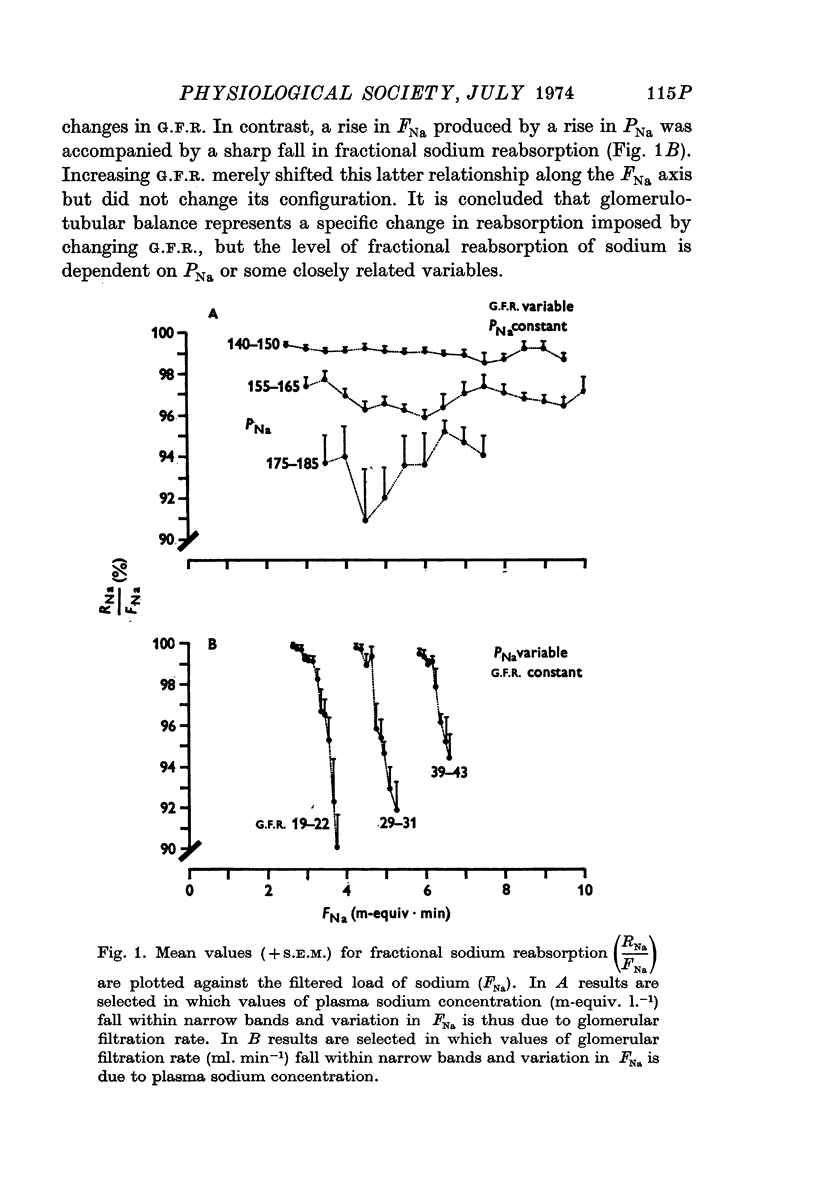
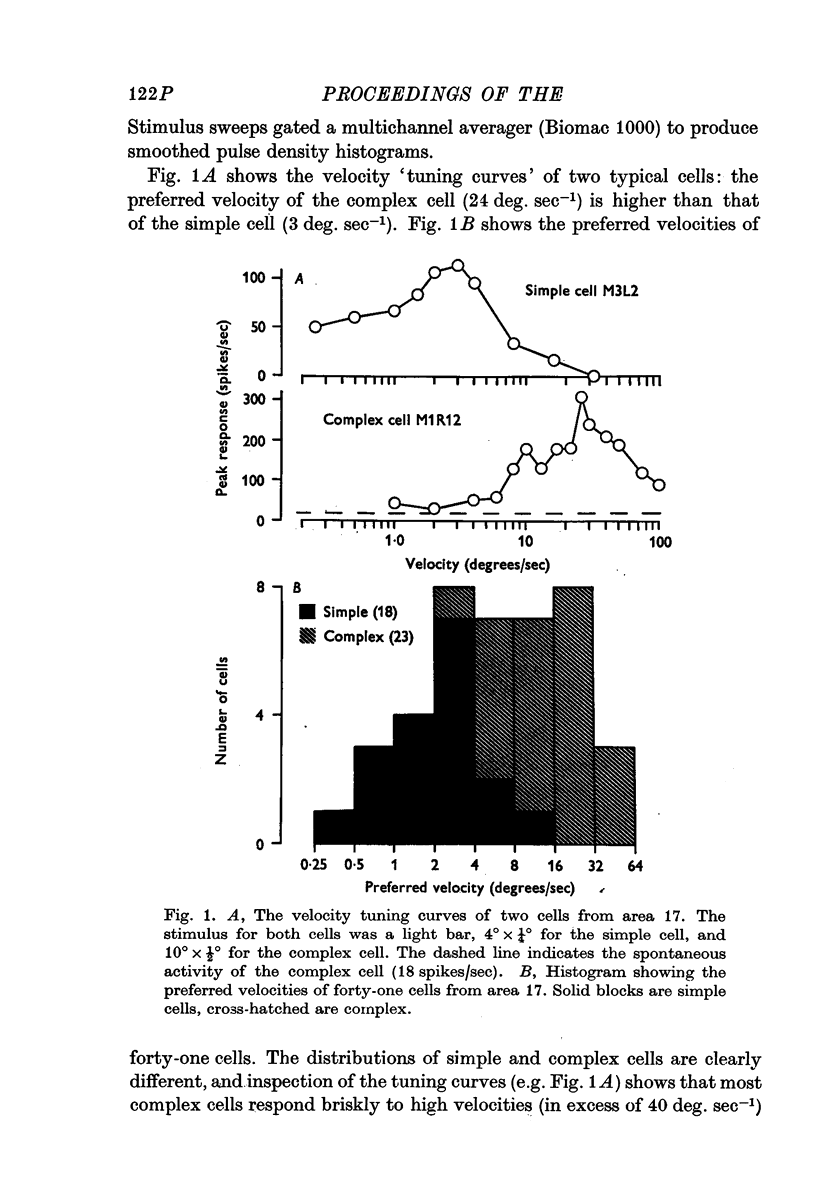
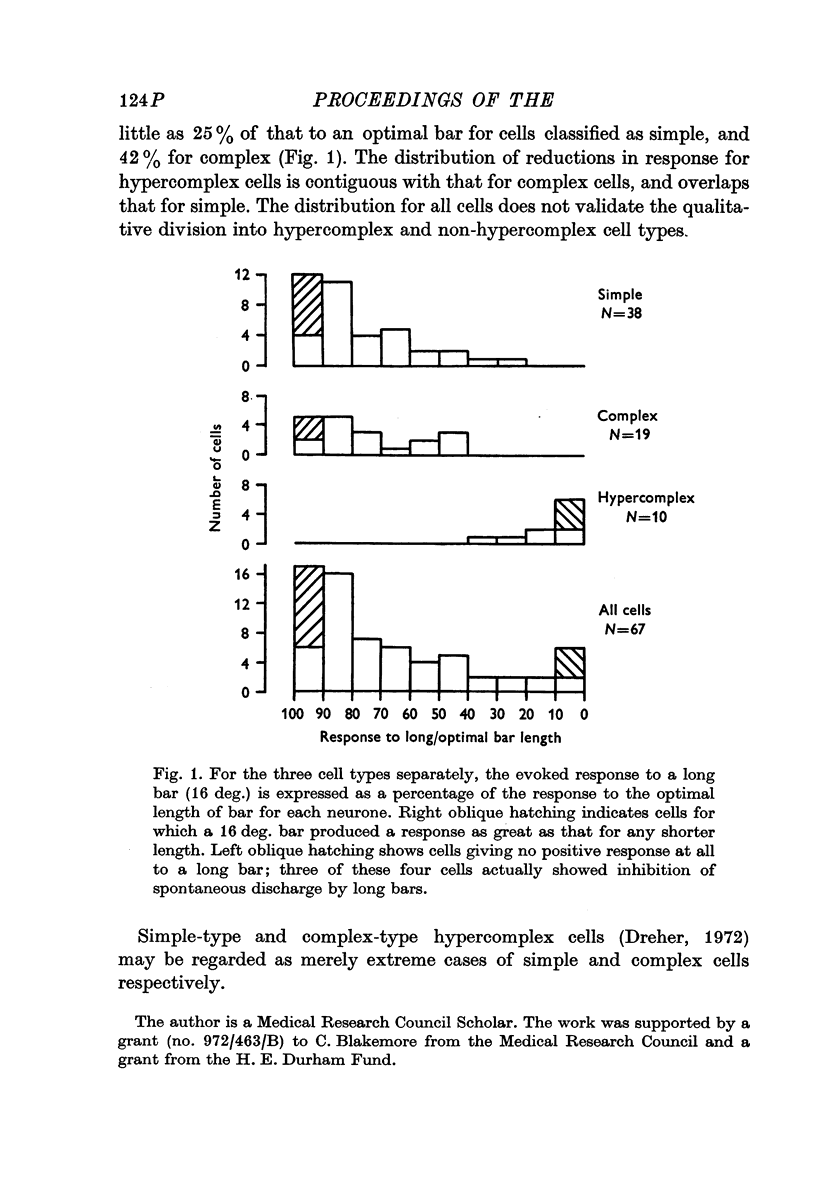
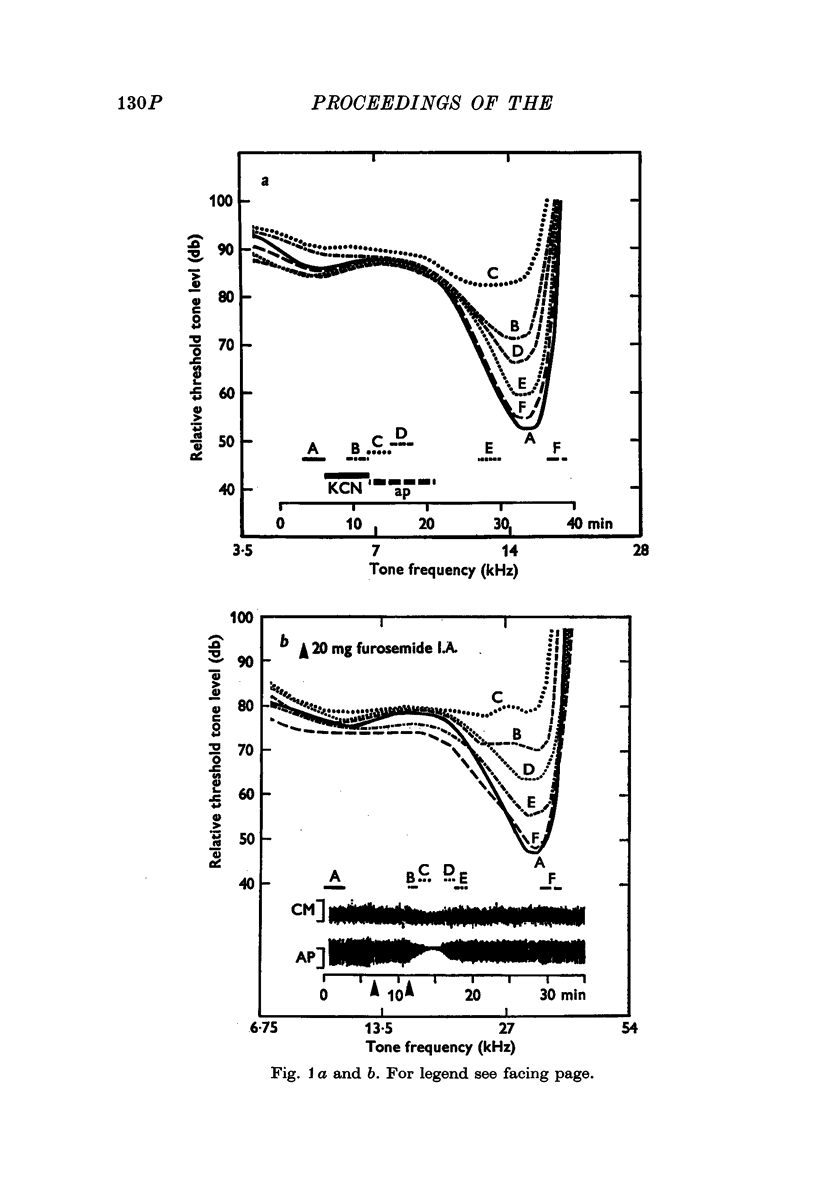
Full text
PDF

























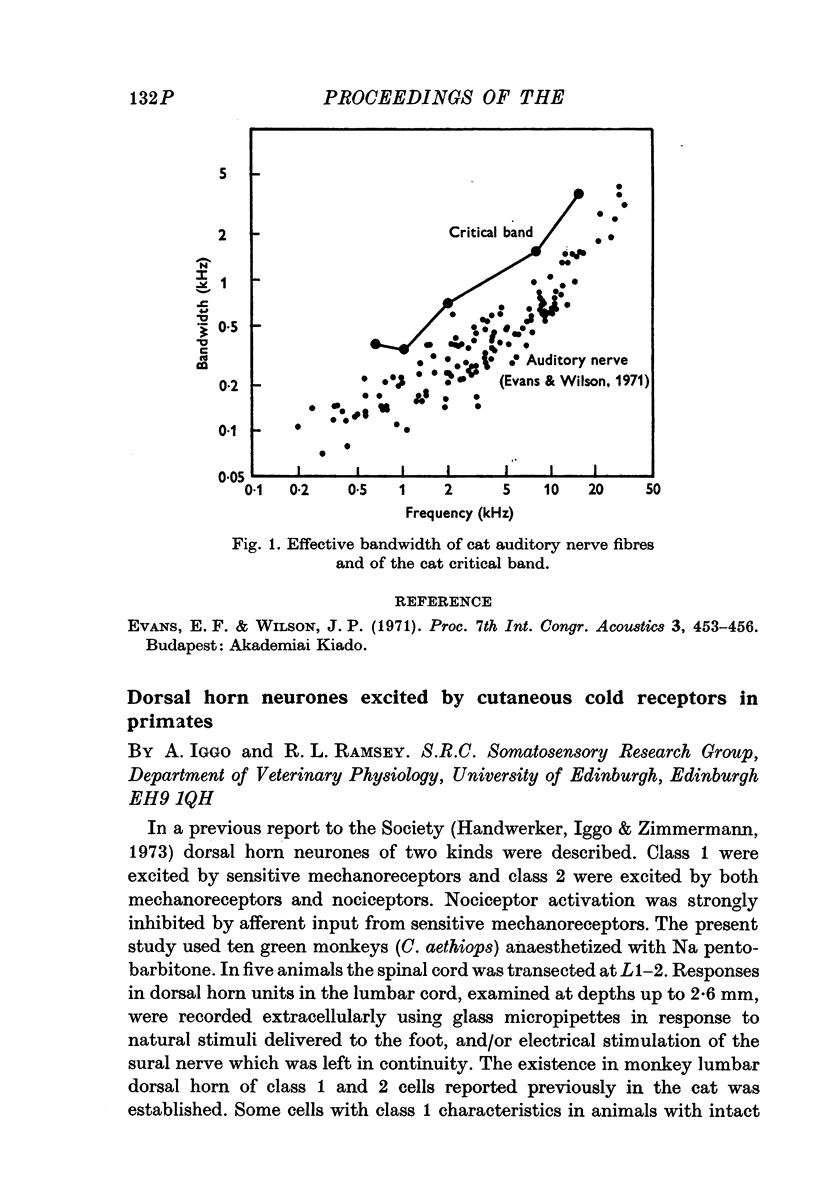






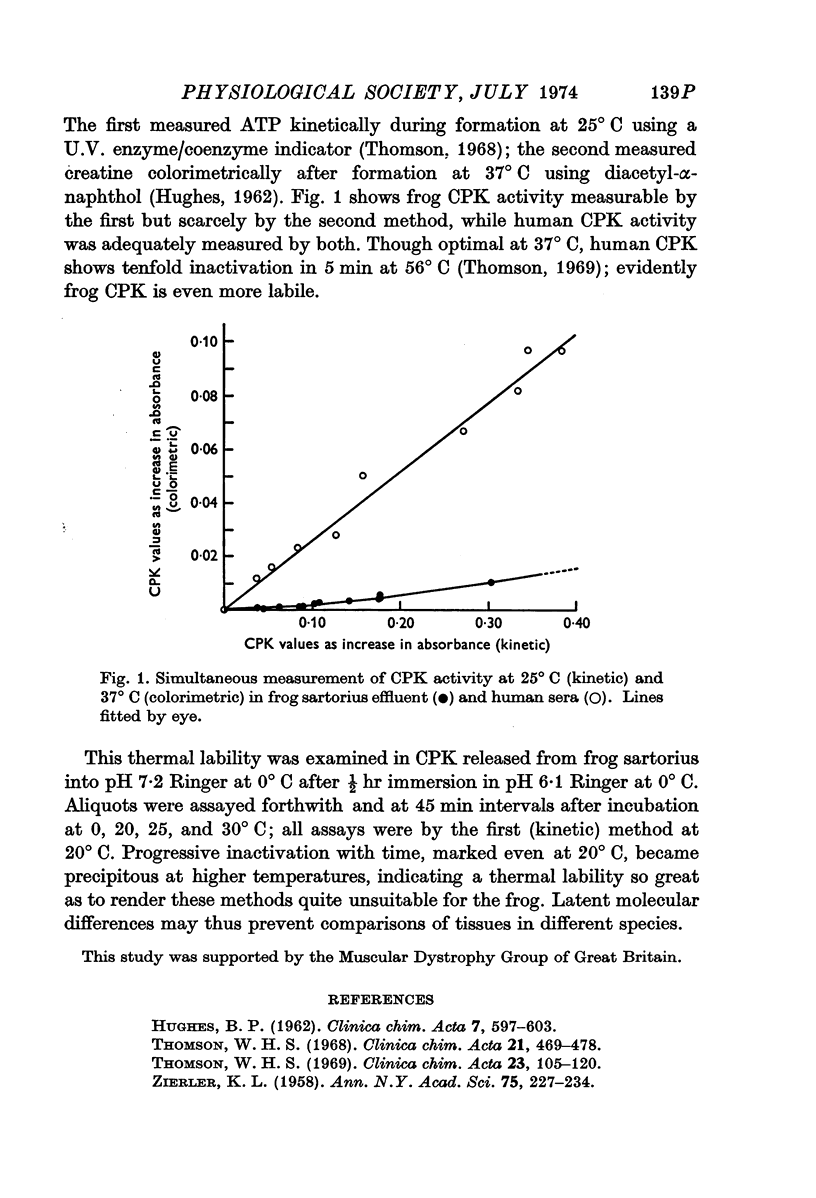




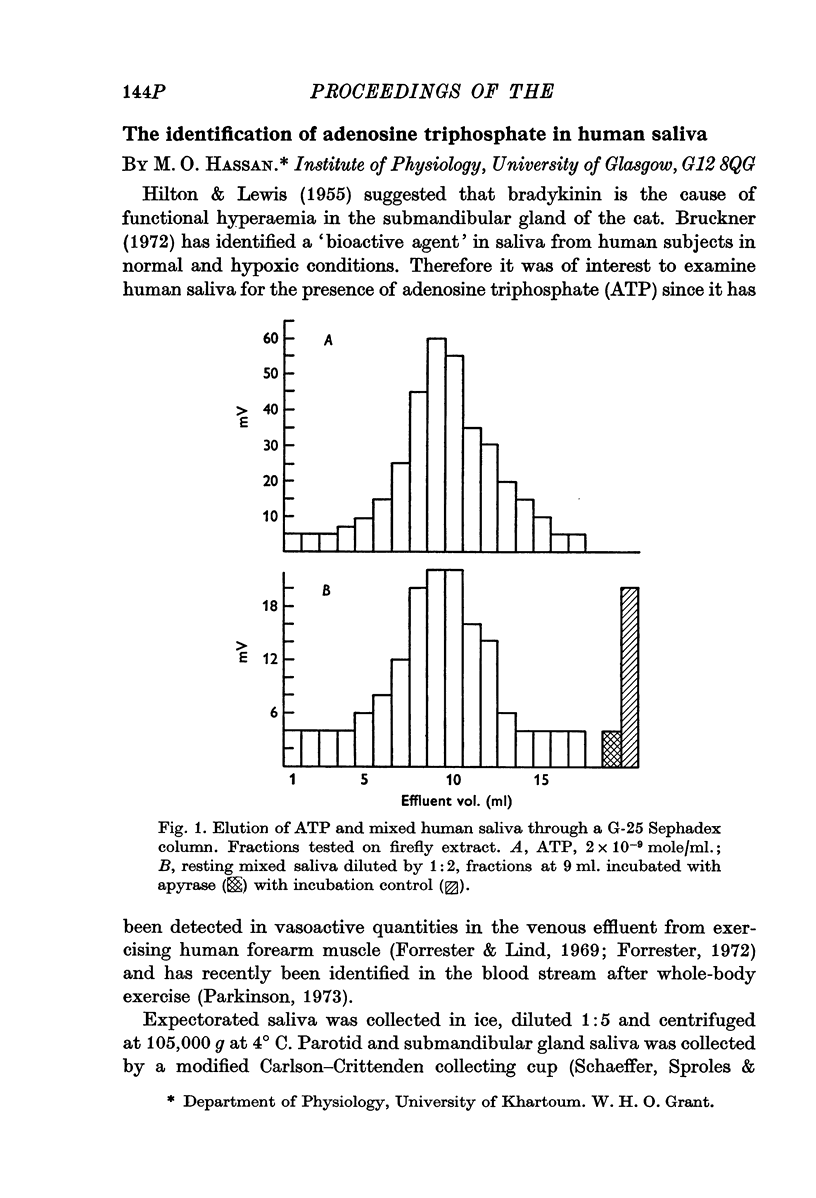

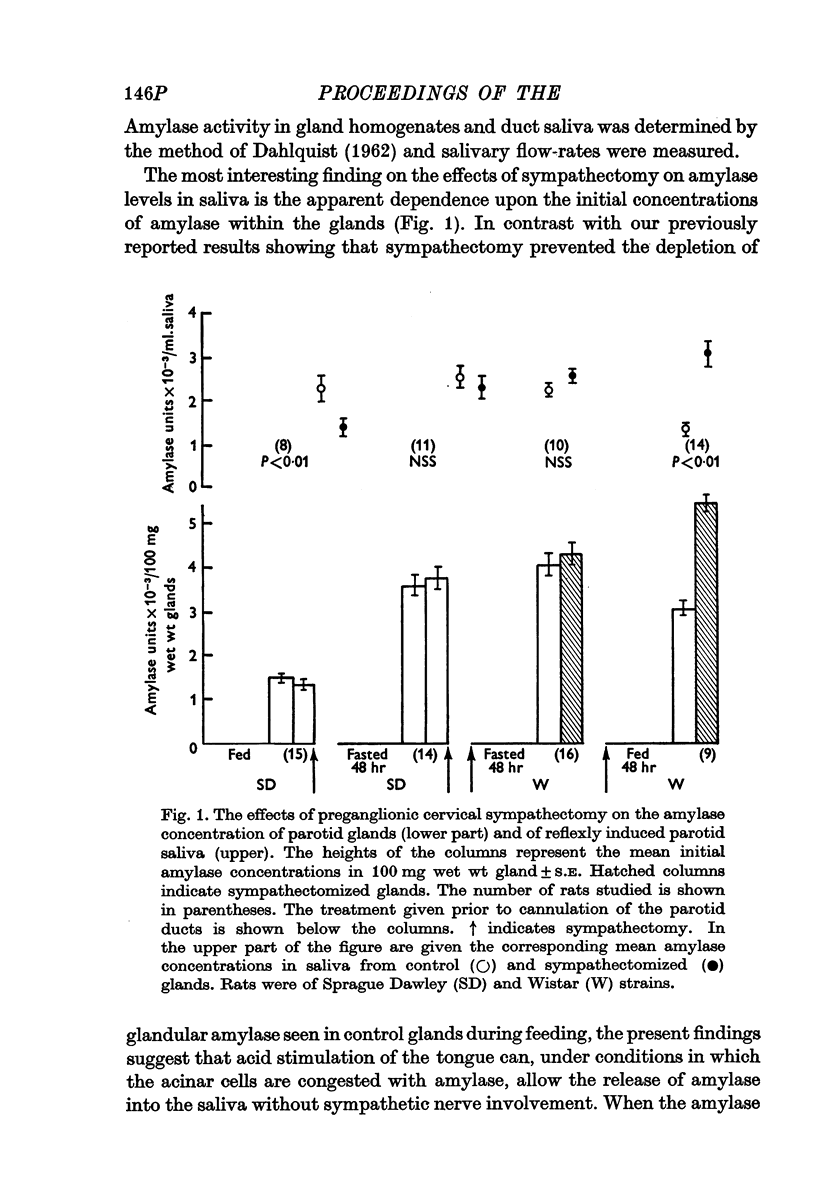

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGEL A., DAWSON G. D. The facilitation of thalamic and cortical responses in the dorsal column sensory path-way by strong peripheral stimulation. J Physiol. 1963 May;166:587–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
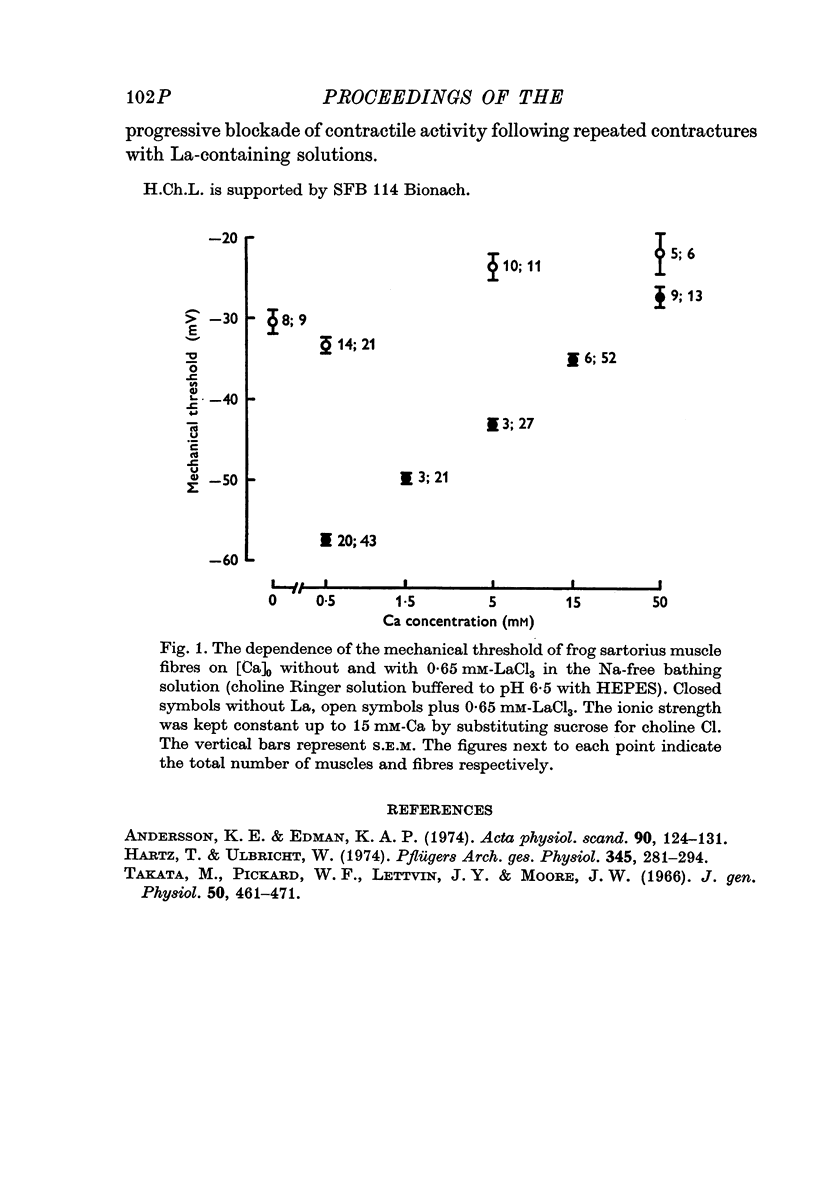
- Andersson K. E., Edman K. A. Effects of lanthanum on potassium contractures of isolated twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):124–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel A., Berridge D. A., Unwin J. The effect of anaesthetic agents on primary cortical evoked responses. Br J Anaesth. 1973 Aug;45(8):824–836. doi: 10.1093/bja/45.8.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aursnes I. Increased permeability of capillaries to protein during thrombocytopenia. An experimental study in the rabbit. Microvasc Res. 1974 May;7(3):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(74)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTTER F. C., DELEA C. S. A map of blood and urinary changes related to circadian variations in adrenal cortical function in normal subjects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 30;98:969–983. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb30612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMER F., STOUPEL N. Facilitation et inhibition des potentiels évoqués corticaux dans l'éveil cérébral. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1959 Apr;67(2):240–275. doi: 10.3109/13813455909074432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Ortiz O. Further evidence for a potassium-like action of lithium ions on sodium efflux in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):675–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. Dual vasoconstrictor and vasodilator innervation of the uterine arterial supply in the guinea pig. Circ Res. 1968 Aug;23(2):279–289. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. O., Coombs J. S., Henry G. H. Receptive fields of simple cells in the cat striate cortex. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):31–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Scott D., Wright R. D. The role of aldosterone in renal sodium conservation during sodium depletion. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Oct;46(5):525–529. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Fiorentini A., Maffei L. A second neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):725–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C. The representation of three-dimensional visual space in the cat's striate cortex. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):155–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanski D. F., Blaszkowski T. P., Tissari A. H. Mechanisms of biogenic amine transport and storage. IV. Relationship between K+ and the Na+ requirement for transport and storage of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine in synaptosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):521–532. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanski D. F., Tissari A. H., Brodie B. B. Mechanism of transport and storage of biogenic amines. 3. Effects of sodium and potassium on kinetics of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine transport by rabbit synaptosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W. The intracerebral movement of proteins injected into blood and cerebrospinal fluid of mice. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:19–40. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. D., Cotter M., Hudlicka O., Smith M. E., Vrbová G. Proceedings: The effect of long-term stimulation of fast muscles on their ability to withstand fatigue. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):47P–48P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARMELIET E. E. INFLUENCE OF LITHIUM IONS ON THE TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL AND CATION CONTENT OF CARDIAC CELLS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:501–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Smith A. D. Proceedings: Release of an isoenzyme of acetylcholinesterase from the perfused adrenal gland. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):97P–98P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. G., Whitteridge D. The basis of stereoscopic vision in the sheep. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):22P–23P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan J. P., Scoggins B. A. Measurement of aldosterone in peripheral blood of man and sheep. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Oct;27(10):1470–1486. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-10-1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. E., Bangham A. D. Diffusion of small non-electrolytes across liposome membranes. