Abstract
1. The onset and time course of baroreceptor inhibition of pre- and post-ganglionic sympathetic reflex activity has been examined in the anaesthetized cat.
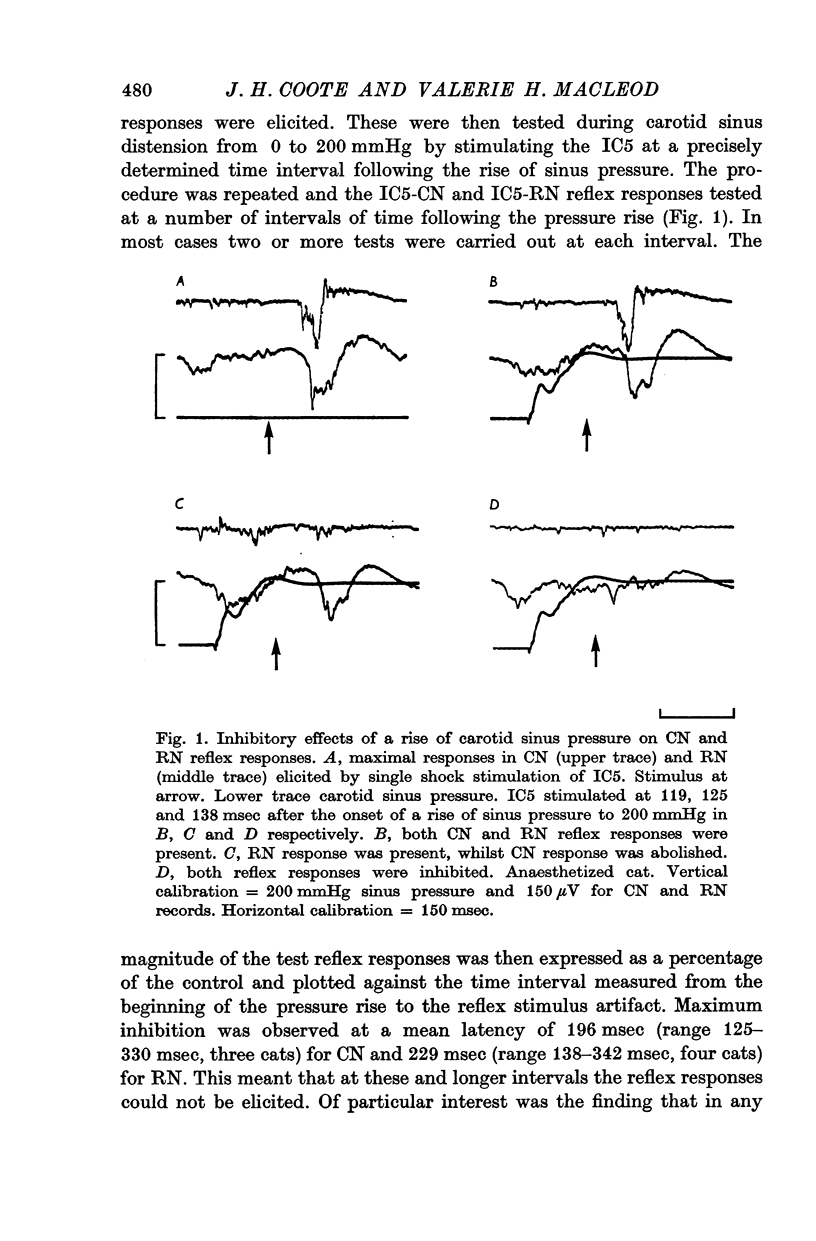
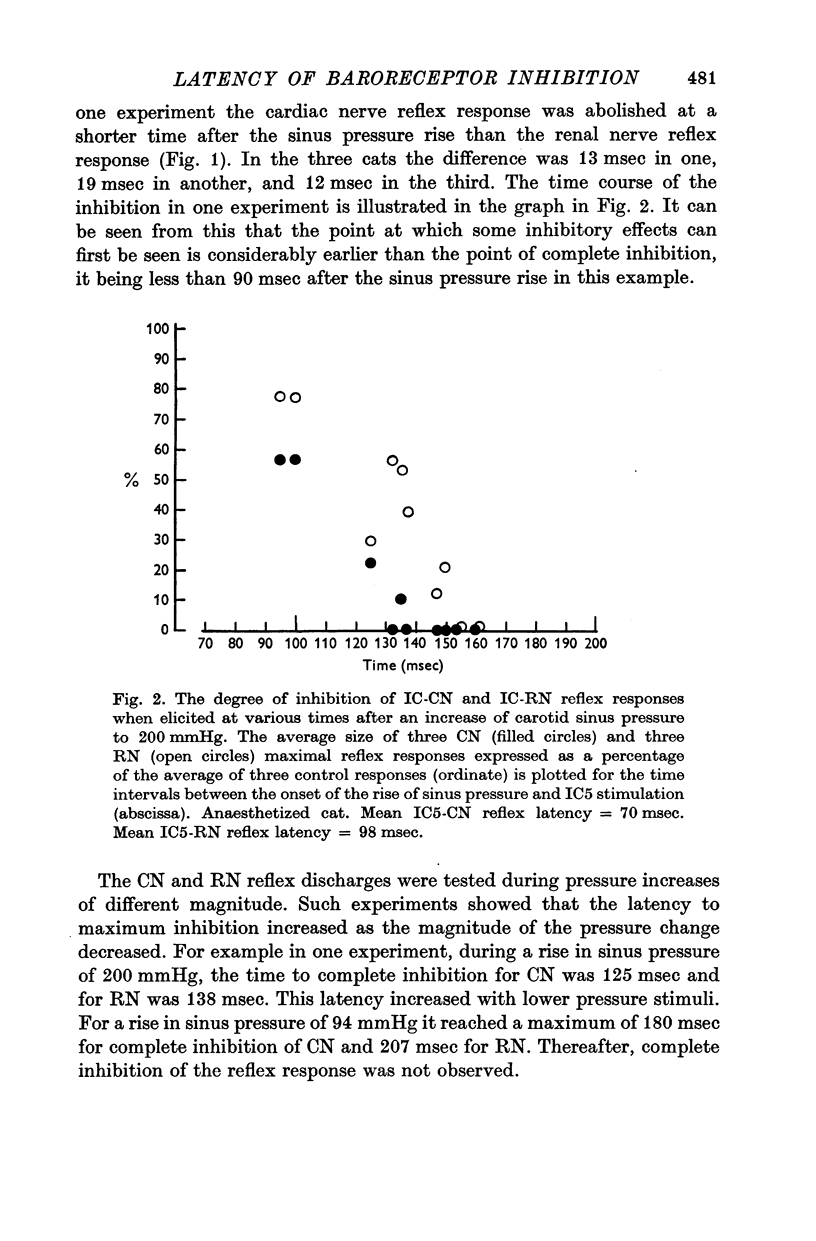
2. The shortest time to the onset of inhibition of an intercostal evoked reflex response in cardiac and renal nerve was less than 90 msec following a rise in pressure in a carotid sinus blind sac, and around 55 msec following stimulation of the ipsilateral sinus nerve. The cardiac nerve response was completely inhibited before the renal nerve response.
3. Because of the long delays in the somato-sympathetic reflex pathway it is argued that these minimum times will be much less than the real central delay of baroreceptor inhibition. These were estimated by adding on the central times for the somato-sympathetic reflexes to give latencies of 94-143 msec for the inhibition.
