Abstract
1. The binding of [3H]tetrodotoxin and [125I]iodo-α-bungarotoxin to innervated and denervated rat diaphragm muscle has been measured.
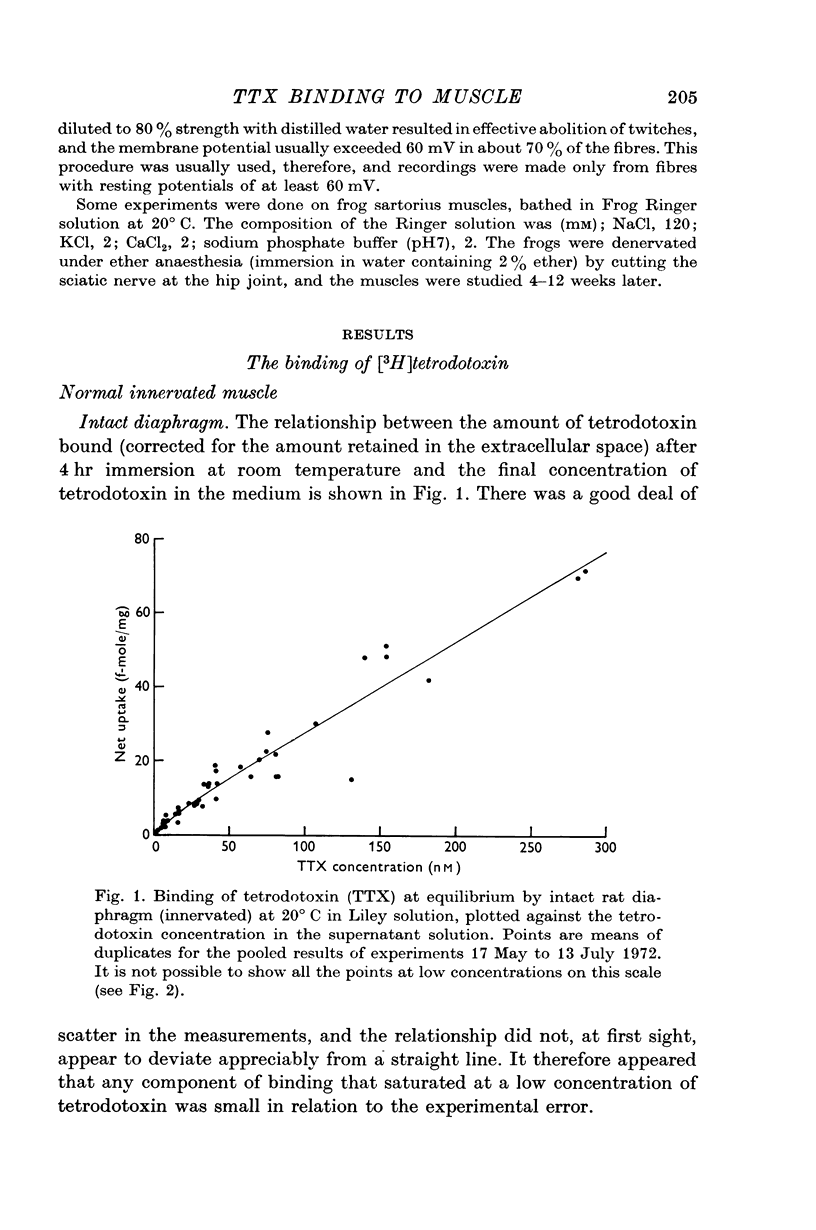
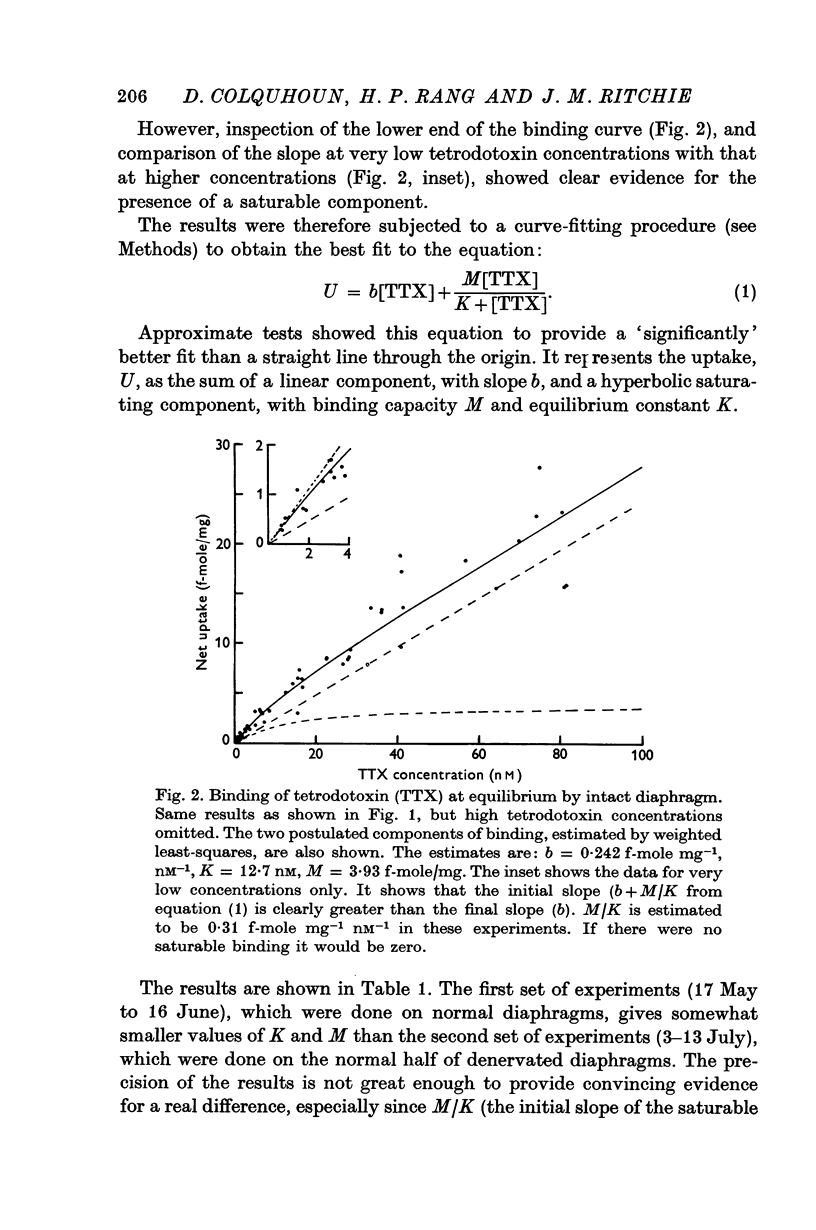
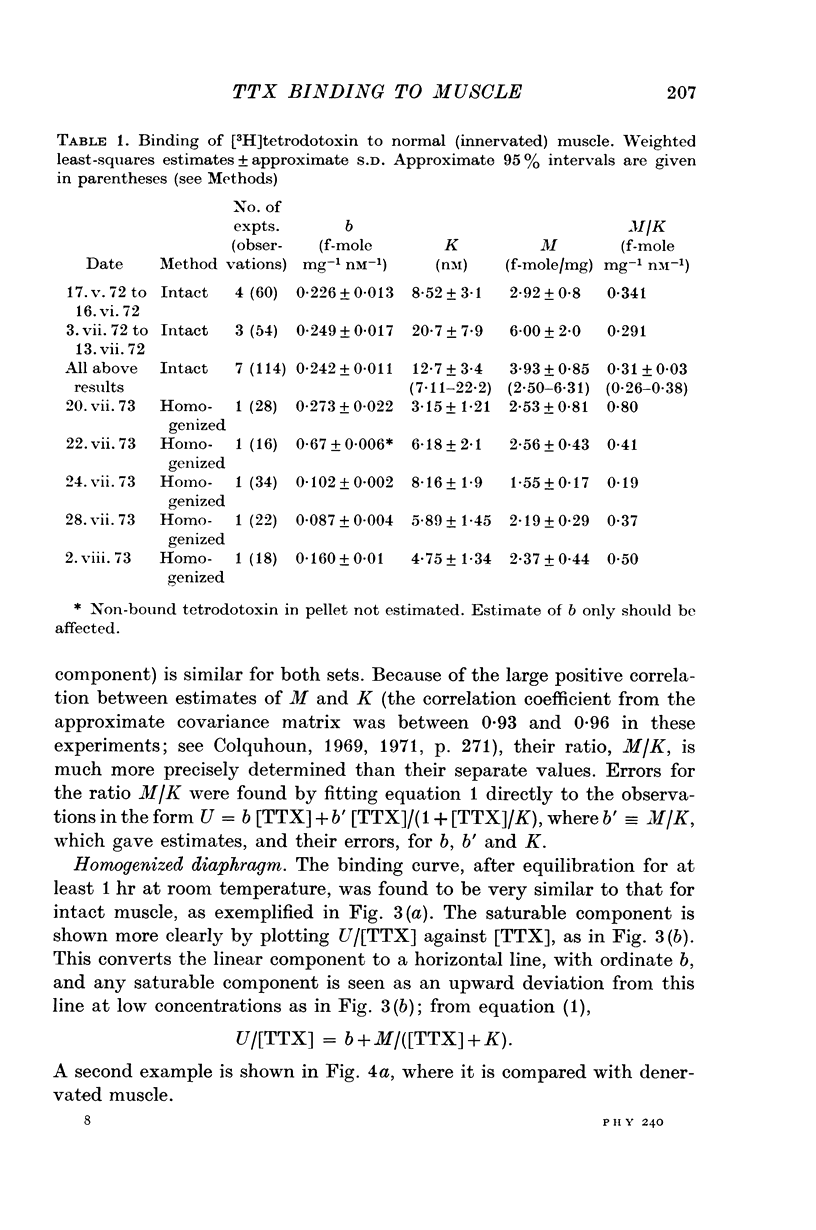
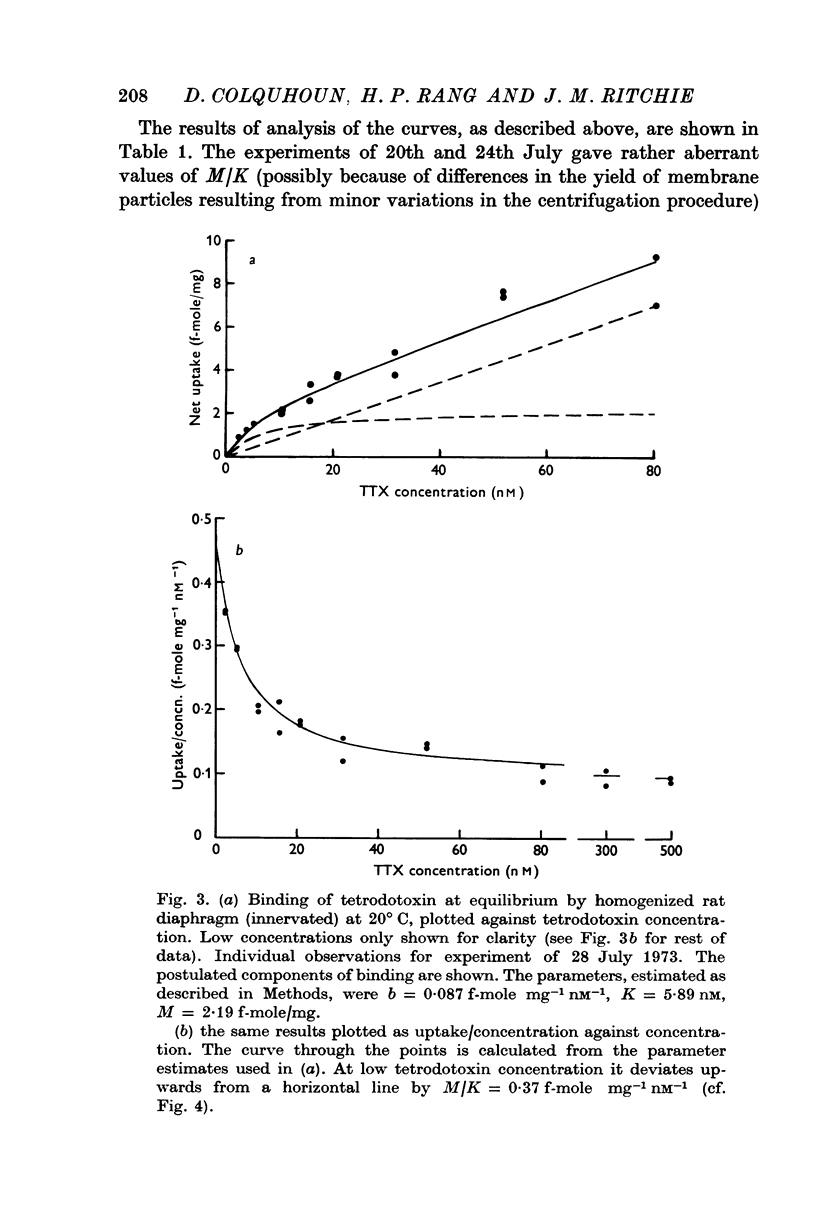
