Abstract
1. Foetal breathing movements, electrocortical activity, arterial pressure and heart rate were recorded continuously in chronically catheterized sheep, 97-145 days pregnant.
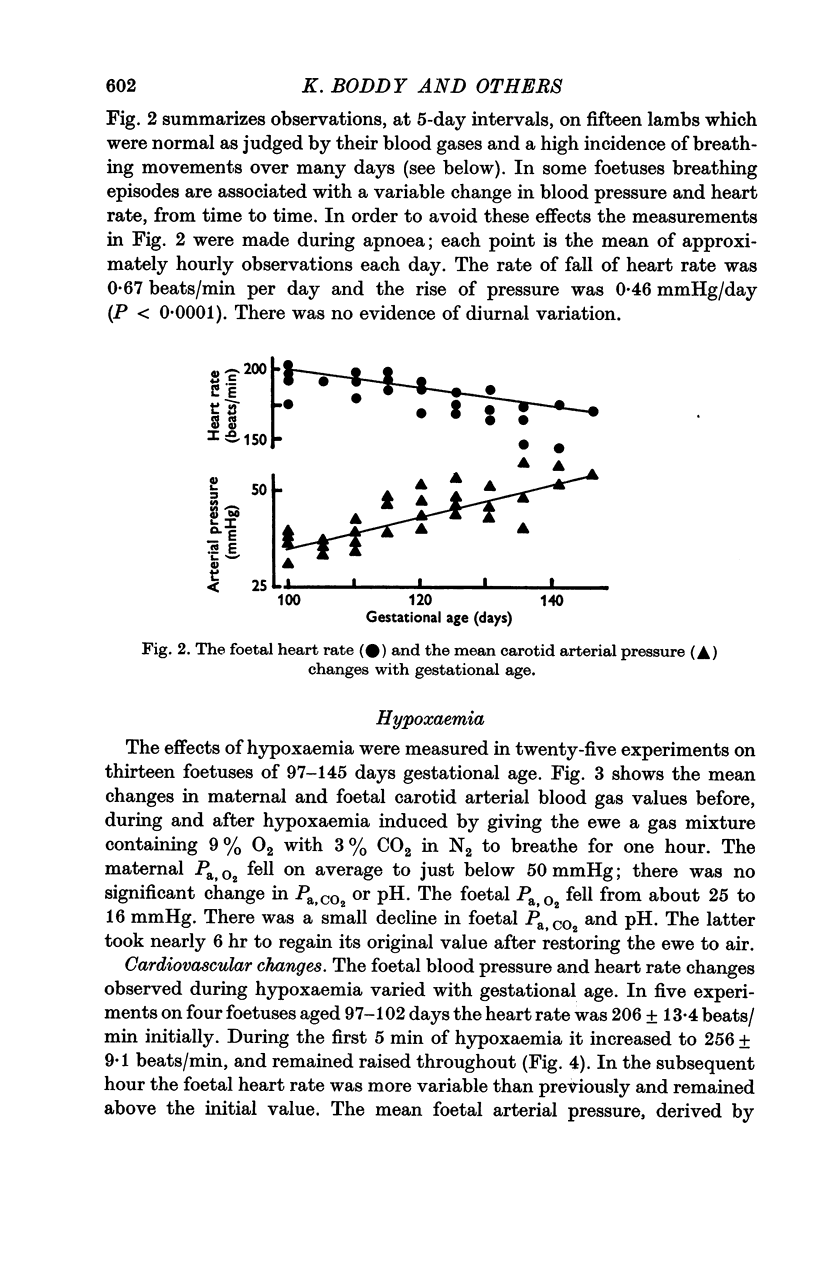
2. With increasing gestational age there was a fall in heart rate of 0·67 beats/day and a rise in arterial pressure of 0·46 mmHg/day.
