Abstract
1. The structure and function of the epithelial lining of the urinary bladder of sheep foetuses was investigated by electron microscopic studies made in conjunction with a series of experiments in which the permeability of the bladder to sodium and water was measured in vitro. Measurements were made at gestational ages ranging from 50 to 141 days (term = 147 days) Osmolarity and electrolyte concentrations of urine found in the foetal bladder were also measured.
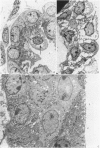
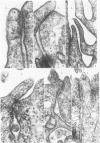
2. The development of tight junctions between the bladder epithelial cells was investigated by incubating the tissue with solutions containing 1 mM-LaCl3 on the mucosal surface. No penetration of the junctions by lanthanum was observed in foetuses of 90 days or older. In younger bladders, the epithelial layer was stripped by treatment with lanthanum, but tight junctions appeared to be fully developed in early bladders incubated without lanthanum.
3. The surface structure of the luminal (mucosal) plasmalemma was fully developed at 50 days.
4. Unidirectional fluxes of labelled sodium and water were measured with identical solutions bathing the two surfaces of the bladder wall. No net water movement occurred; the mean ratio of efflux to influx in nine bladders was 1·002 ± 0·039 (S.E. of mean). Under these conditions, the flux ratio for sodium was 1·735 ± 0·143 (S.E. of mean) in twelve bladders.
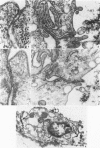
5. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) had no effect on net water movement but reduced the net efflux of sodium so that the flux ratio became 1·285 ± 0·255 (S.E. of mean) n = 8. ADH also had a striking effect on the structure of the epithelium, causing marked swelling of the intercellular spaces. The tight junctions remained an effective barrier to lanthanum penetration under these conditions; lanthanum was not observed in the enlarged spaces.
Full text
PDF























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER D. P., NIXON D. A., WIDDAS W. F., WOHLZOGEN F. X. Gestational variations in the composition of the foetal fluids and foetal urine in the sheep. J Physiol. 1958 Jan 23;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aceves J., Erlij D. Sodium transport across the isolated epithelium of the frog skin. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):195–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY P. J. The effects of neurohypophysial extracts on the water transfer across the wall of the isolated urinary bladder of the toad Bufo marinus. J Endocrinol. 1958 Sep;17(3):201–209. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Crowder J., Desai S., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M., Saunders N. R. Electrolytes and water in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of the foetal sheep and guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):591–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., HERRERA F. C., FLANIGAN W. J. The effect of Ca and antidiuretic hormone on Na transport across frog skin. II. Sites and mechanisms of action. J Gen Physiol. 1963 May;46:1011–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SOLOMON A. K. Ion and water fluxes in the ileum of rats. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):143–168. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J. M. TRANSPORT OF SALT AND WATER IN RABBIT AND GUINEA PIG GALL BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:1–14. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLUND S. E. Observations on the migration of some labelled substances between the urinary bladder and the blood in the rabbit. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1956;(135):1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firth J. A., Hicks R. M. Membrane specialization and synchronized cell death in developing rat transitional epithelium. J Anat. 1972 Oct;113(Pt 1):95–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham E. L., Rankin J. H., Makowski E. L., Meschia G., Battaglia F. C. An evaluation of fetal renal function in a chronic sheep preparation. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):149–156. doi: 10.1172/JCI106785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKIM A. A., LIFSON N., CREEVY C. D. FLUXES OF NA+ AND CL- IN THE DOG URINARY BLADDER. Invest Urol. 1965 Jan;2:348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON C. B., WEBBER W. A. AMINO ACID TRANSPORT ACROSS RAT BLADDER. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1964 Mar;42:275–276. doi: 10.1139/y64-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBNER G., STAEBER H., LUDEWIG R. ZUR WASSERPERMEABILITAET DER HARNBLASE VON RATTEN. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1964;12:663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks R. M., Ketterer B. Isolation of the plasma membrane of the luminal surface of rat bladder epithelium, and the occurrence of a hexagonal lattice of subunits both in negatively stained whole mounts and in sectioned membranes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):542–553. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King V. A study of the mechanism of water transfer across frog skin by a comparison of the permeability of the skin to deuterated and tritiated water. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):529–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., HAYS R. M. Permeability of the isolated toad bladder to solutes and its modification by vasopressin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:921–932. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. Some actions of neurohypophyseal hormones on a living membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 May;43:175–189. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.5.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love A. H., Mitchell T. G., Neptune E. M., Jr Transport of sodium and water by rabbit ileum, in vitro and in vivo. Nature. 1965 Jun 12;206(989):1158–1158. doi: 10.1038/2061158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machen T. E., Erlij D., Wooding F. B. Permeable junctional complexes. The movement of lanthanum across rabbit gallbladder and intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):302–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCANCE R. A., WIDDOWSON E. M. Renal function before birth. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1953 Sep;141(905):489–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Stanier M. W. The function of the metanephros of foetal rabbits and pigs. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151(3):479–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor D. J., Slater J. S. Daily changes in foetal urine and relationships with amniotic and allantoic fluid and maternal plasma during the last two months of pregnancy in conscious, unstressed ewes with chronically implanted catheters. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):503–525. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Kenyon K., Badenhausen S. Specializations of the unit membrane. Protoplasma. 1967;63(1):262–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPOPORT A., NICHOLSON T. F., YENDT E. R. Movement of electrolytes across the wall of the urinary bladder in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:191–194. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. I. SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT AND NA FLUXES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:567–584. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP G. W., LEAF A. BIOLOGICAL ACTION OF ALDOSTERONE IN VITRO. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1185–1188. doi: 10.1038/2021185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A., Chlapowski F. J., Bonneville M. A. Lumenal plasma membrane of the urinary bladder. I. Three-dimensional reconstruction from freeze-etch images. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):73–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Longley W., Robertson J. D. A hexagonal arrangement of subunits in membrane of mouse urinary bladder. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 28;46(3):593–596. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizsolyi E., Perks A. M. New neurohypophysial principle in foetal mammals. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1169–1171. doi: 10.1038/2231169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vye M. V., Fischman D. A. The morphological alteration of particulate glycogen by en bloc staining with uranyl acetate. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Nov;33(3):278–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT G. H., NIXON D. A. Absorption of amniotic fluid in the gut of foetal sheep. Nature. 1961 May 27;190:816–816. doi: 10.1038/190816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]