2. A saturable component of tetrodotoxin binding, which was inhibited by saxitoxin, was detected in addition to considerable non-saturable binding. The saturable component had an equilibrium constant of K = 6·1 nM (limits 4·7-7·8 nM) and binding capacity M = 2·5 f-mole/mg wet wt. (limits 2·1-2·8 f-mole/mg).
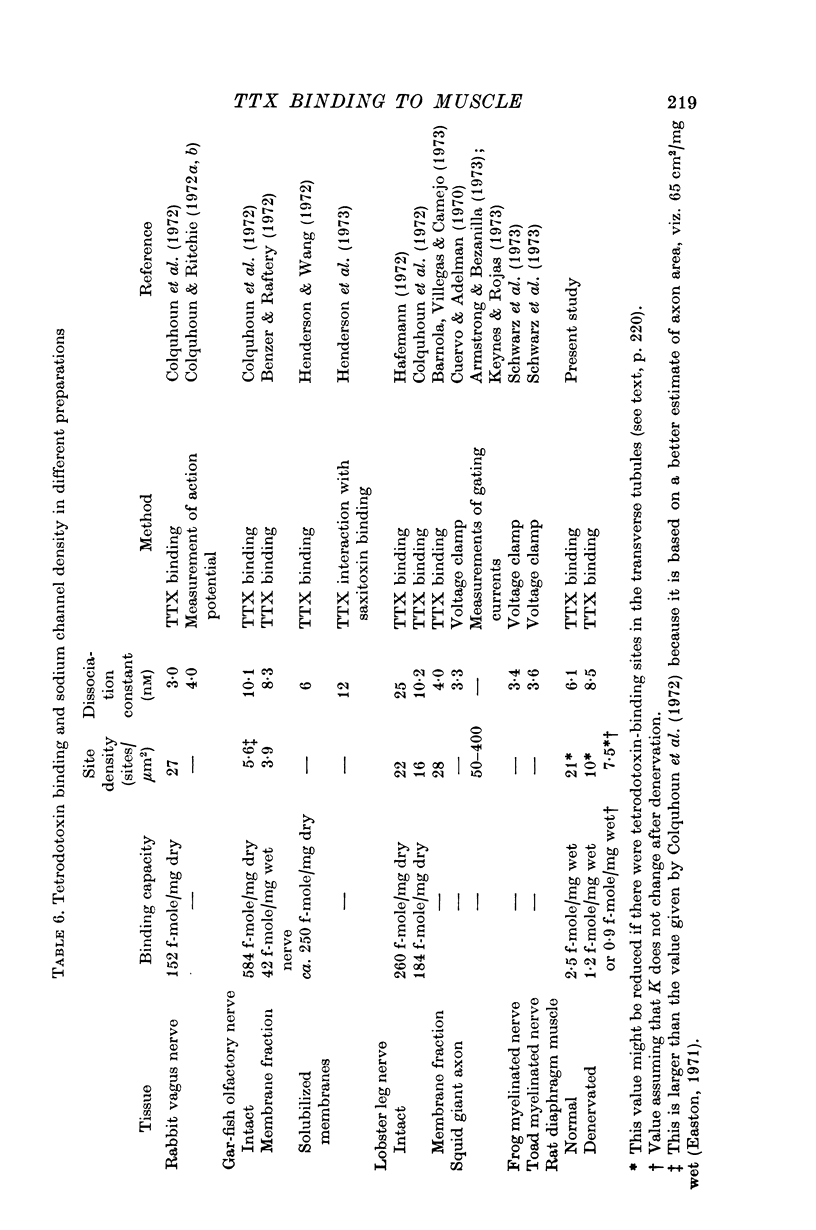
3. If the saturable component consisted of one-to-one binding of tetrodotoxin to sodium channels, the density of sodium channels would be about 21/μm2 of surface membrane, a figure similar to that found in other excitable membranes.
