Abstract
1. Both cardiovascular and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) responses to some neural inputs were examined in paralysed anaesthetized cats.
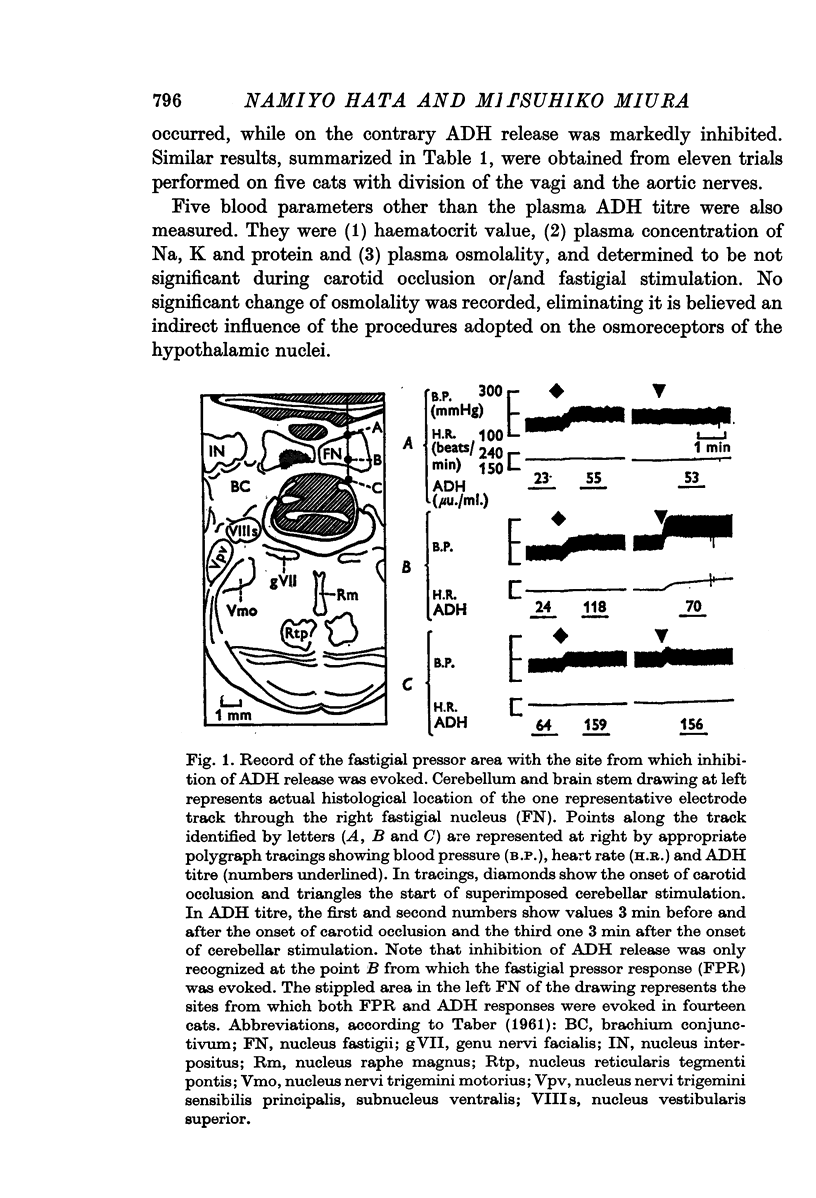
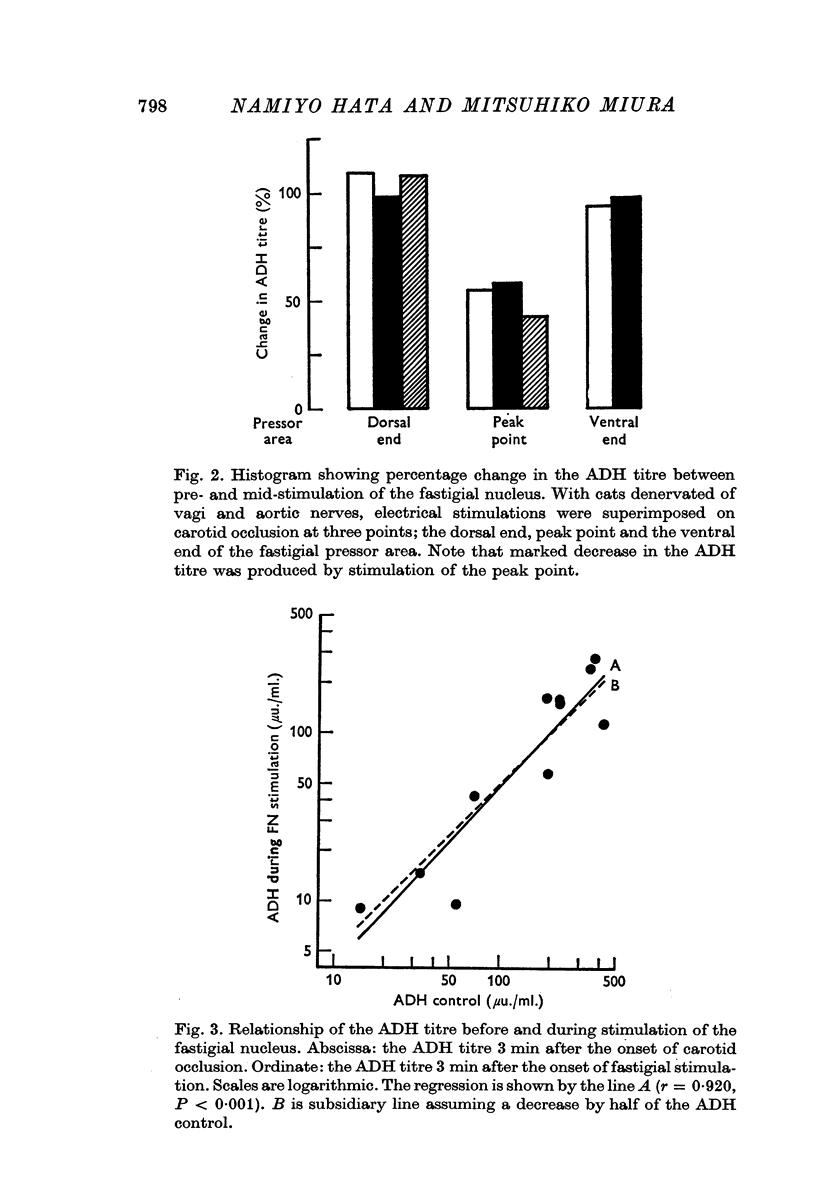
2. Carotid occlusion elicited cardiovascular responses and increased ADH secretion. When the electrical stimulation of discrete loci of the cerebellar fastigial nucleus (fastigial pressor area) was superimposed on carotid occlusion, cardiovascular responses were further facilitated, while ADH secretion was inhibited.
3. The fastigial stimulation alone elicited facilitory cardiovascular responses composed of hypertension and tachycardia, and the fastigial pressor response (FPR), but did not evoke any consistent ADH response.
4. These facts indicate that cerebellar modulation of ADH secretion occurs not directly via the hypothalamo-hypophysial system but through the lower brain stem to which both carotid sinus nerves and outflows from the fastigial pressor area project.
