Abstract
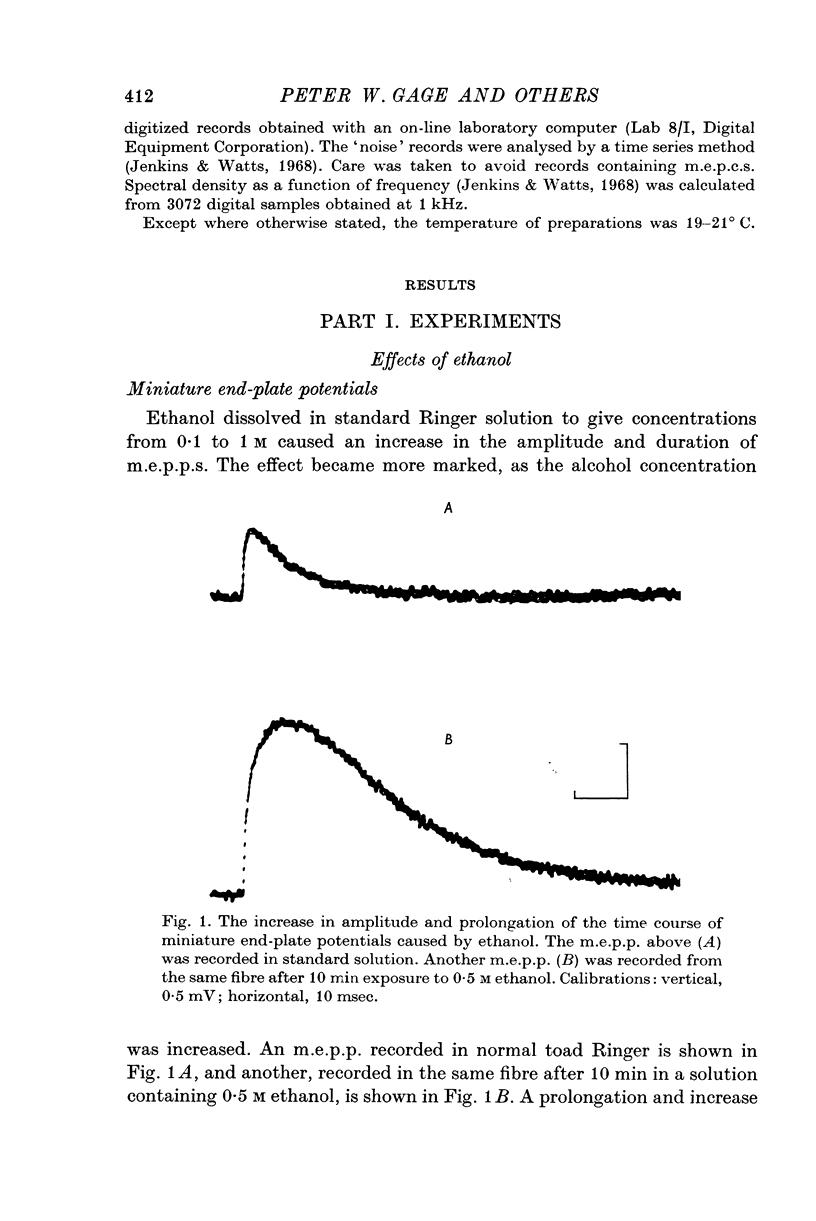
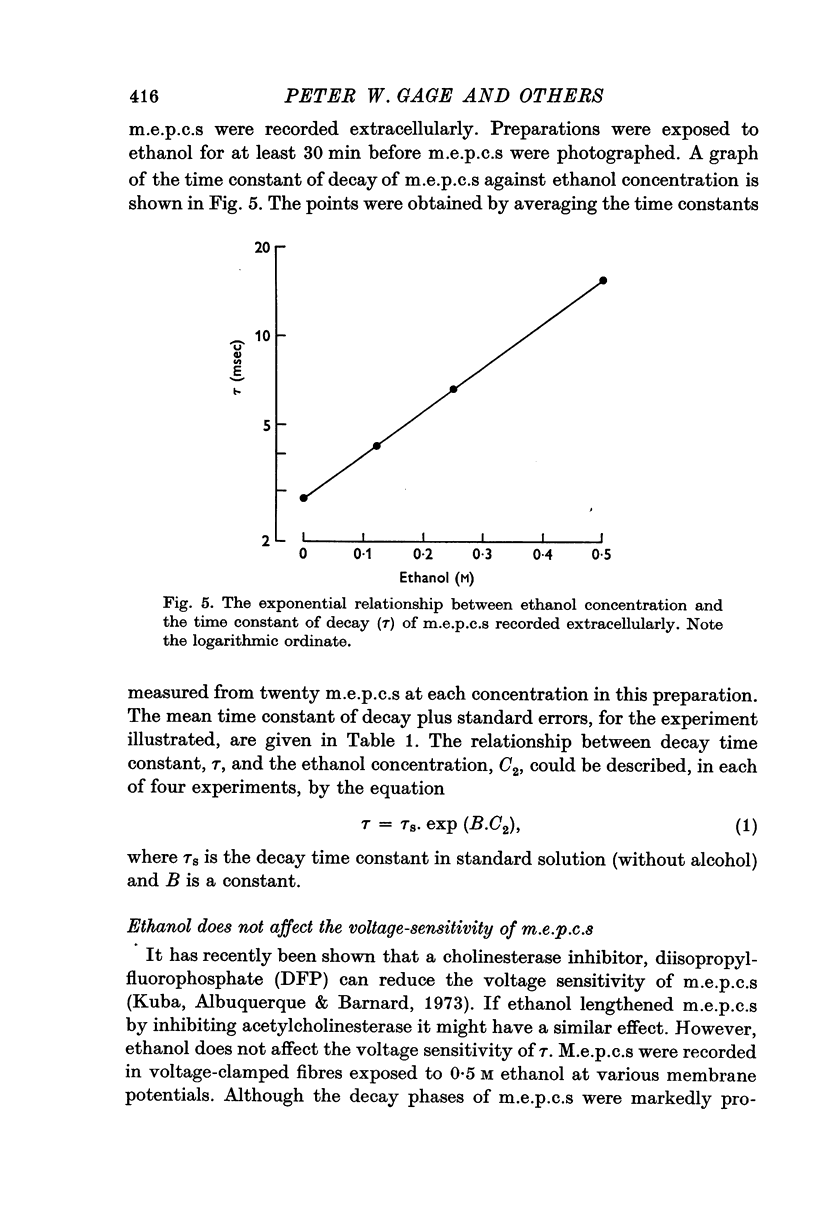
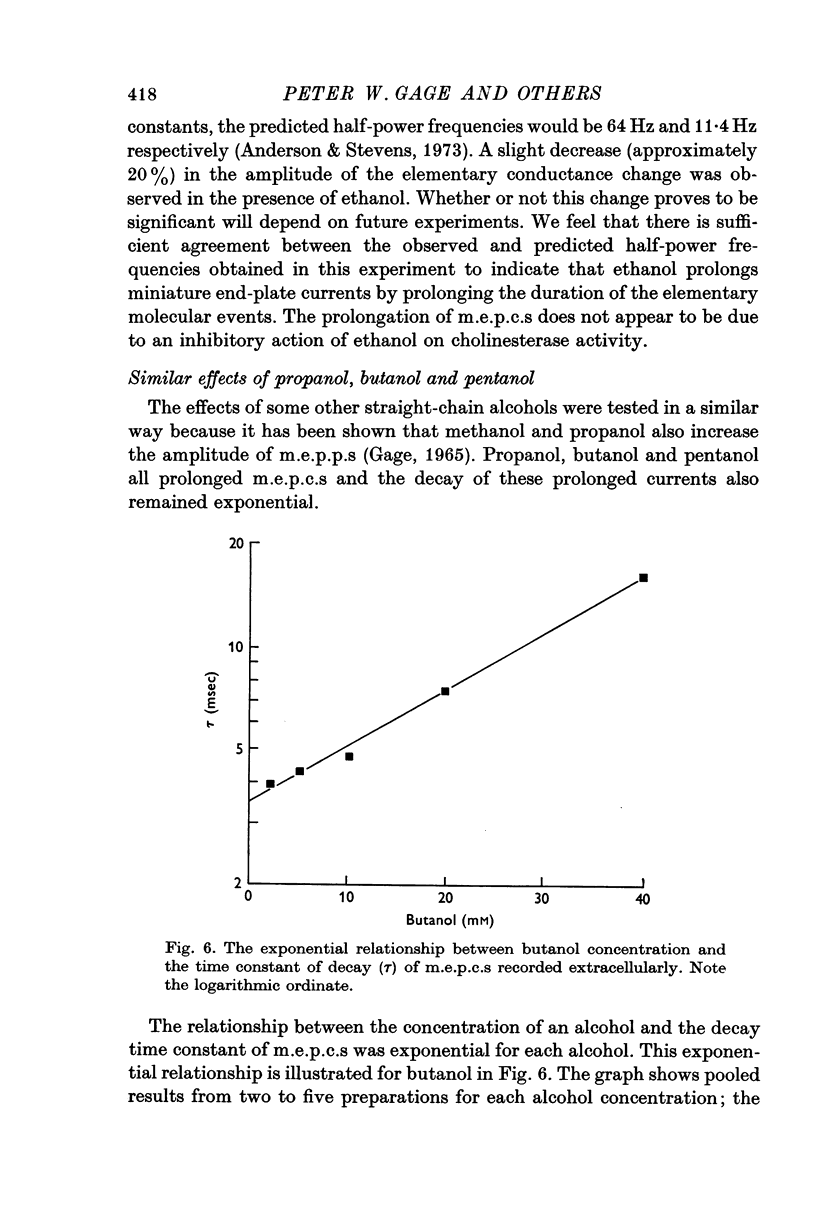
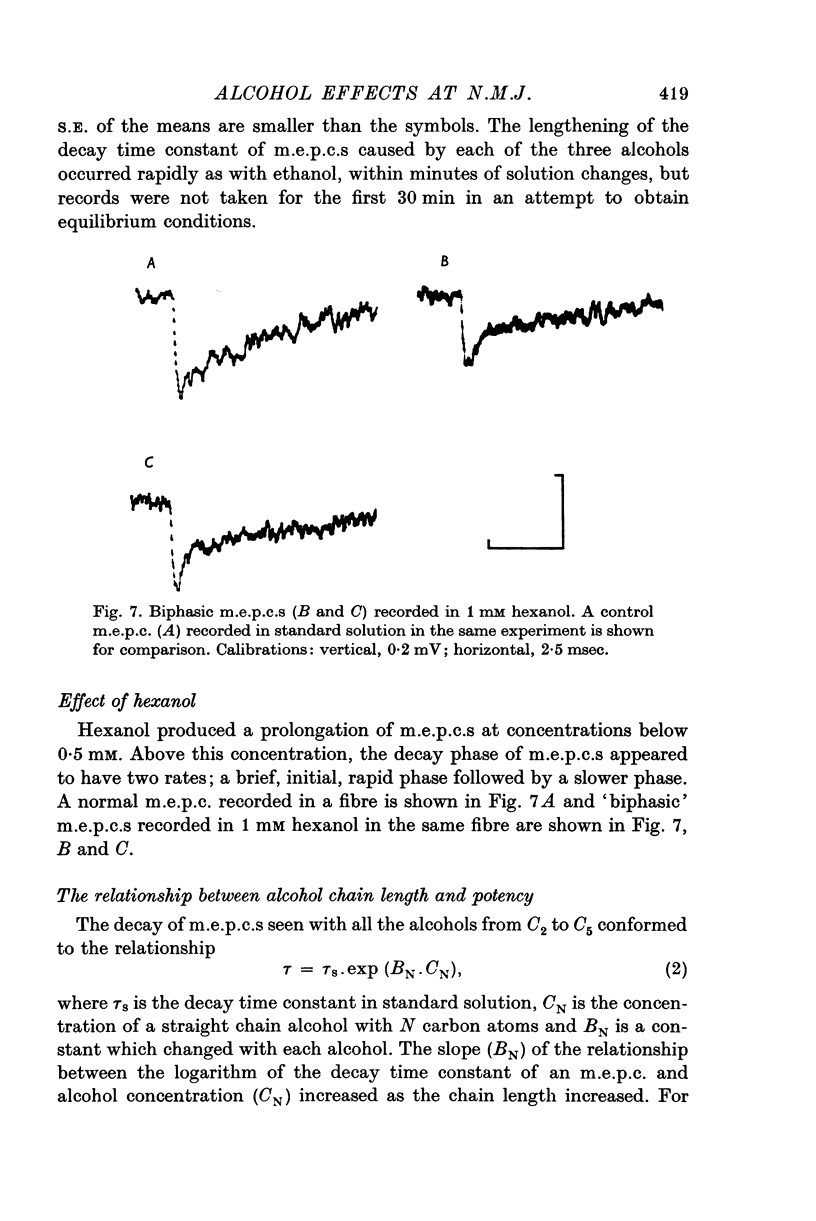
1. The post-synaptic effects of the aliphatic alcohols, ethanol to hexanol, were investigated at the neuromuscular junctions of toads, with particular emphasis on the effects of ethanol. 2. The alcohols increased the amplitude and duration of miniature end-plate potentials. It is shown that this effect was due to the prolongation of the decay phase of miniature end-plate currents (m.e.p.c.s). There was no effect of alcohols on the growth phase of m.e.p.c.s. 3. The prolonged decay of m.e.p.c.s in ethanol remained exponential and was normally sensitive to membrane potential. Prolonged m.e.p.c.s were associated with an equivalent prolongation of the mean duration of elementary events, as determined from power spectra of acetylcholine noise in 0-5 M ethanol. 4. The relationship betweeen the time constant of decay of m.e.p.c.s (tau) and the concentration of an alcohol of carbon chain length N (C-N) was exponential, conforming to the equation tau equals tau-s exp (B-N-C-N), in which tau-s is the decay time constant in standard solution and B-N is a constant, different for each alcohol. 