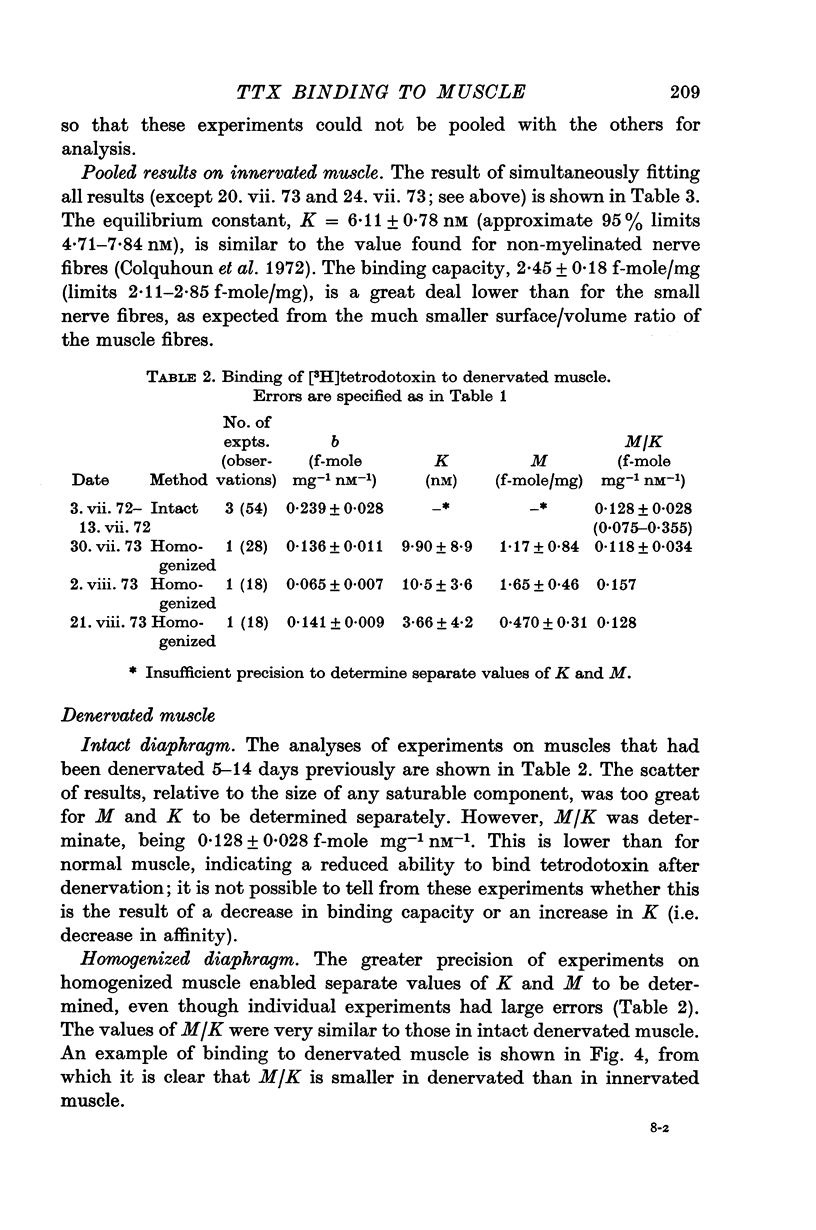
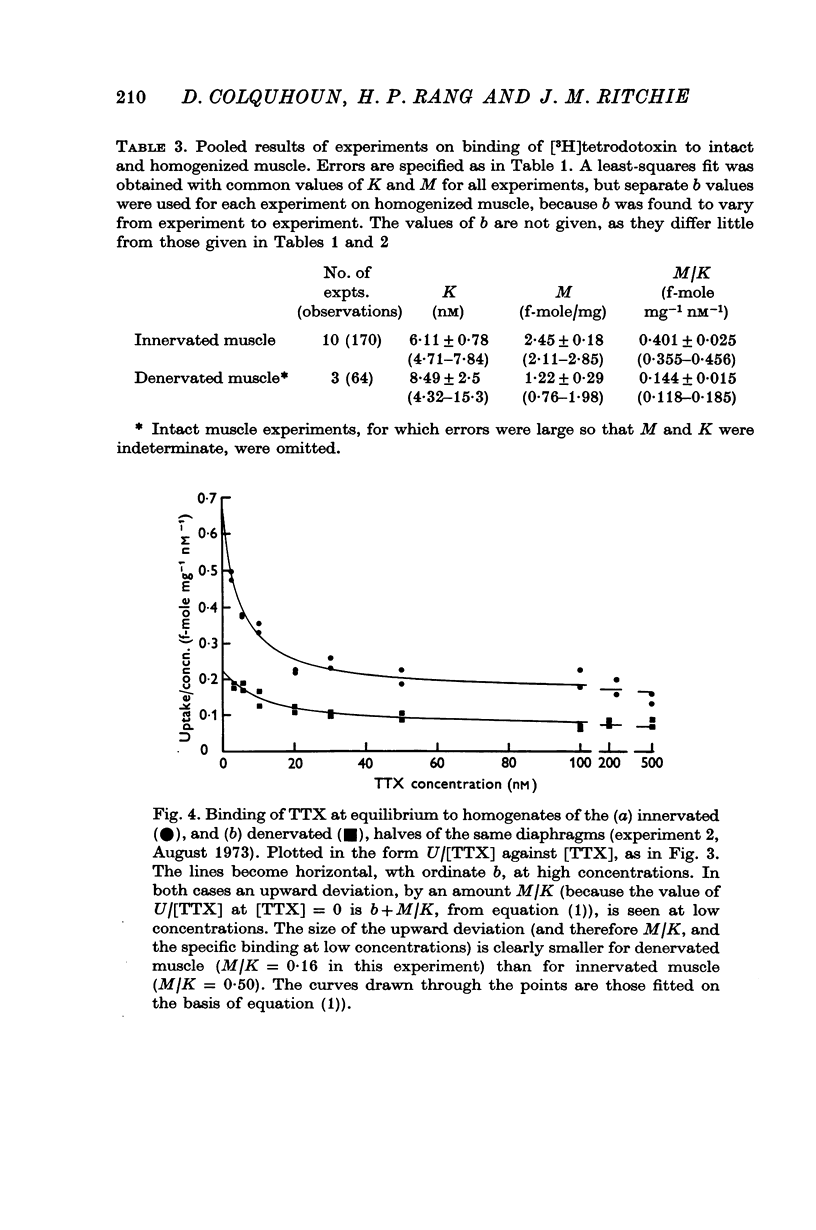
4. After denervation the specific tetrodotoxin binding, as measured by the ratio M/K, fell by a factor of 2·8. This change appeared to be due to a fall in binding capacity rather than a decrease in affinity.