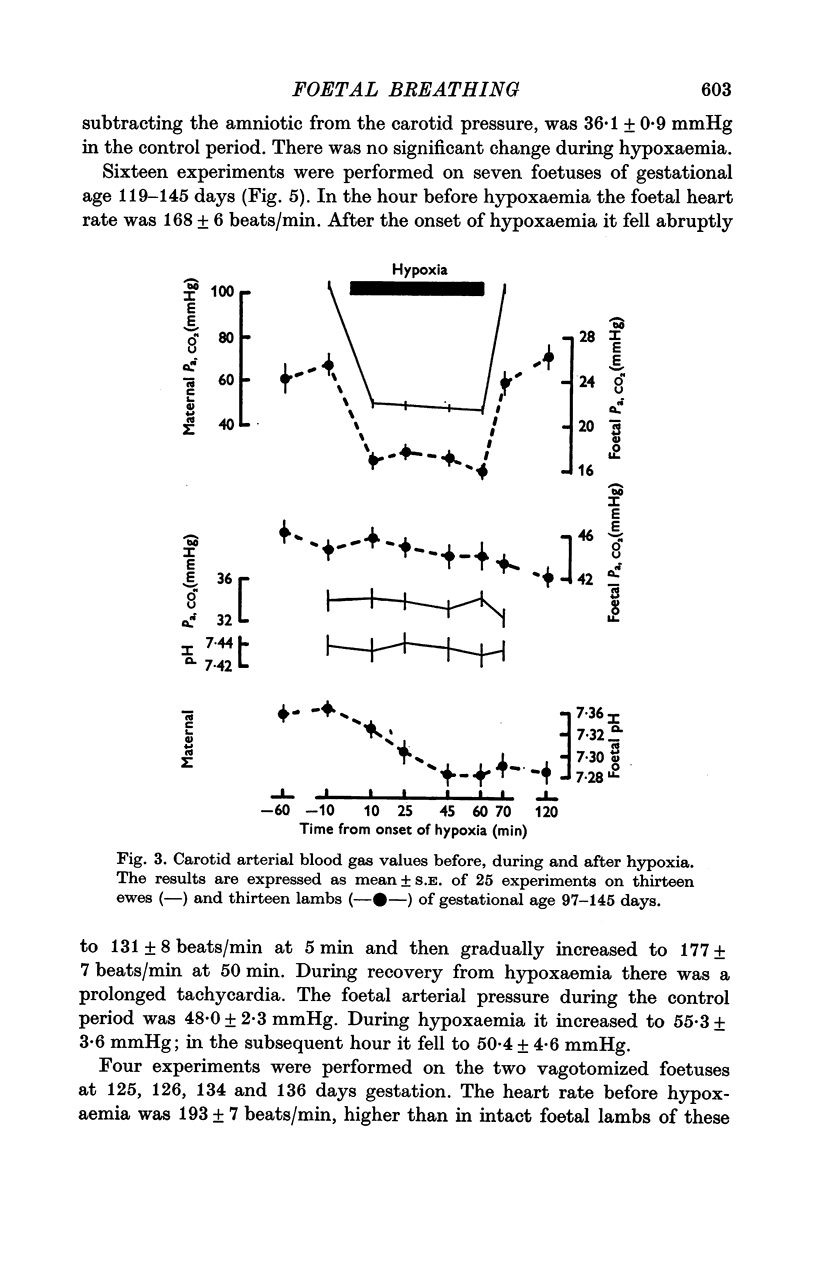
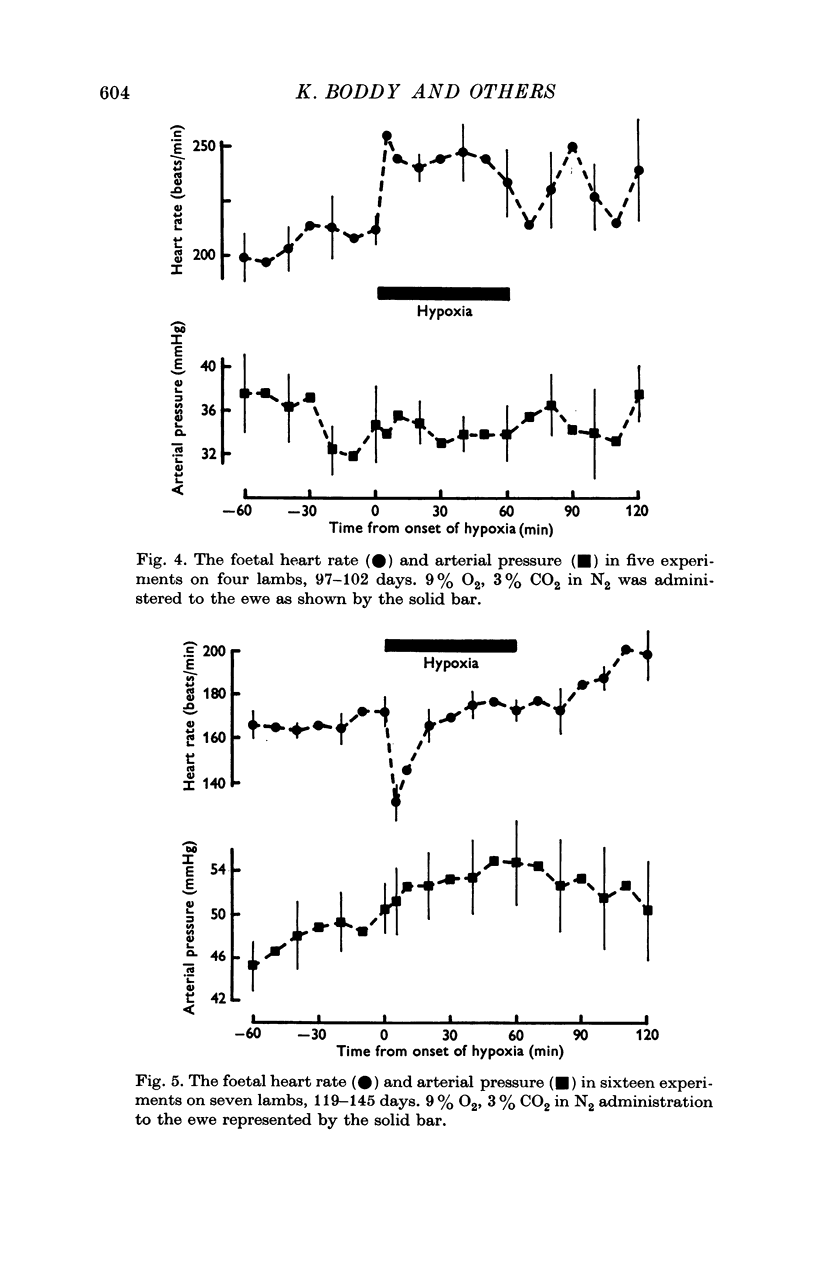
3. Hypoxaemia in the foetus was induced by allowing the ewe to breathe low oxygen mixtures, 9% O2 with 3% CO2 in N2. In the younger foetuses there was an initial rise in heart rate whereas in the older foetuses there was a fall. After the end of hypoxia there was a persistent tachycardia in both groups. In the older foetuses there was a rise of arterial pressure.