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):173–174. doi: 10.1038/236173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter M., Hudlická O., Pette D., Staudte H., Vrbová G. Changes of capillary density and enzyme pattern in fast rabbit muscles during long-term stimulation. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(1):34P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON G. D., PODACHIN V. P., SCHATZ S. W. Facilitation of cortical responses by competing stimuli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:363–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONT S., DELL P. Facilitations spécifiques et non-spécifiques des réponses visuelles corticales. J Physiol (Paris) 1958 Mar;50(2):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., Sargeant A. J. Physiological responses to one- and two-leg exercise breathing air and 45 percent oxygen. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Feb;36(2):142–148. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daw N. W., Pearlman A. L. Cat colour vision: one cone process or several? J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):745–764. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
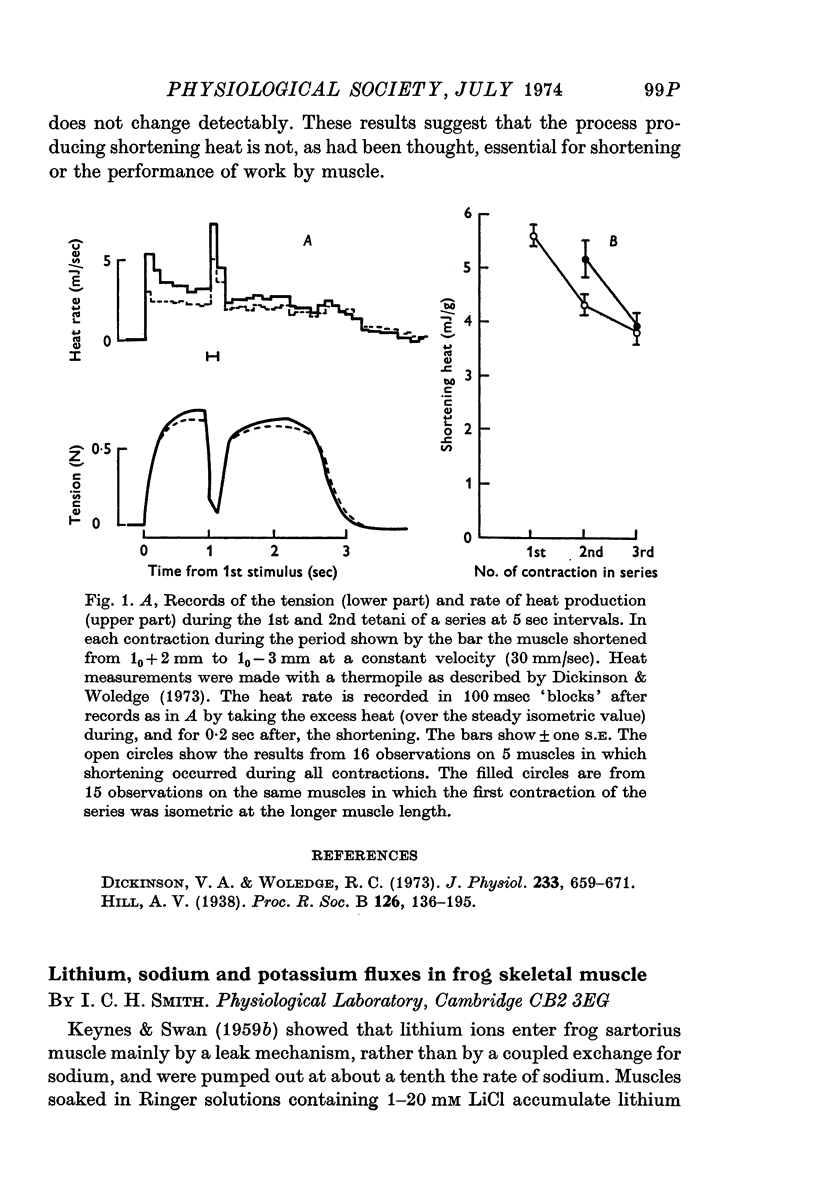
- Dickinson V. A., Woledge R. C. The thermal effects of shortening in tetanic contractions of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):659–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher B. Hypercomplex cells in the cat's striate cortex. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 May;11(5):355–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. F. Proceedings: The effects of hypoxia on the tuning of single cochlear nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):65P–67P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
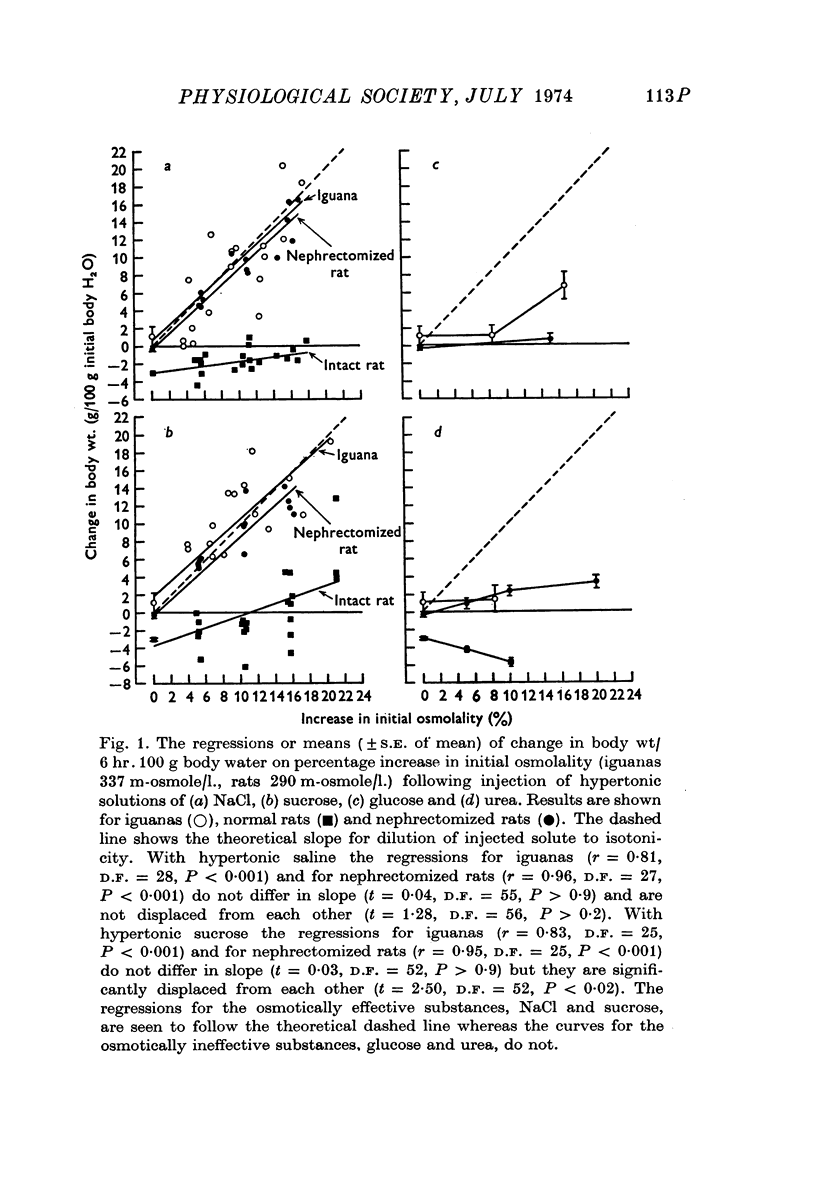
- FITZSIMONS J. T. Drinking by nephrectomized rats injected with various substances. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:563–579. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOUTS J. R., HART L. G. HEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM DURING THE PERINATAL PERIOD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 12;123:245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb12263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P. Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Fever produced in rabbits and cats by prostaglandin E1 injected into the cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Further studies on prostaglandin E 1 fever in cats. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):739–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Further studies on prostaglandin E 1 fever in cats. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):739–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. M. Proceedings: A diencephalic island for the study of thermally responsive neurones in the cat's hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):67P–68P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester T. An estimate of adenosine triphosphate release into the venous effluent from exercising human forearm muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):611–628. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester T., Lind A. R. Identification of adenosine triphosphate in human plasma and the concentration in the venous effluent of forearm muscles before, during and after sustained contractions. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):347–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. H., MacDonald I. C. Proceedings: Assessment of gait in patients recovering from leg injuries. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):79P–80P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. D. Responsiveness of the terminal vascular bed in fast and slow skeletal muscles to -adrenergic stimulation. Angiologica. 1971;8(6):285–296. doi: 10.1159/000157902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The mechanism of the functional hyperaemia in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1955 Aug 29;129(2):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURE IN TWO NONSTRIATE VISUAL AREAS (18 AND 19) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Mar;28:229–289. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES B. P. A method for the estimation of serum creatine kinase and its use in comparing creatine kinase and aldolase activity in normal and pathological sera. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Sep;7:597–603. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerker H., Iggo A., Zimmermann M. Proceedings: Dorsal horn neurones driven by cutaneous input: interaction between mechanoreceptors and nociceptors. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):84P–85P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz T., Ulbricht W. Comparison of the effects of calcium and lanthanum on the crayfish giant axon. Pflugers Arch. 1973;345(4):281–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00585847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier P., Knapp M. S. Proceedings: The domiciliary measurement of human physiological rhythms. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M., Jeffries M. G., Vrbová G. Functional specializations of the vascular bed of soleus. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):543–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson C., Speirs R. L. The effect of preganglionic cervical sympathectomy on the amylase content of parotid glands in fasted and fed rats. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):56P–57P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Stereoscopic vision in macaque monkey. Cells sensitive to binocular depth in area 18 of the macaque monkey cortex. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):41–42. doi: 10.1038/225041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A. Cutaneous thermoreceptors in primates and sub-primates. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):403–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirku H., Hogsander U., Levitz M. 15-alpha-hydroxyestrone "sulfate": a biliary metabolite of estrone sulfate in the non-pregnant female. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 6;137(3):588–591. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juchau M. R., Niswander K. R., Yaffe S. J. Drug metabolizing systems in homogenates of human immature placentas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Feb 1;100(3):348–356. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(15)33701-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMM D. E., LEVINSKY N. G. EFFECT OF PLASMA SODIUM ELEVATION ON RENAL SODIUM REABSORPTION. Am J Physiol. 1964 May;206:1131–1136. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.5.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The permeability of frog muscle fibres to lithium ions. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:626–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann P. Die Meerschweinchenplacenta und ihre Entwicklung. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1969;129(1):83–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. Inhibition of the sodium-retaining influence of aldosterone by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1237–1245. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggins G. C., Fairclough R. J., Grieves S. A., Kendall J. Z., Knox B. S. The mechanism of initiation of parturition in the ewe. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1973;29:111–159. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571129-6.50007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONEY W. L., DANCIS J. Technique for the in situ study of placental transport in the pregnant guinea pig. