Abstract
1. Measurements of the specific membrane properties and neuronal geometry of cat motoneurones were used to calculate the excitatory postsynaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) produced by unit (quantal) conductance changes occurring at various locations on the dendritic tree.
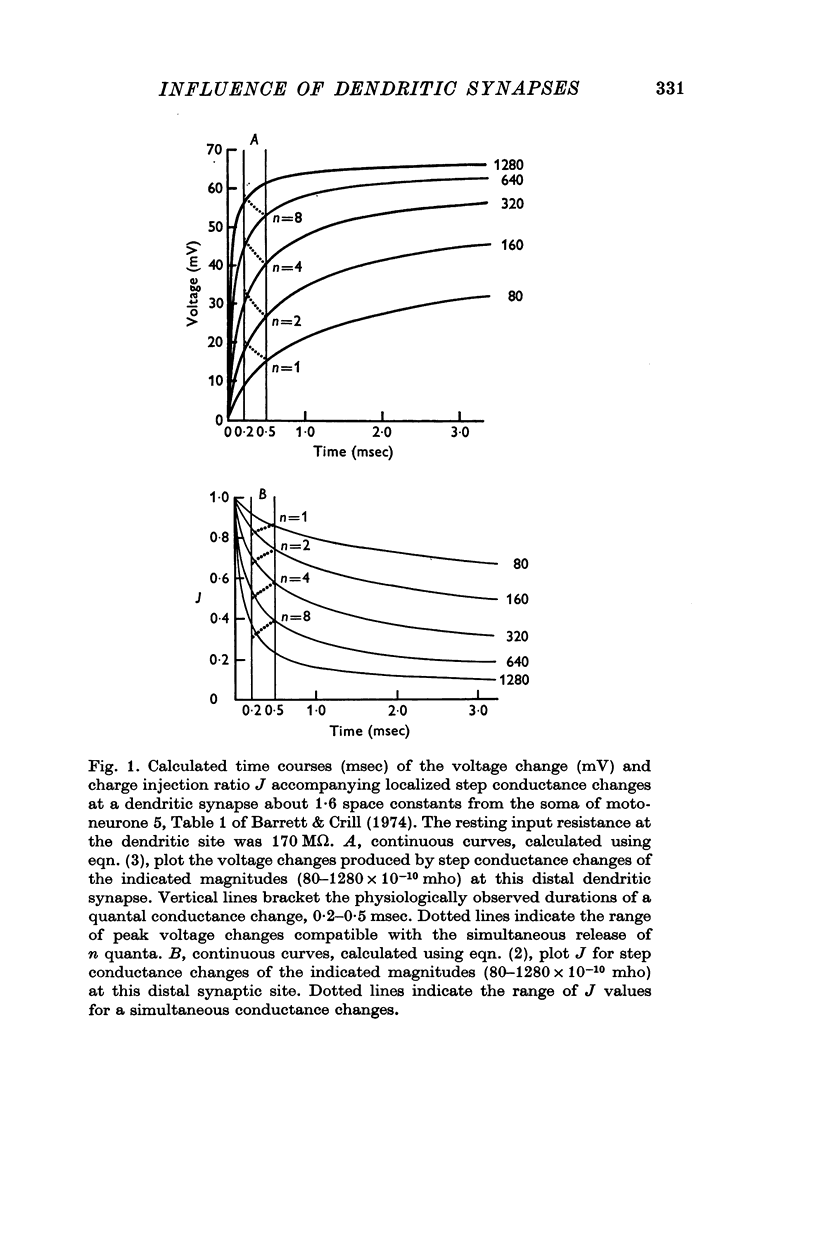
2. Calculations demonstrate that conductance changes of 80-190 × 10-10 mho are required to produce e.p.s.p.s having the same rise time and peak amplitude as the quantal e.p.s.p.s recorded in motoneurones by Kuno & Miyahara (1969b). Because quantal conductance changes are so large, synaptic activity can significantly reduce the effective specific resistance of the motoneuronal membrane.
