Abstract
1. The Na, K, Ca, and Mg contents were determined in longitudinal smooth muscles of the guinea-pig ileum incubated in various physiological solutions with or without ouabain or in a solution containing LaCl3 10 mM instead of CaCl2.
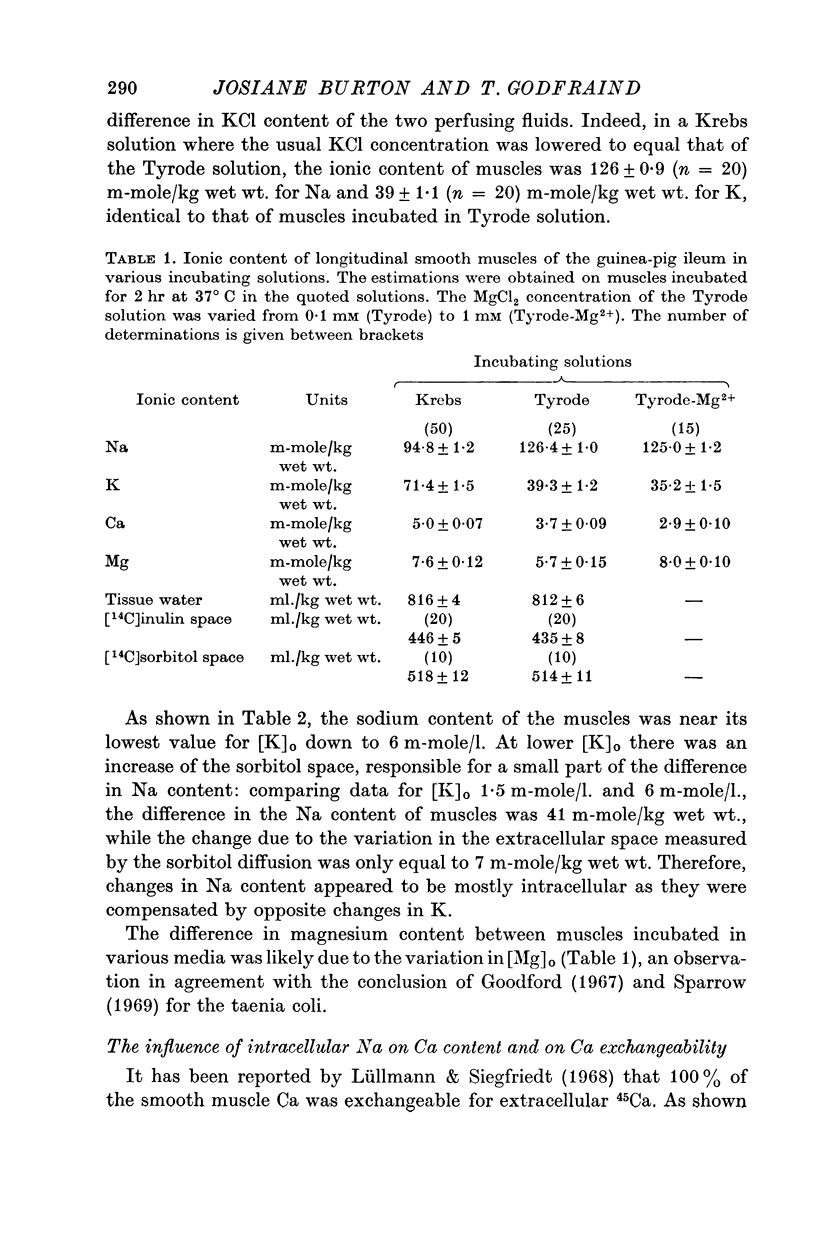
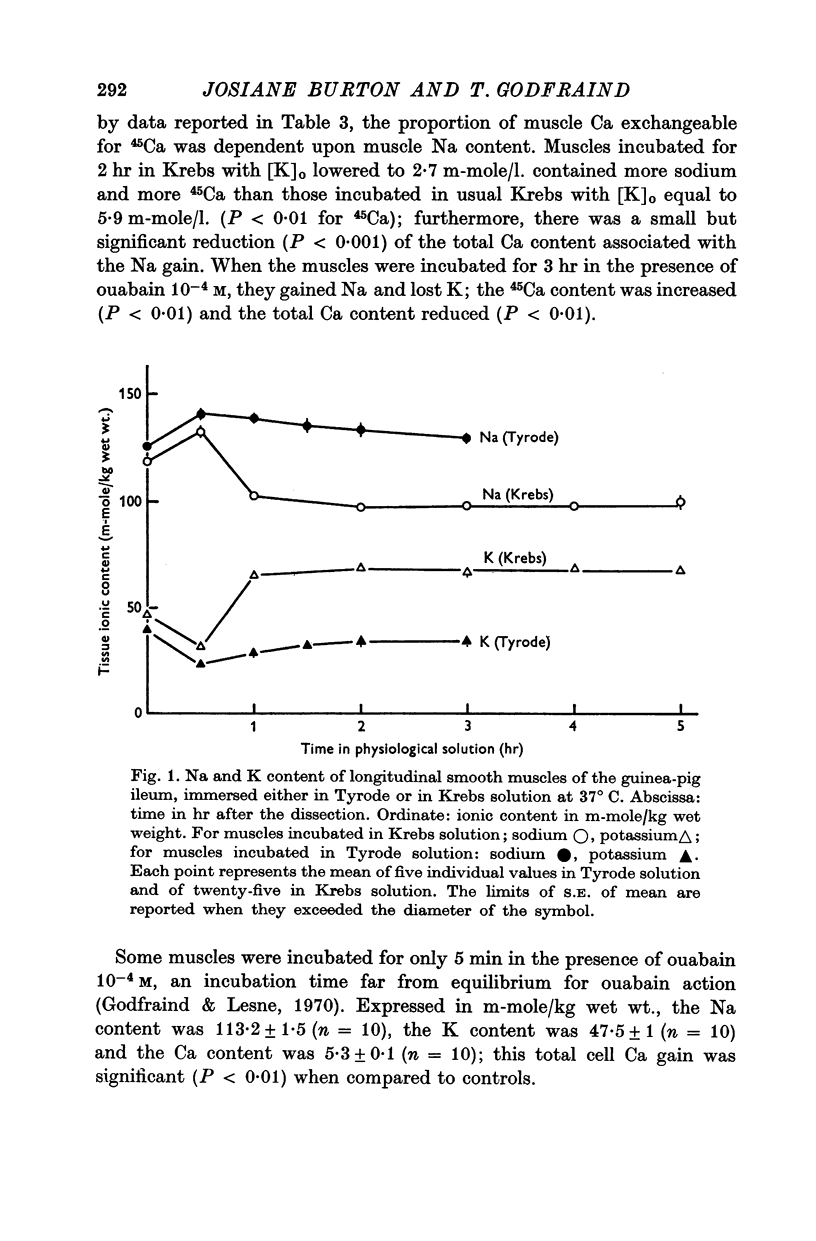
2. The Na and K contents were dependent upon the K concentration of the physiological solution. A decrease in [K]o below 6 m-mole/l. increased tissue Na.