5. There was also an exponential relationship between B-N and N, which closely followed the relationship between membrane-buffer partition coefficient and carbon chain length for the different alcohols, indicating that the alcohols are active in the lipid phase of the post-synaptic membrane. 6. It is suggested that the alcohols act by causing a change in the dielectric constant of the post-synaptic membrane which forms the environment of the rate-limiting reaction responsible for the decay of the end-plate conductance. On the assumption that this reaction involves dipoles, it is shown that the small changes in dielectric constant, calculated from the partition coefficients of the alcohols and by assuming an initial lipid dielectric constant of 3, would give an exponential relationship between the time constant of decay of m.e.p.c.s and alcohol concentration. 7. The results support the hypothesis that the decay (but not the onset) of acetylcholine-induced conductance changes is rate-limited by a first-order reaction which involves dipoles and occurs in the lipid environment of the post-synaptic membrane.
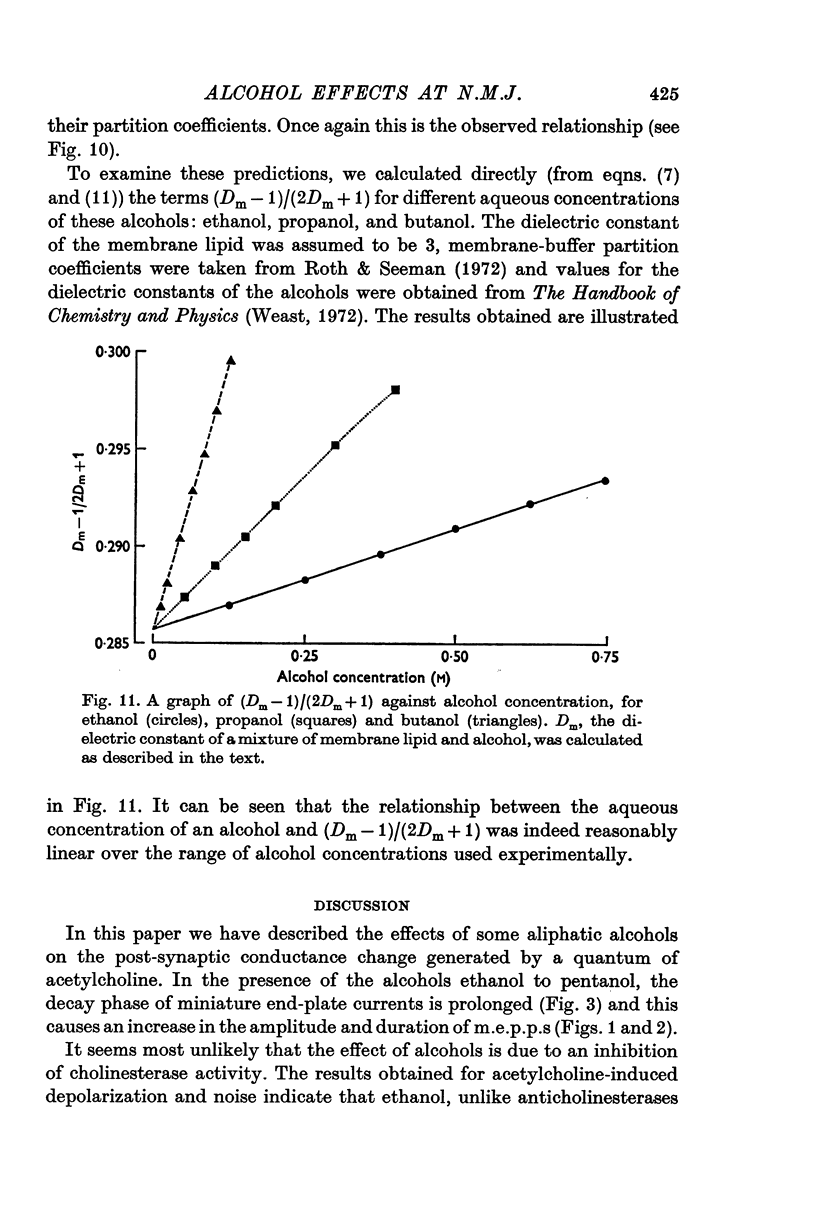