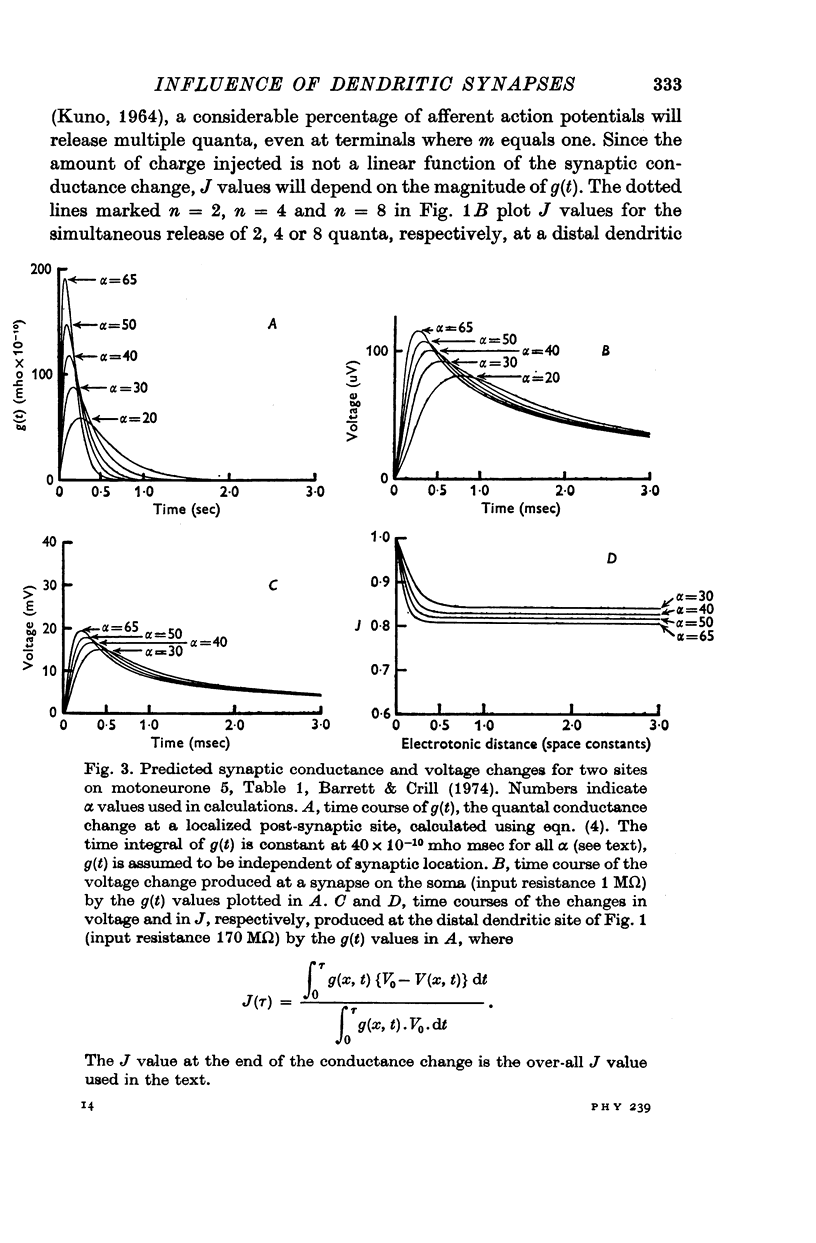
3. A quantal conductance change occurring at a high-impedance distal dendritic site is calculated to produce an e.p.s.p. of 15-20 mV peak amplitude at that site. Significant non-linear summation will occur between the e.p.s.p.s produced by conductance changes occurring simultaneously on the same dendritic branch.
