Abstract
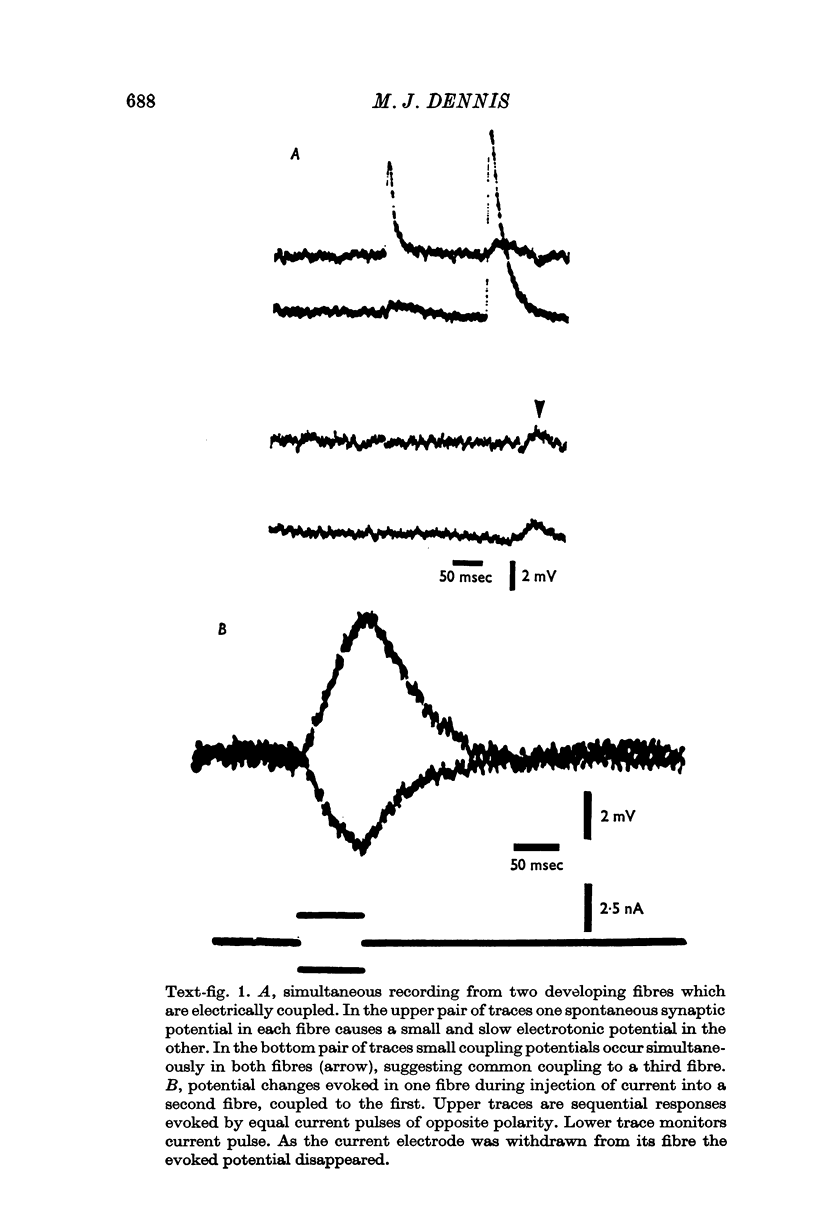
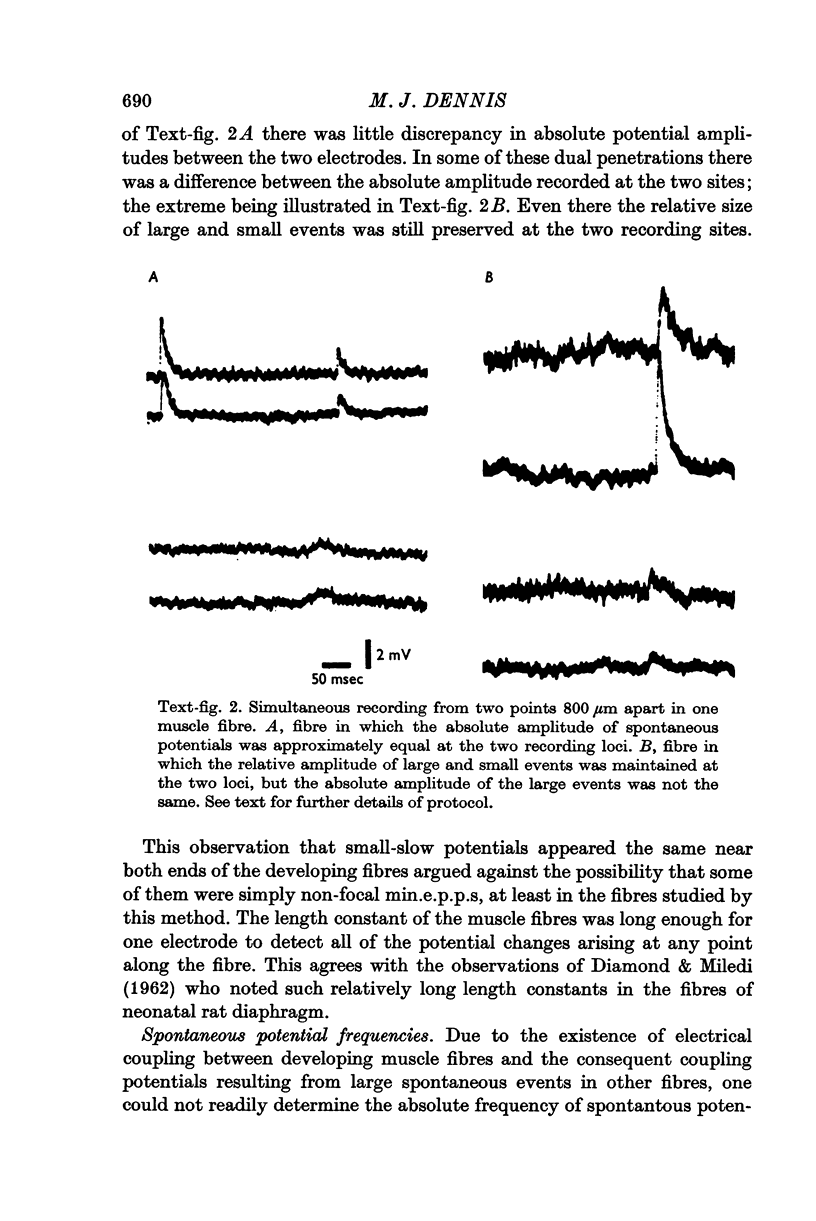
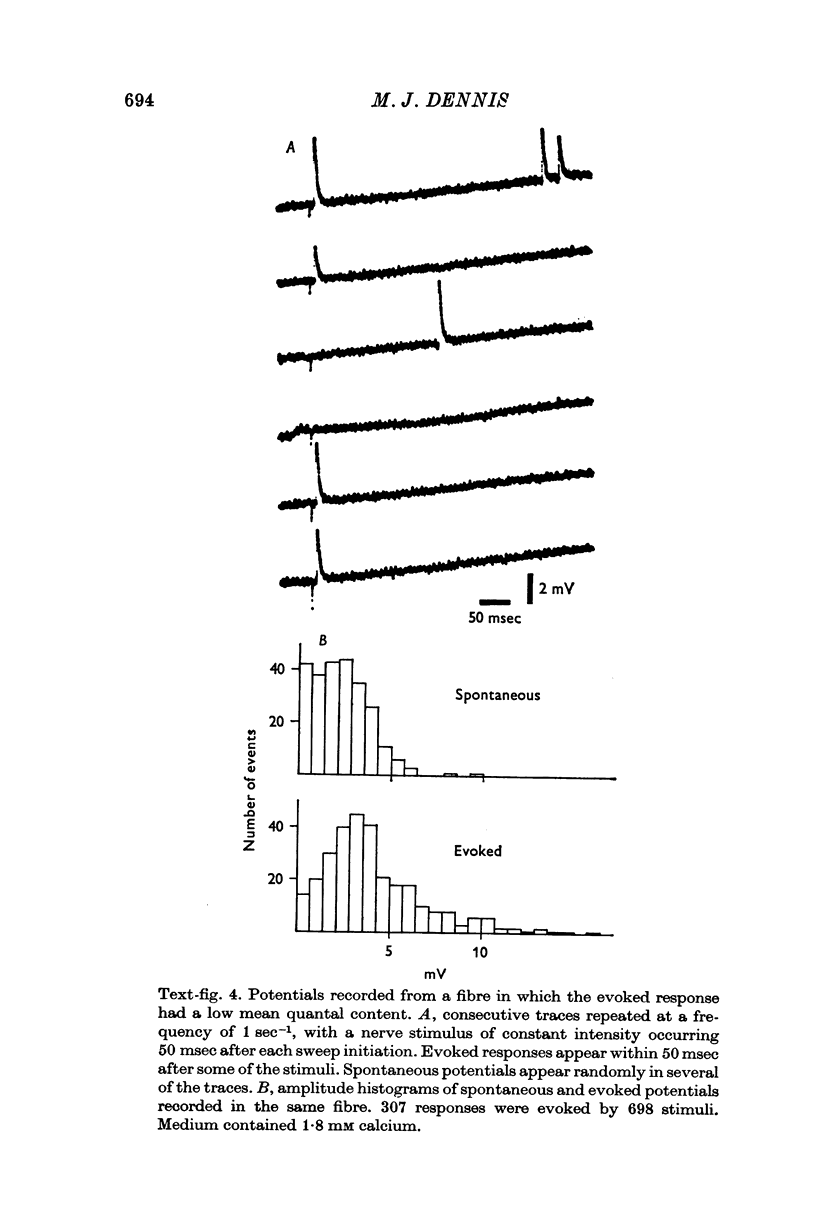
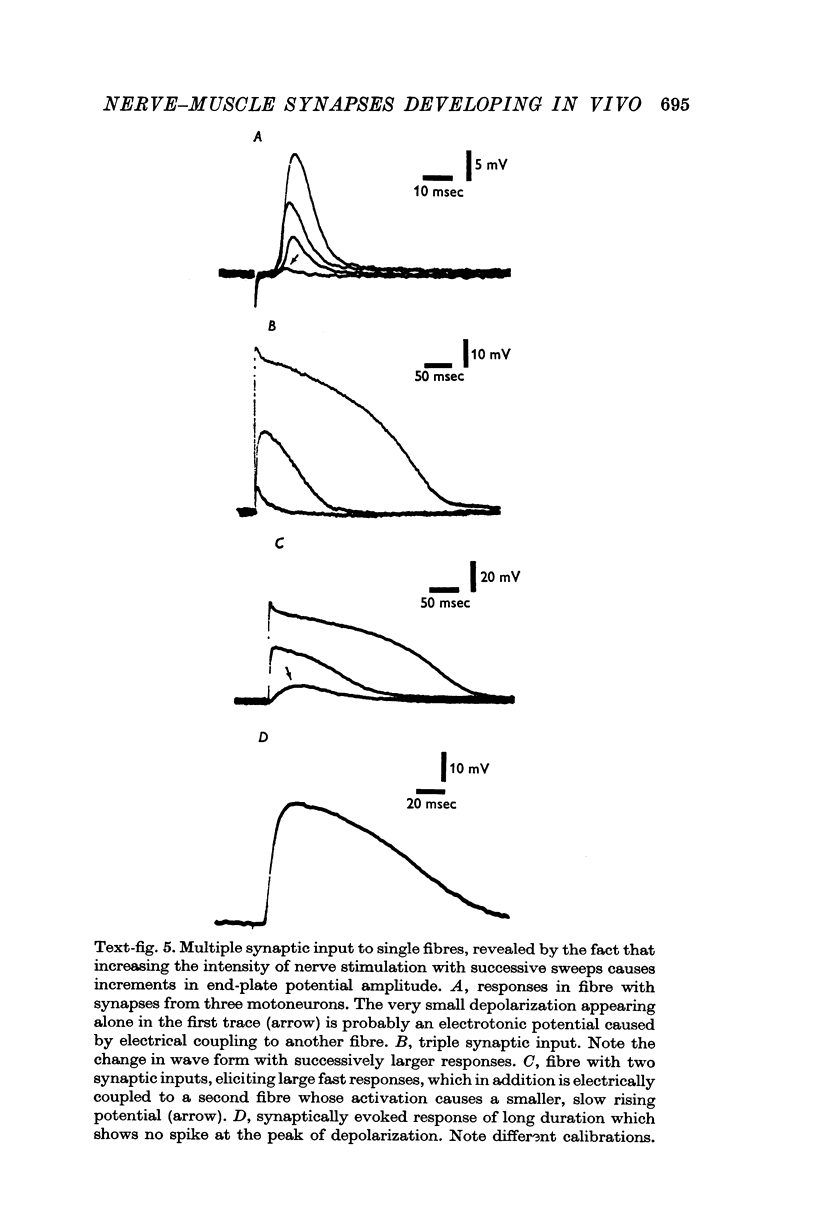
1. Physiological properties of developing nerve-muscle junctions were studied in regenerating limbs of adult salamanders. 2. During the period of synapse formation the muscle fibres had diameters of 4-10 mum, resting potentials of minus 90 to minus 100 mV and input resistances of 10-50 Momega. Some, but not all, pairs of adjacent muscle fibres were electrically coupled. 3. At the stage when muscle fibres could first be identified, some of them were not innervated, at least as determined by electrophysiological criteria. 4. During muscle innervation the neuromuscular synapses were encountered in several intermediate phases of maturity. (i) At the least mature junctions small spontaneous synaptic potentials occurred, but stimulation of the motor nerve trunk did not evoke synchronous transmitter release. (ii) At other junctions maximal nerve stimulation evoked only a single end-plate potential of low quantum content. (iii) More mature fibres received synaptic input from as many as four motor neurons, which could be distinguished by their discrete stimulus thresholds. 5. During this period of synapse development the fibres lacked an action potential but often showed a prolonged response to depolarization. 6. Fibres in normal adult muscles had from one to three synaptic inputs, were not electrically coupled, and responded to depolarization with an action potential.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRKS R., KATZ B., MILEDI R. Physiological and structural changes at the amphibian myoneural junction, in the course of nerve degeneration. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:145–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE W. Spontaneous potentials in slow muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):511–521. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. Polyneuronal innervation of kitten skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):241–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in mammalian striated muscle reinnervated with autonomic preganglionic nerves. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):501–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in reinnervated mammalian striated muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):481–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in reinnervated and cross-reinnervated adult avian muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):331–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Grampp W., Miledi R. Further observations on Schwann-cell m.e.p.p.s. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):88P–89P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blioch Z. L., Glagoleva I. M., Liberman E. A., Nenashev V. A. A study of the mechanism of quantal transmitter release at a chemical synapse. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):11–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. W. The development of neuromuscular connexions in the presence of D-tubocurarine. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 22;41(2):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J., MILEDI R. A study of foetal and new-born rat muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:393–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBassio W. A., Schnitzler R. M., Parsons R. L. Influence of lanthanum on transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Neurobiol. 1971;2(3):263–278. doi: 10.1002/neu.480020307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Miledi R. Characteristics of transmitter release at regenerating frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):571–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Miledi R. Non-transmitting neuromuscular junctions during an early stage of end-plate reinnervation. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):553–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elul R., Miledi R., Stefani E. Neurotrophic control of contracture in slow muscle fibres. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1274–1275. doi: 10.1038/2171274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MEVES H. The effect of magnesium and calcium on the frog myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):360–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J. The effects of osmotic pressure changes on the spontaneous activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):689–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Nameroff M., Nelson P. G. Electrical properties of chick skeletal muscle fibers developing in cell culture. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):289–299. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind C. K., Atwood H. L., Lang F. Synaptic differentiation in a regenerating crab-limb muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):822–826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J., Miledi R. Effects of lanthanum ions on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 14;179(1056):247–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Shimada Y. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in chick skeletal muscle cells differentiated in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Feb;81(1):85–89. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Development of action potentials in a clonal rat skeletal muscle cell line. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):158–159. doi: 10.1038/newbio241158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Turkanis S. A., Weakly J. N. Correlation between nerve terminal size and transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):545–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmesser L. Contractile and electrical responses of vagus-innervated frog sartorius muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):707–725. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L. Development of the neuromuscular junction. I. Cytological and cytochemical studies on the neuromuscular junction of differentiating muscle in the regenerating limb of the newt Triturus. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):431–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Properties of regenerating neuromuscular synapses in the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:190–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle J. J., Albuquerque E. X. A study of the reinnervation of fast and slow mammalian muscles. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jan;61(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., DeHaan R. L. Ion levels and membrane potential in chick heart tissue and cultured cells. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jan;61(1):89–109. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins N., Yonezawa T. Physiological studies during formation and development of rat neuromuscular junctions in tissue culture. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):467–481. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



