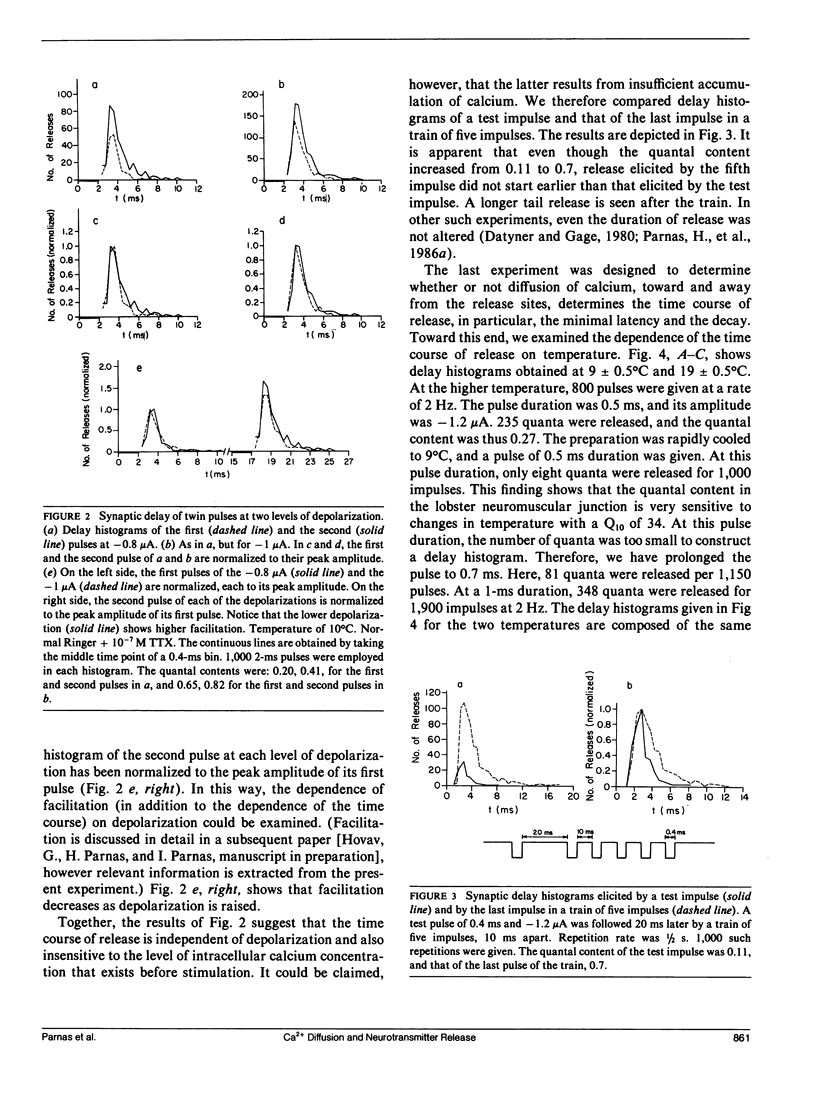
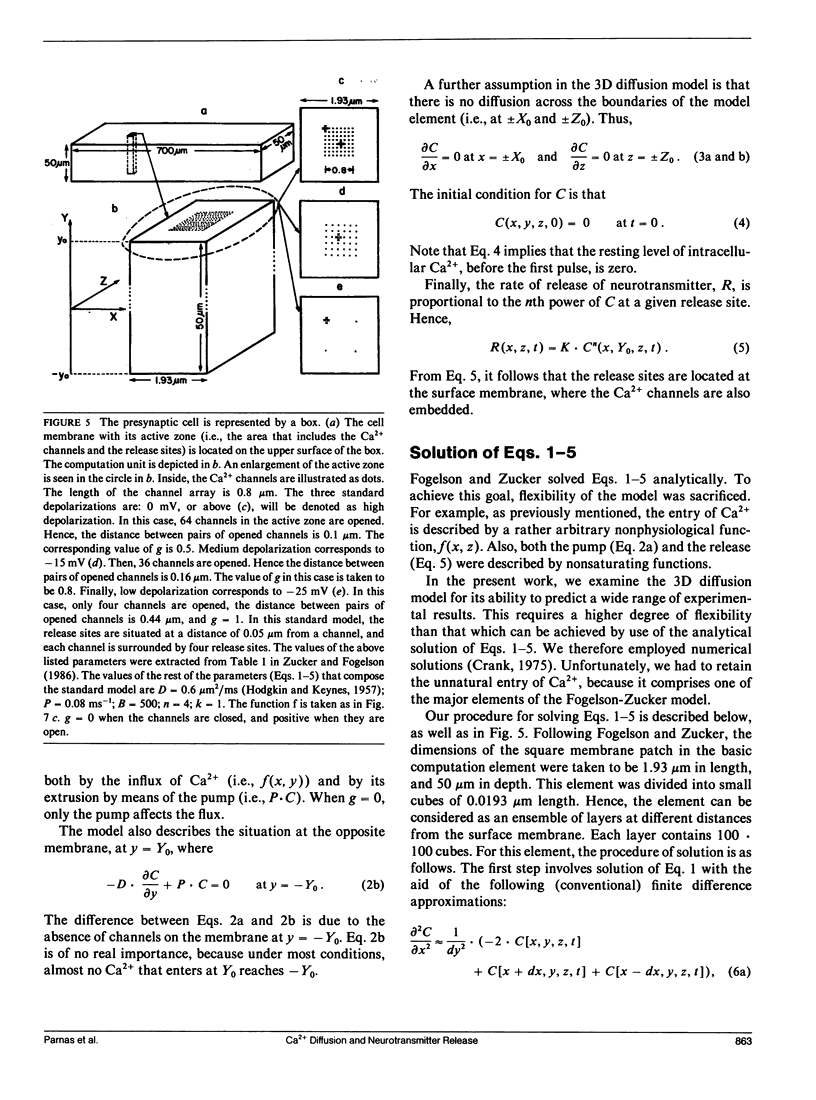
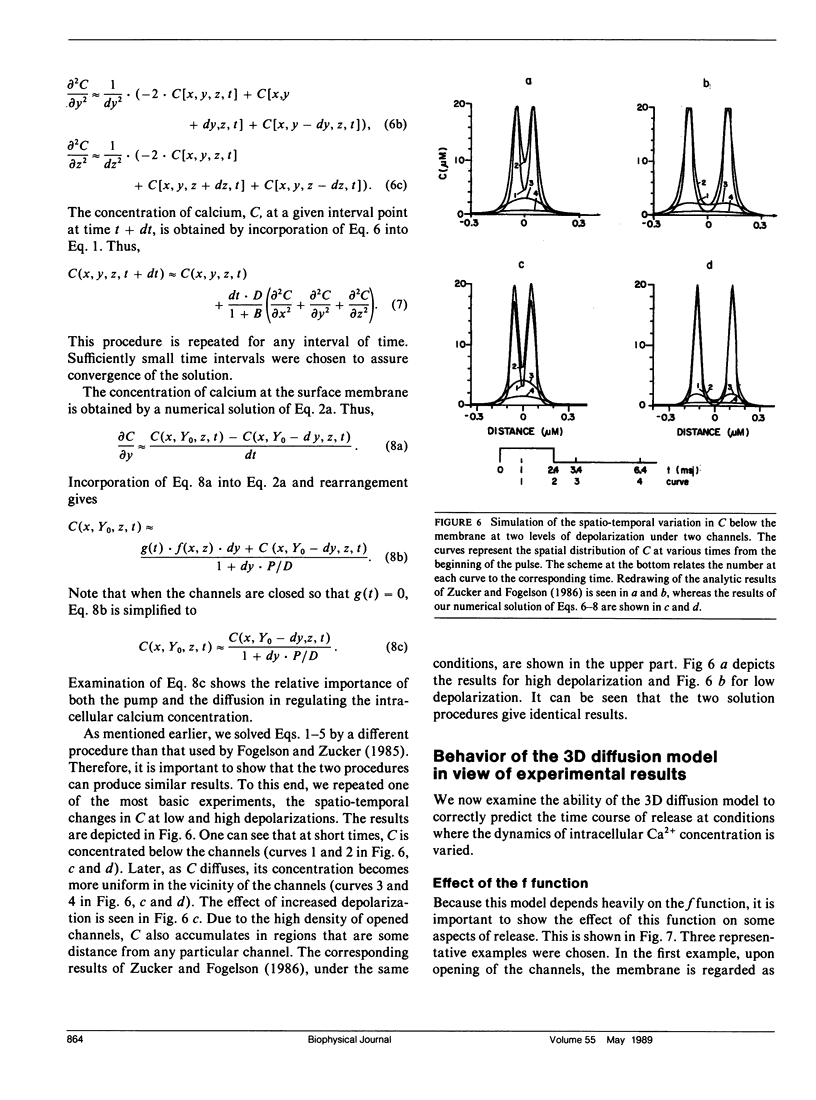
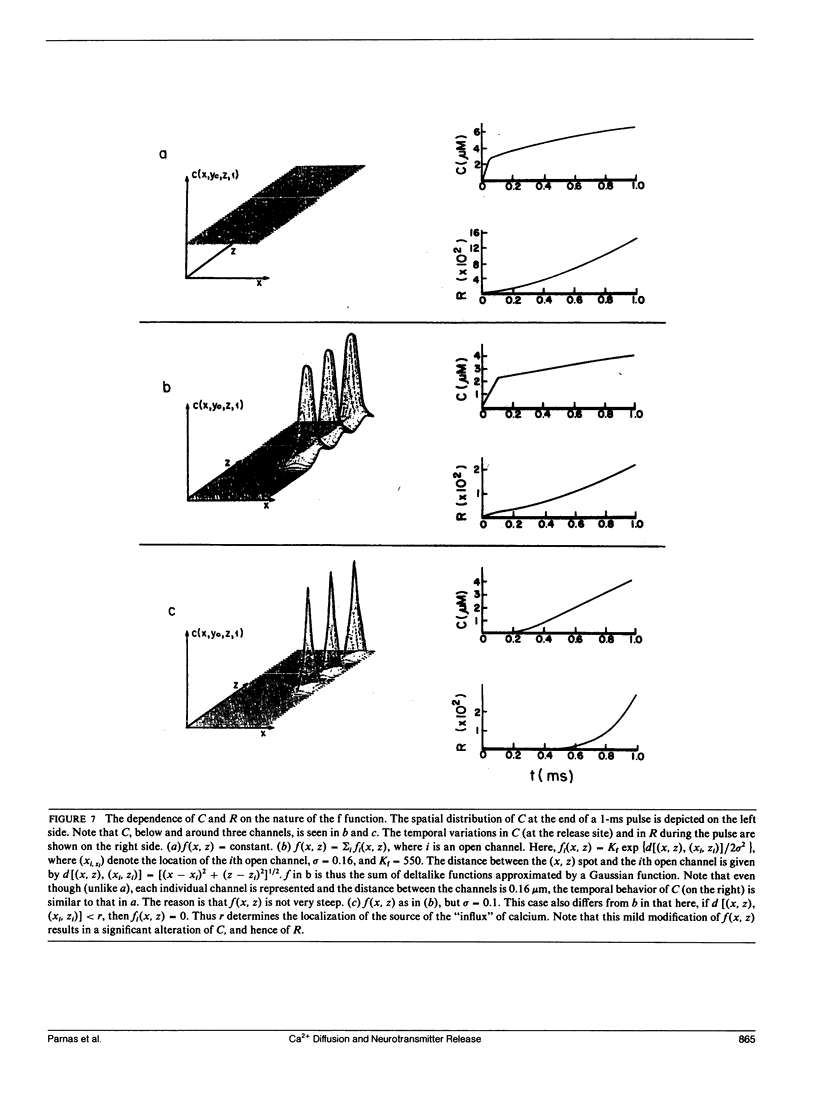
Abstract
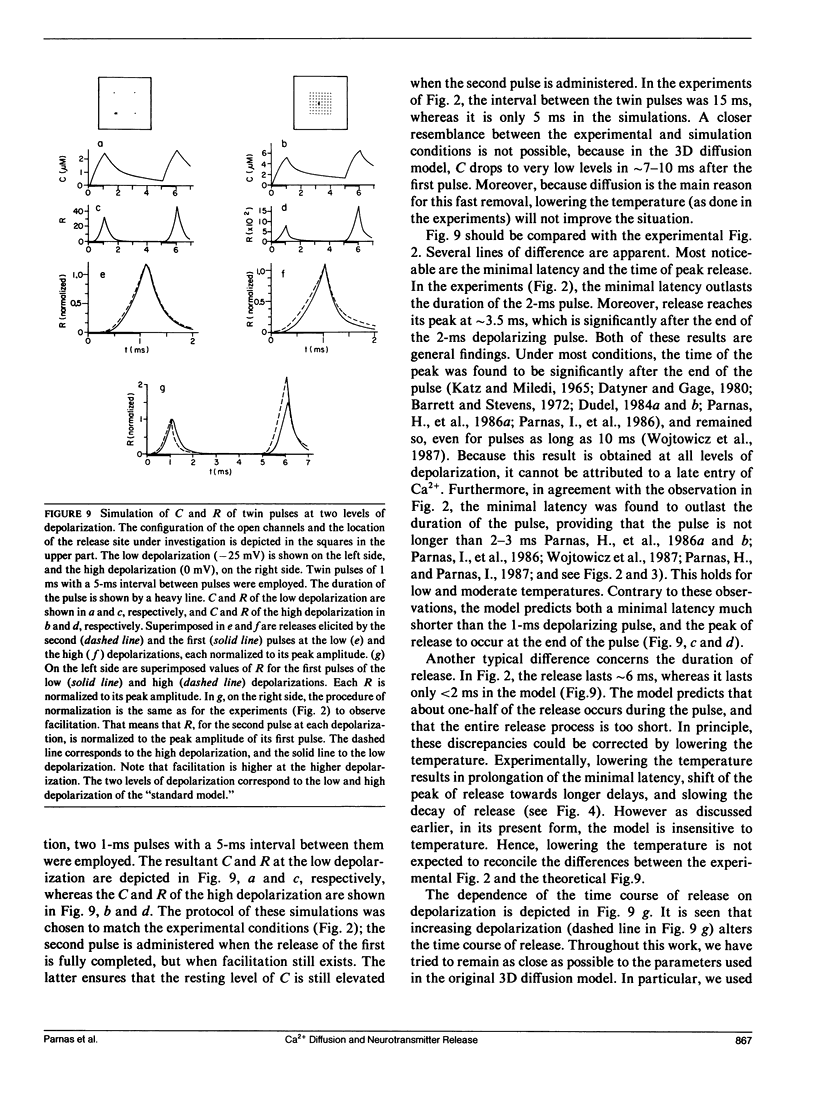
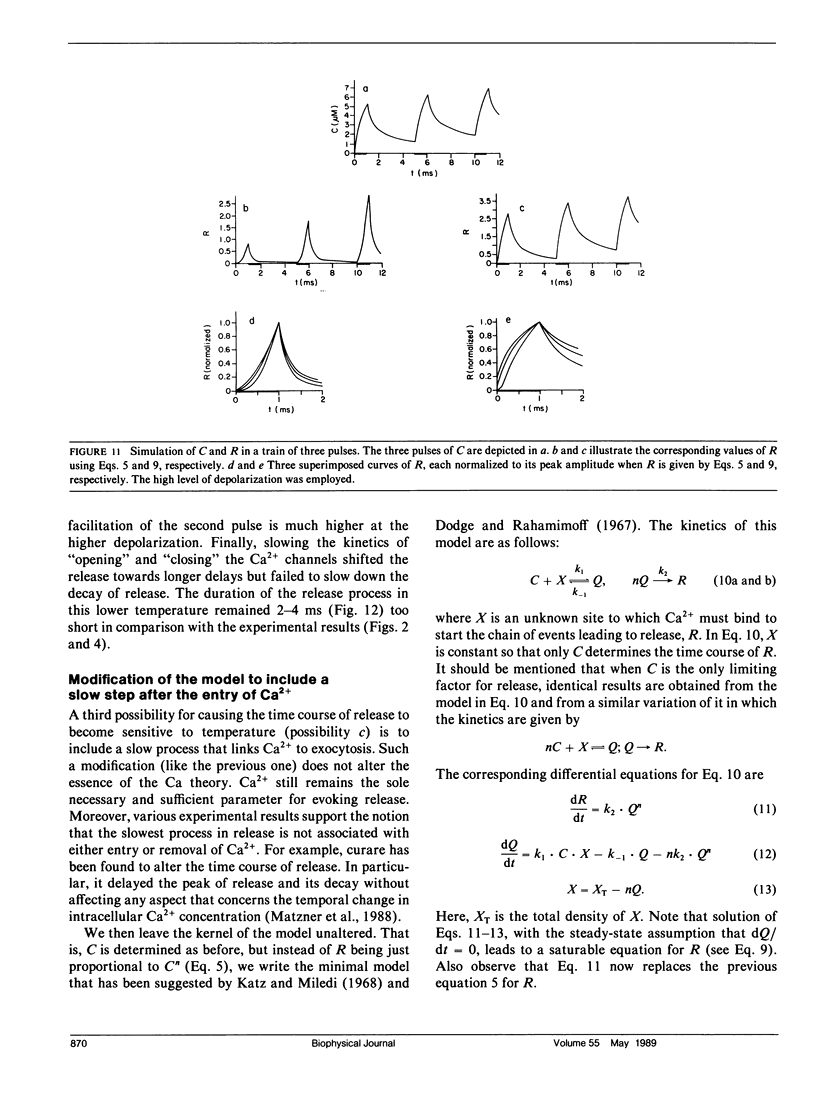
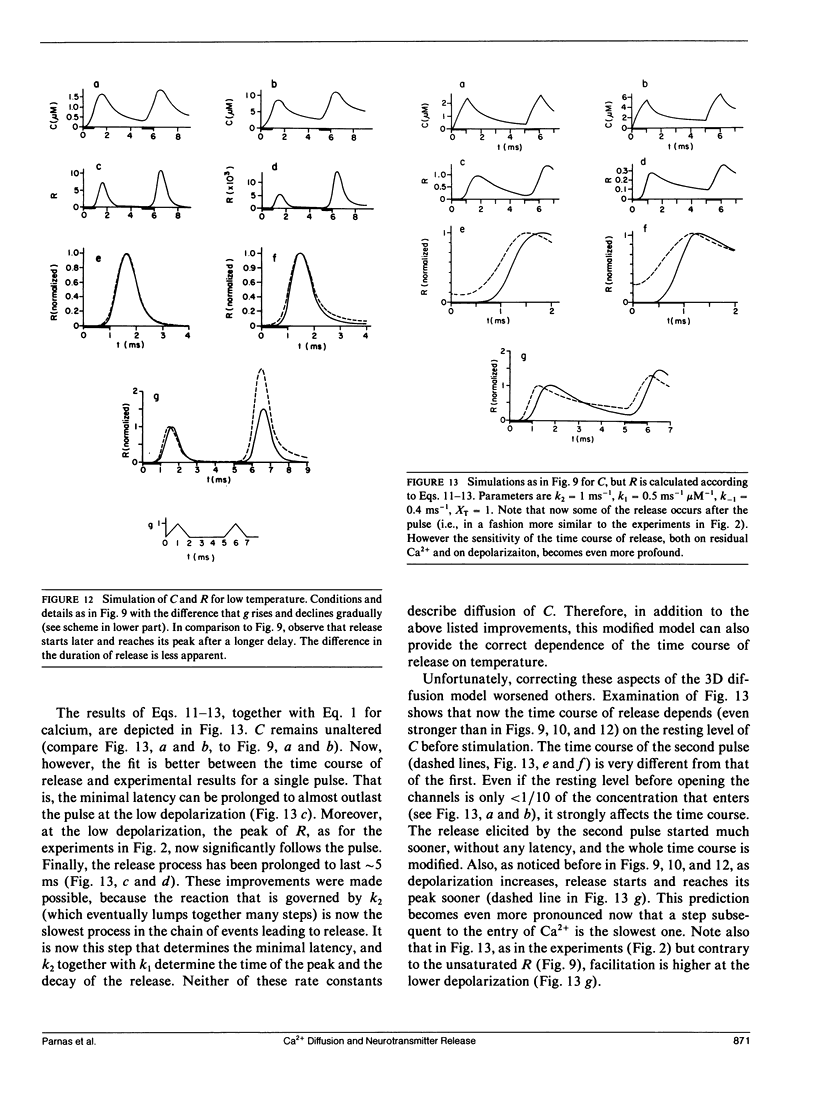
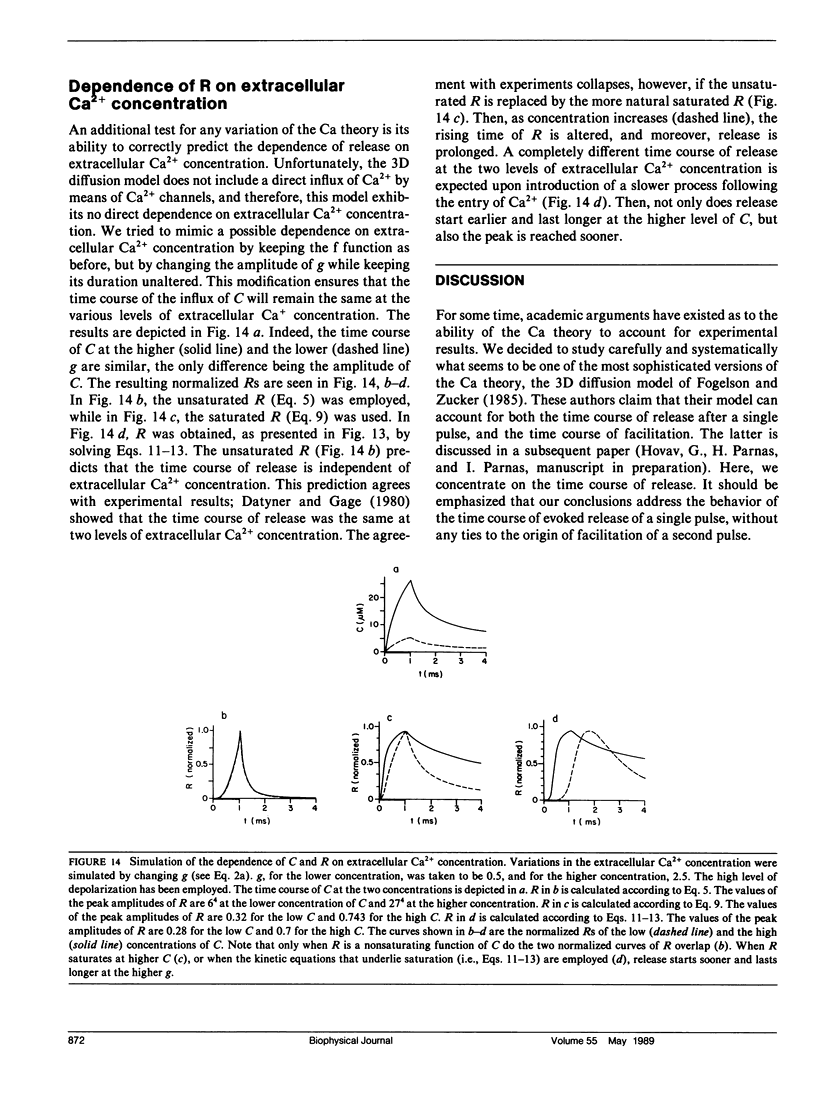
The three-dimensional (3D) diffusion model of Fogelson, A. L., and R. S. Zucker (1985. Biophys. J. 48: 1003-1017) has been employed as the basis of a refined version of the "Ca theory" for neurotransmitter release. As such, it has been studied here as to its ability to predict the time course of release under various conditions. In particular, conditions were chosen in which the temporal variations in intracellular Ca2+ concentration, the sole factor controlling the release according to the Ca theory, were modified and tested experimentally. The predictions of this model were compared with the experimental results. It