Abstract
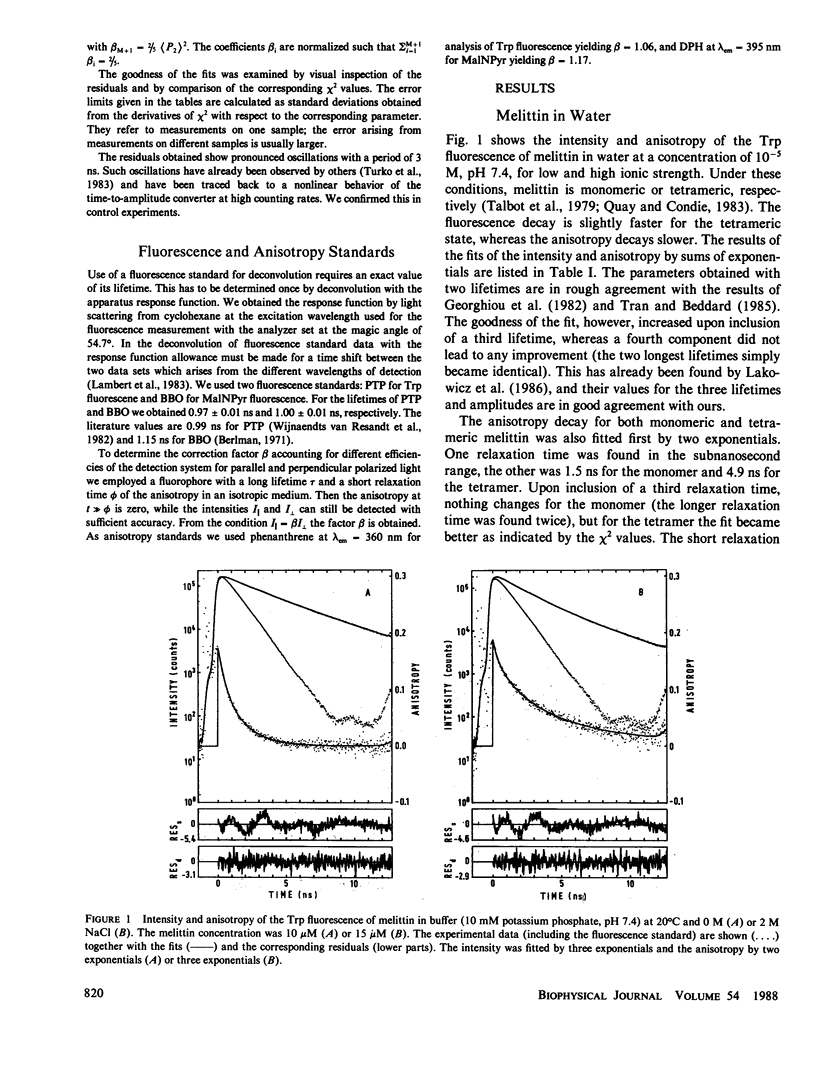
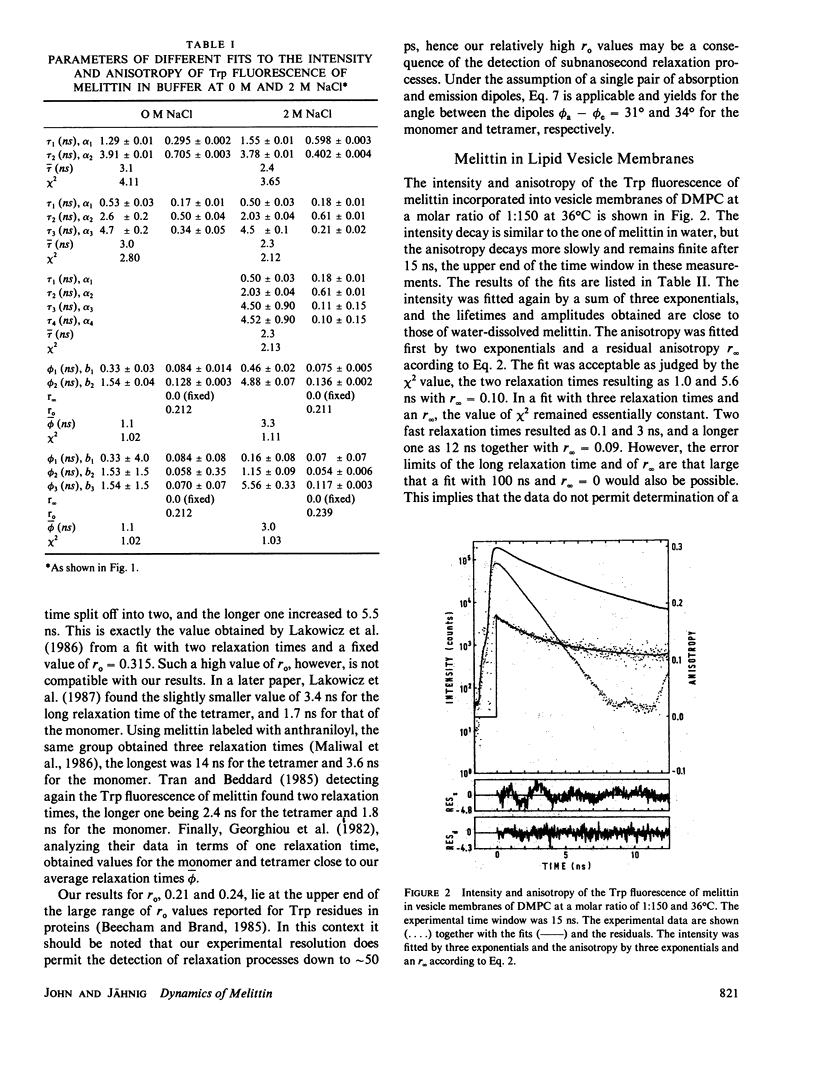
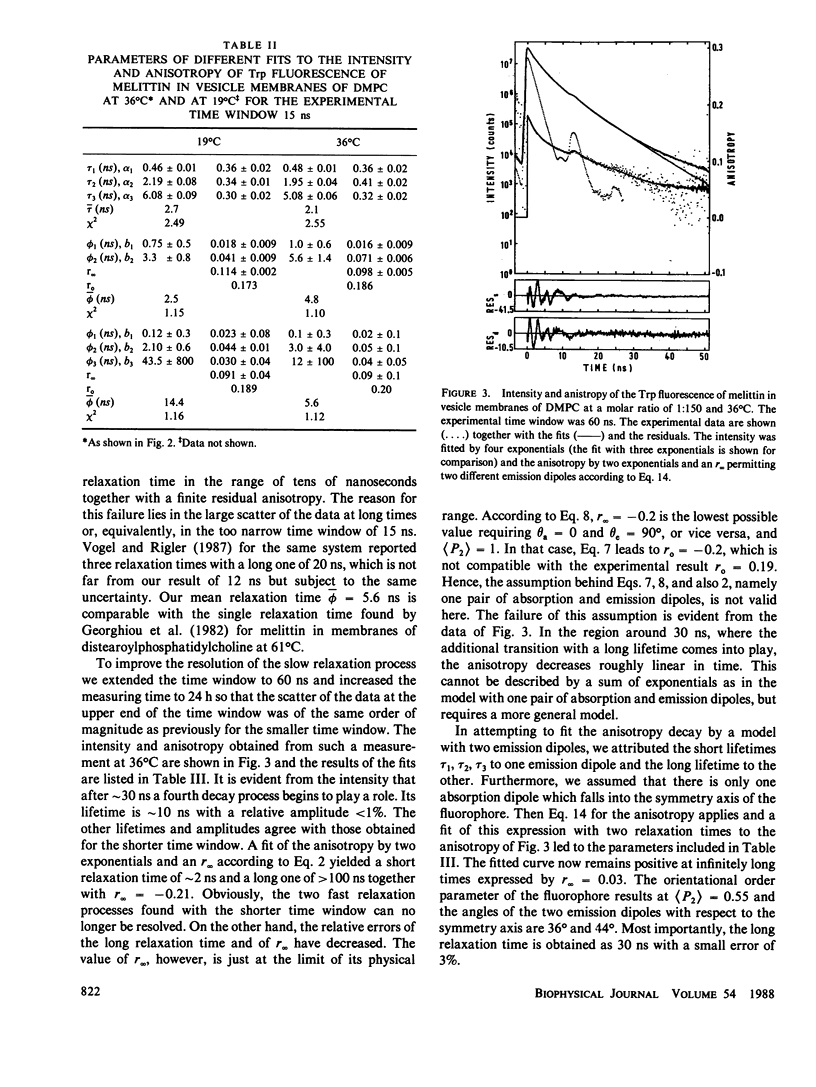
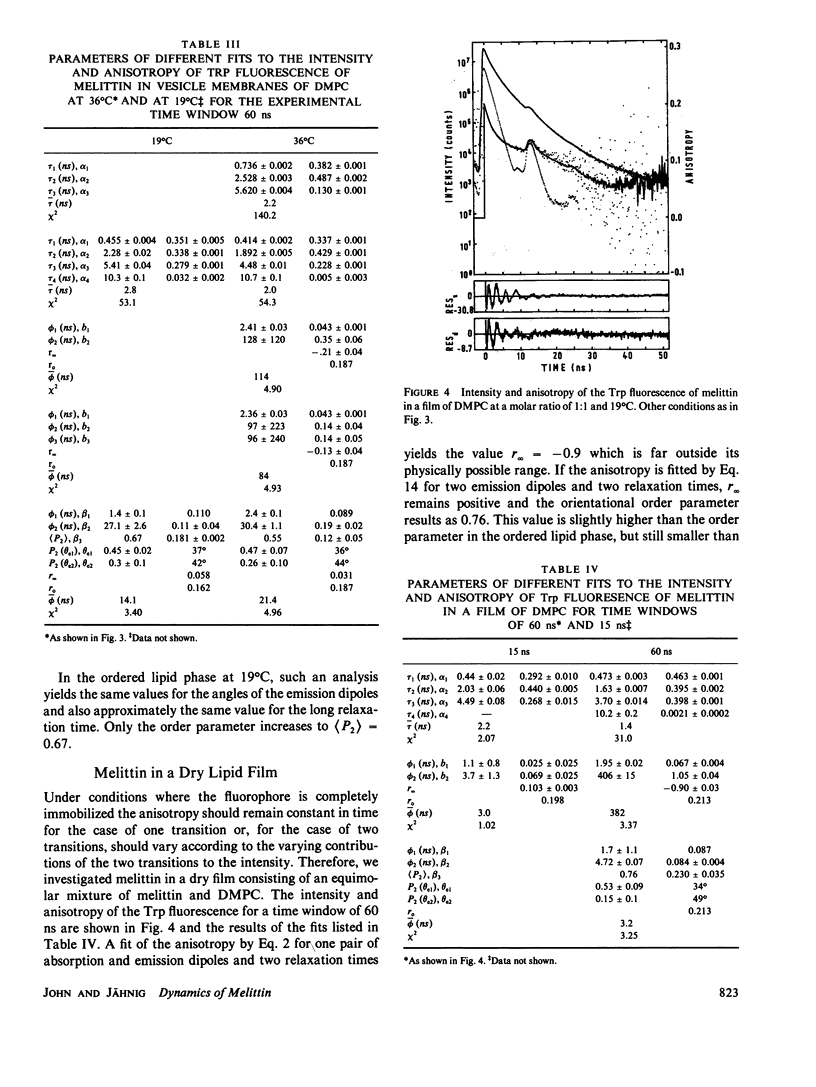
Fluorescence anisotropy decay measurements were performed on melittin in water and in membranes of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. The fluorescence of the single tryptophan residue of melittin and of a pyrene label attached to melittin was detected. In water, the slowest relaxation process in the anisotropy decay occurs with a relaxation time of 1.5 or 5.5 ns in the case of low or high ionic strength and corresponds to rotational diffusion of monomeric or tetrameric melittin. Superimposed on this slow process are fast processes in the subnanosecond range reflecting fluctuations of the fluorophores relative to the polypeptide backbone. In membranes, the fast relaxation processes are not much altered. A slow process with a relaxation time of 35 ns is observed and assigned to orientational fluctuations of the melittin helices in membranes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beechem J. M., Brand L. Time-resolved fluorescence of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georghiou S., Thompson M., Mukhopadhyay A. K. Melittin-phospholipid interaction studied by employing the single tryptophan residue as an intrinsic fluorescent probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90355-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Methfessel C., Wilmsen H. U., Katz E., Jung G., Boheim G. Melittin and a chemically modified trichotoxin form alamethicin-type multi-state pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 5;727(1):108–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermetter A., Lakowicz J. R. The aggregation state of mellitin in lipid bilayers. An energy transfer study. