Abstract
Binding of the fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye fura-2 by intracellular constituents has been investigated by steady-state optical measurements. Fura-2's (a) fluorescence intensity, (b) fluorescence emission anisotropy, (c) fluorescence emission spectrum, and (d) absorbance spectra were measured in glass capillary tubes containing solutions of purified myoplasmic proteins; properties b and c were also measured in frog skeletal muscle fibers microinjected with fura-2. The results indicate that more than half, and possibly as much as 85%, of fura-2 molecules in myoplasm are in a protein-bound form, and that the binding changes many properties of the dye. For example, in vitro characterization of the Ca2+-dye reaction indicates that when fura-2 is bound to aldolase (a large and abundant myoplasmic protein), the dissociation constant of the dye for Ca2+ is three- to fourfold larger than that measured in the absence of protein. The problems raised by intracellular binding of fura-2 to cytoplasmic proteins may well apply to cells other than skeletal muscle fibers.
Full text
PDF






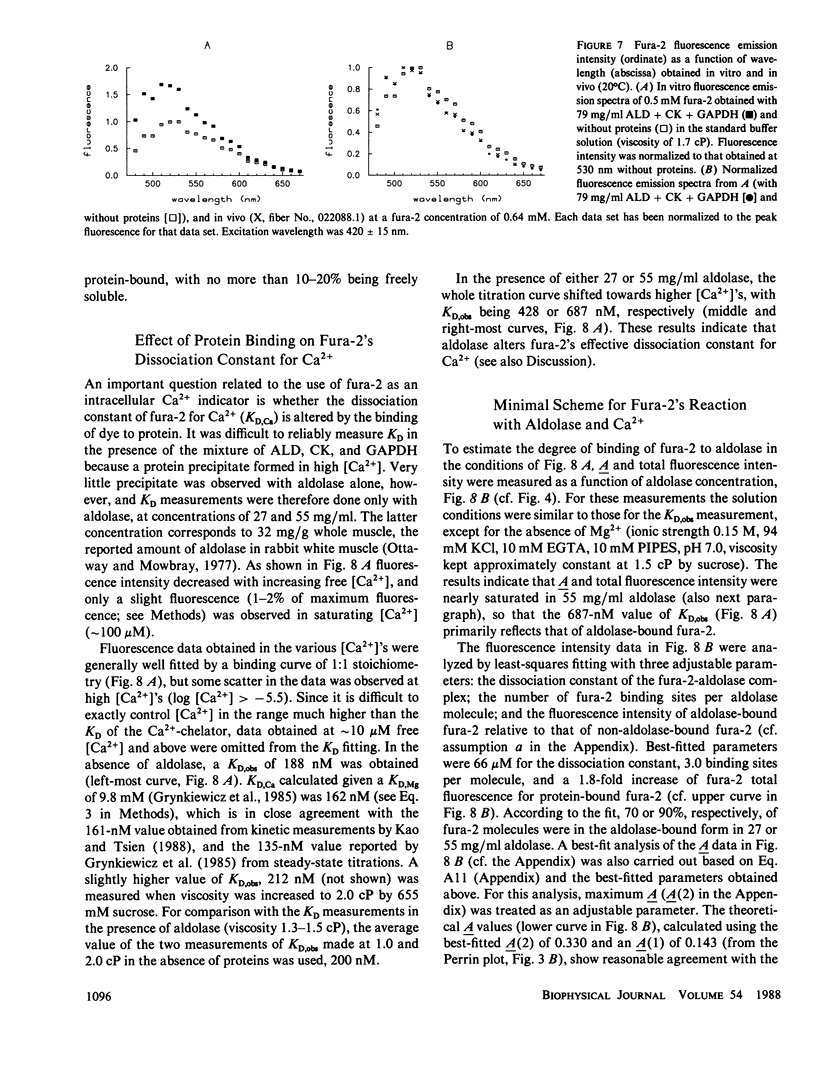

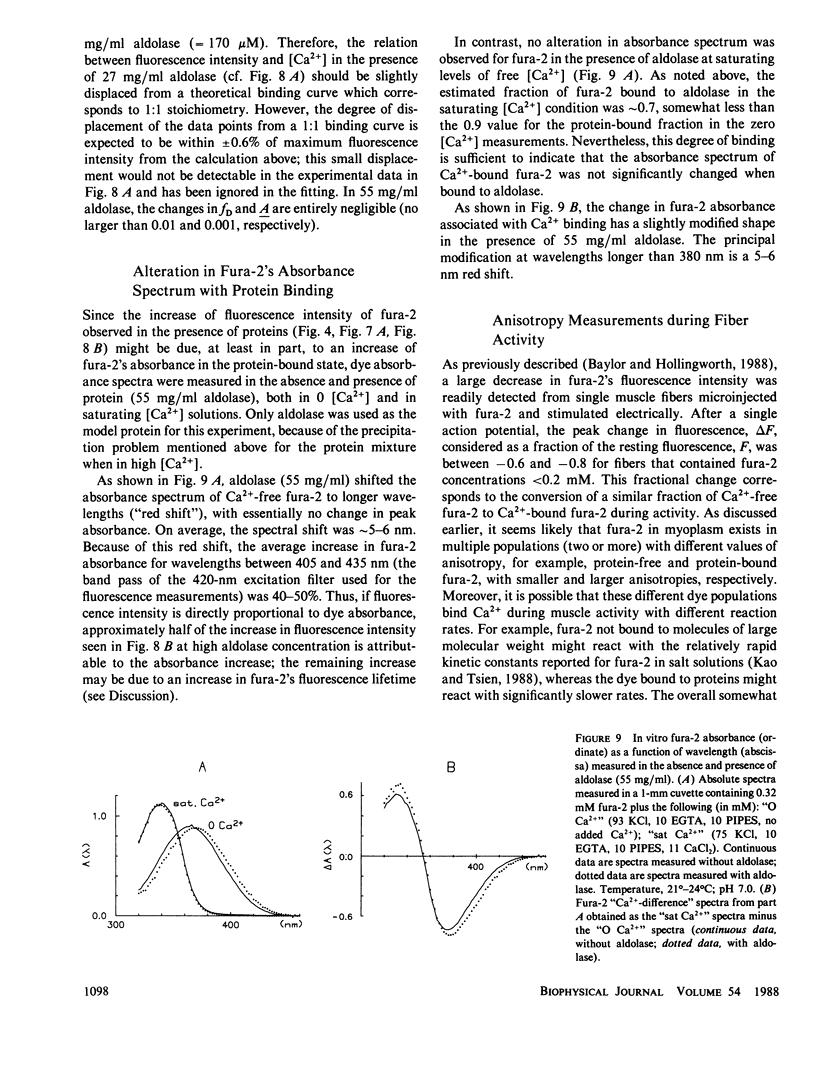






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aogaichi T., Evans J., Gabriel J., Plaut G. W. The effects of calcium and lanthanide ions on the activity of bovine heart nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of aldolase and triosephosphate dehydrogenase to F-actin and modification of catalytic properties of aldolase. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):360–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of glycolytic enzymes to structure proteins of the muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(2):163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Dichroic components of Arsenazo III and dichlorophosphonazo III signals in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:179–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S., Hui C. S., Quinta-Ferreira M. E. Properties of the metallochromic dyes Arsenazo III, Antipyrylazo III and Azo1 in frog skeletal muscle fibres at rest. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:89–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Photobleaching of fura-2 and its effect on determination of calcium concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C613–C618. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler T. J., Schibeci A., Martonosi A. The binding of arsenazo III to cell components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN R. F., BOWMAN R. L. FLUORESCENCE POLARIZATION: MEASUREMENT WITH ULTRAVIOLET-POLARIZING FILTERS IN A SPECTROPHOTOFLUOROMETER. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):729–732. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Boron W. F. Intracellular calibration of a pH-sensitive dye in isolated, perfused salamander proximal tubules. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Dec;86(6):765–794. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.6.