4. Two vagotomized older foetuses showed cardiovascular responses similar to those of the younger foetuses.
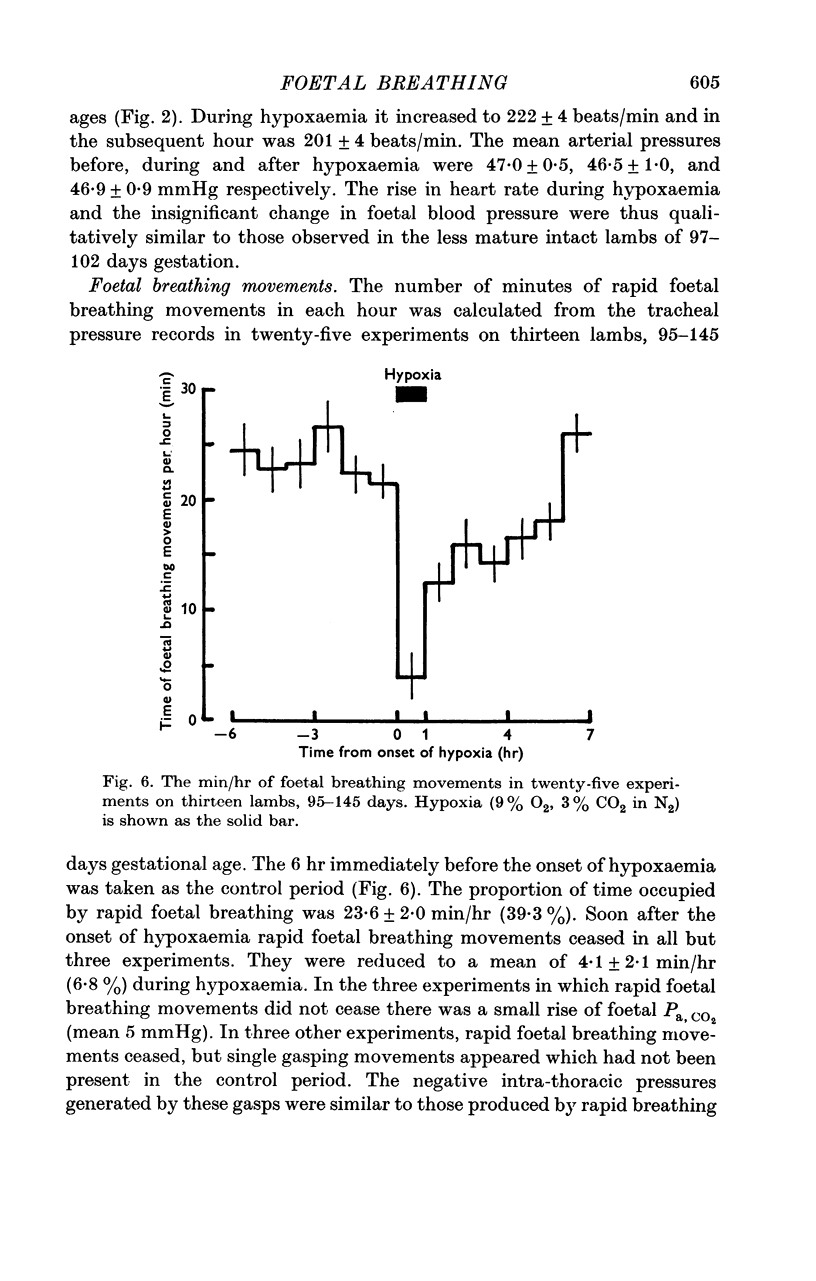
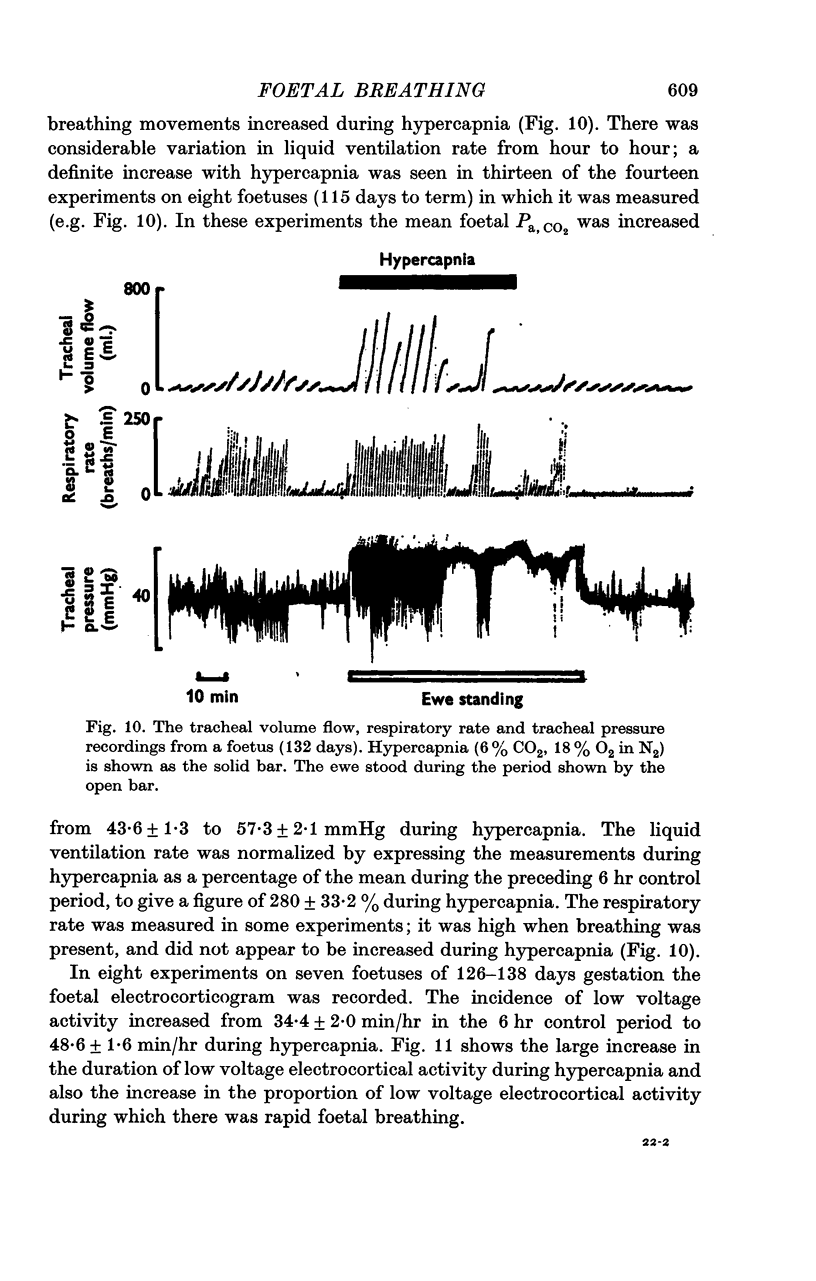
5. Foetal breathing movements were abolished by hypoxaemia in twenty-two of twenty-five experiments. In the three exceptional experiments there was a small rise in Pa, CO2.
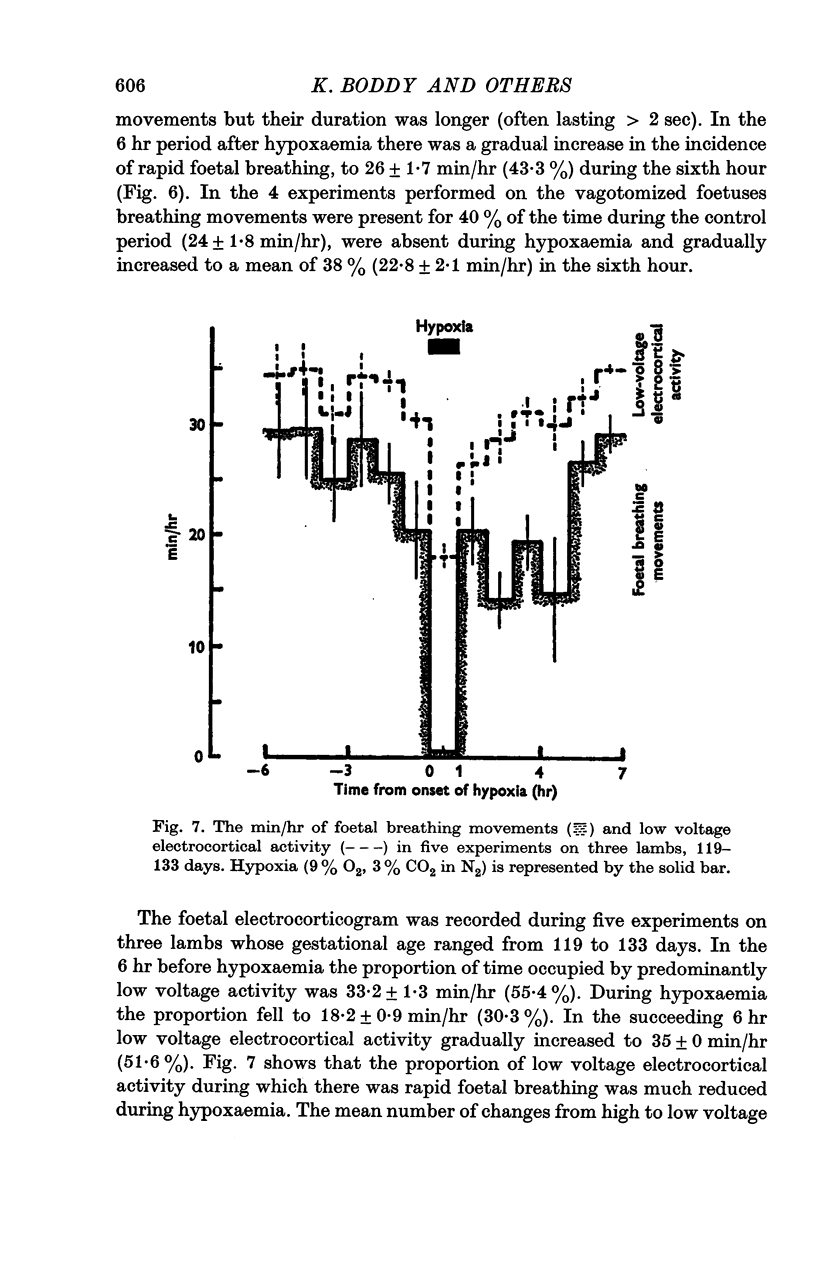
6. The proportion of time occupied by low voltage electrocortical activity in the foetus was reduced by hypoxaemia.
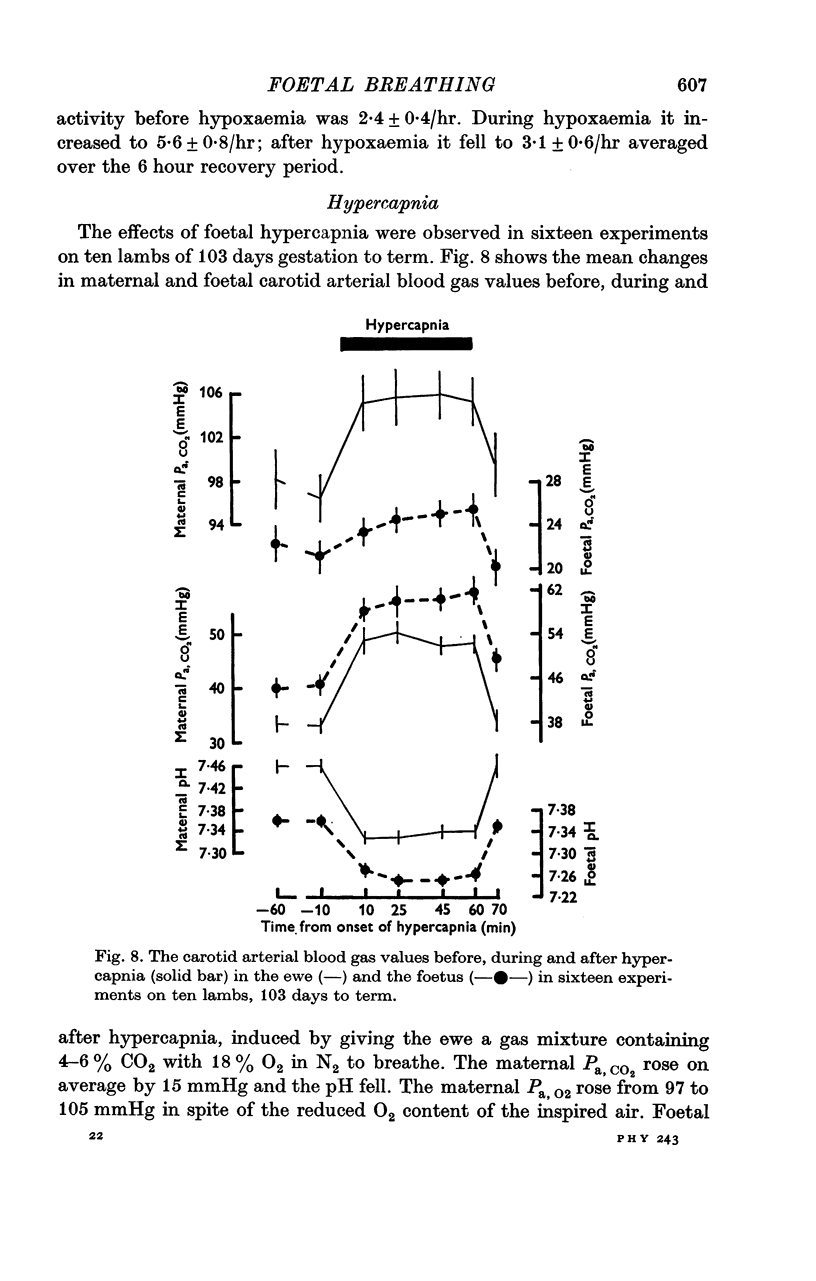
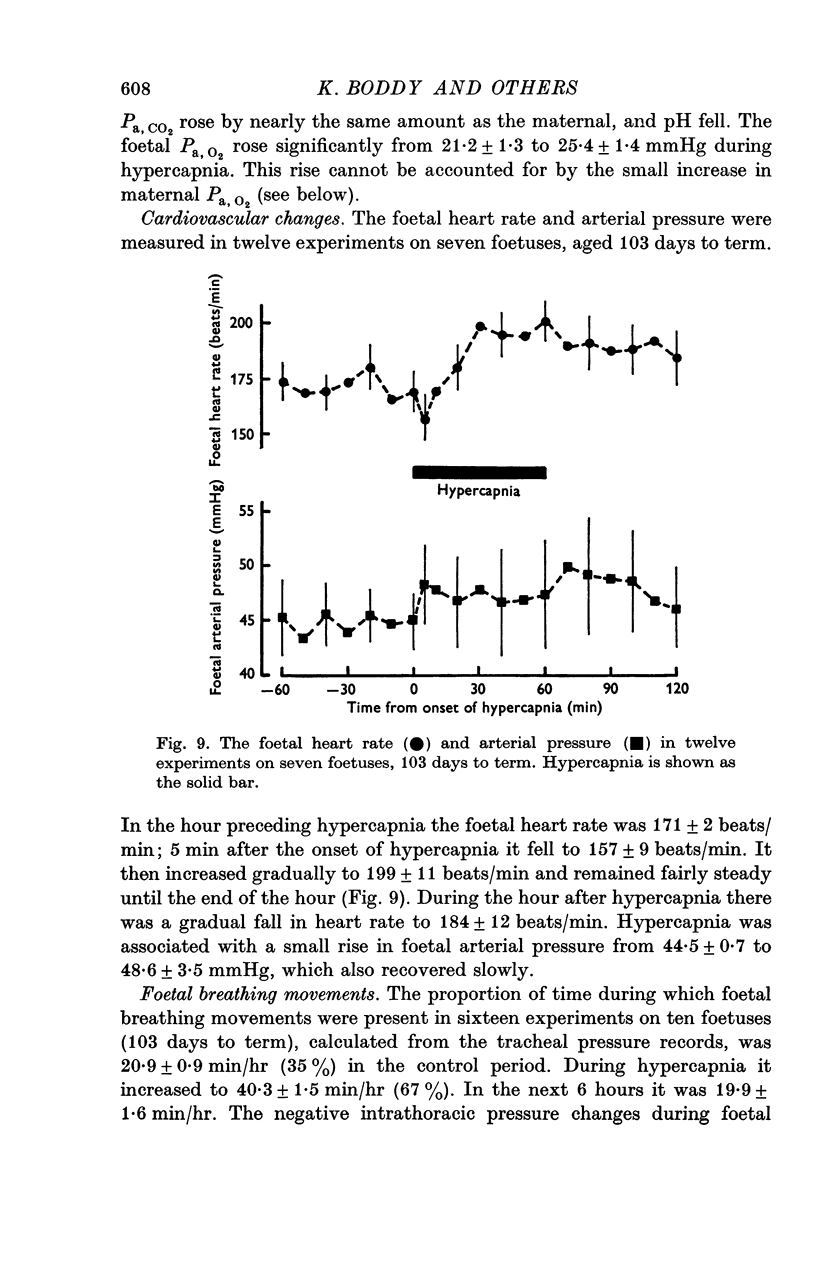
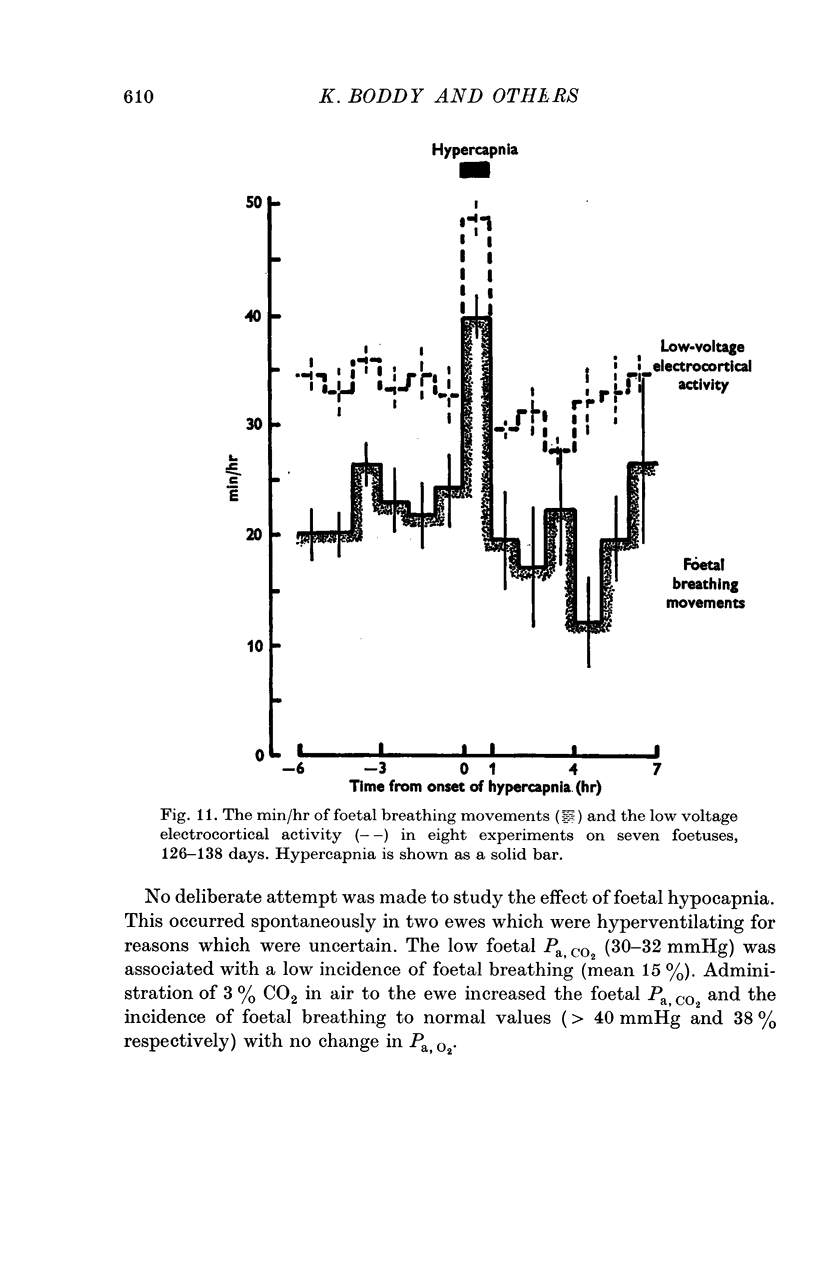
7. Hypercapnia was induced by giving the ewe 4-6% CO2 with 18% O2 in N2 to breathe. After an initial slight fall the foetal heart rate increased and there was a small rise in foetal arterial pressure.
8. The proportion of time occupied by low voltage electrocortical activity and breathing movements was increased by hypercapnia.
