Abstract
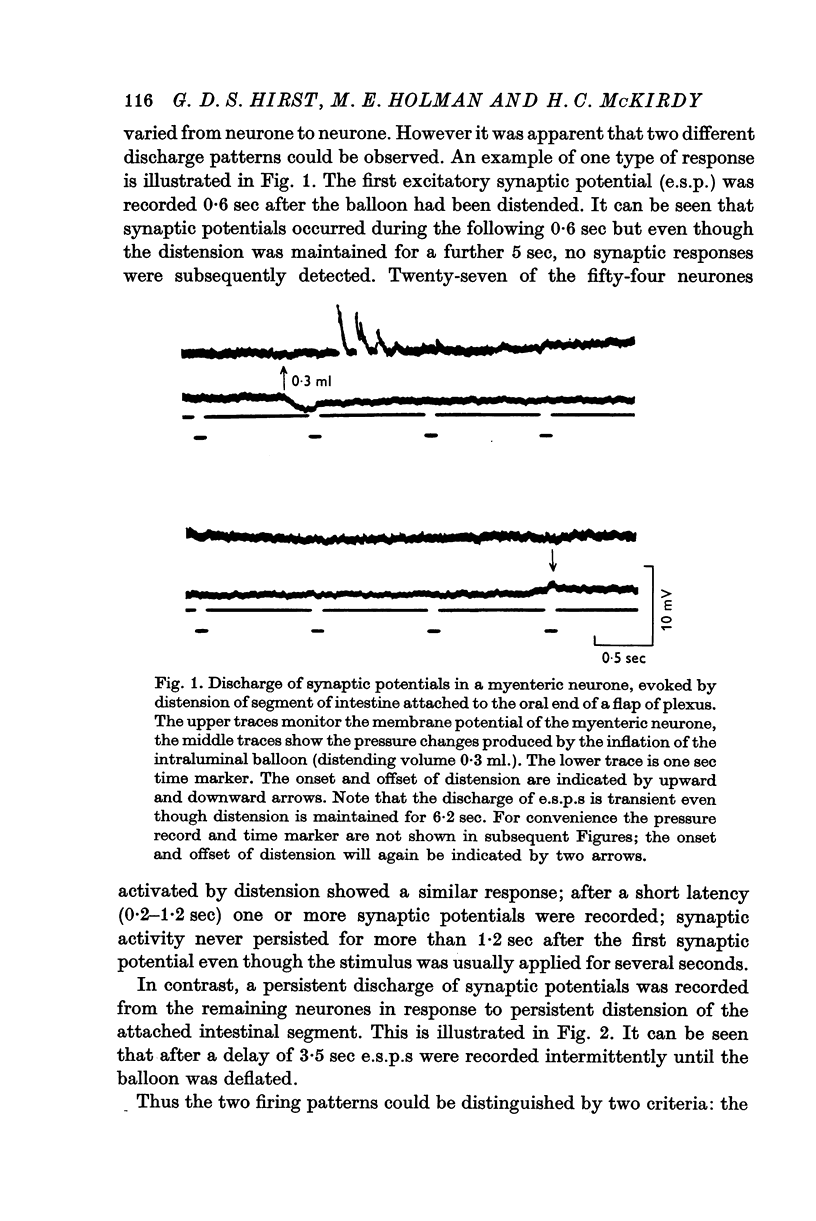
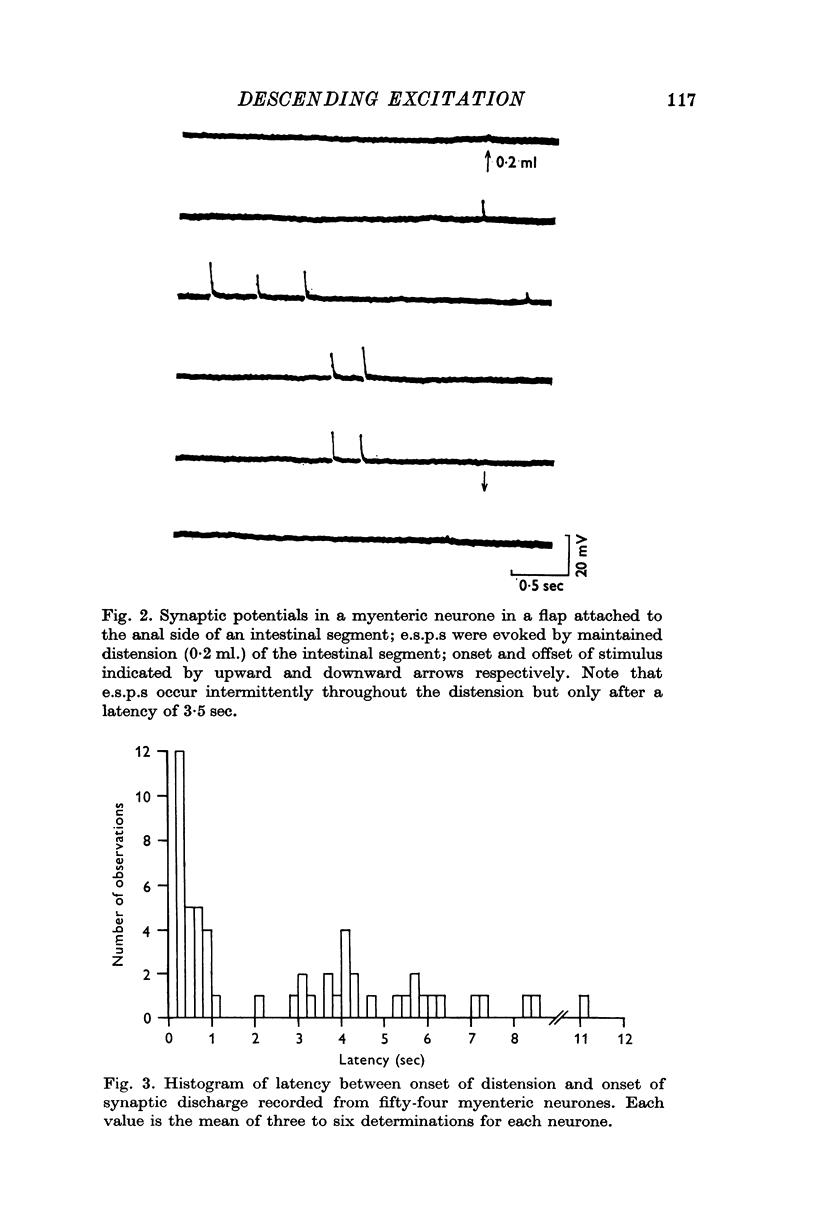
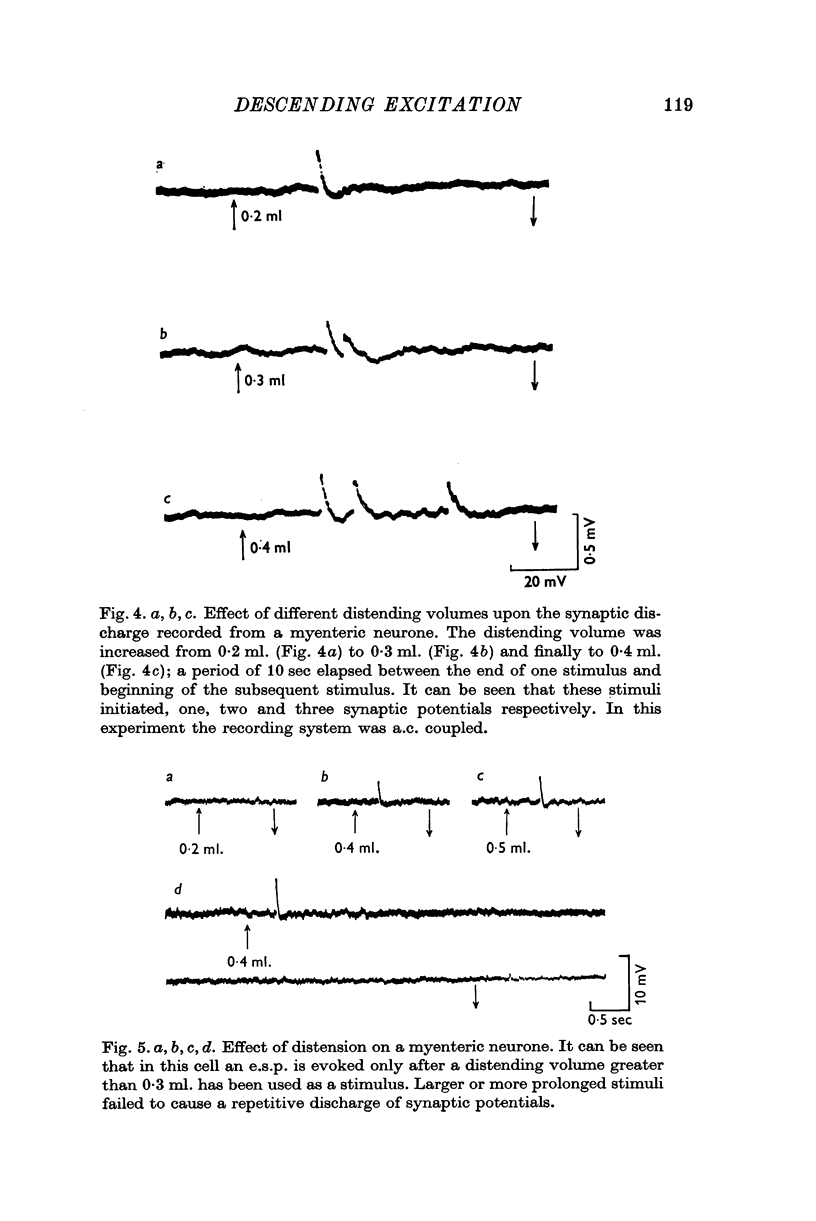
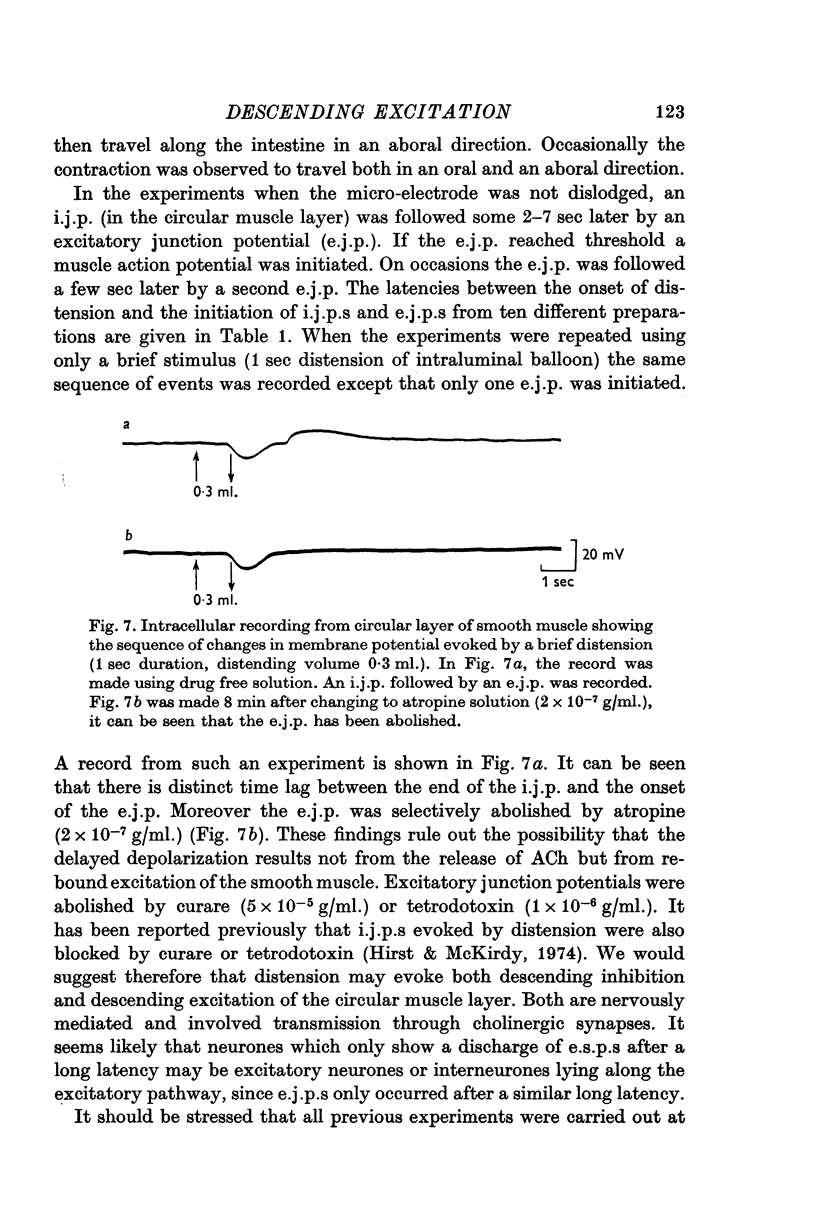
1. Intracellular recordings were made from myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig small intestine in preparations which had a synaptic input from an orally situated segment of intestine. 2. Excitatory synaptic potentials could be evoked in most neurones by distension of the attached intestinal segment. 3. It was possible to distinguish two distinct firing patterns of synaptic potentials in response to distension. A transient short latency discharge was recorded from some neurones. From the others, a persistent synaptic discharge was recorded only after a long latency (2-11 sec). 4. Distension of intestinal segments evoked short latency transient inhibitory junction potentials in the circular muscle layer followed by excitatory junction potentials in both the circular and longitudinal muscle layers. 5. It is suggested that distension may cause both descending inhibition and, after a delay, descending excitation of the guinea-pig small intestine.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The movements and innervation of the small intestine. J Physiol. 1899 May 11;24(2):99–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1899.sp000752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G. Innervation of the intestinal muscular coat. J Neurocytol. 1972 Dec;1(4):341–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01102939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUKUHARA T., YAMAGAMI M., NAKAYAMA S. On the intestinal intrinsic reflexes. Jpn J Physiol. 1958 Mar 30;8(1):9–20. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.8.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. A nervous mechanism for descending inhibition in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):129–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Osa T., Toida N. Electrophysiological study of the intestinal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):239–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