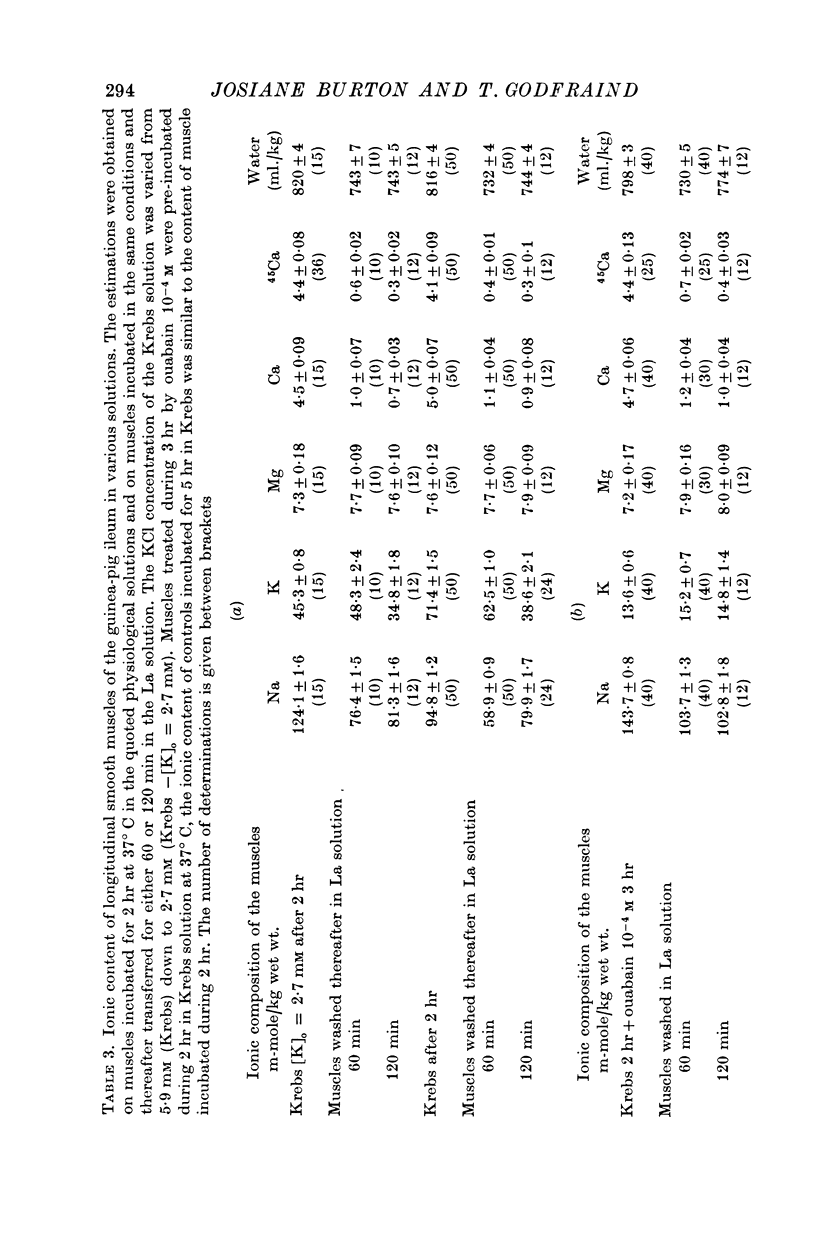
3. A rise in [Na]i was followed by an increase of total cell Ca preceding a secondary decrease of total Ca, as well as by an increased 45Ca content occurring even when total Ca was decreased.
4. Muscles washed in the lanthanum solution contained less Ca and Na than those incubated in the physiological solution. The Mg content was not significantly modified in the presence of La.
