Abstract
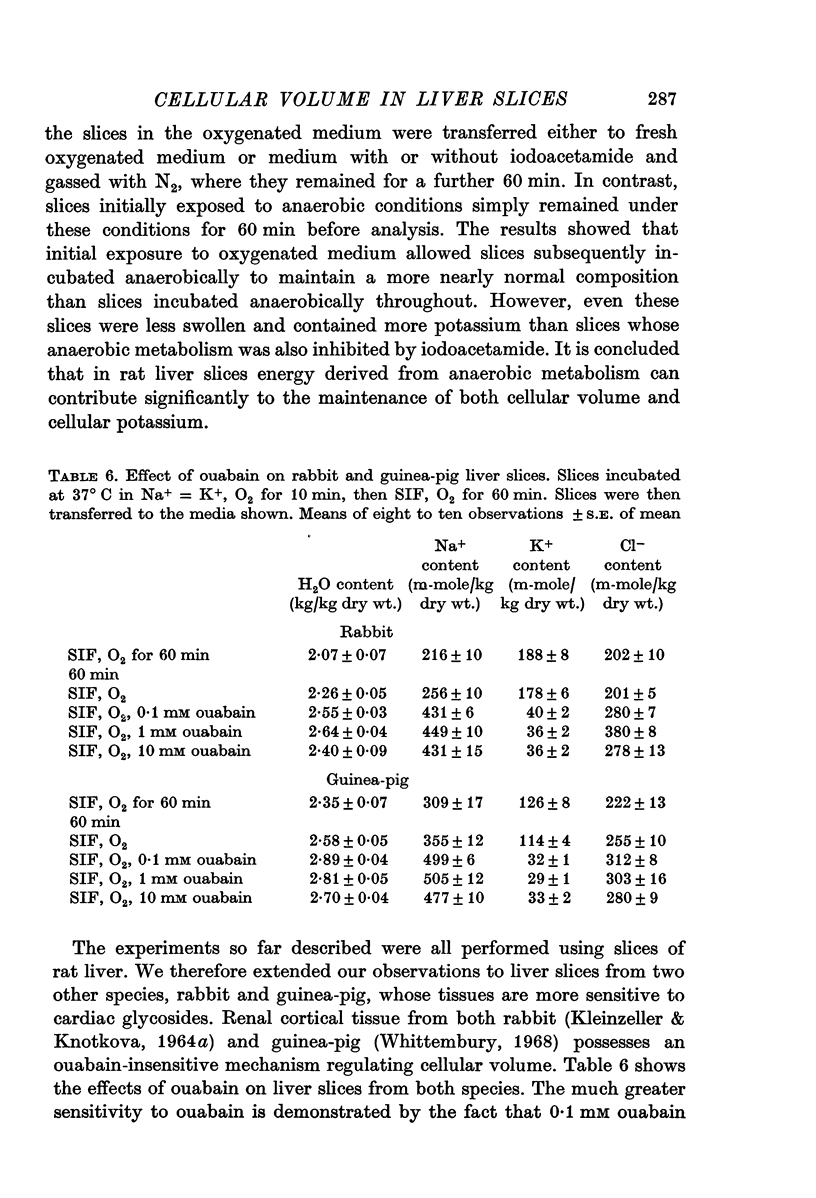
1. Rat, rabbit and guinea-pig liver slices were incubated in media at 37° C to study effects of ouabain and of metabolic inhibition on tissue composition.
