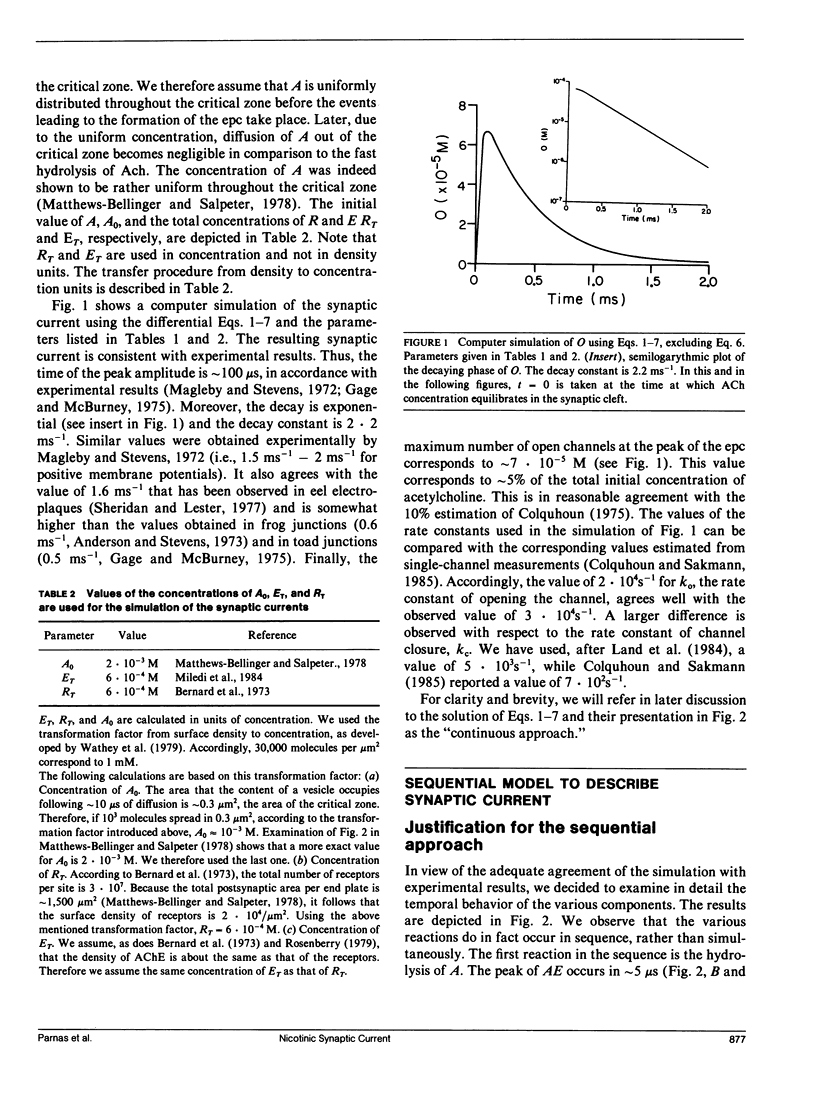
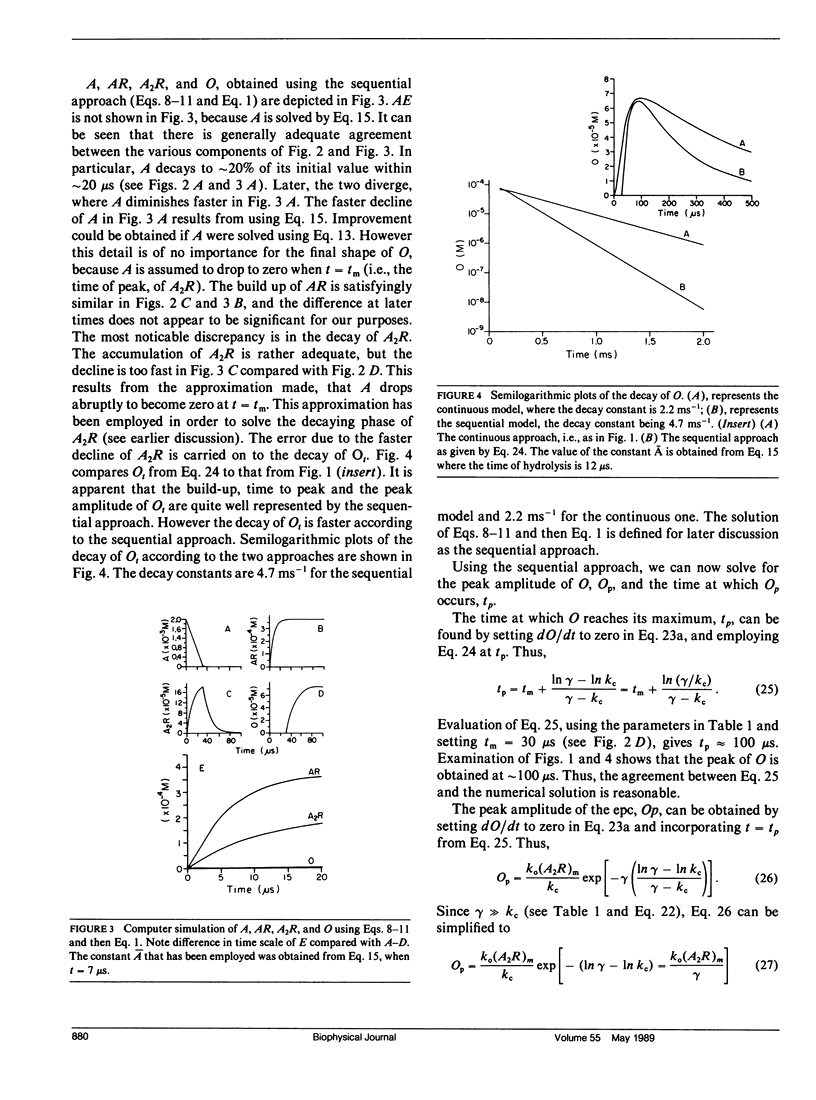
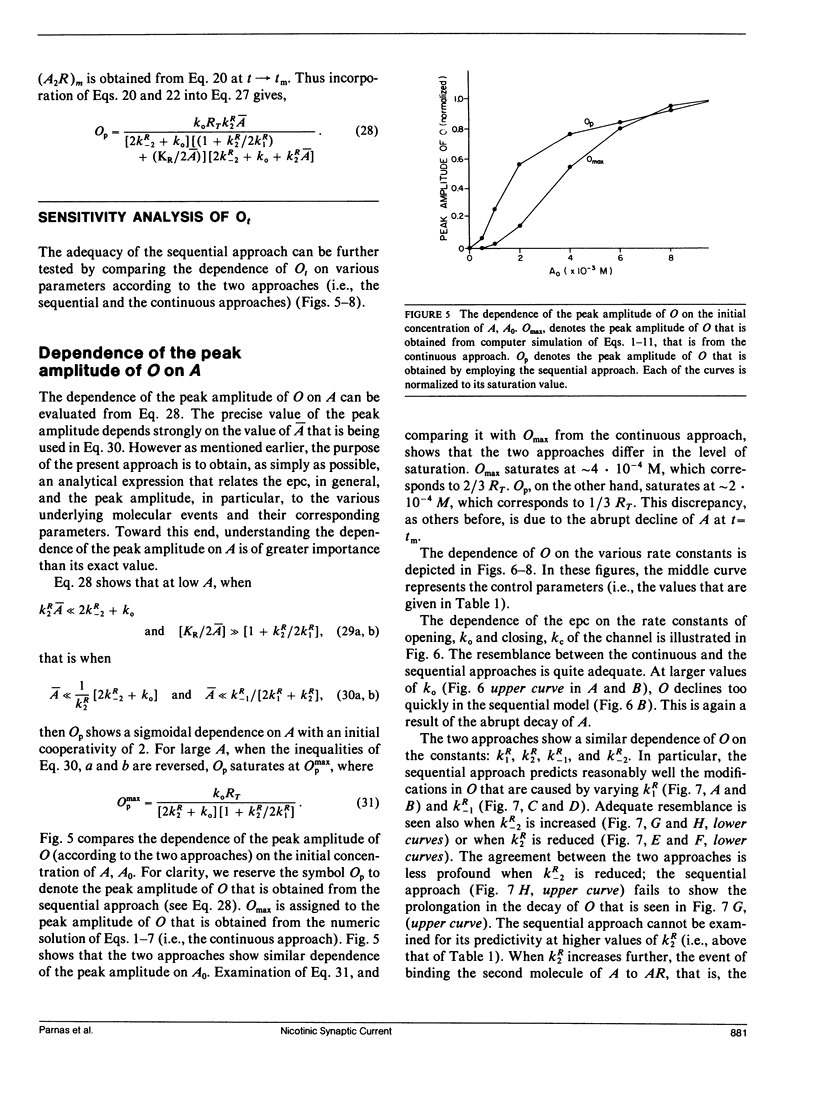
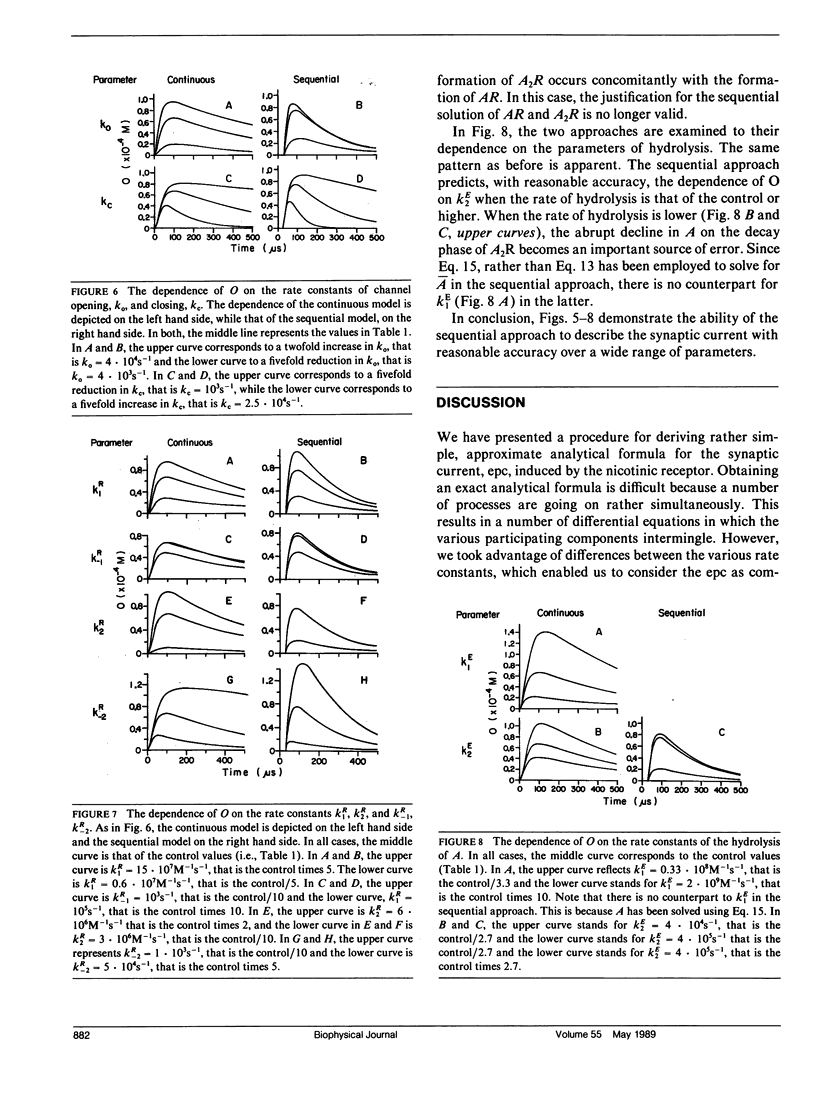
Abstract
An analytical formula is derived to describe the synaptic end plate current (epc) at the nicotinic receptor. Various concurrently occurring underlying processes, including (a) diffusion, (b) hydrolysis of acetylcholine, and (c) its binding to the dimeric receptor, were considered in order to develop the equation. Numeric solution of the equations that describe the events underlying the epc showed that these events occur in sequence, rather than concurrently. This sequential occurrence of the processes allowed for simplifications, which were used as the basis for the new description of the epc. The resulting formula serves as a tool for evaluating the relative contribution of the various processes in formation of the natural occurring transient epc.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D. Mechanisms of drug action at the voluntary muscle endplate. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:307–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Dudel J. Liquid filament switch for ultra-fast exchanges of solutions at excised patches of synaptic membrane of crayfish muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 15;77(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90586-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. On the role of junctional cholinesterase in determining the time course of the end-plate current. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):133–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Harris W. V., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Diffusion and binding constants for acetylcholine derived from the falling phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M., Martin A. R. Non-linear summation of end-plate potentials in the frog and mouse. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:307–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molenaar P. C., Polak R. L. Acetylcholinesterase activity in intact and homogenized skeletal muscle of the frog. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:663–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:103–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Bernhard S. A. Studies of catalysis by acetylcholinesterase. Synergistic effects of inhibitors during the hydrolysis of acetic acid esters. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4308–4321. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L. Quantitative simulation of endplate currents at neuromuscular junctions based on the reaction of acetylcholine with acetylcholine receptor and acetylcholinesterase. Biophys J. 1979 May;26(2):263–289. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85249-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel L. A. On the validity of the steady state assumption of enzyme kinetics. Bull Math Biol. 1988;50(6):579–593. doi: 10.1007/BF02460092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathey J. C., Nass M. M., Lester H. A. Numerical reconstruction of the quantal event at nicotinic synapses. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):145–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85208-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