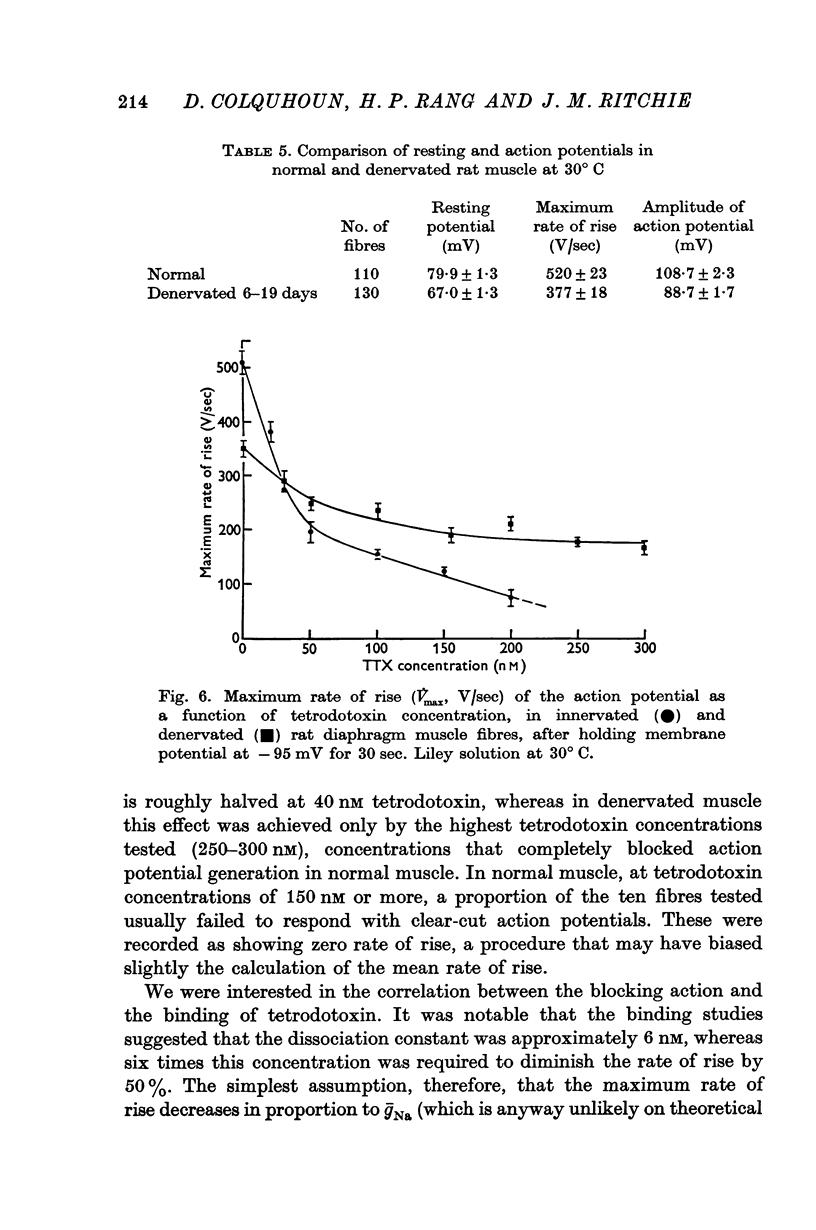
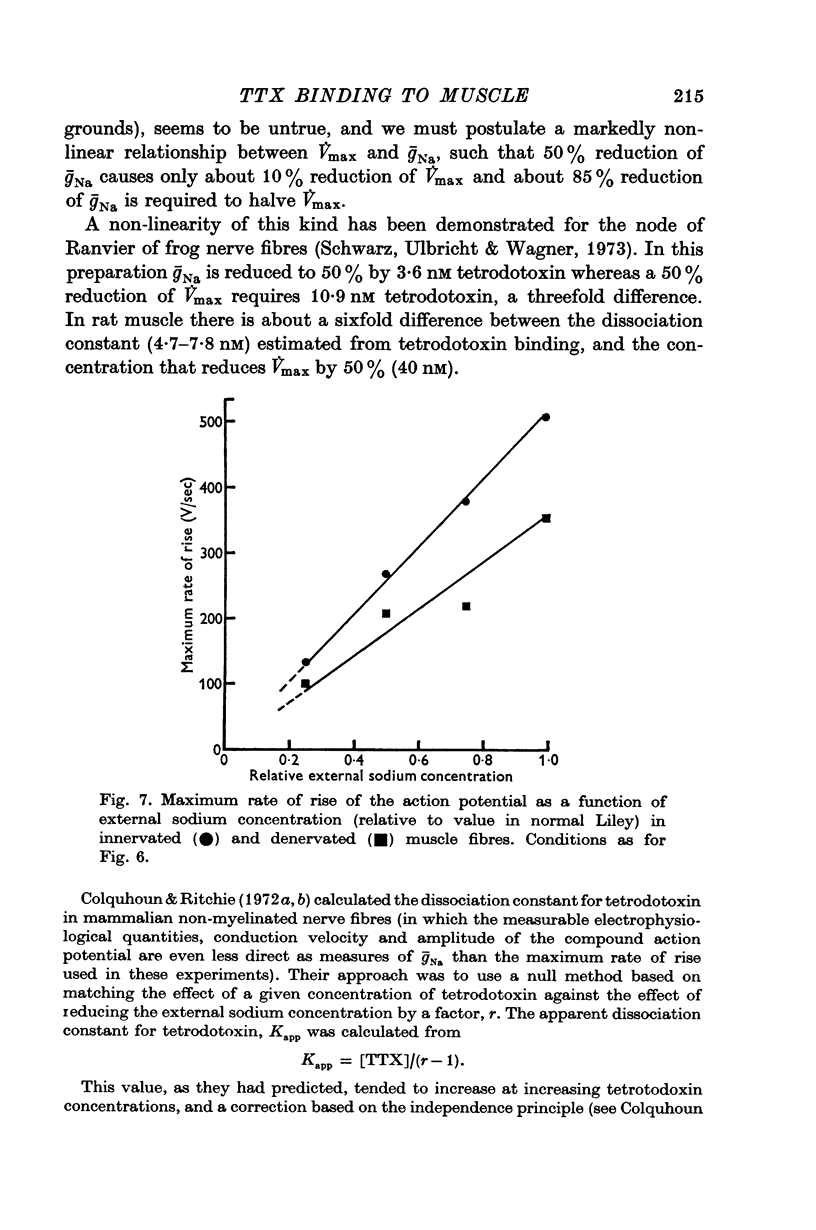
5. After denervation the maximum rate of rise of the action potential fell by 27% and became partially resistant to tetrodotoxin. The maximum rate of rise was at first reduced by tetrodotoxin in similar concentrations to those affecting normal muscle, but even large concentrations which completely blocked normal muscle only reduced the maximum rate of rise by a factor of about 2.