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Aug;80:209–214. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(60)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. S. The effect of oestrus on "free" water intake in zebu-type heifers. Vet Rec. 1967 Mar 18;80(11):361–362. doi: 10.1136/vr.80.11.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvaux P., Beckers C. Serum thyrotrophin response to thyrotrophin-releasing hormone in normal children and in patients with short stature and various endocrine or genetic diseases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1973 Jul;2(3):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1973.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell A. R. Changes in voluntary sodium intake during the oestrous cycle of sheep. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):42P–44P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisticò G., Marley E. Central effects of prostaglandin E1 in adult fowls. Neuropharmacology. 1973 Nov;12(11):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(73)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswender G. D., Midgley A. R., Jr, Monroe S. E., Reichert L. E., Jr Radioimmunoassay for rat luteinizing hormone with antiovine LH serum and ovine LH-131-I. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):807–811. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue S. E. Distribution of pethidine and chlorpromazine in maternal, foetal and neonatal biological fluids. Nature. 1971 Jan 8;229(5280):124–125. doi: 10.1038/229124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson P. I. Proceedings: The effect of graduated exercise on the concentration of adenine nucleotides in plasma. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):72P–74P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Thomas R. C. Effect of intracellular lithium on snail neurones. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):578–580. doi: 10.1038/249578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepeu G. The release of acetylcholine from the brain: an approach to the study of the central cholinergic mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol. 1973;2(3):259–288. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(73)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Smith M. E., Staudte H. W., Vrbová G. Effects of long-term electrical stimulation on some contractile and metabolic characteristics of fast rabbit muscles. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Feb 6;338(3):257–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00587391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D., Nikara T., Bishop P. O. Responses to moving slits by single units in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(4):373–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00233185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. W., Mancuso S., Diczfalusy E. Isolation of 16-oxo-testosterone from human placentas perfused in situ. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 4;152(2):438–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds M. L., Young M. The transfer of free alpha-amino nitrogen across the placental membrane in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):583–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Blakemore C. An analysis of orientation selectivity in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Apr 30;20(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00239014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Blakemore C. An analysis of orientation selectivity in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Apr 30;20(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00239014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskam J. The hemostatic paradox and its present problems. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Nov 15;14(3-4):626–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELKURT E. E., POST R. S. Renal clearance of sodium in the dog: effect of increasing sodium load on reabsorptive mechanism. Am J Physiol. 1950 Sep;162(3):639–648. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.162.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L. D., Sproles A., Krakowski A. Detection of cyclic AMP in parotid saliva of normal individuals. J Dent Res. 1973 May-Jun;52(3):629–629. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520034101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M. Proceedings: Modification of the receptive field properties of neurones in the visual cortex by bicuculline, a GABA antagonist. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):36P–37P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabenfeldt G. H., Holt J. A., Ewing L. L. Peripheral plasma progesterone levels during the ovine estrous cycle. Endocrinology. 1969 Jul;85(1):11–15. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. Morphology and physiology of the geniculocortical synapse in the cat: the question of parallel input to the striate cortex. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 May;11(5):338–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Pickard W. F., Lettvin J. Y., Moore J. W. Ionic conductance changes in lobster axon membrane when lanthanum is substituted for calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):461–471. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson W. H. An investigation of physical factors influencing the behaviour in vitro of serum creatine phosphokinase and other enzymes. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Jan;23(1):105–120. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson W. H. Determination and statistical analyses of the normal ranges for five serum enzymes. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn G. D., Bassett J. M., Smith I. D. Progesterone concentration in the peripheral plasma of sheep during the oestrous cycle. J Endocrinol. 1969 Nov;45(3):459–469. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0450459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft A. D., Boyns A. R., Cole E. N., Groom G. V., Hunter W. M., Irvine W. J. The effect of thyrotrophin-releasing hormone on plasma prolactin and thyrotrophin levels in primary hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1973 Jul;2(3):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1973.tb00430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
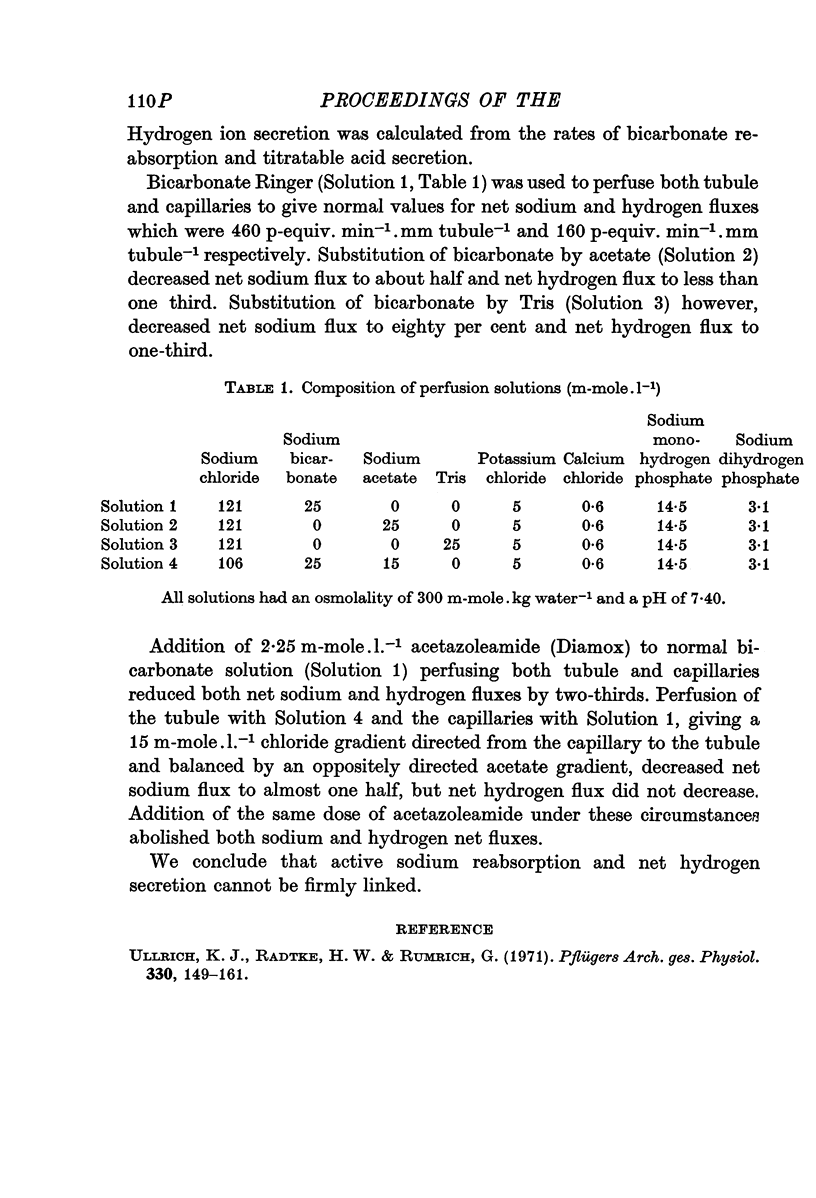
- Ullrich K. J., Radtke H. W., Rumrich G. The role of bicarbonate and other buffers on isotonic fluid absorption in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(2):149–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00643031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace A. L., Stacy B. D., Thorburn G. D. Regulation of growth hormone secretion in the ovine foetus. J Endocrinol. 1973 Jul;58(1):89–95. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0580089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D., Paton D. M. Effects of external Na + and K + on the initial rates of noradrenaline uptake by synaptosomes prepared from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):116–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman P. The quantitative determination of glycosaminoglycans in urine with Alcian Blue 8GX. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):351–357. doi: 10.1042/bj1310351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise L., Ballinger W. F., 2nd The effect of histalog on canine gastric acid, mucus and pepsin secretion. Ann Surg. 1970 Feb;171(2):229–235. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197002000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Muscle membrane as a dynamic structure and its permeability to aldolase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