is shown that the 3D diffusion model, similarly to earlier simpler versions of the Ca theory, predicts that the time course of release is highly sensitive to both the level of depolarization and the level of the resting concentration of intracellular Ca2+ Moreover, the 3D diffusion model predicts that the time course of release is insensitive to changes in temperature. In contrast, the experimental results show that the time course of release is invariant to the level of depolarization and to the resting level in intracellular Ca2+, but highly sensitive to variations in temperature.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datyner N. B., Gage P. W. Phasic secretion of acetylcholine at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:299–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Control of quantal transmitter release at frog's motor nerve terminals. I. Dependence on amplitude and duration of depolarization. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):225–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00585504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Parnas I., Parnas H. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish muscle. VI. Release determined by both, intracellular calcium concentration and depolarization of the nerve terminal. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Sep;399(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00652515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. The effect of reduced calcium on quantal unit current and release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jul;391(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00580691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelson A. L., Zucker R. S. Presynaptic calcium diffusion from various arrays of single channels. Implications for transmitter release and synaptic facilitation. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):1003–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Suppression of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):465–469. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzner H., Parnas H., Parnas I. Presynaptic effects of d-tubocurarine on neurotransmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:109–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Dudel J., Parnas I. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. I. Saturation kinetics of release, and of entry and removal of calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Mar;393(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00582384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Dudel J., Parnas I. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. VII. Another voltage dependent process beside Ca entry controls the time course of phasic release. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):121–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00586672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Parnas I. Influence of depolarizing pulse duration on the time course of transmitter release in lobster. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:487–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Parnas I., Segel L. A new method for determining co-operativity in neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1986 Apr 21;119(4):481–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Segel L. A. A theoretical explanation for some effects of calcium on the facilitation of neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1980 May 7;84(1):3–29. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(80)81035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Segel L. A. Exhaustion of calcium does not terminate evoked neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1984 Apr 7;107(3):345–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(84)80096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I., Atwood H. L. Phasic and tonic neuromuscular systems in the abdominal extensor muscles of the crayfish and rock lobster. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1966 Aug;18(4):701–723. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(66)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I., Parnas H. Calcium is essential but insufficient for neurotransmitter release: the calcium-voltage hypothesis. J Physiol (Paris) 1986;81(4):289–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I., Parnas H., Dudel J. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. VIII. Modulation of release by hyperpolarizing pulses. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00586673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I., Parnas H. The 'Ca-voltage' hypothesis for neurotransmitter release. Biophys Chem. 1988 Feb;29(1-2):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)87027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockbridge N., Moore J. W. Dynamics of intracellular calcium and its possible relationship to phasic transmitter release and facilitation at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci. 1984 Mar;4(3):803–811. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-03-00803.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtowicz J. M., Parnas I., Parnas H., Atwood H. L. Latency of transmitter release at crayfish motor nerve endings examined by intracellular depolarization. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;65(1):105–108. doi: 10.1139/y87-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Fogelson A. L. Relationship between transmitter release and presynaptic calcium influx when calcium enters through discrete channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3032–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