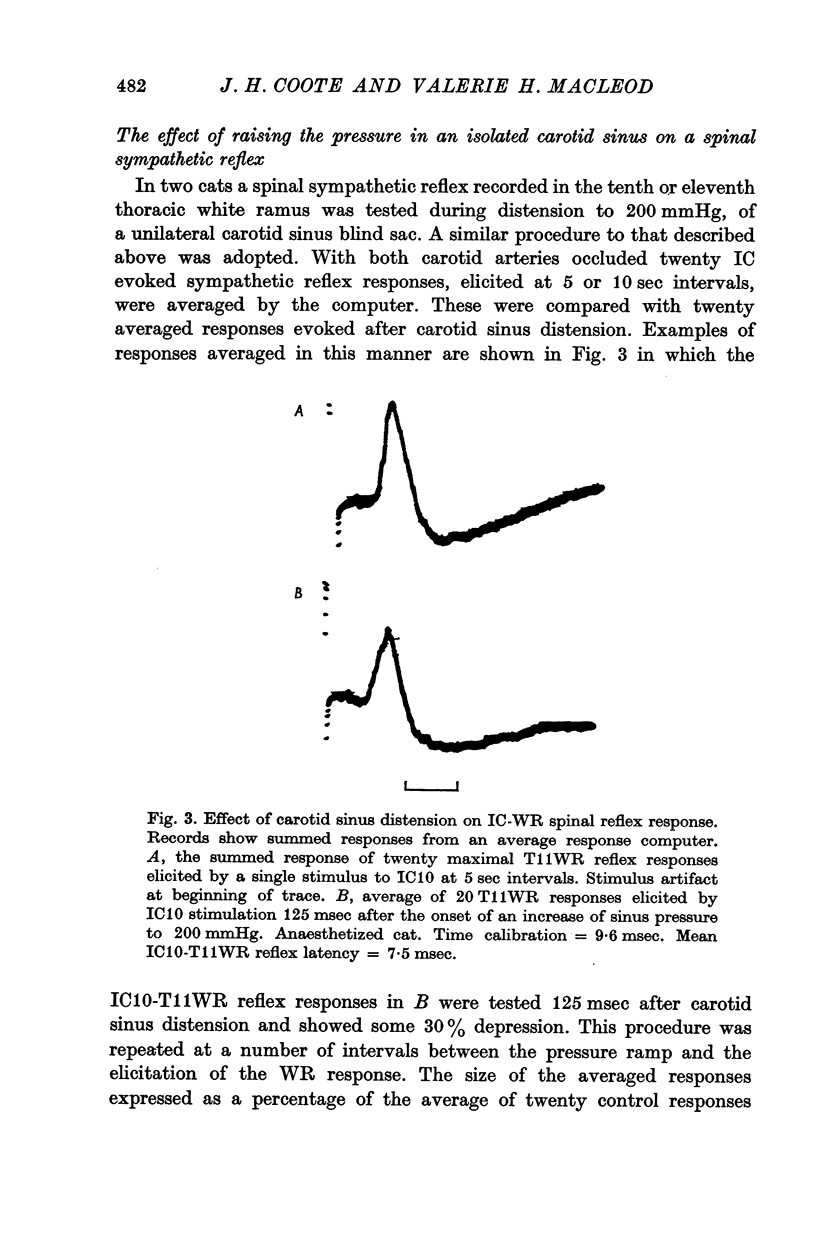
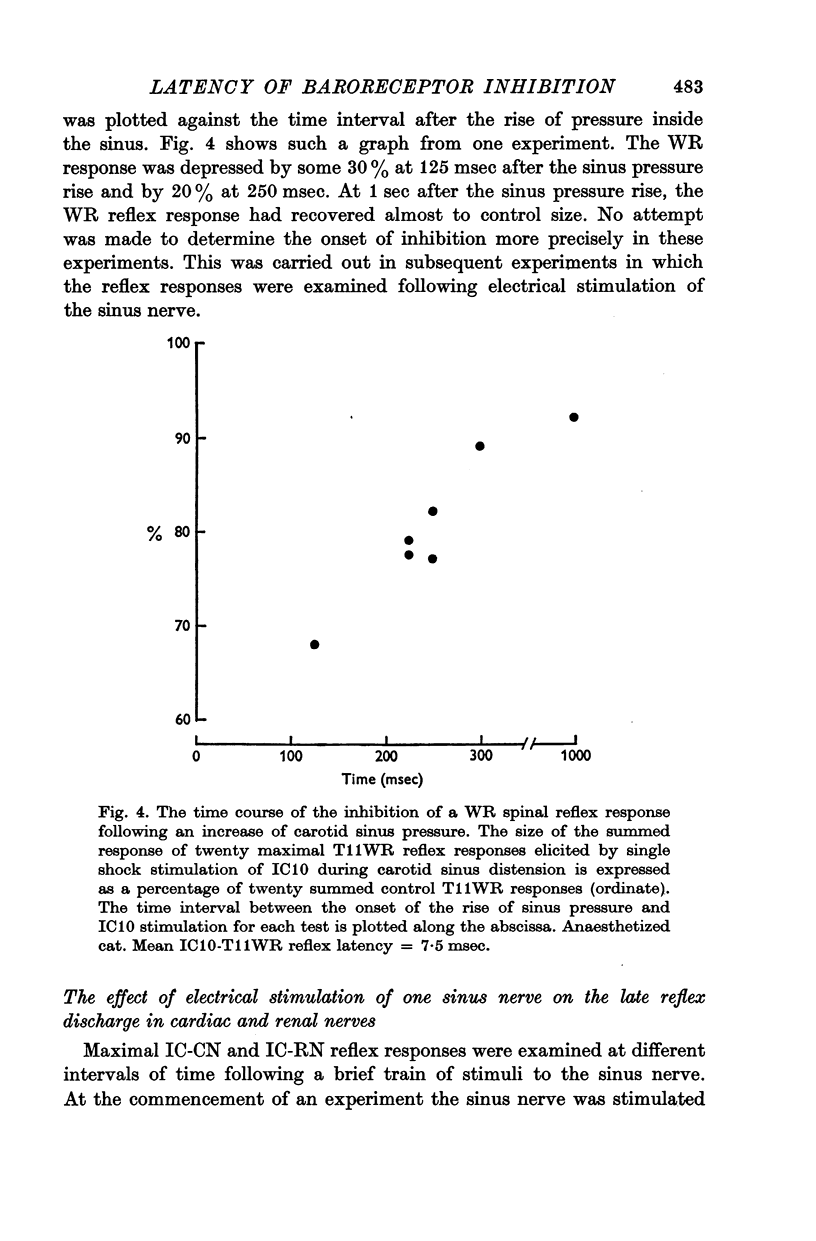
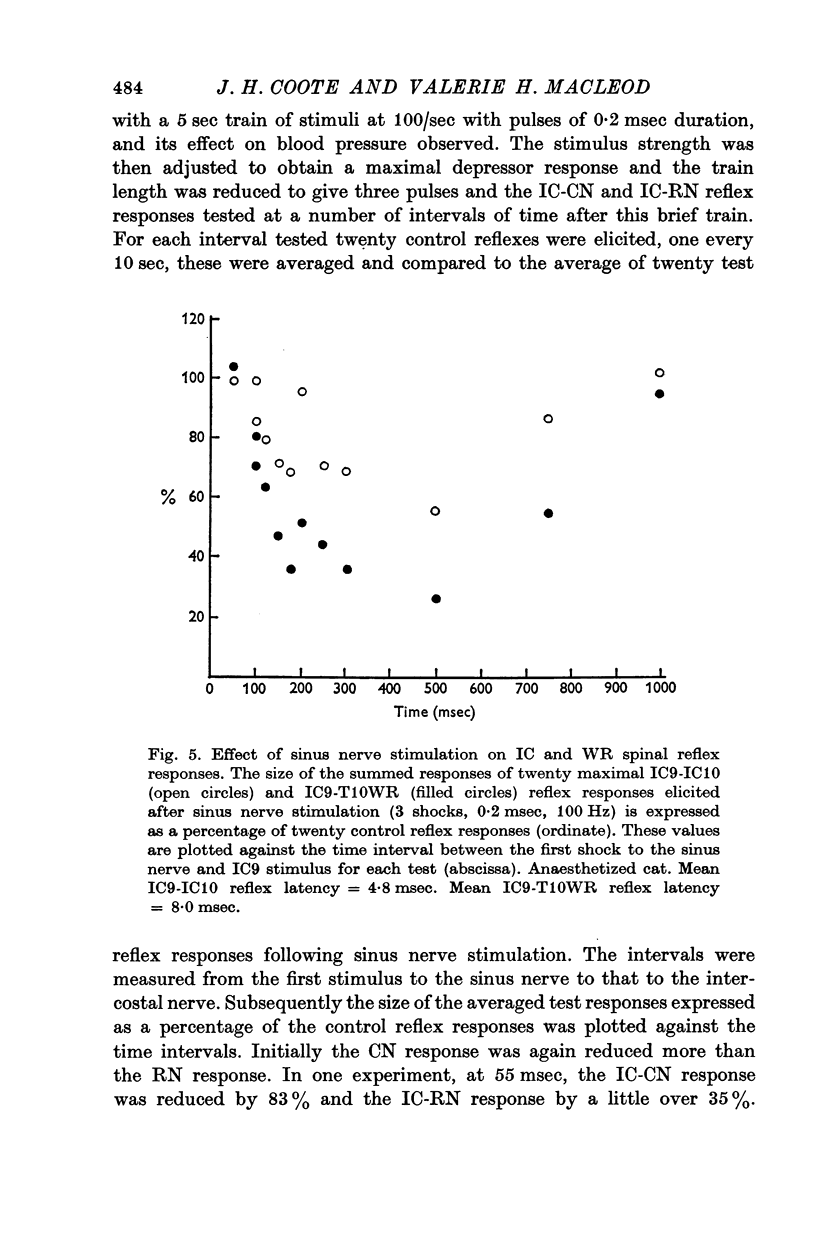
4. A spinal sympathetic reflex was inhibited by 30-75% following a rise in pressure in a carotid sinus blind sac or sinus nerve stimulation. The minimum time for this inhibition was around 100 msec.