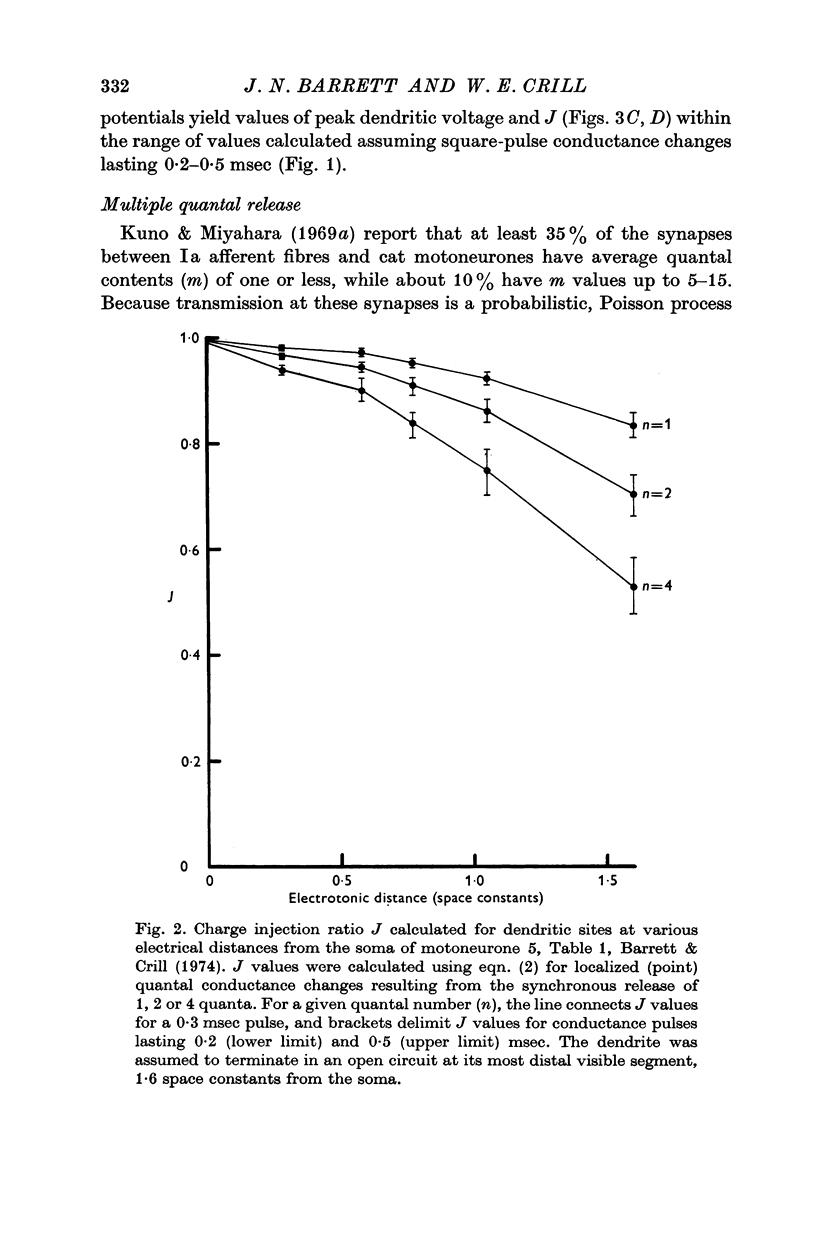
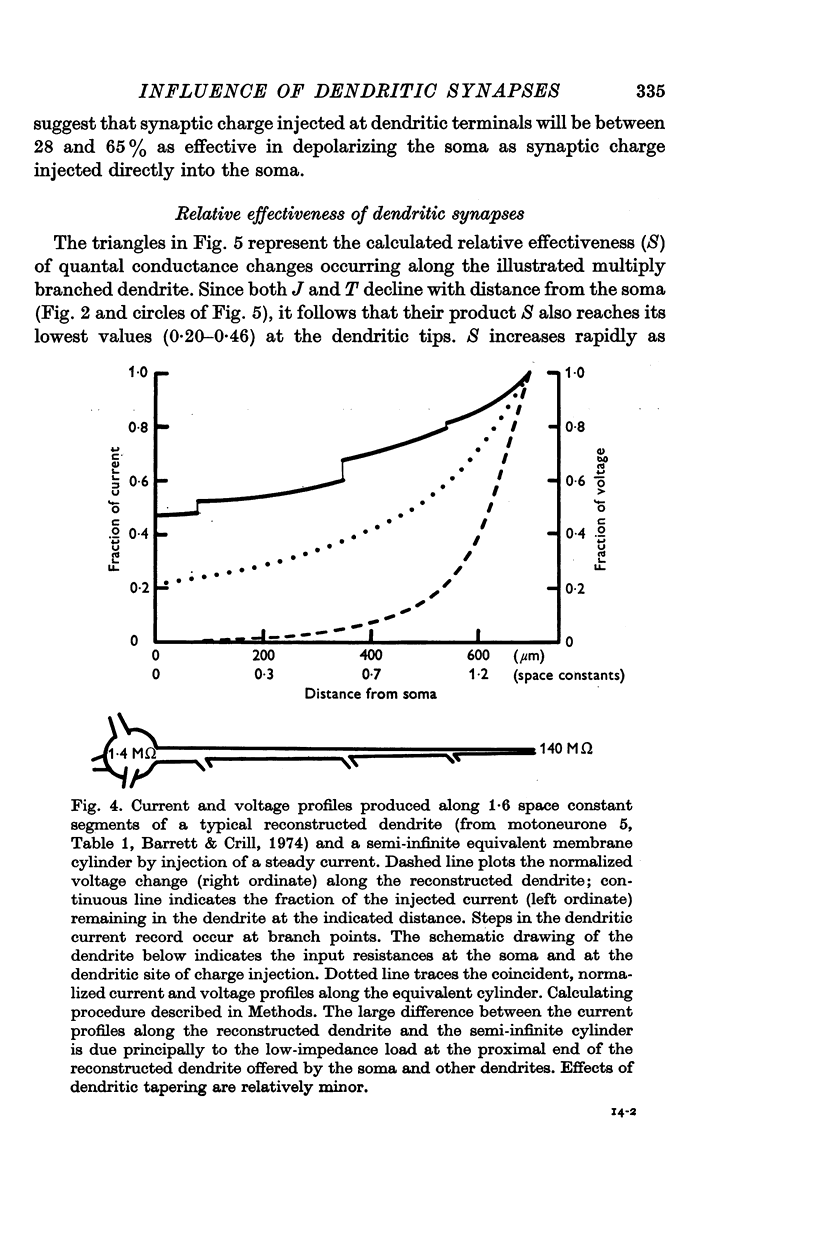
4. Calculations which take into account both non-linear summation and the loss of synaptic charge through dendritic membranes predict that for these motoneurones the time integral of soma-recorded quantal e.p.s.p.s originating on distal dendrites should be at least 20% as great as the time integral of a quantal e.p.s.p. originating directly on the soma. Quantal conductance changes occurring on 76% of the dendritic tree should produce soma e.p.s.p. time integrals at least 50% as great as those produced by somatic synapses.