9. Maternal hyperoxia, induced by giving 50% O2 in N2, did not significantly increase foetal breathing movements unless the ewe was in labour. In labour the foetuses had lower Pa, O2 values initially and a reduced incidence of foetal breathing, both of which were increased by maternal hyperoxia.
Full text
PDF

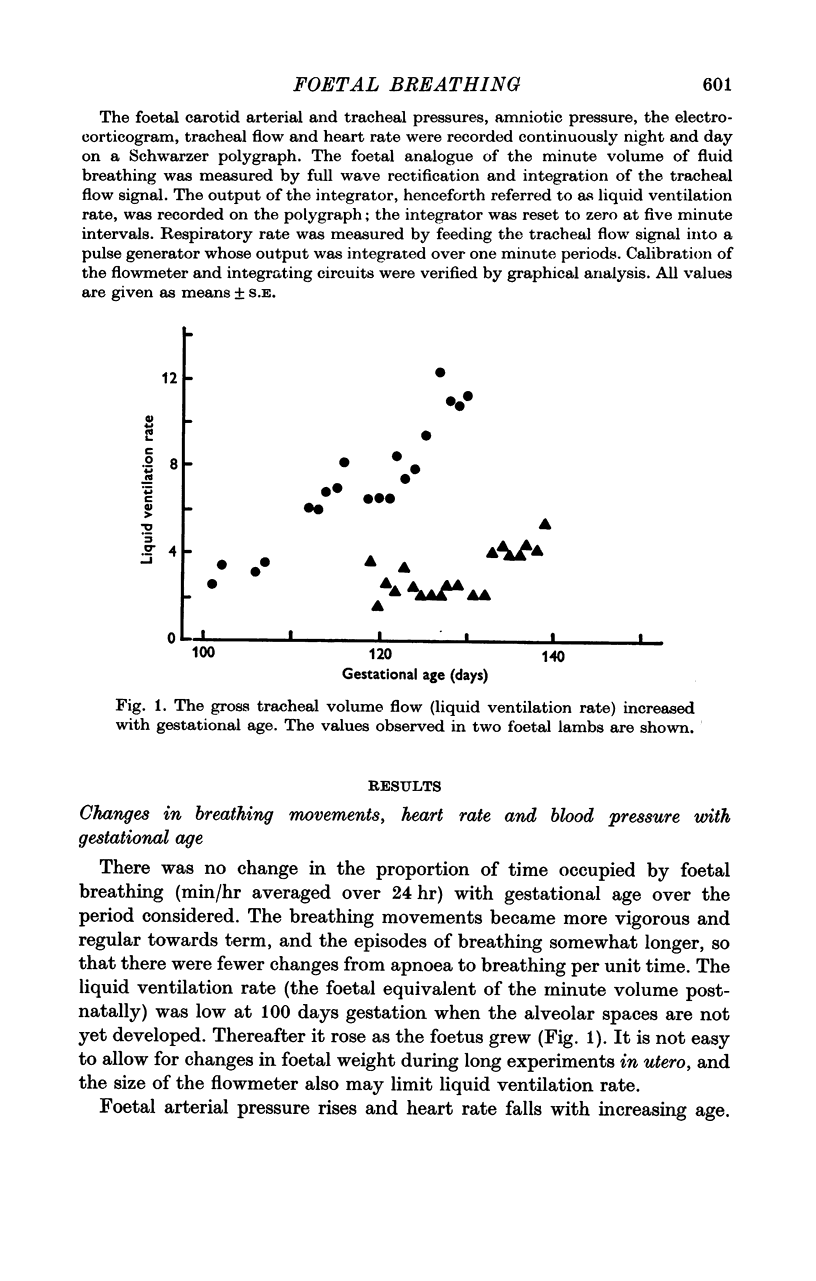








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMSONS K., Jr Breathing and the thermal environment in young rabbits. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:144–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLATTEIS C. M. HYPOXIA AND THE METABOLIC RESPONSE TO COLD IN NEW-BORN RABBITS. J Physiol. 1964 Aug;172:358–368. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Purves M. J. Carotid body chemoreceptor activity in the new-born lamb. J Physiol. 1967 Jun;190(3):443–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Purves M. J., Sampson S. R. Types of nervous activity which may be recorded from the carotid sinus nerve in the sheep foetus. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Jones C. T., Mantell C., Ratcliffe J. G., Robinson J. S. Changes in plasma ACTH and corticosteroid of the maternal and fetal sheep during hypoxia. Endocrinology. 1974 Feb;94(2):588–591. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-2-588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Mantell C. D. Observations of fetal breathing movements transmitted through maternal abdominal wall. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1219–1220. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Robinson J. S. External method for detection of fetal breathing in utero. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1231–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMLINE R. S., SILVER I. A., SILVER M. FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE STIMULATION OF THE ADRENAL MEDULLA DURING ASPHYXIA IN THE FOETAL LAMB. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:211–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMLINE R. S., SILVER M. The release of adrenaline and noradrenaline from the adrenal glands of the foetal sheep. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:424–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS K. W., DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C. Anoxia, oxygen consumption and cardiac output in new-born lambs and adult sheep. J Physiol. 1959 May 19;146(2):316–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. G., Dawes G. S., Fishman A. P., Hyman A. I. Regional redistribution of blood flow in the mature fetal lamb. Circ Res. 1967 Aug;21(2):229–235. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C. Reflex respiratory activity in the new-born rabbit. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):85–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Duncan S. L., Lewis B. V., Merlet C. L., Owen-Thomas J. B., Reeves J. T. Cyanide stimulation of the systemic arterial chemoreceptors in foetal lambs. J Physiol. 