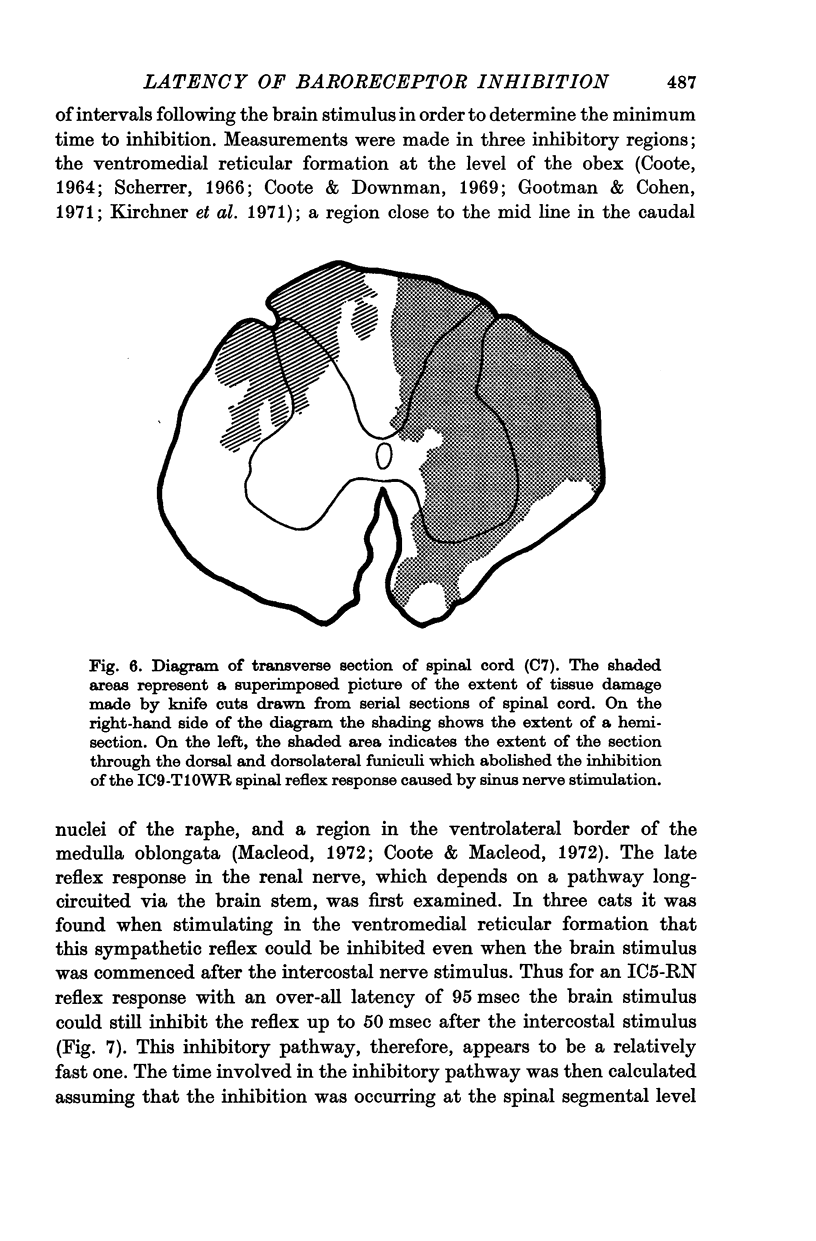
5. The baroreceptor inhibition of the spinal sympathetic reflex was abolished following section of a restricted region in the dorsolateral part of the lateral funiculus of the cervical spinal cord.