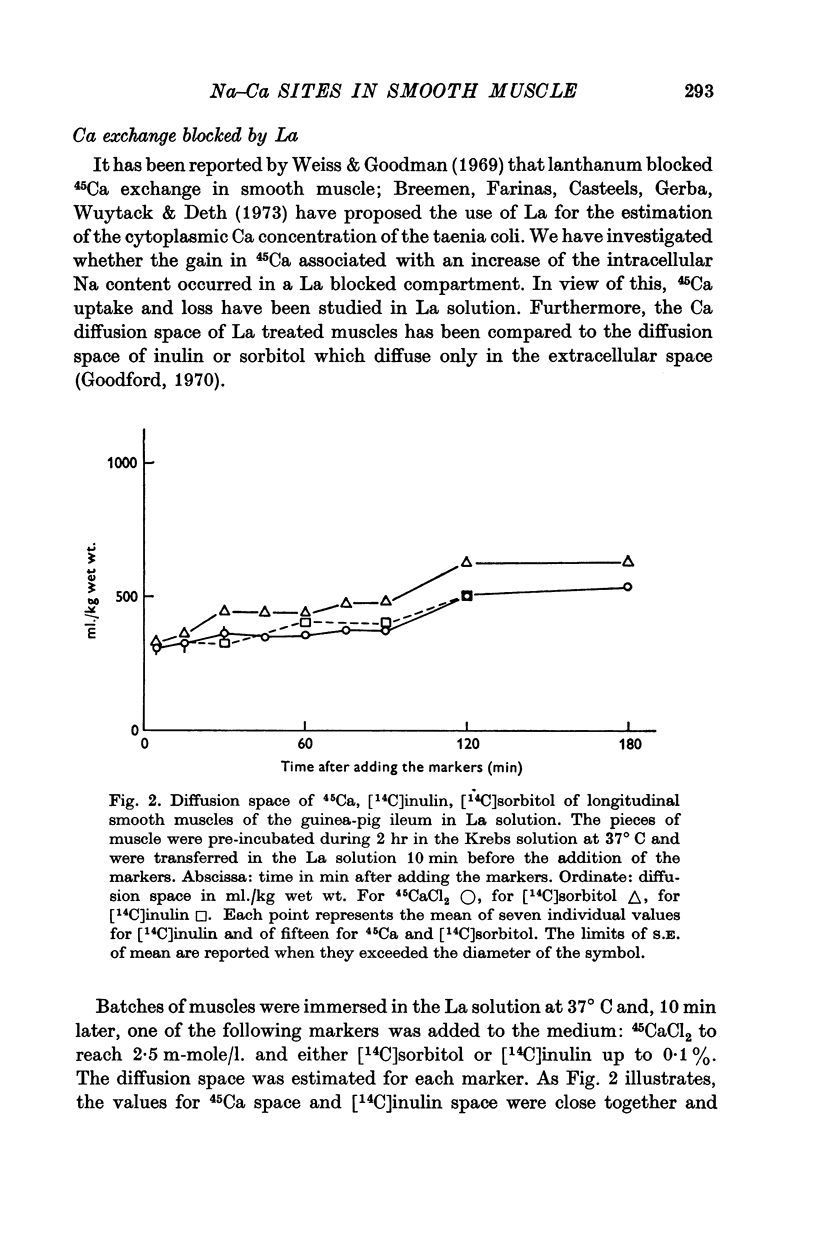
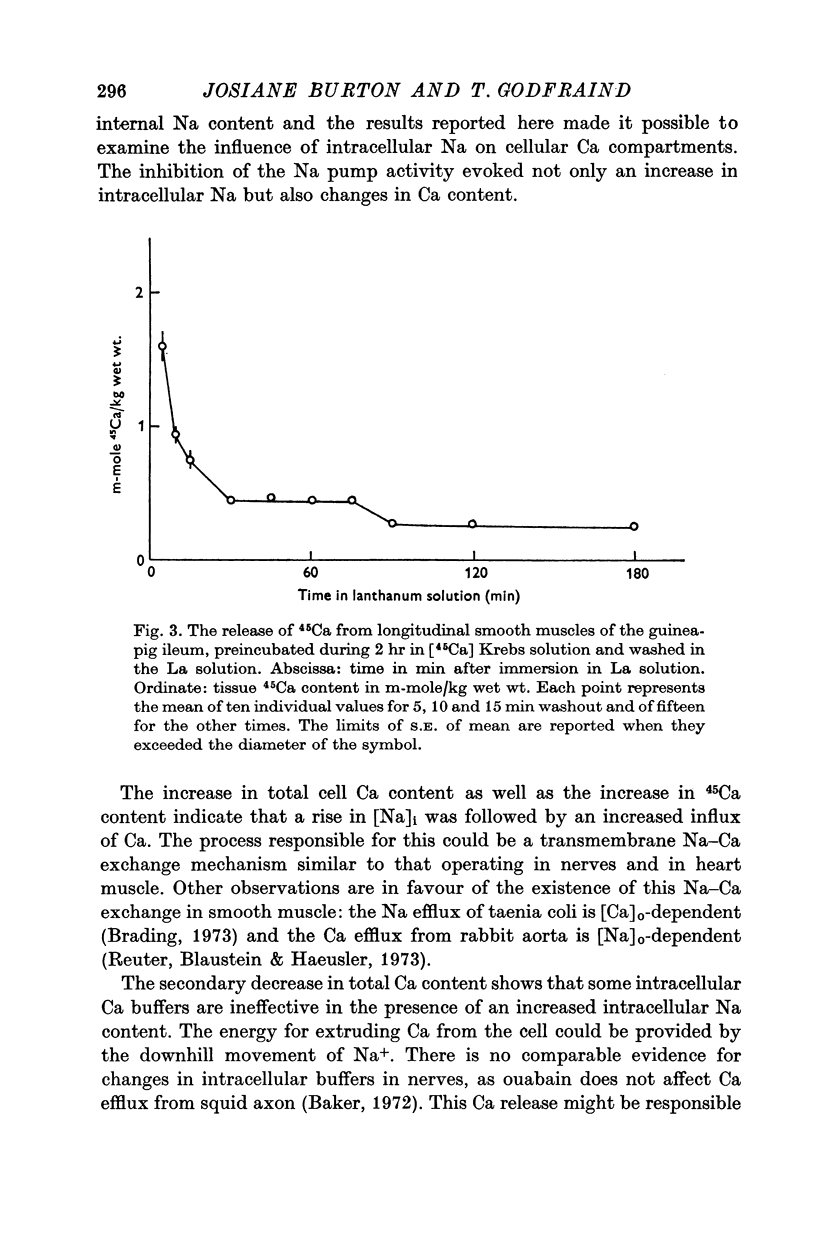
5. In the La solution, the 45Ca diffusion space was not different from the [14C]inulin diffusion space, indicating that there was no Ca entry within the cell nor Ca binding at superficial sites. 45Ca content of preloaded muscles decreased; this decrease was blocked after 30 min washout in the La solution: this arrest lasted a further 45 min.
6. The cell Ca fraction displaced by increased [Na]i originated from a Ca compartment which was not blocked by La.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P. Sodium-dependent uptake of calcium by crab nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 3;150(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODFRAIND T., GODFRAIND-DE BECKER A. [Rhythmic activity of the isolated intestine induced by the combination of digitoxin and calcium]. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1962 Jul 1;138:169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFORD P. J., HERMANSEN K. Sodium and potassium movements in the unstriated muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1961 Oct;158:426–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase and cation transport. Br Med Bull. 1968 May;24(2):165–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Lesne M. The uptake of cardiac glycosides by intestinal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig in relation to digitalis receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;38(2):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb08522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. The calcium content of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalix P. Uptake and release of calcium in rabbit vagus nerve. Pflugers Arch. 1971;326(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00586791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüllmann H., Siegfriedt A. Uber den Calcium-Gehalt und den 45Calciumaustausch in Längsmuskulatur des Meerschweinchendünndarms. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;300(2):108–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer C. J., van Breemen C., Casteels T. The action of lanthanum and D600 on the calcium exchange in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig Taenia coli. Pflugers Arch. 1972;337(4):333–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00586650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow M. P. Interaction of 28Mg with Ca and K in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):19–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G. B., Goodman F. R. Effects of lanthanum on contraction, calcium distribution and Ca45 movements in intestinal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):46–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Farinas B. R., Casteels R., Gerba P., Wuytack F., Deth R. Factors controlling cytoplasmic Ca 2+ concentration. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):57–71. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


