Abstract
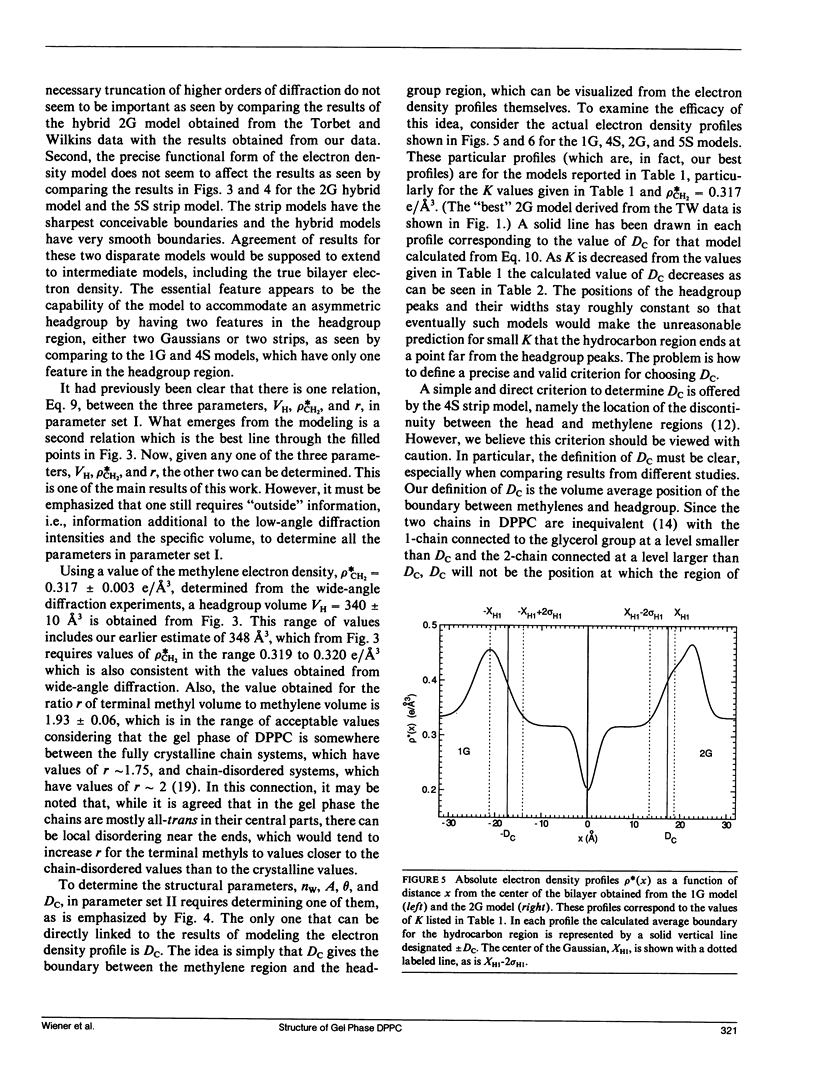
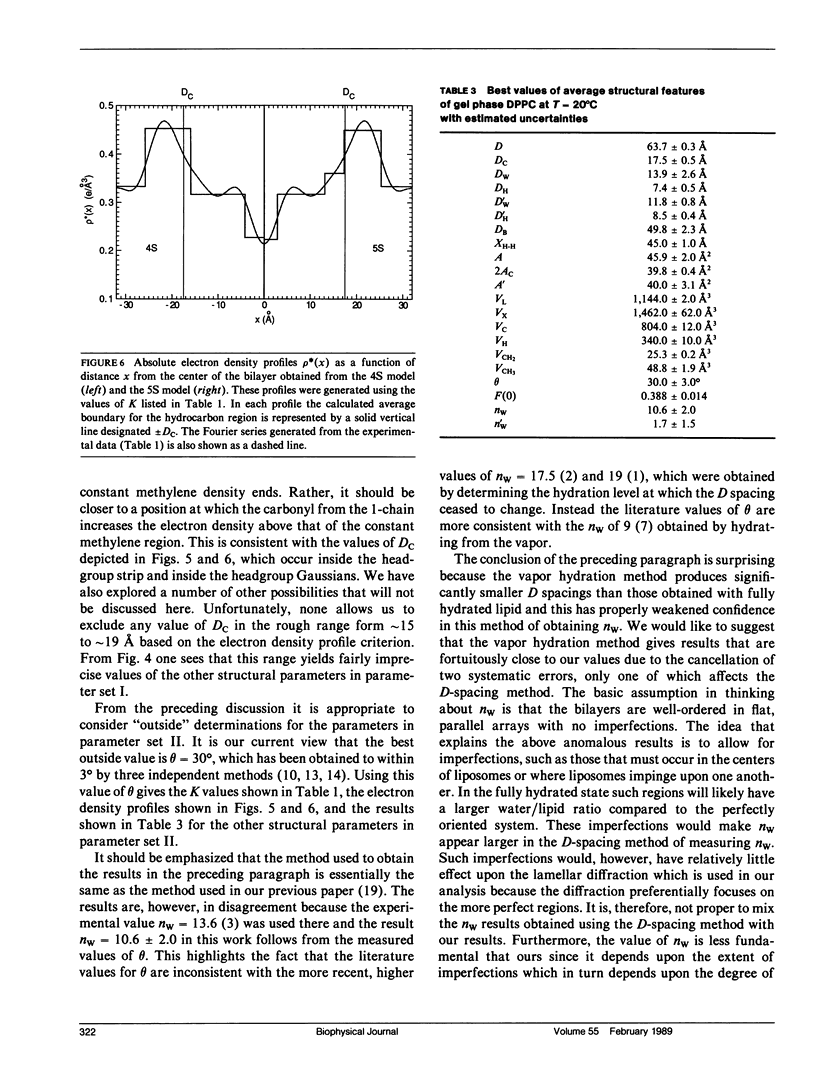
X-ray diffraction intensities for lamellar repeats, h = 1 to 7, and wide-angle x-ray scattering were measured for the gel phase of fully hydrated dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. A hybrid model, which represents the electron density along the lamellar repeat direction as a continuous function composed of constant strips and superimposed Gaussians, is defined. The data were used to determine the best parameters in hybrid models and also in the older strip models. The most successful results were obtained when the density of the methylene region was constrained to the value obtained from the wide-angle scattering. Further analysis utilized the lipid volume obtained from absolute specific volume measurements. Together with the fundamental relations derived in the previous paper, the electron density modeling yielded the headgroup volume (340 +/- 10 A3) and the methylene volume (25.3 +/- 0.2A3). The results were in agreement whether the hybrid model or the strip model was used and whether our data or the data of Torbet and Wilkins were used. Additional structural results, such as the area (45.9 +/- 2.0 A2) and the number of waters of hydration per lipid (10.6 +/- 2.0), required one additional piece of information, which we took to be the tilt angle theta, which is 30 +/- 3 degrees from other experiments in the literature. Absolute electron density profiles, which clearly indicate two features in the headgroup region, are presented. The analysis yielded an accurate value of F(0), which contributes to the continuous scattering transform F(X), which is also given.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig A., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on selectively deuterated phospholipid bilayers. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):182–184. doi: 10.1038/271182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrasiak G. L., Hasty J. H. The hydration of phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jan 23;337(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. I., White S. H. Determining bilayer hydrocarbon thickness from neutron diffraction measurements using strip-function models. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83733-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., McAlister M., Fuller N., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Interactions between neutral phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):657–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Area per molecule and distribution of water in fully hydrated dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4948–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Hydration force and bilayer deformation: a reevaluation. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4058–4066. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui T. X-ray diffraction studies of membranes. Adv Biophys. 1978;10:97–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Relations for lipid bilayers. Connection of electron density profiles to other structural quantities. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):309–313. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82806-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Structure of fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torbet J., Wilkins M. H. X-ray diffraction studies of lecithin bilayers. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Tristram-Nagle S., Wilkinson D. A., Campbell L. E., Nagle J. F. Specific volumes of lipids in fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 18;938(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R., Blaurock A. E. A structural analysis of nerve myelin. Biophys J. 1969 Jul;9(7):970–990. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86431-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R., King G. I., McIntosh T. J. Direct structure determination of multilayered membrane-type systems which contain fluid layers. Biophys J. 1973 May;13(5):480–494. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86001-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R. The interpretation of low-angle X-ray data from planar and concentric multilayered structures. The use of one-dimensional electron density strip models. Biophys J. 1969 Feb;9(2):222–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86381-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