5. We conclude that the fastigial pressor area is specific for not only cardiovascular and other autonomic responses but pituitary hormonal response.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achari N. K., Downman C. B. Autonomic effector responses to stimulation of nucleus fastigius. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):637–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZACZKES J. W., KLEEMAN C. R., KOENIG M. PHYSIOLOGIC STUDIES OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE BY ITS DIRECT MEASUREMENT IN HUMAN PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1625–1640. doi: 10.1172/JCI105038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. J., Silva MR Jr E. An afferent pathway for the selective release of vasopressin in response to carotid occlusion and haemorrhage in the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):529–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doba N., Reis D. J. Cerebellum: role in reflex cardiovascular adjustment to posture. Brain Res. 1972 Apr 28;39(2):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doba N., Reis D. J. Changes in regional blood flow and cardiodynamics evoked by electrical stimulation of the fastigial nucleus in the cat and their similarity to orthostatic reflexes. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):729–747. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUER O. H., HENRY J. P. Circulatory basis of fluid volume control. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jul;43:423–481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauer O. H., Henry J. P., Behn C. The regulation of extracellular fluid volume. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:547–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauer O. H., Tata P. S. Vasopressin studies in the rat. II. The amount of water reabsorbed by the rat kidney after a single i.v. injection of vasopressin: the vasopressin water equivalent. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;290(4):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauer O. H., Tata P. S. Vasopressin studies in the rat. IV. The vasopressin-water-equivalent and vasopressin clearance by the kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;298(3):241–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00362602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. C., Spyer K. M. Inhibition of ADH release by stimulation of afferent cardiac branches of the right vagus in cats. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):15P–16P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Moore W. W., Segar W. E. Small changes in left atrial pressure and plasma antidiuretic hormone titers in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):210–214. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. M., Schlapp W. The action and fate of injected posterior pituitary extracts in the decapitated cat. J Physiol. 1936 Jul 21;87(2):144–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I. Integrative neural cardiovascular control. Physiol Rev. 1971 Apr;51(2):312–367. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUSON H. D., BOCANEGRA M. Clearance of exogenous vasopressin from plasma of dogs. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:493–497. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. A blood pressure response from fastigial nucleus and its relay pathway in brainstem. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1330–1336. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. Cerebellum: a pressor response elicited from the fastigial nucleus and its efferent pathway in brainstem. Brain Res. 1969 May;13(3):595–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. The paramedian reticular nucleus: a site of inhibitory interaction between projections from fastigial nucleus and carotid sinus nerve acting on blood pressure. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):441–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan M. A. Vasomotor projections of the nucleus fastigii to the medulla. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90628-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis D. J., Doba N., Nathan M. A. Predatory attack, grooming, and consummatory behaviors evoked by electrical stimulation of cat cerebellar nuclei. Science. 1973 Nov 23;182(4114):845–847. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4114.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe C. F., Johnson J. A., Moore W. W. Continuous measurement of conductivity of biological fluids. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Dec;23(6):1010–1013. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.6.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARE L. Acute reduction in extracellular fluid volume and the concentration of antidiuretic hormone in blood. Endocrinology. 1961 Nov;69:925–933. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-5-925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARE L. EFFECTS OF CAROTID OCCLUSION AND LEFT ATRIAL DISTENTION ON PLASMA VASOPRESSIN TITER. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:219–223. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARE L., LEVY M. N. Cardiovascular receptors and blood titer of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Physiol. 1962 Sep;203:425–428. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARE L. Rate of disappearance of arginine vasopressin from circulating blood in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1962 Dec;203:1179–1181. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Share L., Claybaugh J. R. Regulation of body fluids. Annu Rev Physiol. 1972;34:235–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.34.030172.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABER E. The cytoarchitecture of the brain stem of the cat. I. Brain stem nuclei of cat. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Feb;116:27–69. doi: 10.1002/cne.901160104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS D. M., KAUFMAN R. P., SPRAGUE J. M., CHAMBERS W. W. Experimental studies of the vermal cerebellar projections in the brain stem of the cat (fastigiobulbar tract). J Anat. 1956 Jul;90(3):371–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN H., BERNE R. M., SACHS H. Vasopressin in blood: effect of hemorrhage. Endocrinology. 1960 May;66:712–718. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-5-712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA S., MOTOHASHI K., IBAYASHI H., OKINAKA S. METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN PLASMA WITH A NOTE ON THE ANTIDIURETIC TITER OF HUMAN PLASMA. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Aug;62:279–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZANCHETTI A., ZOCCOLINI A. Autonomic hypothalamic outbursts elicited by cerebellar stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Sep;17(5):475–483. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