Full text
PDF






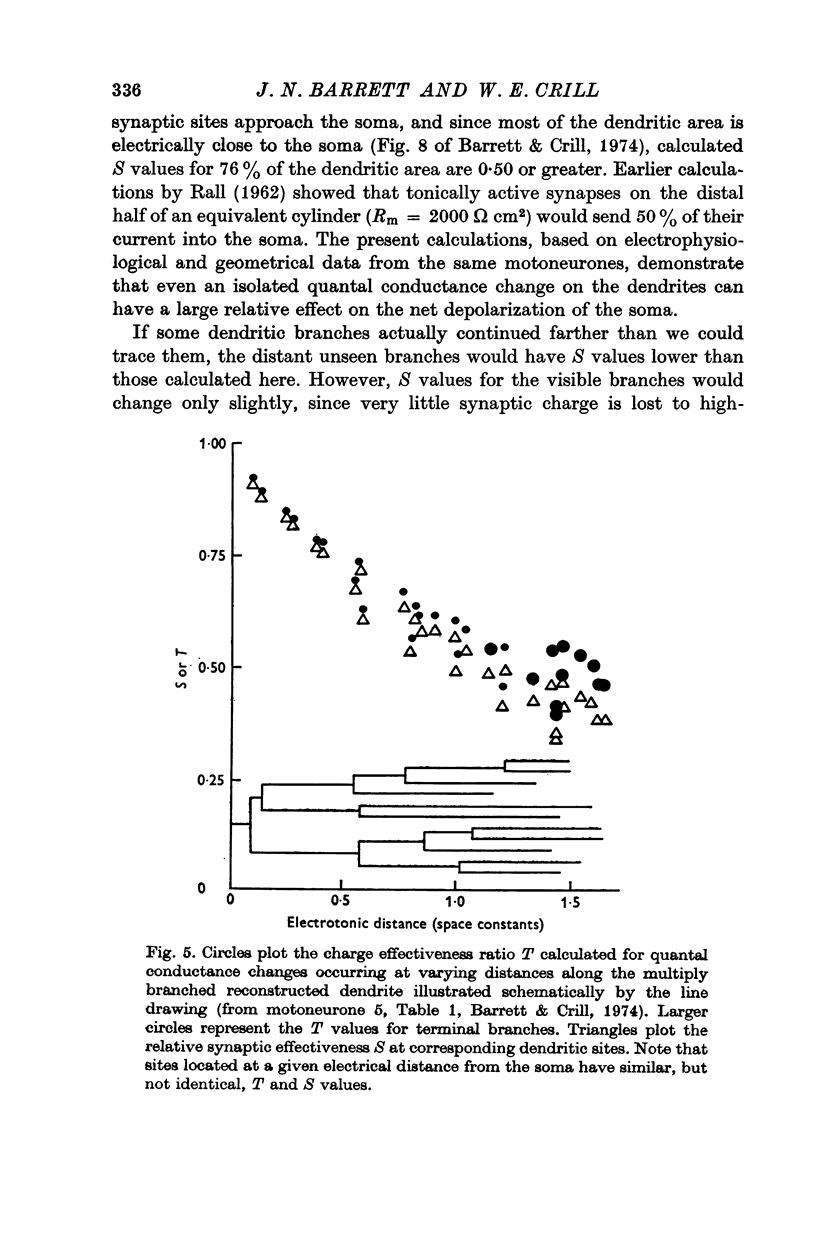
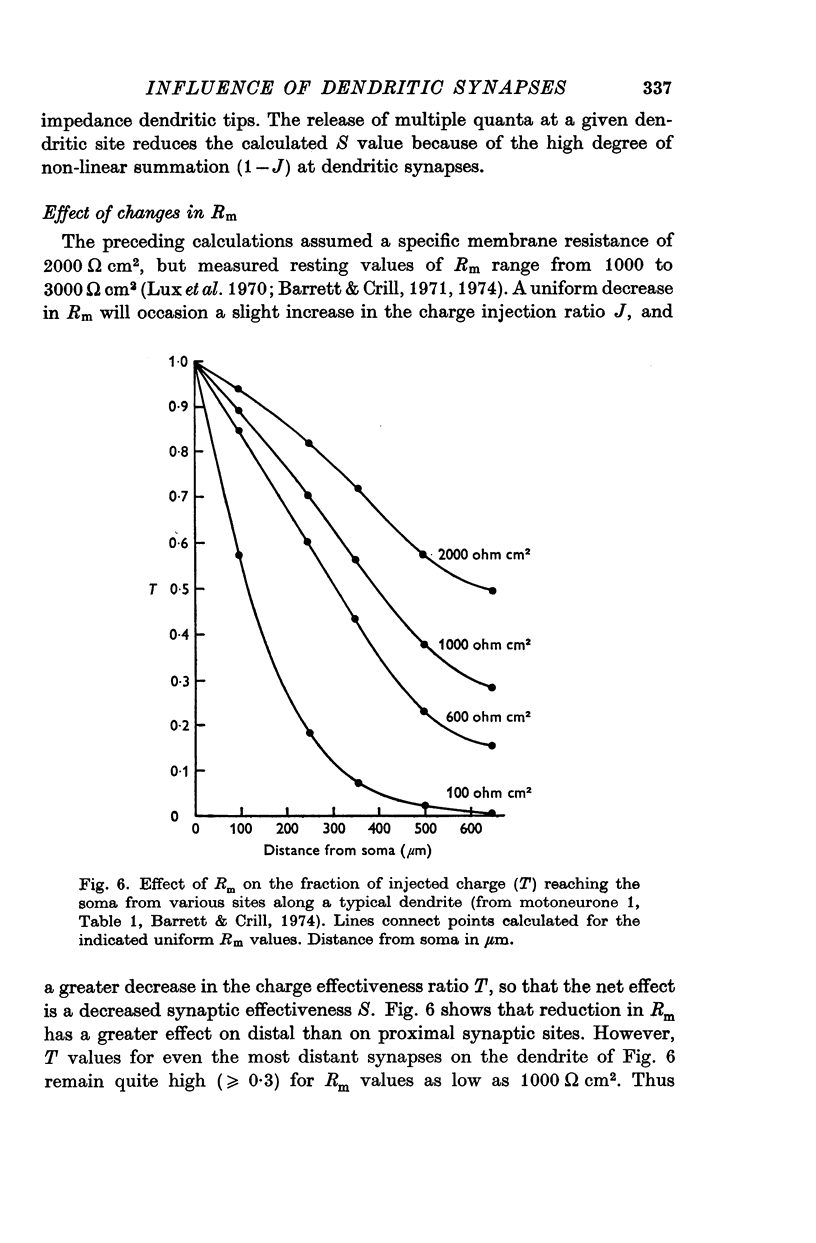








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AITKEN J. T., BRIDGER J. E. Neuron size and neuron population density in the lumbosacral region of the cat's spinal cord. J Anat. 1961 Jan;95:38–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAKI T., TERZUOLO C. A. Membrane currents in spinal motoneurons associated with the action potential and synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:772–789. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane properties of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):301–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane resistivity of dye-injected cat motoneurons. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Composite nature of the monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1114–1137. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Stevens C. F. Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneuron interspike intervals. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jul;31(4):574–587. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Mirolli M. The passive electrical properties of the membrane of a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):35–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kernell D., Lamarre Y. Algebraical summation in synaptic activation of motoneurones firing within the 'primary range' to injected currents. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):379–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Oshima T. Electrical behaviour of the motoneurone membrane during intracellularly applied current steps. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):607–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. The propagation of transient potentials in some linear cable structures. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):283–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. QUANTAL COMPONENTS OF EXCITATORY SYNAPTIC POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:81–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. Input resistance, electrical excitability, and size of ventral horn cells in cat spinal cord. Science. 1966 Jun 17;152(3729):1637–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3729.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyahara J. T. Analysis of synaptic efficacy in spinal motoneurones from 'quantum' aspects. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):479–493. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyahara J. T. Non-linear summation of unit synaptic potentials in spinal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):465–477. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M. Quantum aspects of central and ganglionic synaptic transmission in vertebrates. Physiol Rev. 1971 Oct;51(4):647–678. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Weakly J. N. Quantal components of the inhibitory synaptic potential in spinal mononeurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):287–303. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motor neurons. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):96–98. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Lux H. D. Some electrical measurements of motoneuron parameters. Biophys J. 1970 Jan;10(1):55–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86285-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Theory of physiological properties of dendrites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar 2;96:1071–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb54120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Rinzel J. Branch input resistance and steady attenuation for input to one branch of a dendritic neuron model. Biophys J. 1973 Jul;13(7):648–687. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86014-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASAKI K., OKA H. ACCOMMODATION, LOCAL RESPONSE AND MEMBRANE POTENTIAL IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS OF THE CAT. Jpn J Physiol. 1963 Oct 15;13:508–522. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.13.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


