Abstract
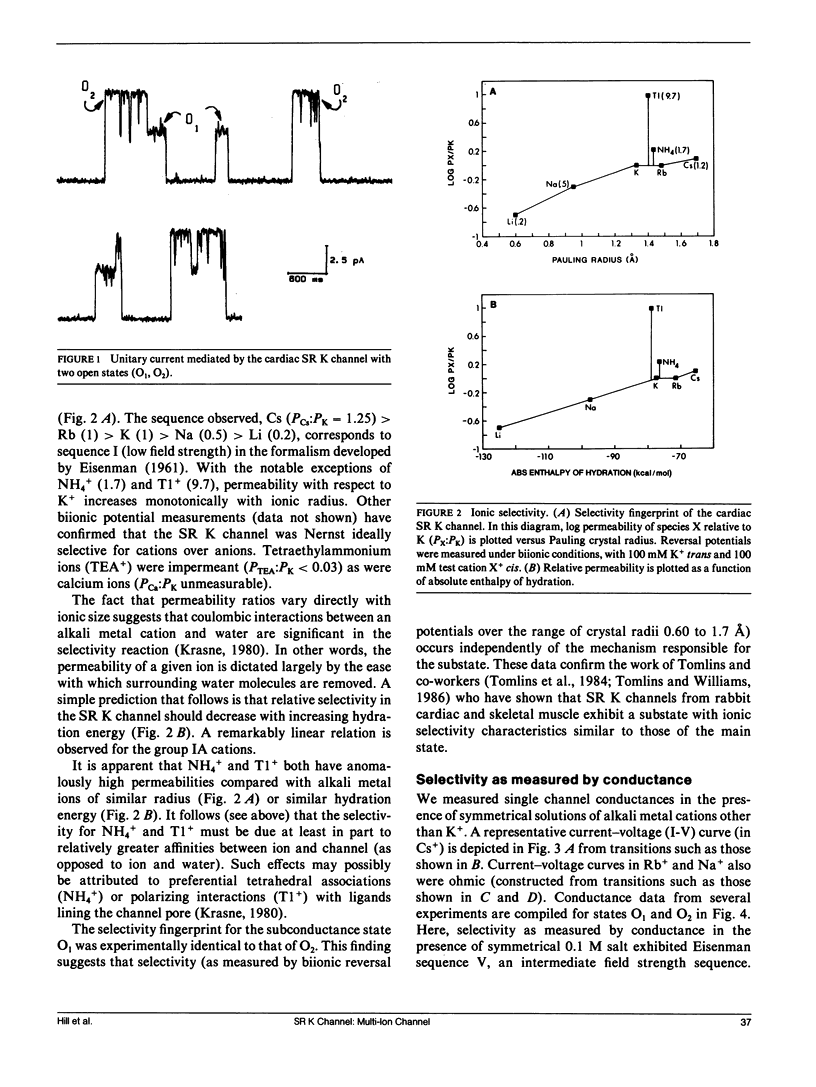
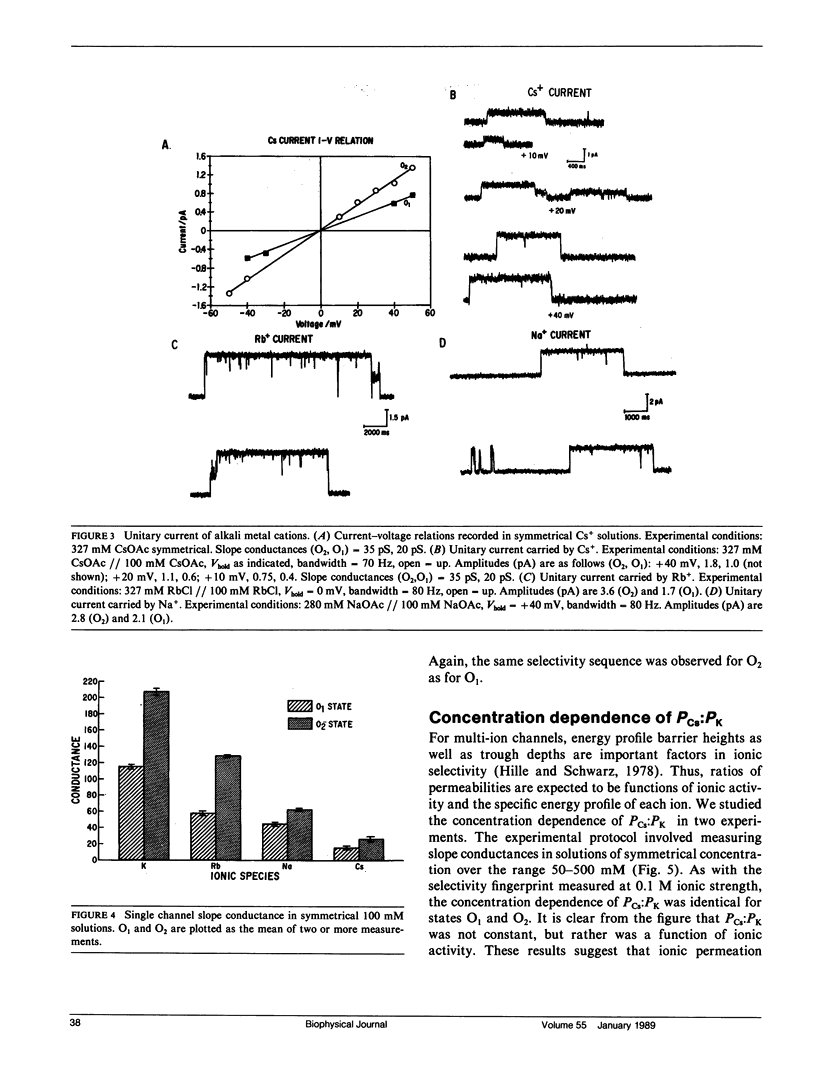
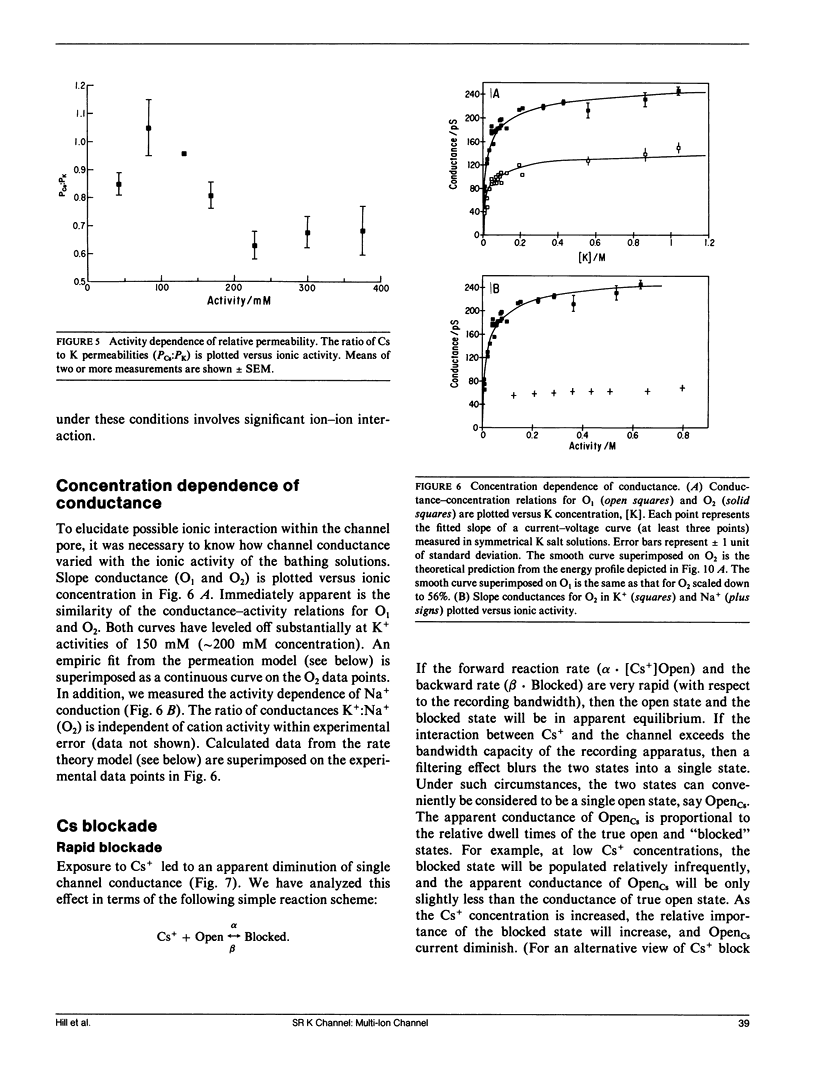
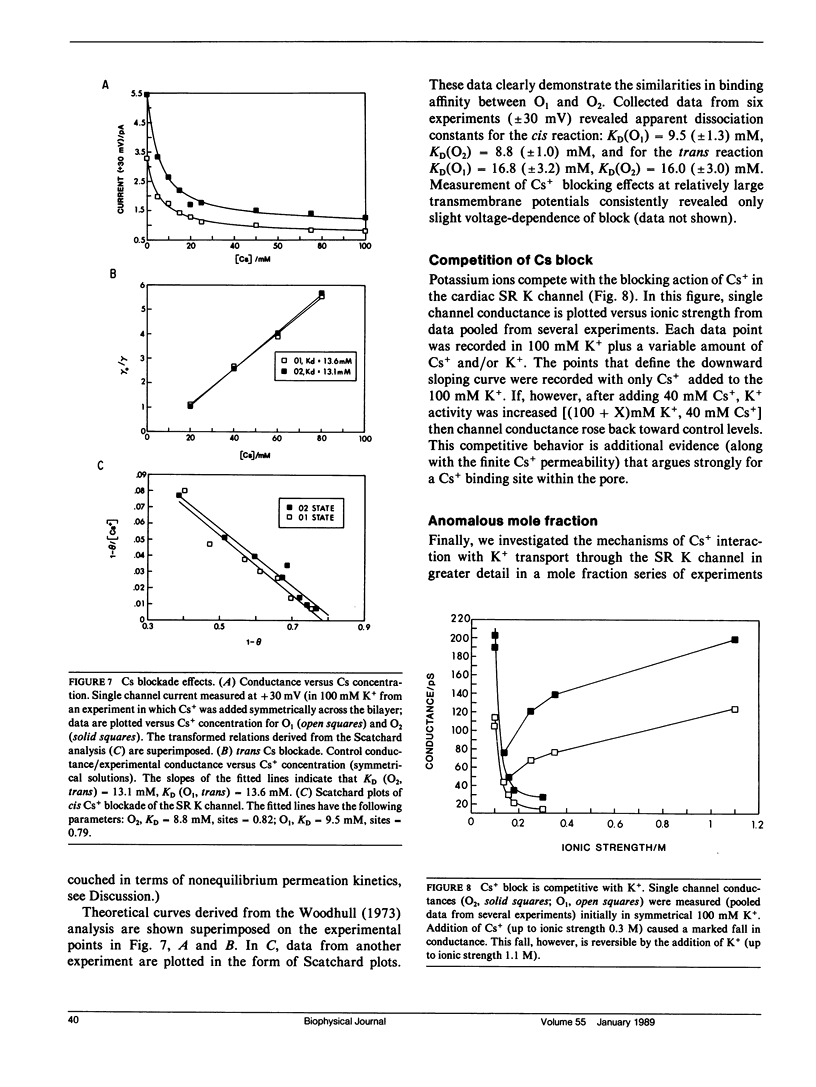
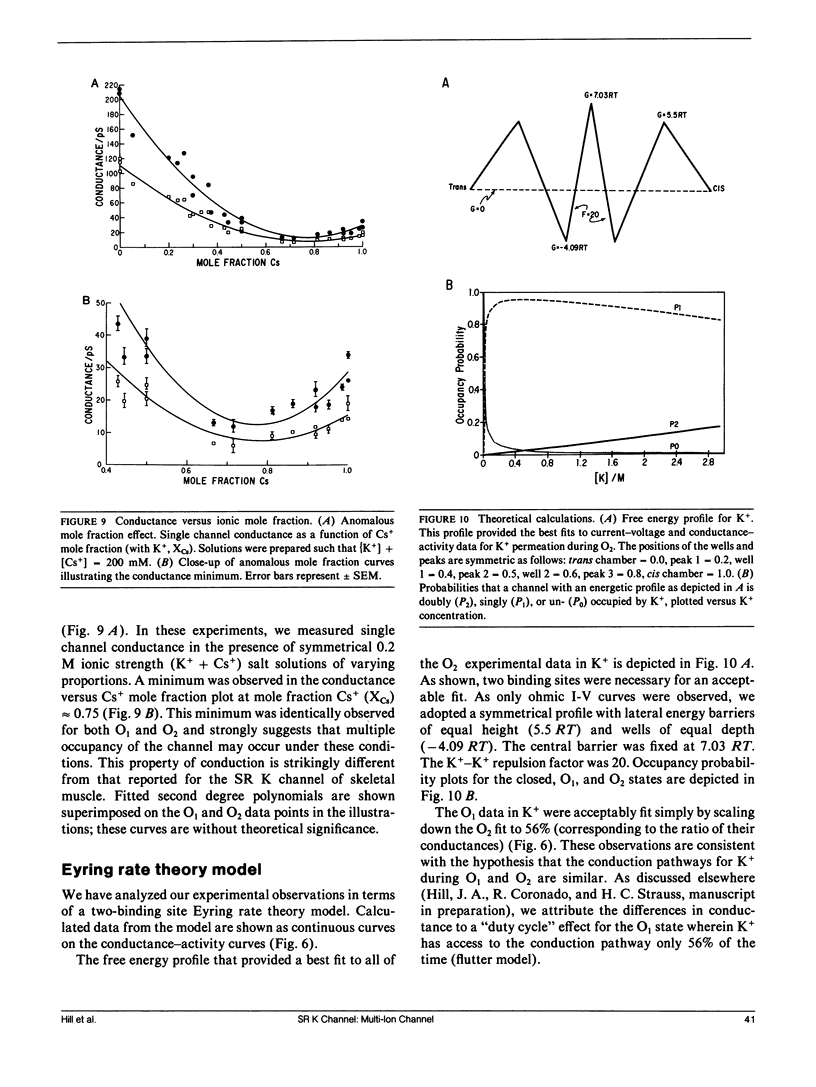
We have characterized mechanisms of ionic permeation in the K channel of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR K channel). Ionic selectivity, as measured by relative permeabilities, followed Eisenman sequence l, a low field strength sequence. Slope conductance measured in symmetrical solutions across the bilayer followed Eisenman sequence V. In all cases, the selectivity characteristics of the prominent subconductance state (O1) were similar to those of the main-state (O2). Further, our studies have revealed that this channel differs in three significant ways from the highly characterized SR K channel of skeletal muscle. First, the ratio of permeabilities Cs+ to K+ was a complex function of ion concentration. Second, the concentration dependence of conductance was not well described by the Michaelis-Menten formalism. Instead, we modeled the observed relations using a more general approach based on classical rate theory. Third, mole fraction experiments (Cs+ with K+) demonstrated a prominent anomalous effect. Certain of our Cs+ data required the Eyring rate theory approach for adequate interpretation. We adopted a symmetrical energy profile incorporating ion-ion interaction and thereby accounted for much of the data. We conclude that the canine cardiac SR K channel is significantly different from that of skeletal muscle, and it may accommodate more than one ion at a time.