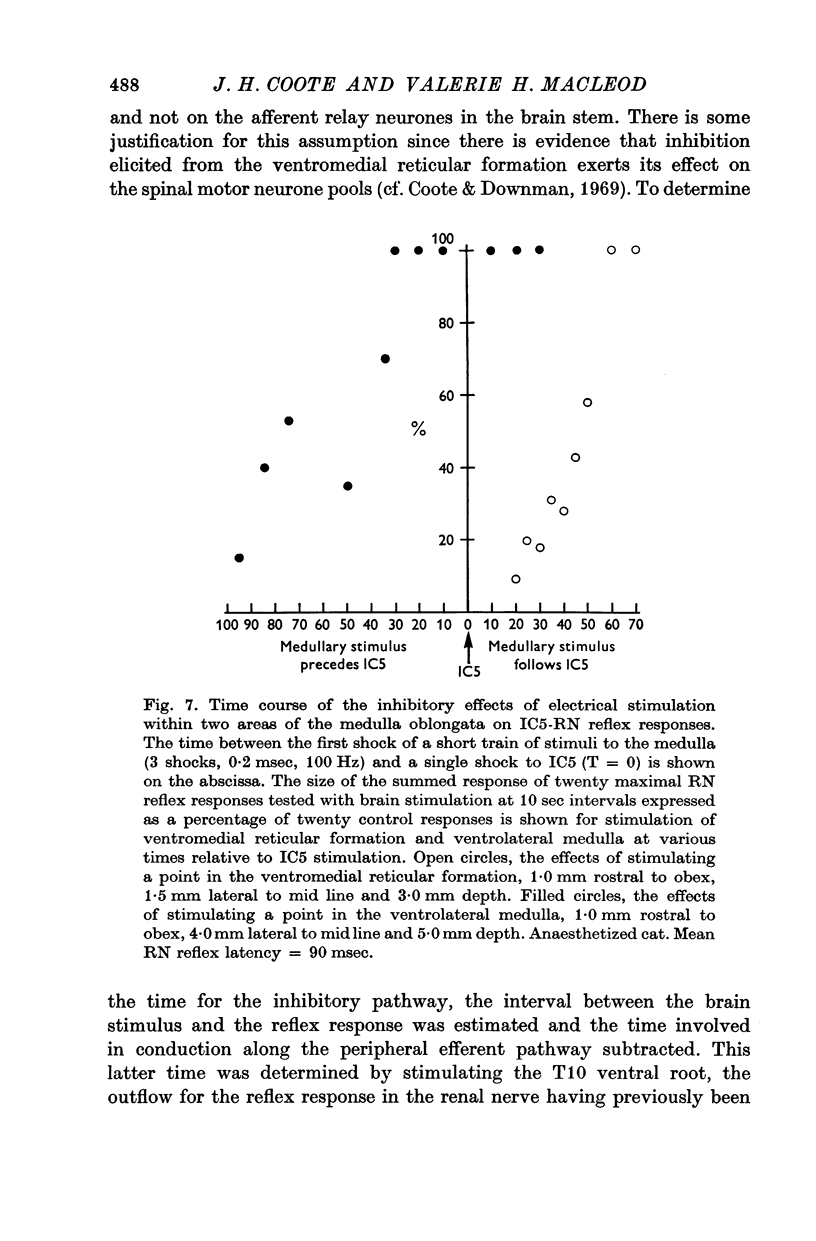
6. Both pre- and post-ganglionic reflexes could be inhibited when stimulating within three regions of the medulla oblongata. The latency to inhibition elicited from the ventromedial reticular formation was short, some 5-30 msec, whereas that elicited from a ventrolateral region or the mid line raphe nucleus was long, some 90-160 msec.
