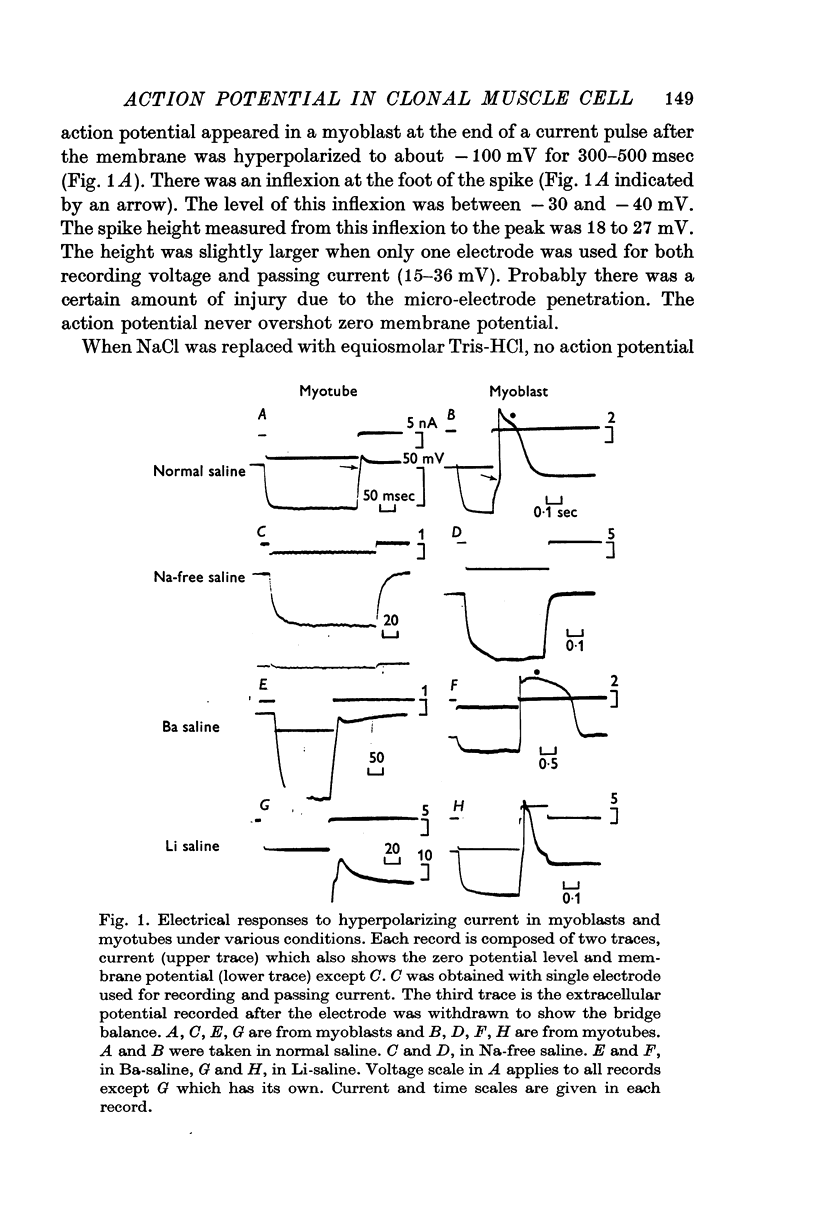
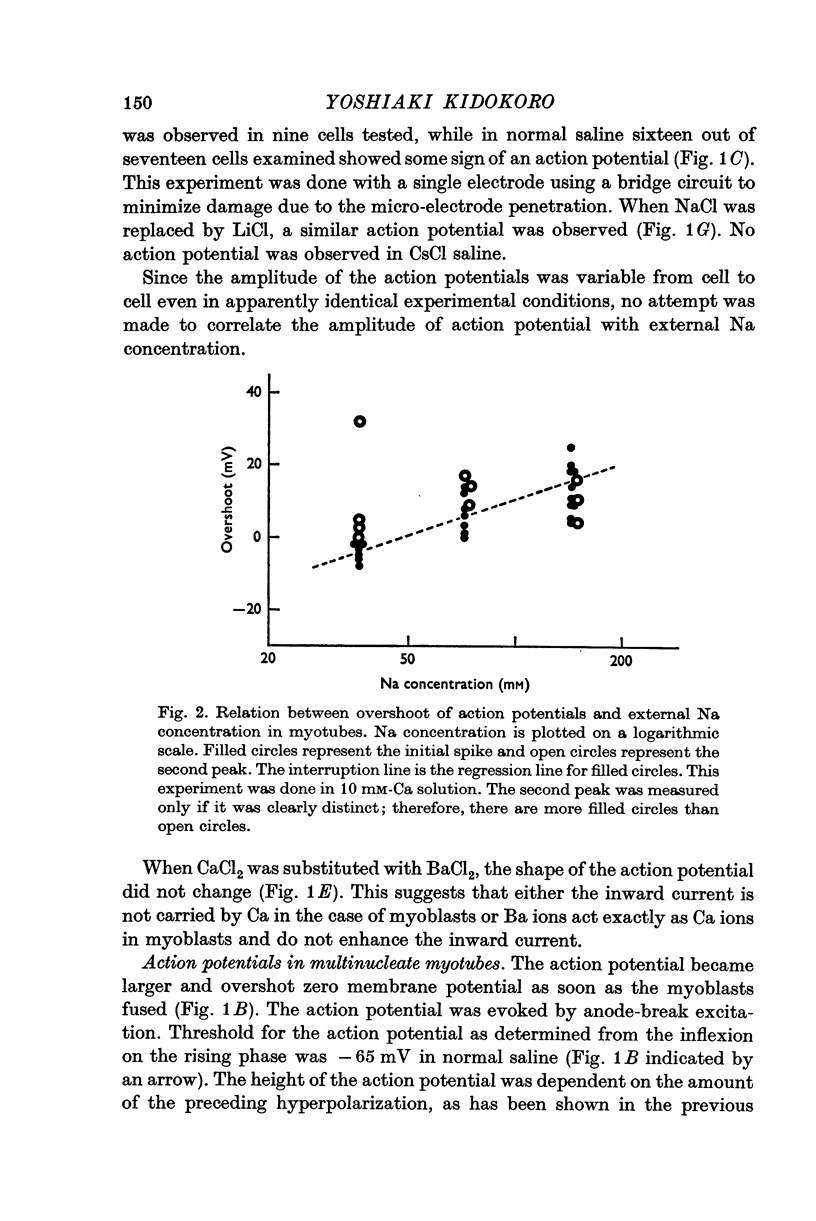
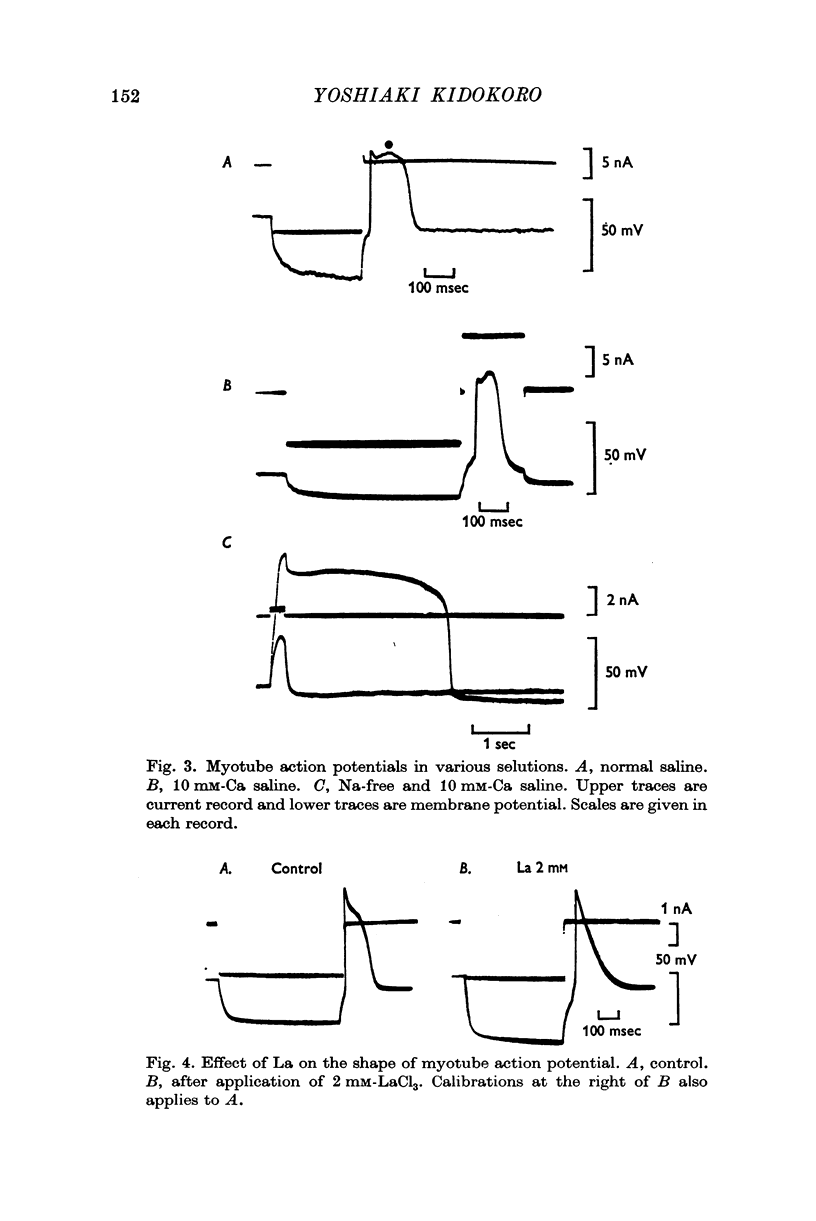
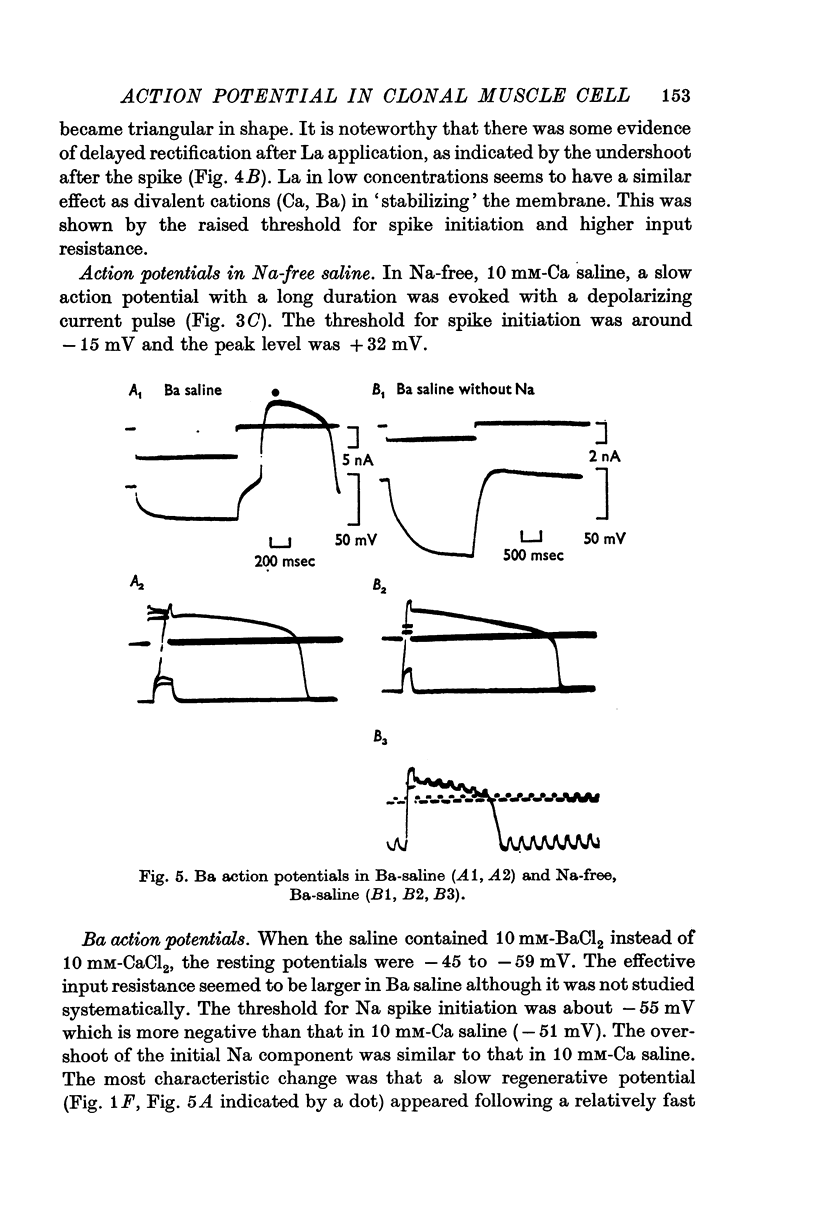
Abstract
1. Developmental changes in action potential properties were studied in a clonal rat skeletal muscle cell line. 2. Small action potentials were evoked in mononucleate myoblasts. No spike was seen in Na-free saline. A similar spike was evoked in a medium where all NaCl was replaced by LiCl. No spike was evoked when NaCl was replaced by CsCl. 3. Action potentials overshot zero membrane potential in multinucleate myotubes. The action potential was composed of two components, an initial fast spike and a hump on the falling phase or in some cases a distinct second peak. 4. Teh overshoot of the initial fast spike decreased when the external Na concentration was decreased. 5. In saline with 10 mM-Ca the second component often formed a distinct peak following the initial fast spike. A slow regenerative potential was evoked in Na-free media with a depolarizing current pulse. 6. In saline containing BaCl-2 instead of CaCl-2 there was always a second peak, the overshoot of which changed with external Ba concentration. A slow regenerative potential was evoked in Na-free, Ba-saline. The membrane conductance at the peak of the Ba-action potential was larger than in the resting state. 7. In adult rat skeletal muscle, the shape of the action potential was not changed when Ca was replaced by Ba. No action potential was evoked in Na-free Ba-saline or Ba-saline with tetrodotoxin (3 times 10-7 M). 8. The significance of the Ca component in the developing muscle is discussed.