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E., Thulin E., Boffi A., Forsén S., Brunori M. Evidence for the interaction between the calcium indicator 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid and calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16306–16308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. On the composition of the cytosol of relaxed skeletal muscle of the frog. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):C591–C604. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.5.C591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Aldrich R. W., Baylor S. M. In vitro calibration of the equilibrium reactions of the metallochromic indicator dye antipyrylazo III with calcium. Biophys J. 1987 Mar;51(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83360-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuti K. Mechanism of contracture on cooling of caffeine-treated frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:131–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Ca2+ binding kinetics of fura-2 and azo-1 from temperature-jump relaxation measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):635–639. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83142-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Szucs G., Schneider M. F. Simultaneous recording of calcium transients in skeletal muscle using high- and low-affinity calcium indicators. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):971–988. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83178-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronman M. J., Bratcher S. C. An experimental artifact in the use of chelating metal ion buffers. Binding of chelators to bovine alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5707–5709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENCE D. J. R. A study of the adsorption of dyes on bovine serum albumin by the method of polarization of fluorescence. Biochem J. 1952 May;51(2):168–180. doi: 10.1042/bj0510168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Boyarsky G., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing tetramethylmurexide. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):145–176. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):83–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Comparison of arsenazo III optical signals in intact and cut frog twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):41–81. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway J. H., Mowbray J. The role of compartmentation in the control of glycolysis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1977;12:107–208. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152812-6.50010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parello J., Reimarsson P., Thulin E., Lindman B. Na+ binding to parvalbumins studied by 23Na NMR. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODKEY F. L. The binding of phenol red by serum and by bovine serum albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Jul;94:38–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Wendt I. R., Forrest Q. G. Non-uniform ion distributions and electrical potentials in sarcoplasmic regions of skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):690–692. doi: 10.1038/289690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