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Narahashi T. Effects of procaine on ionic conductances of end-plate membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Feb;176(2):423–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W. Electrical properties of toad sartorius muscle fibres in summer and winter. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):619–641. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T. Properties of the procaine end-plate potential. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;7(3):199–212. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Armstrong C. M. Miniature end-plate currents in voltage-clamped muscle fibre. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):363–365. doi: 10.1038/218363b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. An analysis of the relationship between the current and potential generated by a quantum of acetylcholine in muscle fibers without transverse tubules. J Membr Biol. 1973;12(3):247–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01870004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N., Van Helden D. Endplate currents are shortened by octanol: possible role of membrane lipid. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 1;14(11):2277–2283. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. The effect of methyl, ethyl and n-propyl alcohol on neuromuscular transmission in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Nov;150(2):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue F., Frank G. B. Effects of ethyl alcohol on excitability and on neuromuscular transmission in frog skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 May;30(1):186–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further observations on acetylcholine noise. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio232124b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Membrane noise produced by acetylcholine. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):962–963. doi: 10.1038/226962a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. I. The effects of prostigmine and of the ratio of Mg 2+ to Ca 2+ . J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):317–332. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. II. Temperature. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):333–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. The effect of membrane polarization on the time course of the end-plate current in frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):493–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Albuquerque E. X., Barnard E. A. Diisopropylfluorophosphate: suppression of ionic conductance of the cholinergic receptor. Science. 1973 Aug 31;181(4102):853–856. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4102.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T. Analysis of sodium and potassium conductances in the procaine end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):592–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K. Effects of alcohols and acetone on the neuromuscular junction of frog. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Jun;17(3):245–261. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Seeman P. The membrane concentrations of neutral and positive anesthetics (alcohols, chlorpromazine, morphine) fit the Meyer-Overton rule of anesthesia; negative narcotics do not. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach A. B. Alteration by xylocaine (lidocaine) and its derivatives of the time course of the end plate potential. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jul;52(1):144–161. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Diamond J. M. Patterns of non-electrolyte permeability. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 18;171(1028):227–271. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