Full text
PDF





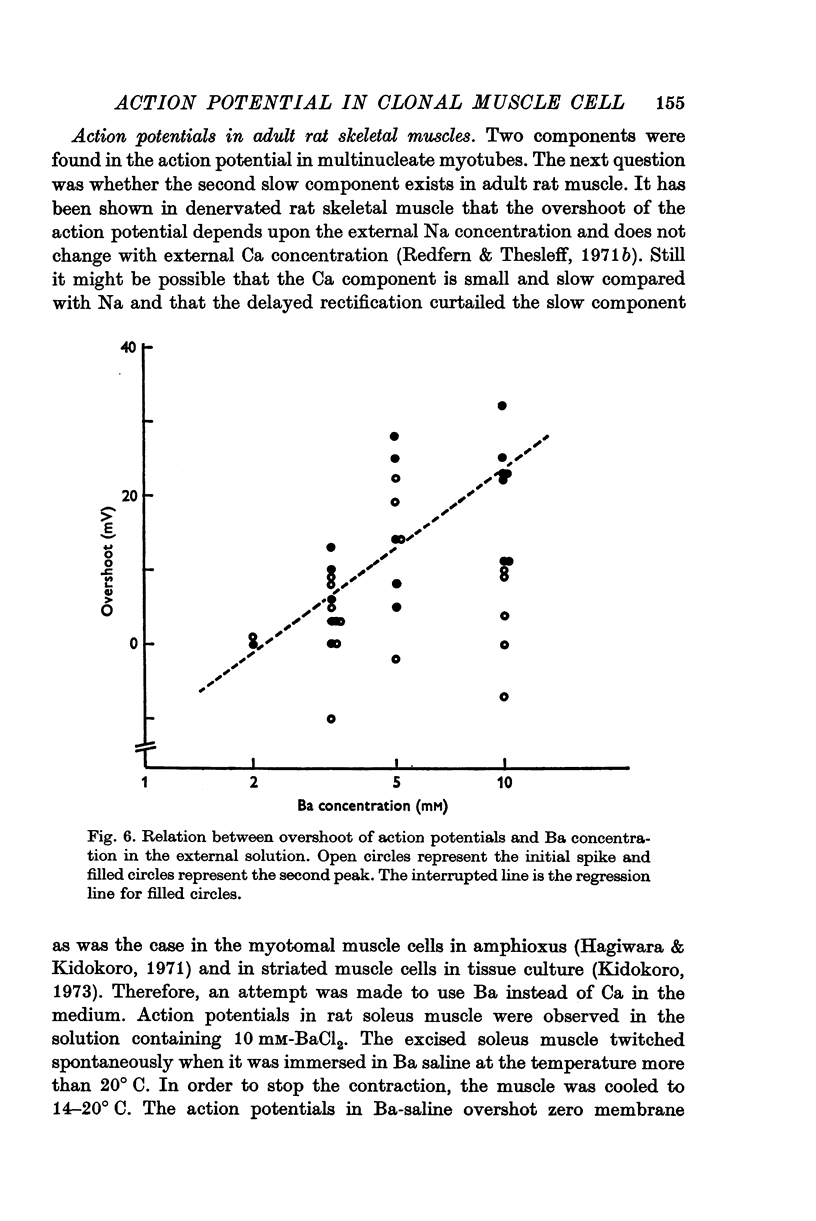
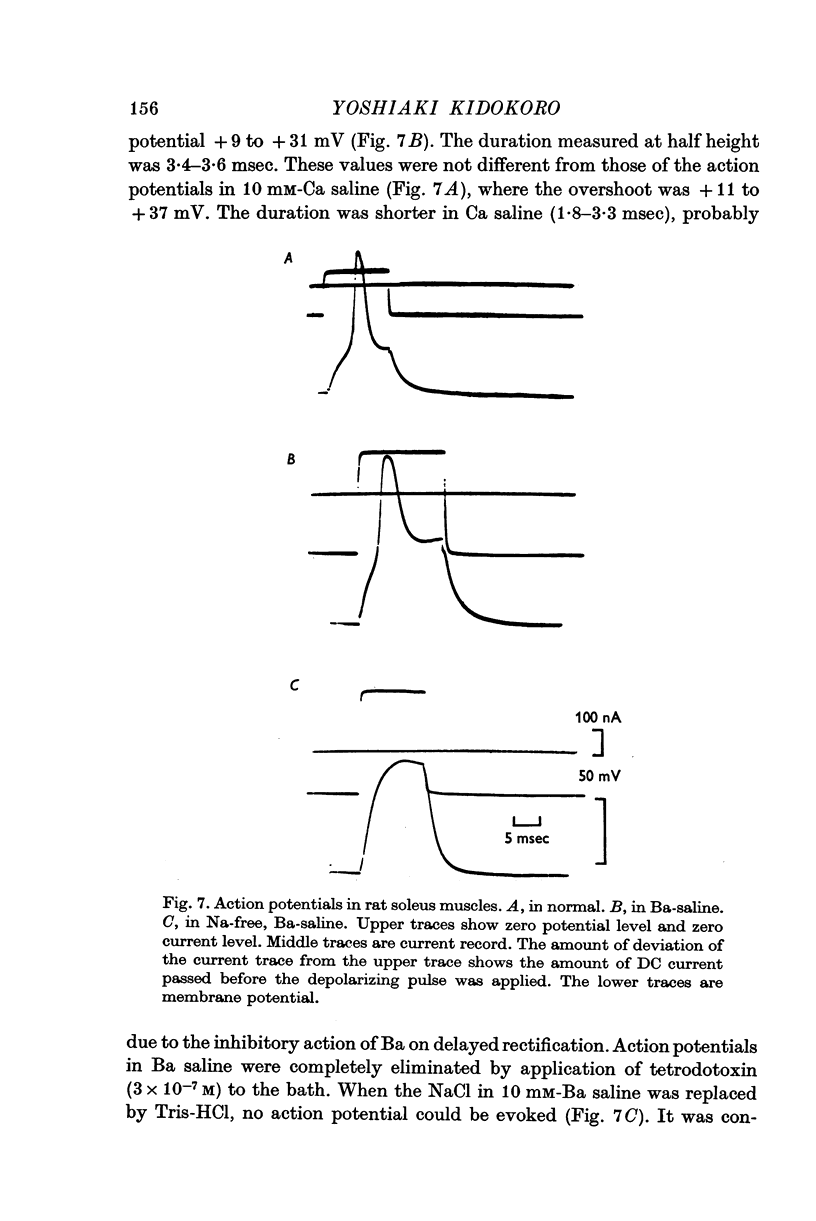



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., NAKA K. I. THE INITIATION OF SPIKE POTENTIAL IN BARNACLE MUSCLE FIBERS UNDER LOW INTRACELLULAR CA++. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:141–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y. Na and Ca components of action potential in amphioxus muscle cells. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):217–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Development of action potentials in a clonal rat skeletal muscle cell line. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):158–159. doi: 10.1038/newbio241158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S. I., Takahashi K., Tsuda K. Electrical excitability in the egg cell membrane of the tunicate. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):37–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S. I., Takahashi K., Tsuda K., Yoshii M. Analysis of non-linearity observed in the current-voltage relation of the tunicate embryo. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):55–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Takahashi K., Tsuda K. Calcium and sodium contributions to regenerative responses in the embryonic excitable cell membrane. Science. 1972 Jun 30;176(4042):1441–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Blaustein M. P., Anderson N. C., Narahashi T. Basis of tetrodotoxin's selectivity in blockage of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAJIMA S., IWASAKI S., OBATA K. Delayed rectification and anomalous rectification in frog's skeletal muscle membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Sep;46:97–115. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. The potassium chloride contracture of the heart and its modification by calcium. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):584–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUBEN J. P., GAINER H. Membrance conductance during depolarizing postsynaptic potentials of crayfish muscle fibres. Nature. 1962 Jan 13;193:142–143. doi: 10.1038/193142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Miyazaki S. I., Kidokoro Y. Development of excitability in embryonic muscle cell membranes in certain tunicates. Science. 1971 Jan 29;171(3969):415–418. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3969.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. Graded and all-or-none electrogenesis in arthropod muscle. II. The effects of alkali-earth and onium ions on lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:997–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


