Abstract
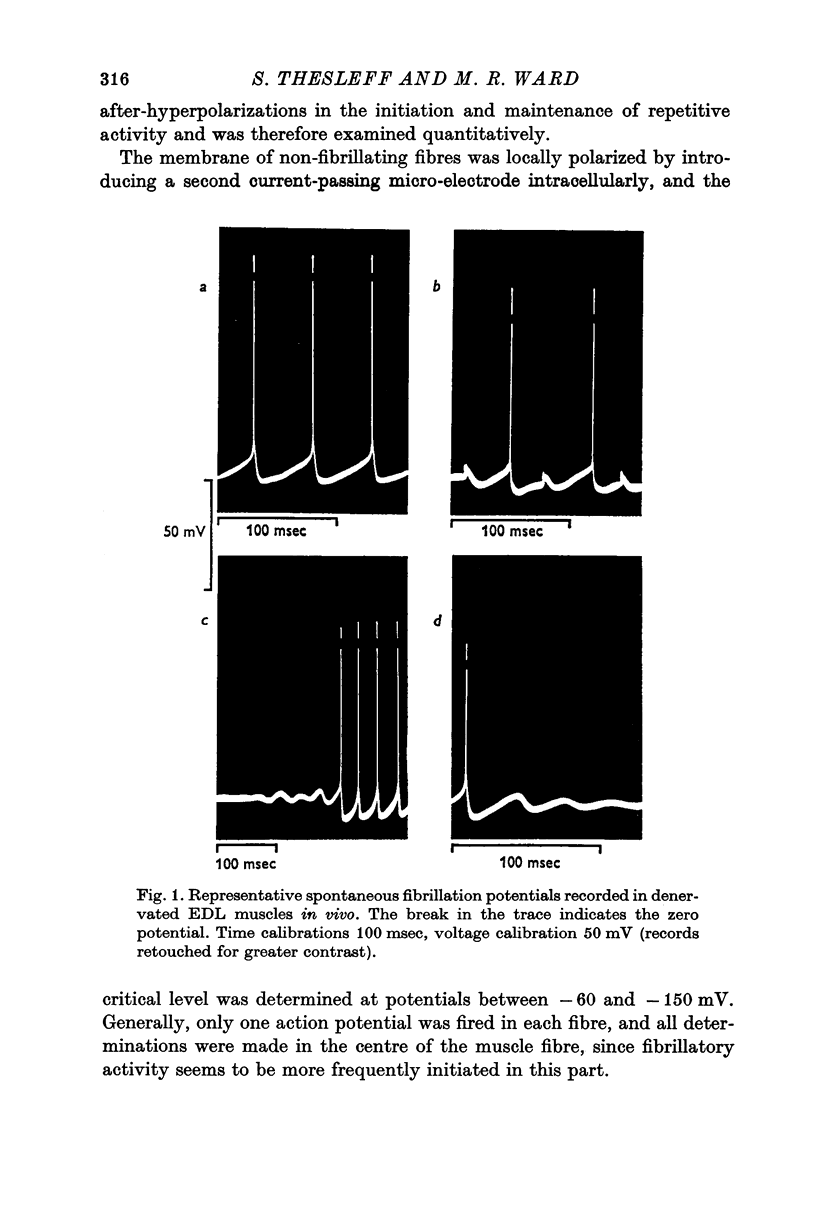
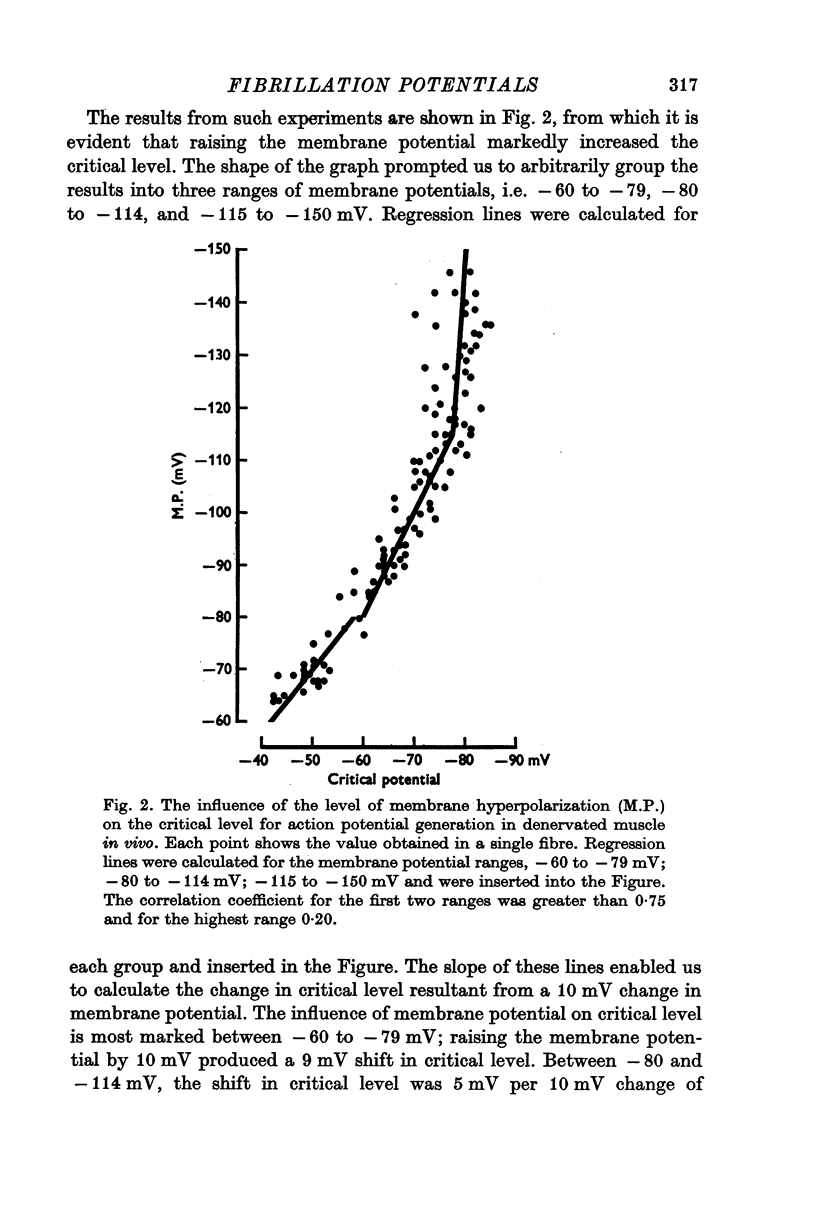
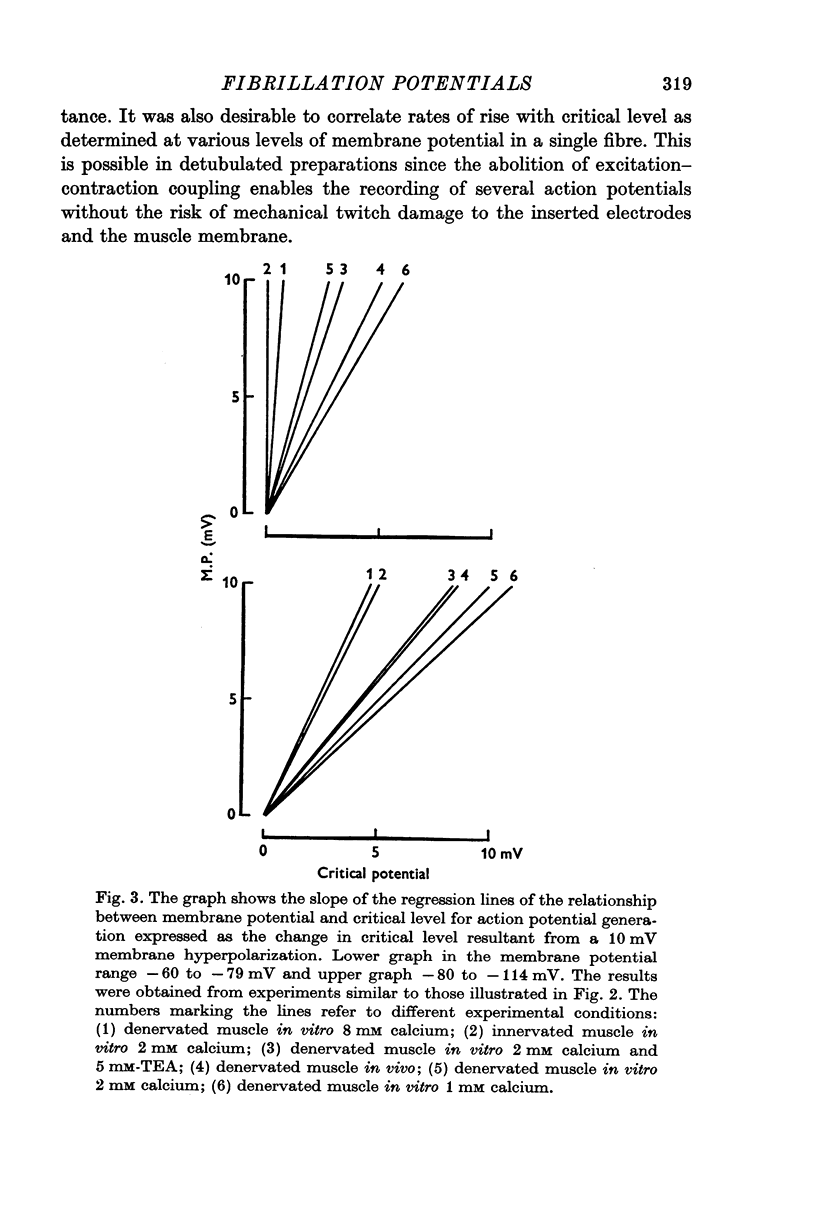
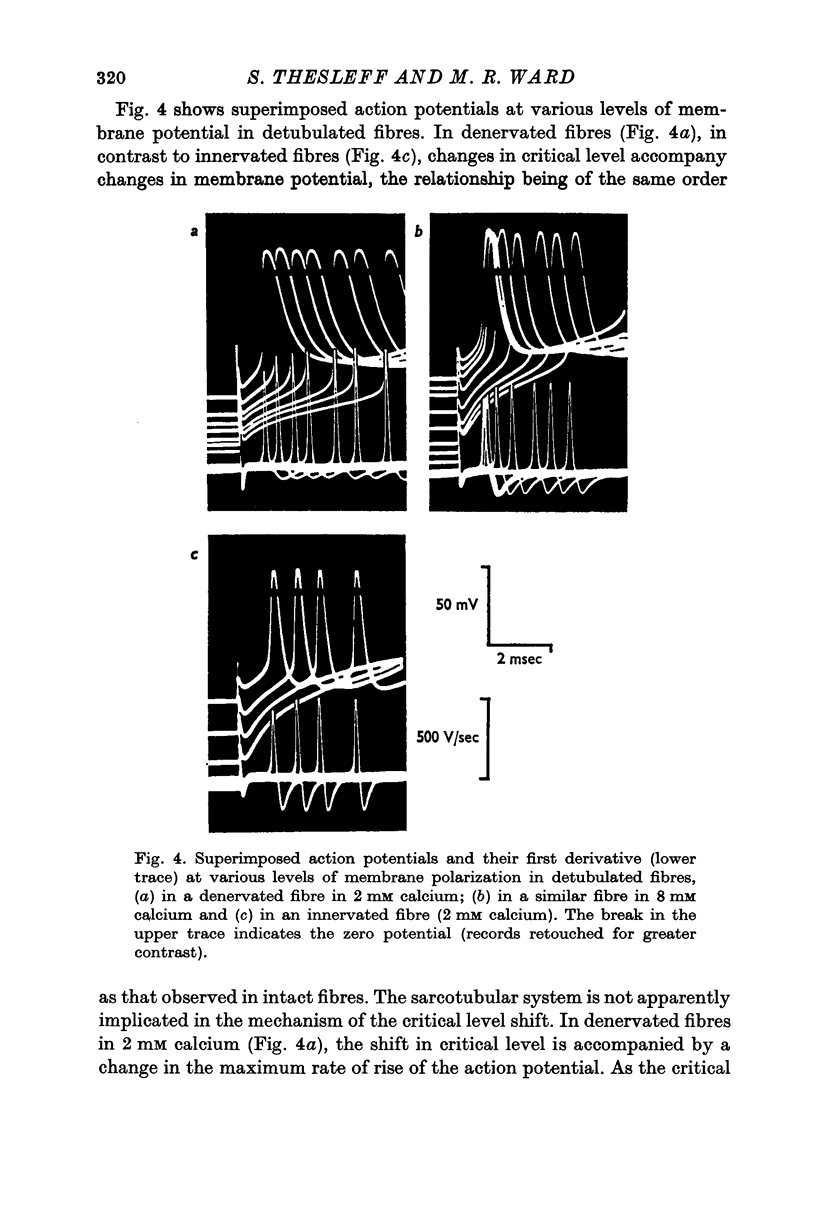
1. Intracellular electrodes were used to study the origin of fibrillation potentials in chronically denervated rat muscle. 2. Fibrillation potentials were observed to start from spontaneous biphasic membrane potential oscillations. Each action potential was followed by an after-hyperpolarization which in turn served as a pre-potential for the next spike. The critical level (threshold) for the initiation of the first spike in a train was lower than that of the next and subsequent spikes. 3. A correlation was found between the level of membrane potential and the critical level for action potential generation. This relation was most marked around the resting membrane potential (minus 60 to minus 80 mV) where 