Abstract
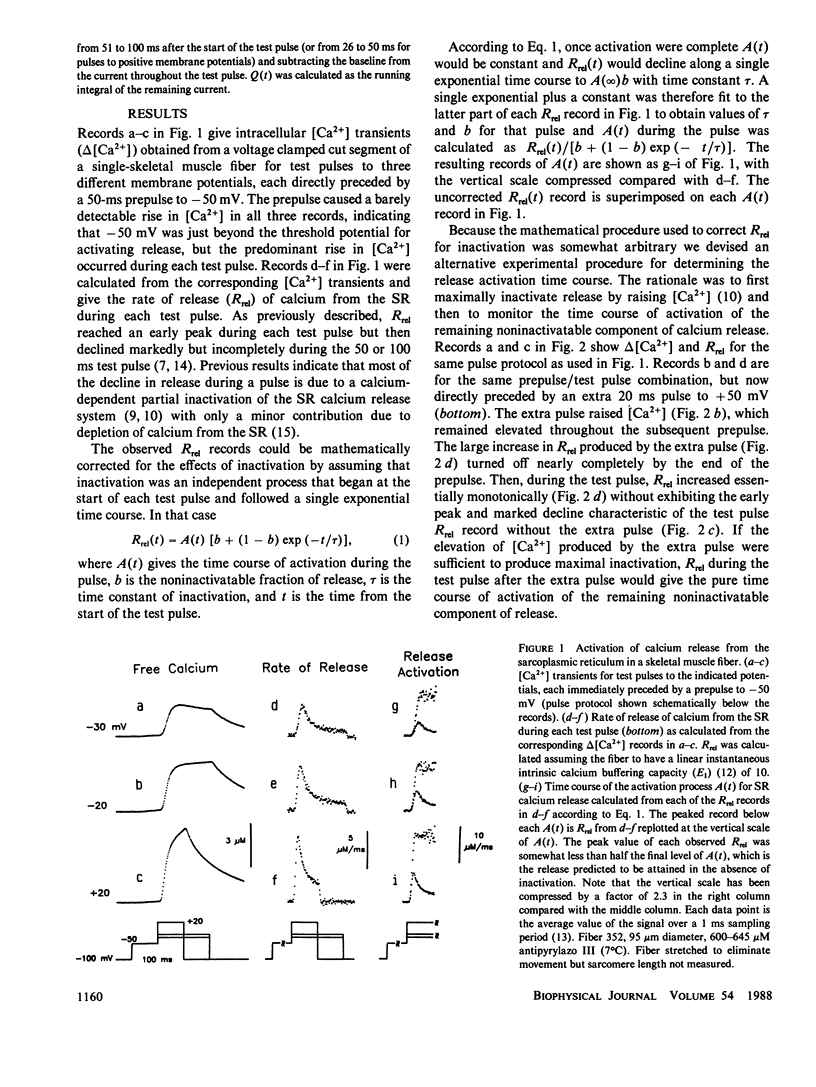
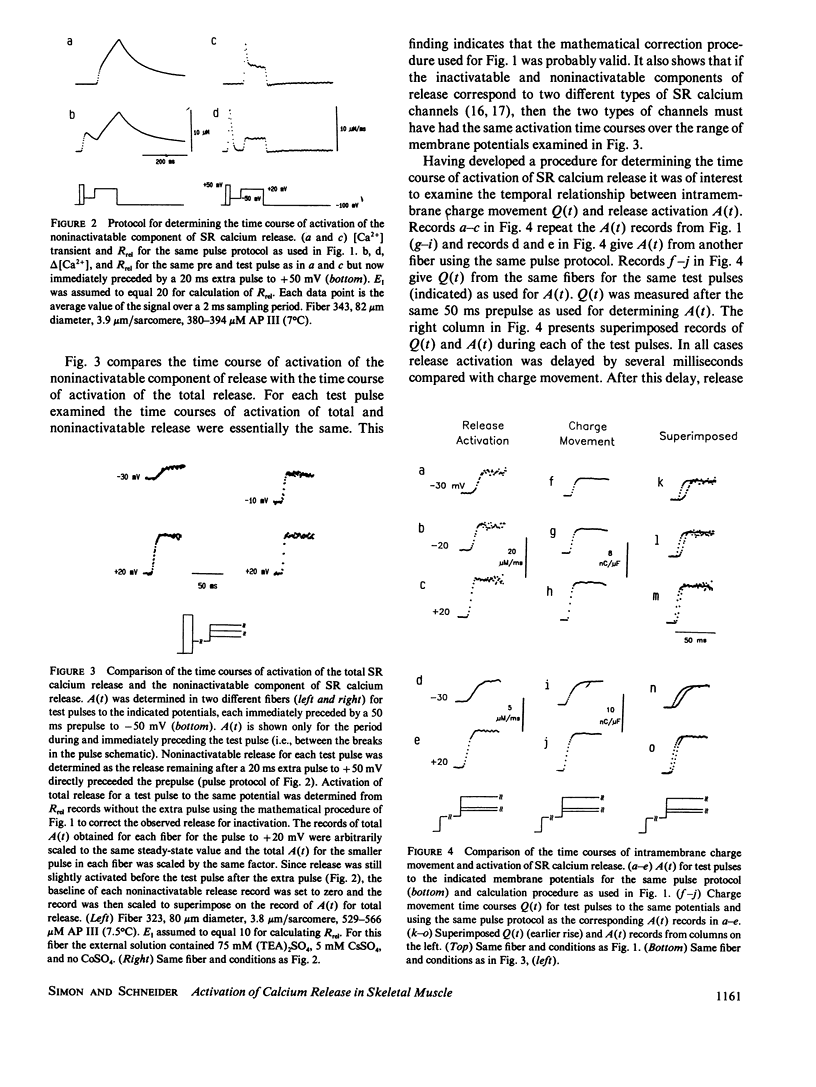
Myoplasmic free calcium transients were measured with antipyrylazo III in voltage clamped segments of frog skeletal muscle fibers and were used to calculate the rate of release (Rrel) of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Intramembrane charge movement was measured for the same pulses in the same fibers. During a depolarizing pulse Rrel rose to an early peak and then decayed relatively rapidly but incompletely due to calcium-dependent inactivation (Schneider M.F., and B.J. Simon. 1988. J. Physiol. (Lond.). 405:727-745). Two approaches were used to determine release activation independent of the effects of inactivation: (a) a mathematical correction based on the assumption that inactivation was a process occurring in parallel with and independently of activation; (b) an experimental procedure in which release was maximally inactivated by a large short prepulse and then the remaining noninactivatable component of release was monitored during a subsequent test pulse. Both procedures gave the same time course of activation of release. Release activation paralleled the time course of intramembrane charge movement but was delayed by a few milliseconds.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Calmodulin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:227–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. A general procedure for determining the rate of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):849–863. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83413-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Time course of calcium release and removal in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):637–641. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84203-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:481–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J. Inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:727–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Depletion of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum during calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:167–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single-channel calcium and barium currents of large and small conductance from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):921–928. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83533-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Orozco C., Heller P. F., Froehlich J. P. Single calcium channels in native sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7741–7745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


