 10-kD fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran as a contents-mixing label. However, over a range of variables, the number of contents-mixing events usually considerably exceeded the number of membrane-mixing events, although the discrepancy was less at higher ionic strength. However, when the dielectrophoretic force holding the membranes in contact was turned off after the pulse, Brownian motion caused some of the groups of ghosts in which contents mixing occurred to eventually separate from one another, showing that they could not represent fusion events. Separate experiments showed, conversely, that fusion did occur in the groups that did not separate after the dielectrophoresis was turned off.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balasubramanian A., McLaughlin S. Electro-osmosis at the surface of phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 8;685(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge L. J., Almers W. Final steps in exocytosis observed in a cell with giant secretory granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Jain R. K. Membrane stability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 4;779(4):437–468. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Neher E., Gomperts B. D. Capacitance measurements reveal stepwise fusion events in degranulating mast cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):453–455. doi: 10.1038/312453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Gaining access to the cytosol: the technique and some applications of electropermeabilization. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2340497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Steck T. L. A description of the holes in human erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11651–11659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Mimicry and mechanism in phospholipid models of membrane fusion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:201–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol D. P., Decker G. L., Lennarz W. J., Tsong T. Y., Teissie J. Induction of calcium-dependent, localized cortical granule breakdown in sea-urchin eggs by voltage pulsation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):346–355. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. A long-lived fusogenic state is induced in erythrocyte ghosts by electric pulses. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. Characterization of electric field-induced fusion in erythrocyte ghost membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1989–1996. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E., Lieber M. R. Electropore diameters, lifetimes, numbers, and locations in individual erythrocyte ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 15;205(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80893-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. The long-lived fusogenic state induced in erythrocyte ghosts by electric pulses is not laterally mobile. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1015–1020. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83294-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teissie J., Rols M. P. Fusion of mammalian cells in culture is obtained by creating the contact between cells after their electropermeabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y. Voltage modulation of membrane permeability and energy utilization in cells. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):487–505. doi: 10.1007/BF01120693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Curran M., Cohen F. S., Brodwick M. Simultaneous electrical and optical measurements show that membrane fusion precedes secretory granule swelling during exocytosis of beige mouse mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U. Electric field-mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):227–277. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]