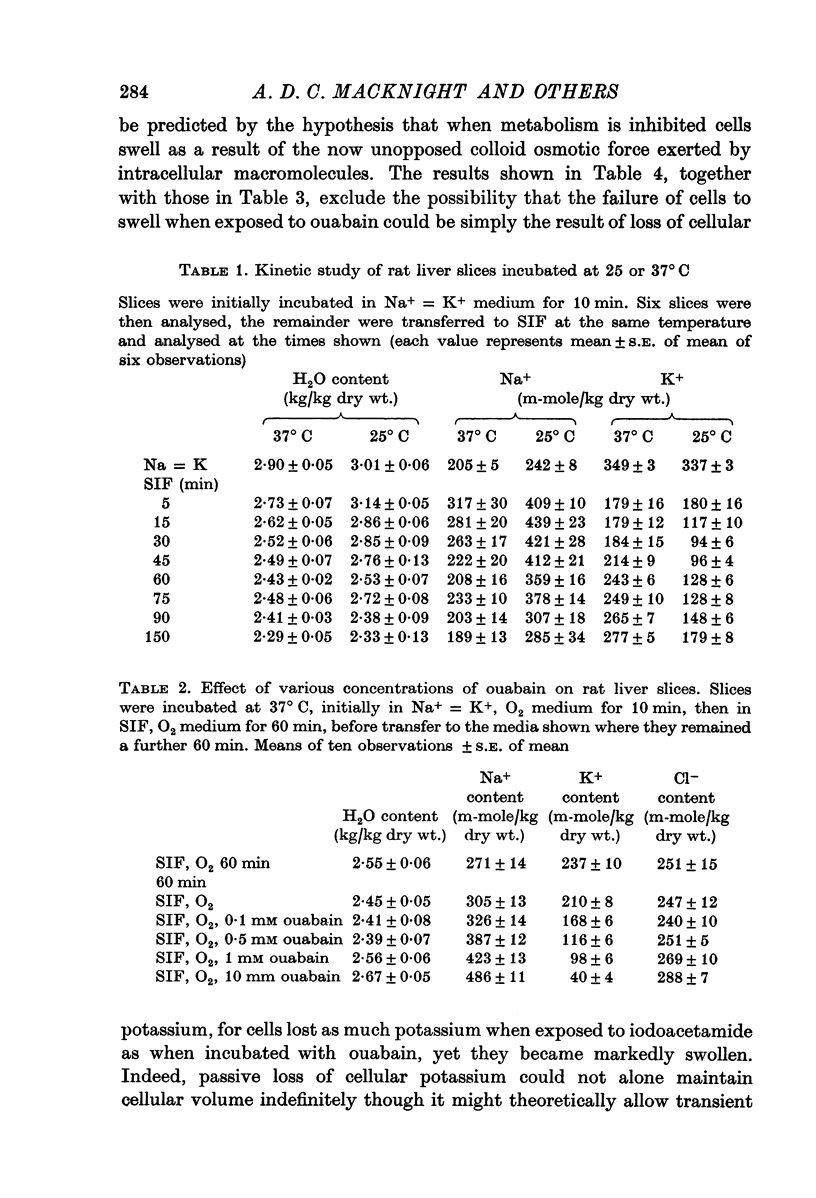
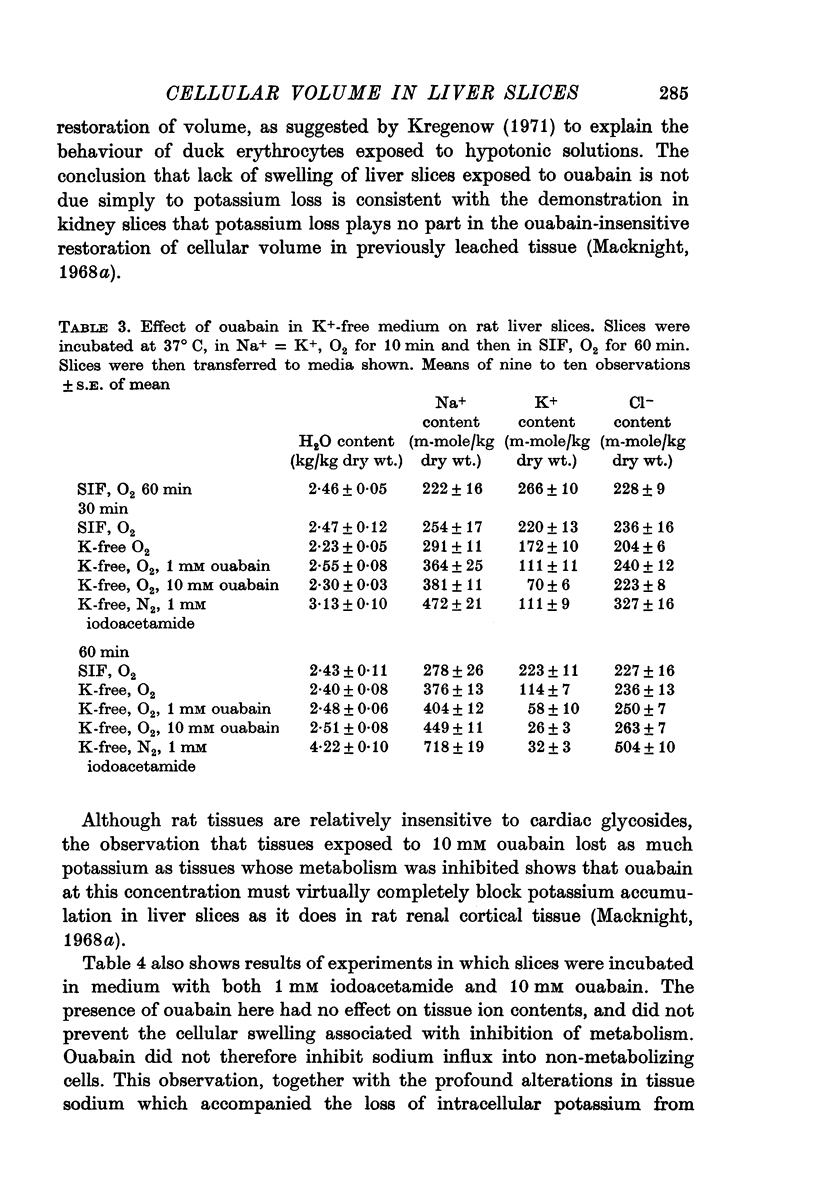
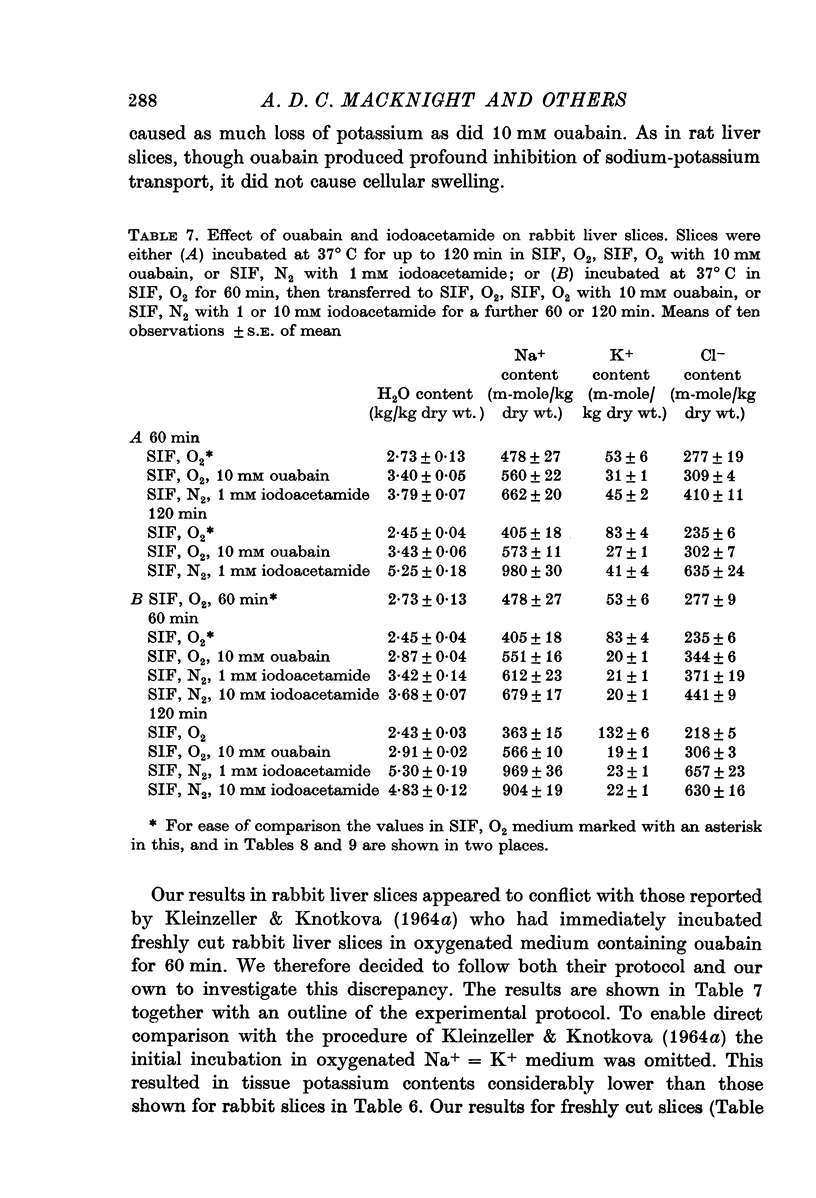
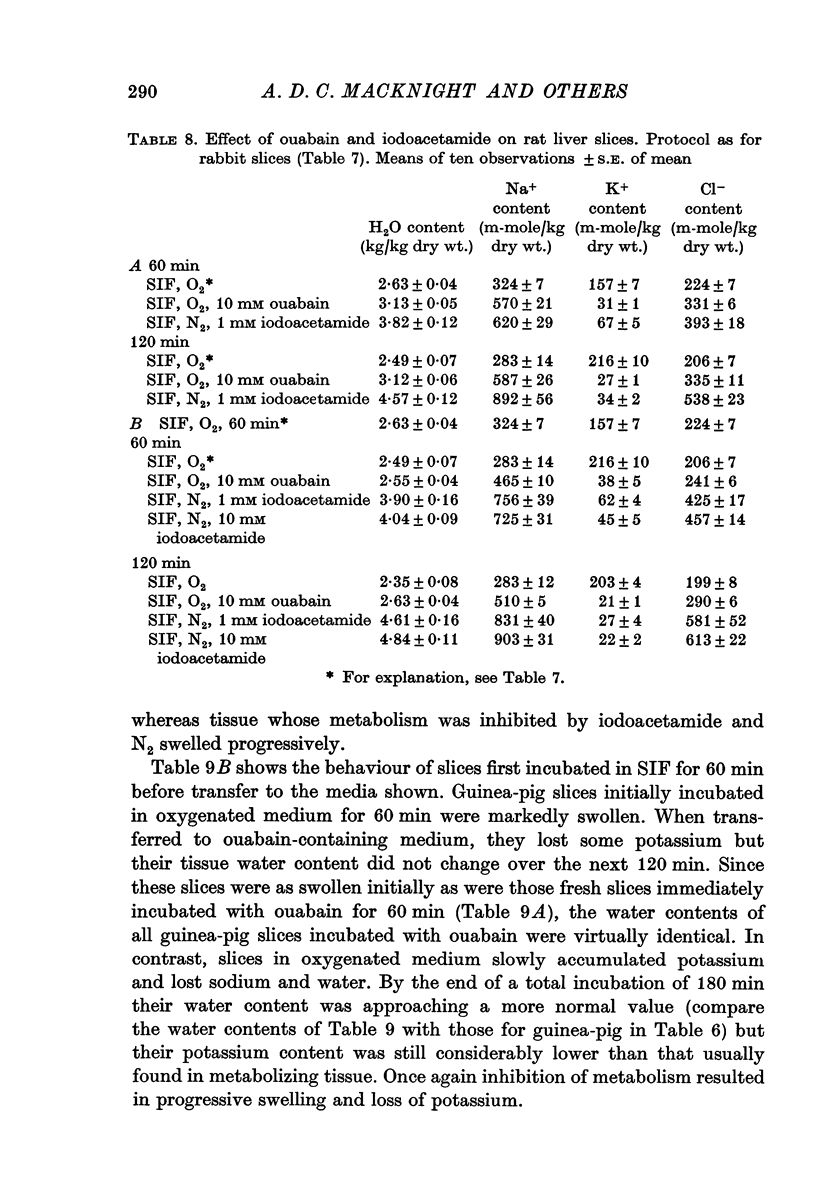
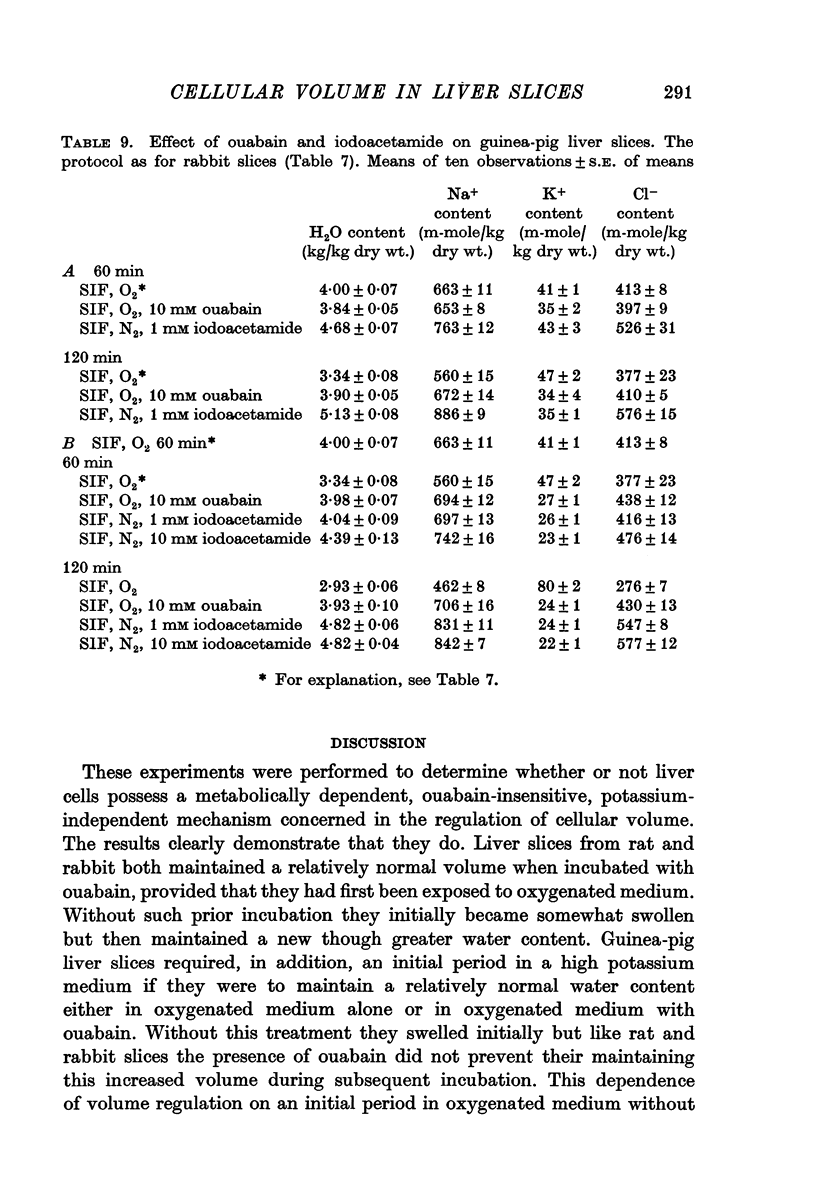
2. Slices initially incubated in oxygenated balanced medium did not swell when exposed to either balanced media or potassium-free media containing ouabain in concentrations ranging from 0·1 to 10 mM though they lost potassium and gained a comparable amount of sodium.
3. Without prior incubation in oxygenated medium slices initially swelled when incubated with ouabain but then maintained their new volume.
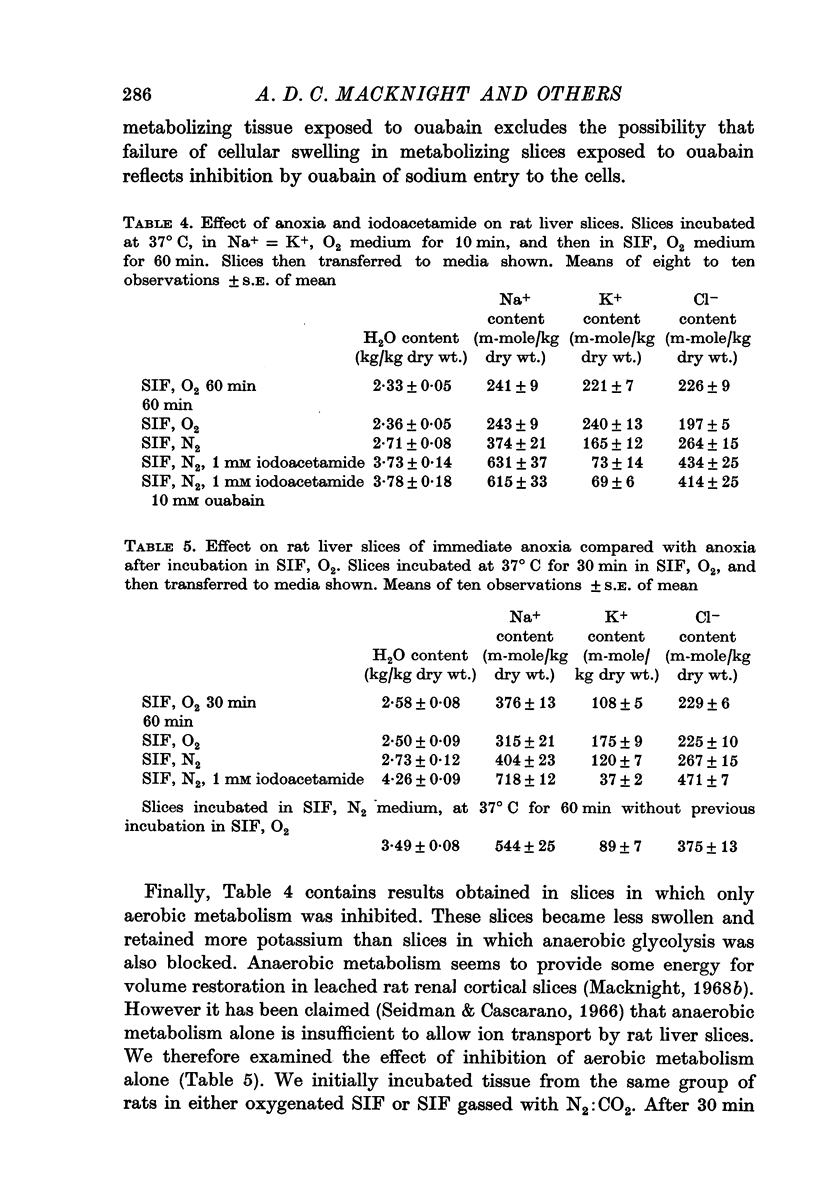
4. Slices whose metabolism was inhibited by incubation with nitrogen and 1 or 10 mM iodoacetamide lost as much potassium as slices exposed to 10 mM ouabain but became swollen with the uptake of sodium, chloride and water.