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8243–8248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiye T., Karplus M. Fluorescence depolarization of tryptophan residues in proteins: a molecular dynamics study. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2884–2893. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N., Van Renswoude J., Pincus M., Blumenthal R. Voltage-dependent trans-bilayer orientation of melittin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2469–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H., Gryczynski I., Joshi N., Johnson M. L. Enhanced resolution of fluorescence anisotropy decays by simultaneous analysis of progressively quenched samples. Applications to anisotropic rotations and to protein dynamics. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):755–768. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83402-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Laczko G., Gryczynski I., Cherek H. Measurement of subnanosecond anisotropy decays of protein fluorescence using frequency-domain fluorometry. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2240–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavialle F., Adams R. G., Levin I. W. Infrared spectroscopic study of the secondary structure of melittin in water, 2-chloroethanol, and phospholipid bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliwal B. P., Hermetter A., Lakowicz J. R. A study of protein dynamics from anisotropy decays obtained by variable frequency phase-modulation fluorometry: internal motions of N-methylanthraniloyl melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 26;873(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Cherry R. J. Lateral and rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid bilayers: experimental test of the Saffman-Delbrück equations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quay S. C., Condie C. C. Conformational studies of aqueous melittin: thermodynamic parameters of the monomer-tetramer self-association reaction. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):695–700. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. C., Dufourcq J., de Bony J., Faucon J. F., Lussan C. Conformational change and self association of monomeric melittin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. C., Faucon J. F., Dufourcq J. Different states of self-association of melittin in phospholipid bilayers. A resonance energy transfer approach. Eur Biophys J. 1987;15(3):147–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00263679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Weissman L., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin's lytic and surface activities. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):353–361. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84683-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Levy J. J., Caporale L. H., Rosenblatt M., Tosteson D. C. Solid-phase synthesis of melittin: purification and functional characterization. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6627–6631. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. The sting. Melittin forms channels in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84719-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran C. D., Beddard G. S. Studies of the fluorescence from tryptophan in melittin. Eur Biophys J. 1985;13(1):59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00266310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. Comparison of the conformation and orientation of alamethicin and melittin in lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4562–4572. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F., Hoffmann V., Stümpel J. The orientation of melittin in lipid membranes. A polarized infrared spectroscopy study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F. The structure of melittin in membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Oct;50(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83497-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Wright J. K., Jähnig F. The structure of the lactose permease derived from Raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3625–3631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltman J. K., Szaro R. P., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Dowben R. M., Bunting J. R., Cathou B. E. N-(3-pyrene)maleimide: a long lifetime fluorescent sulfhydryl reagent. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3173–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer W., Pottel H., Herreman W., Ameloot M., Hendrickx H., Schröder H. Effect of orientational order on the decay of the fluorescence anisotropy in membrane suspensions. A new approximate solution of the rotational diffusion equation. Biophys J. 1984 Oct;46(4):515–523. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84049-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