1969 Mar;201(1):117–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Duncan S. L., Lewis B. V., Merlet C. L., Owen-Thomas J. B., Reeves J. T. Hypoxaemia and aortic chemoreceptor function in foetal lambs. J Physiol. 1969 Mar;201(1):105–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Fox H. E., Leduc B. M., Liggins G. C., Richards R. T. Respiratory movements and rapid eye movement sleep in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):119–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnihoo D. R., Quilligan E. J. Carotid blood flow distribution in the in utero sheep fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Jul 1;116(5):648–656. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(15)33129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman W. F. The intrinsic physiologic properties of the developing heart. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(1):87–111. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(72)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann L. I., Prichard J. W., Symmes D. The effect of glucose loading on the fetal response to hypoxia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Jun 15;107(4):610–618. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33949-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlet C., Hoerter J., Devilleneuve C., Tchobroutsky C. Mise en évidence de mouvements respiratoires chez le foetus d'agneau in utero au cours du dernier mois de la gestation. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 May 20;270(20):2462–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves M. J. The effects of hypoxia in the new-born lamb before and after denervation of the carotid chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):60–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinebourne E. A., Vapaavuori E. K., Williams R. L., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Development of baroreflex activity in unanesthetized fetal and neonatal lambs. Circ Res. 1972 Nov;31(5):710–718. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.5.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