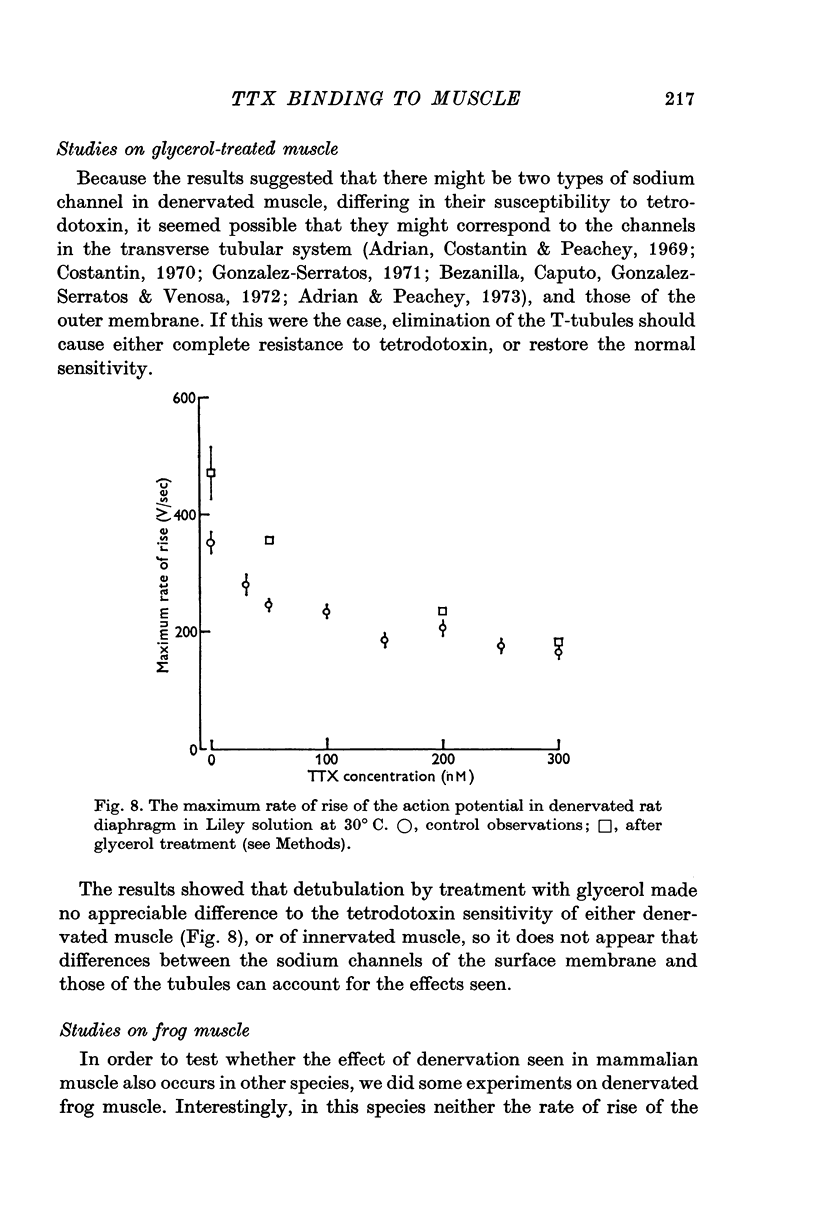
6. Detubulation with glycerol did not appreciably affect the tetrodotoxin sensitivity of normal or denervated muscle.
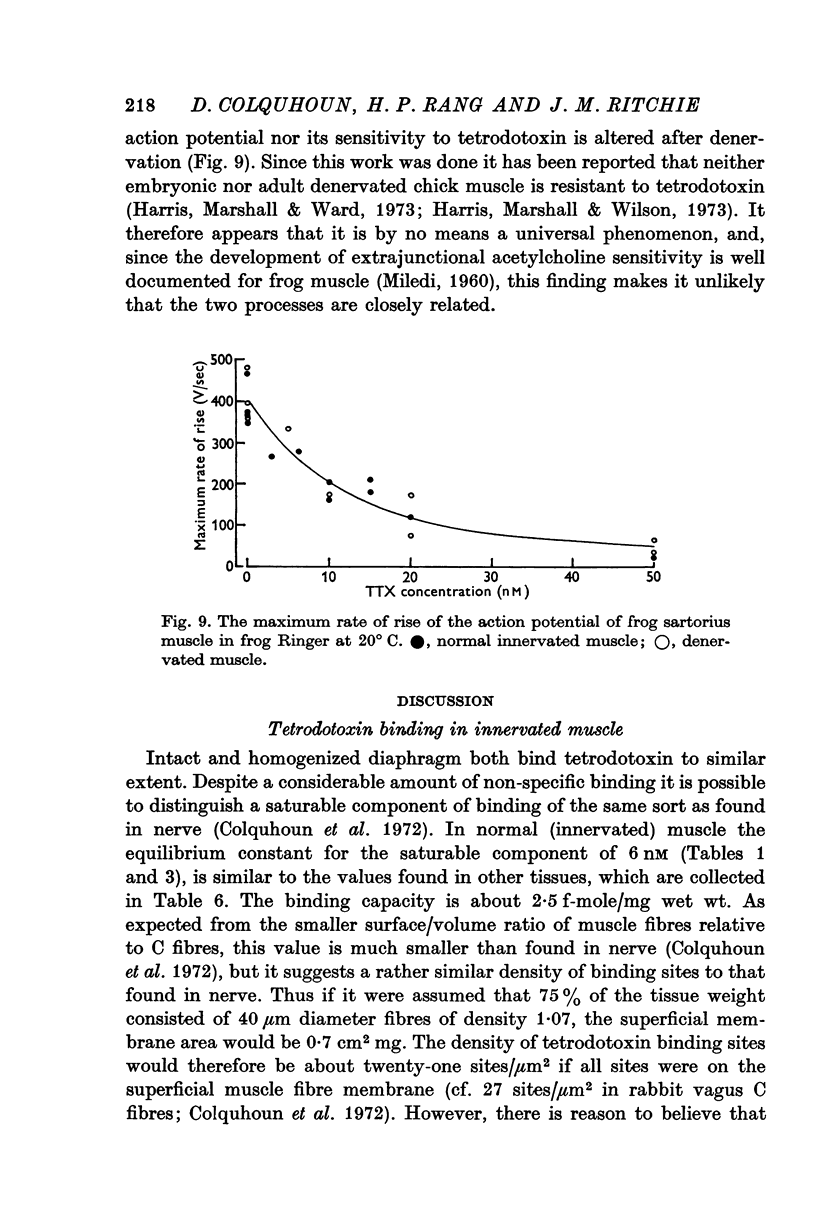
7. Tetrodotoxin resistance was not observed after denervation of the frog sartorius muscle.