10 mV hyperpolarization caused a 9 m V increase in the critical potential level. At higher membrane potentials the correlation was less pronounced. In innervated muscles a similar correlation existed but it was less marked and was present only at membrane polarizations below the resting potential. 4. Increasing the external calcium concentration from 2 to 8 mM reduced the membrane potential-critical level relationship in denervated fibres towards that of innervated ones. 5. As critical level changes with membrane hyperpolarization, the rate of rise of the action potential increased, suggesting a progressive removal of sodium inactivation. 6. It is suggested that a mechanism similar to anode break excitation is important for the induction and maintenance of fibrillation potentials.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belmar J., Eyzaguirre C. Pacemaker site of fibrillation potentials in denervated mammmalian muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1966 May;29(3):425–441. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B., Eisenberg R. S. Selective disruption of the sarcotubular system in frog sartorius muscle. A quantitative study with exogenous peroxidase as a marker. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):451–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):245–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAUS W., LUELLMANN H., MUSCHOLL E. [Potassium flux of normal and denervated rat diaphragm]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:761–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernan R. P., McCarthy I. Effects of denervation on 42 K influx and membrane potential of rat soleus muscles measured in vivo. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):62P–63P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. W., Ward M. R. Anode break excitation in denervated rat skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):413–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchnik S., Ruarte A. C., Kotsias B. A. On the mechanism of denervatory electrical activity of single muscle fibers as tested in vivo with tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1973;23(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Sakmann B. Membrane properties underlying spontaneous activity of denervated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):125–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff S., Vyskocil F., Ward M. R. The action potential in end-plate and extrajunctional regions of rat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jun;91(2):196–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