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader H., Sen A. K. (K+)-dependent acyl phosphatase as part of the (na+ + K+)-dependent ATPase of cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T. B., Cahalan M. D. Sodium channel permeation in squid axons. I: Reversal potential experiments. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:217–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé J., Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;46(3):185–239. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Miller C. Conduction and block by organic cations in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum incorporated into planar phospholipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):529–547. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Miller C. Decamethonium and hexamethonium block K+ channels of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):495–497. doi: 10.1038/288495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Rosenberg R. L., Miller C. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Oct;76(4):425–446. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S., Yellen G., Miller C. The K+ channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. A new look at Cs+ block. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):477–484. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83803-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Ciani S. M., Szabo G. Some theoretically expected and experimentally observed properties of lipid bilayer membranes containing neutral molecular carriers of ions. Fed Proc. 1968 Nov-Dec;27(6):1289–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Wells J. B. Sodium ions as blocking agents and charge carriers in the potassium channel of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):707–724. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. A., Montgomery R. A., Williams A. J. Asymmetric block of a monovalent cation-selective channel of rabbit cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum by succinyl choline. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(1):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01871216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in sodium channels. A four-barrier model. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Nov;66(5):535–560. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.5.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R. Rapid preparation of canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by sucrose flotation. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:85–91. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. How pore mouth charge distributions alter the permeability of transmembrane ionic channels. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83336-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasne S., Eisenman G. Influence of molecular variations of ionophore and lipid on the selective ion permeability of membranes: I. Tetranactin and the methylation of nonactin-type carriers. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 25;30(1):1–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01869658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P. P., Miller C. A K+-selective, three-state channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog leg muscle. J Membr Biol. 1981;61(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01870750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):321–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley D., Meissner G. Evidence for a K+, Na+ permeable channel in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1978 Dec 15;44(2):159–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01976037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., McKinley D. Permeability of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles to K+, Na+, H+, and Cl-. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7704–7711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1976;30(3):283–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01869673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Williams A. J., Montgomery R. A. The characterization of a monovalent cation-selective channel of mammalian cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(2):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01868775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Williams A. J. Solubilisation and reconstitution of the rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel into liposomes suitable for patch clamp studies. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):341–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00585312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