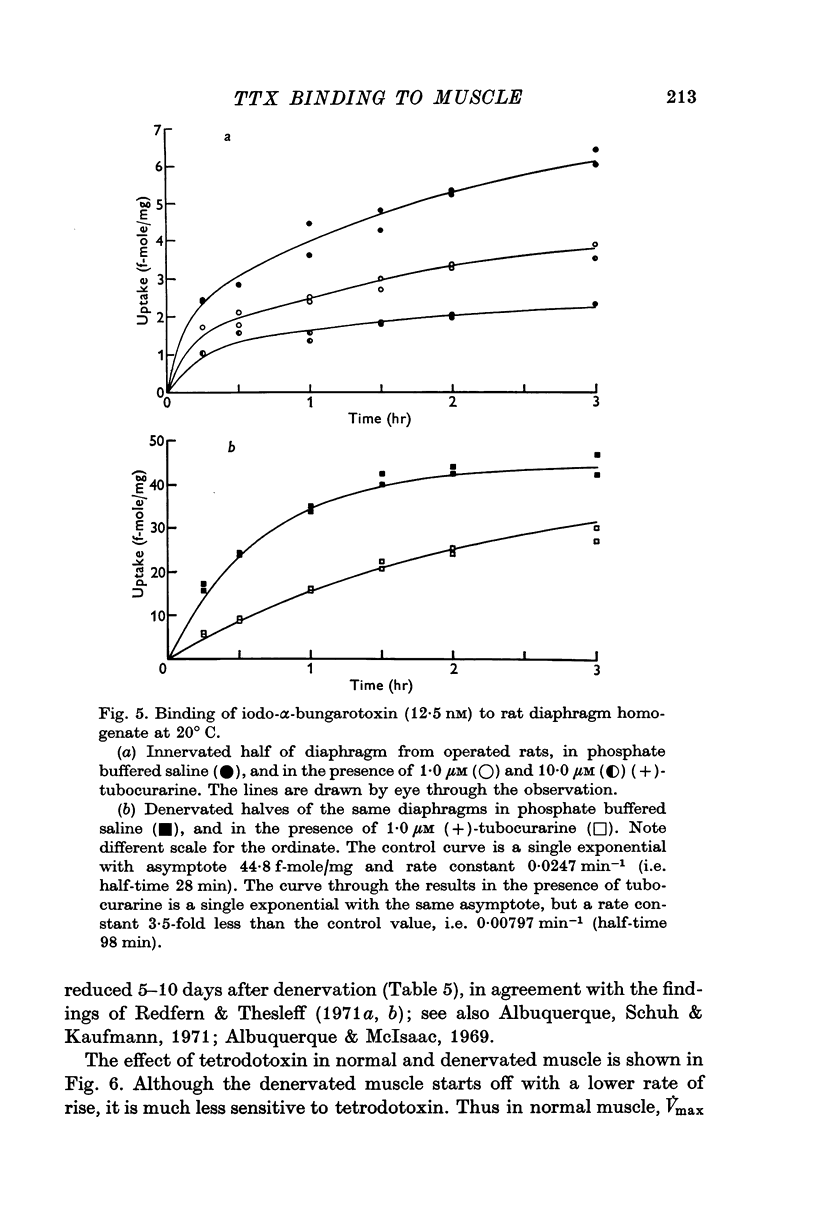
8. [125I]iodo-α-bungarotoxin binding amounted to 3·8 ± 0·7 f-mole/mg in innervated muscle and 44·5 ± 2·1 f-mole/mg in denervated muscle. Most of the uptake was inhibitable by (+)-tubocurarine.
