Abstract
The first detection of the magnetic field of a stimulated peripheral nerve in man is presented. The measurement was performed noninvasively and in vivo on a healthy subject. The spatio-temporal field distribution is utilized to calculate the location of bioelectric activity on the basis of the equivalent current dipole model. The localization of the active nerve tissue is confirmed by a computer tomography image of the upper arm cross-section. Furthermore, a calculation of the total current distribution in the nerve explains the observed morphology of the signal.
Full text
PDF

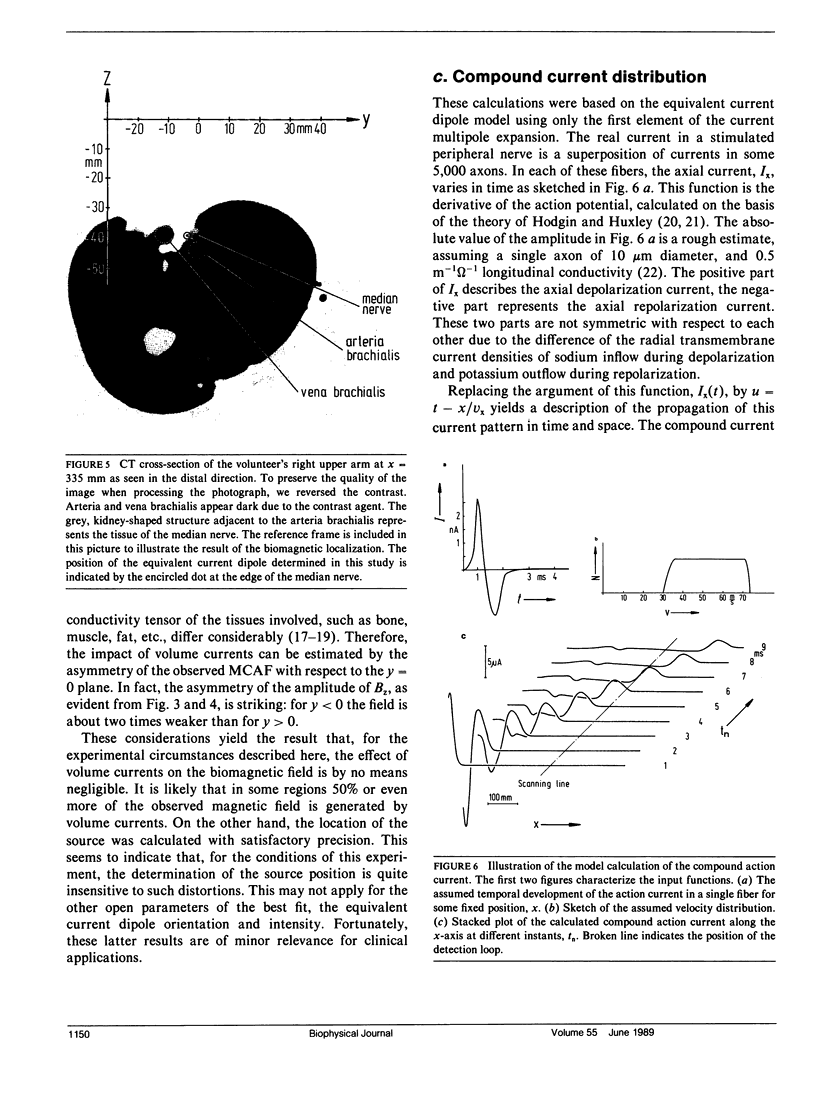



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen D., Hosaka H. Part II: magnetic field produced by a current dipole. J Electrocardiol. 1976;9(4):409–417. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(76)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins K. L., Dorfman L. J., Perkel D. H. Nerve fiber conduction-velocity distributions. II. Estimation based on two compound action potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1979 Jun;46(6):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(79)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes L. A., Baker L. E. The specific resistance of biological material--a compendium of data for the biomedical engineer and physiologist. Med Biol Eng. 1967 May;5(3):271–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02474537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari R., Hällström J., Tiihonen J., Joutsiniemi S. L. Multichannel detection of magnetic compound action fields of median and ulnar nerves. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1989 Mar;72(3):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(89)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M. J., Elias P. J. On the magnetic field and the electrical potential generated by bioelectric sources in an anisotropic volume conductor. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1988 Nov;26(6):617–623. doi: 10.1007/BF02447500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer H. J. Line frequency rejection for biomedical application. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1987 Jan;34(1):68–69. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1987.326017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. C., Pilkington T. C., Morrow M. N. The effects of thoracic inhomogeneities on the relationship between epicardial and torso potentials. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1986 Mar;33(3):273–284. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1986.325711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegeman D. F., De Weerd J. P. Modelling compound action potentials of peripheral nerves in situ. I. Model description: evidence for a non-linear relation between fibre diameter and velocity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982 Oct;54(4):436–448. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(82)90207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegeman D. F., De Weerd J. P. Modelling compound action potentials of peripheral nerves in situ. II. A study of the influence of temperature. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982 Nov;54(5):516–529. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(82)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherling W. W., Crandall P. H., Cahan L. D., Barth D. S. The magnetic field of epileptic spikes agrees with intracranial localizations in complex partial epilepsy. Neurology. 1988 May;38(5):778–786. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.5.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherling W. W., Crandall P. H., Engel J., Jr, Darcey T. M., Cahan L. D., Barth D. S. The magnetic field of complex partial seizures agrees with intracranial localizations. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jun;21(6):548–558. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikswo J. P., Barach J. P., Freeman J. A. Magnetic field of a nerve impulse: first measurements. Science. 1980 Apr 4;208(4439):53–55. doi: 10.1126/science.7361105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]