5. The results show that liver cells, like renal cortical cells, possess a metabolically dependent, ouabain-insensitive, potassium-independent mechanism concerned in the regulation of cellular volume.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretag A. H. Synthetic interstitial fluid for isolated mammalian tissue. Life Sci. 1969 Mar 1;8(5):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Effect of temperature and medium K on Na and K fluxes in separated renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):1005–1010. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E., TRANTHAM H. V., BOWMAN R. L. An instrument and method for automatic, rapid, accurate, and sensitive titration of chloride in biologic samples. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Mar;51(3):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Robinson K. Effects of inhibitors of active transport on 22 Na and 42 K movements and on nucleotide levels in rat uteri at 25 degrees C. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;49(3):178–204. doi: 10.1139/y71-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Boulpaep E. L., Whittembury G. Electrolyte transport in kidney tubule cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Aug 20;262(842):175–196. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINZELLER A., KNOTKOVA A. ELECTROLYTE TRANSPORT IN RAT DIAPHRAGM. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1964;13:317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINZELLER A., KNOTKOVA A. THE EFFECT OF OUABAIN ON THE ELECTROLYTE AND WATER TRANSPORT IN KIDNEY CORTEX AND LIVER SLICES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:172–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinzeller A. The volume regulation in some animal cells. Arch Biol (Liege) 1965;76(2):217–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. The response of duck erythrocytes to nonhemolytic hypotonic media. Evidence for a volume-controlling mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):372–395. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. On the mechanism of fluid exchange of tissues in vitro. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj0620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLE J. R. DETERMINATION OF WATER AND ELECTROLYTES IN TISSUE SLICES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:87–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H., BUDDLE H. L. Techniques in tissue metabolism. I. A mechanical chopper. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):412–420. doi: 10.1042/bj0530412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDGE G. H. Studies on potassium accumulation by rabbit kidney slices; effect of metabolic activity. Am J Physiol. 1951 Apr 1;165(1):113–127. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.165.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D. Regulation of cellular volume during anerobic incubation of rat renal cortical slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 10;163(4):557–559. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D. Water and electrolyte contents of rat renal cortical slices incubated in potassium-free media and media containing ouabain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 1;150(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maude D. L. Effects of K and ouabain on fluid transport and cell Na in proximal tubule in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1199–1206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman I., Cascarano J. Anaerobic cation transport in rat liver slices: effect of metabolites and inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1966 Nov;211(5):1165–1170. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.5.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGGINS P. M. SELECTIVE ACCUMULATION OF POTASSIUM ION BY GEL AND KIDNEY SLICES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 29;88:593–605. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittembury G. Sodium and water transport in kidney proximal tubular cells. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May 1;51(5):303–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