9. The increase in the labelled bungarotoxin binding is much larger than the specific tetrodotoxin binding of innervated muscle, which renders implausible the possibility that the acetylcholine receptors which appear after denervation are related to the tetrodotoxin resistant-sodium channels.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):103–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., McIsaac R. J. Fast and slow mammalian muscles after denervation. Exp Neurol. 1970 Jan;26(1):183–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Warnick J. E. The pharmacology of batrachotoxin. IV. Interaction with tetrodotoxin on innervated and chronically denervated rat skeletal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Mar;180(3):683–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature. 1973 Apr 13;242(5398):459–461. doi: 10.1038/242459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnola F. V., Villegas R., Camejo G. Tetrodotoxin receptors in plasma membranes isolated from lobster nerve fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer T. I., Raftery M. A. Partial characterization of a tetrodotoxin-binding component from nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3634–3637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Caputo C., Gonzalez-Serratos H., Venosa R. A. Sodium dependence of the inward spread of activation in isolated twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):507–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chen T. F., Chuang S. T. N,O-di and N,N,O-tri ( 3 H) acetyl -bungarotoxins as specific labelling agents of cholinergic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):147–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Henderson R., Ritchie J. M. The binding of labelled tetrodotoxin to non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):95–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The binding of labelled tetrodotoxin and cobra toxin by the rat diaphragm. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;47(3):632P–633P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ritchie J. M. The interaction at equilibrium between tetrodotoxin and mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):533–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ritchie J. M. The kinetics of the interaction between tetrodotoxin and mammalian nonmyelinated nerve fibers. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 May;8(3):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):703–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo L. A., Adelman W. J., Jr Equilibrium and kinetic properties of the interaction between tetrodotoxin and the excitable membrane of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Mar;55(3):309–335. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. M. Garfish olfactory nerve: easily accessible source of numerous long, homogeneous, nonmyelinated axons. Science. 1971 May 28;172(3986):952–955. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3986.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B., Eisenberg R. S. Selective disruption of the sarcotubular system in frog sartorius muscle. A quantitative study with exogenous peroxidase as a marker. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):451–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Ionic conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. H. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin, and related substances: their applications in neurobiology. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1972;15:83–166. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Serratos H. Inward spread of activation in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;212(3):777–799. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafemann D. R. Binding of radioactive tetrodotoxin to nerve membrane preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):548–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Marshall M. W., Ward M. R. Action potential generation in singly and multiply innervated avian muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):51P–52P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Marshall M. W., Wilson P. A physiological study of chick myotubes grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):751–766. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Studies on tetrodotoxin resistant action potentials in denervated skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Nov;83(3):382–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Distribution and extrajunctional density in rat diaphragm after denervation correlated with acetylcholine sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):248–262. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):783–804. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Wang J. H. Solubilization of a specific tetrodotoxin-binding component from garfish olfactory nerve membrane. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4565–4569. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Pharmacological modifications of the sodium channels of frog nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):199–219. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. N. A lesion of the transverse tubules of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Roy G. Kinetic properties of the sodium current in striated muscle fibres on the basis of the Hodgkin-Huxley theory. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):419–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y., Nishiyama A. Actions of saxitoxin on peripheral neuromuscular systems. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(1):50–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):997–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M., Rojas E. The binding of tetrodotoxin to nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):235–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Blockade of acetylcholine receptors by cobra toxin: electrophysiological studies. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;8(6):623–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebs D., Narita K., Iwanaga S., Samejima Y., Lee C. Y. Purification, properties and amino acid sequence of -bungarotoxin from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Feb;353(2):243–262. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Narahashi T., Shaw T. I. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in nerve membrane? J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):99–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Chiu T. H., Wieckowski J., Barnard E. A. Types and locations of cholinergic receptor-like molecules in muscle fibres. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):3–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio241003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. A new kind of drug antagonism: evidence that agonists cause a molecular change in acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):394–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Ulbricht W., Wagner H. H. The rate of action of tetrodotoxin on myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis and Rana esculenta. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):167–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Sytkowski A. J., Nirenberg M. W. Acetylcholine receptors of muscle grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waud D. R. The rate of action of competitive neuromuscular blocking agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Oct;158(1):99–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