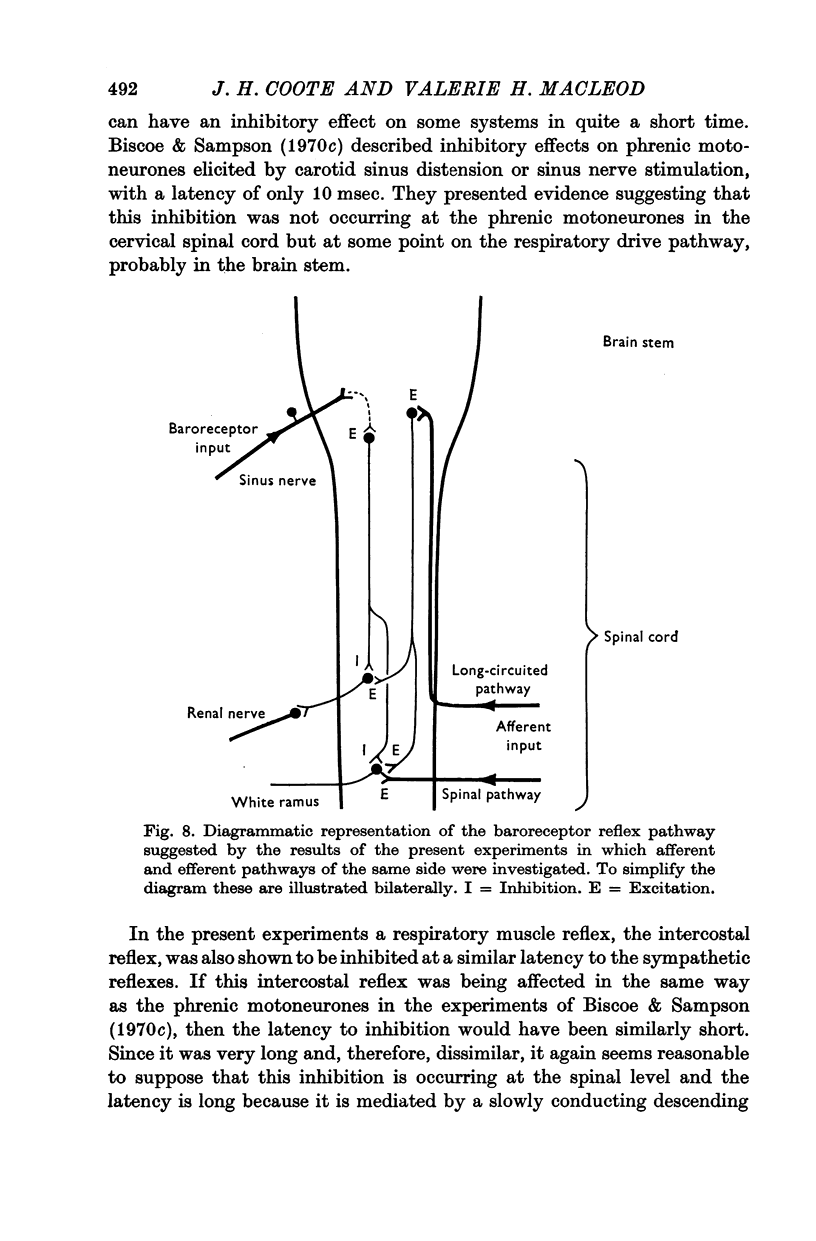
7. The possibility is discussed that the baroreceptor inhibition of both the pre- and post-ganglionic reflexes examined in this study is occurring at the spinal level via a pathway from either the raphe nuclei or ventrolateral medulla.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEACHAM W. S., PERL E. R. CHARACTERISTICS OF A SPINAL SYMPATHETIC REFLEX. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;173:431–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN V. W., WANG G. H. Suprasegmental inhibition of an autonomic reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Nov;19(6):564–572. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.6.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Sampson S. R. An analysis of the inhibition of phrenic motoneurones which occurs on stimulation of some cranial nerve afferents. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):375–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Sampson S. R. Field potentials evoked in the brain stem of the cat by stimulation of the carotid sinus, glossopharyngeal, aortic and superior laryngeal nerves. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):341–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Sampson S. R. Responses of cells in the brain stem of the cat to stimulation of the sinus, glossopharyngeal, aortic and superior laryngeal nerves. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):359–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Downman C. B. Central pathways of some autonomic reflex discharges. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):714–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Downman C. B. Supraspinal control of reflex activity in renal nerves. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):161–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Macleod V. H. The influence of bulbospinal monoaminergic pathways on sympathetic nerve activity. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):453–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Macleod V. H. The possibility that noradrenaline is a sympatho-inhibitory transmitter in the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):44P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crill W. E., Reis D. J. Distribution of carotid sinus and depressor nerves in cat brain stem. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):269–276. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebber G. L., Taylor D. G., Weaver L. C. Electrophysiological studies on organization of central vasopressor pathways. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):470–481. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootman P. M., Cohen M. I. Evoked splanchnic potentials produced by electrical stimulation of medullary vasomotor regions. Exp Brain Res. 1971 Jul 26;13(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00236427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. H., Heffron P. F. Studies upon the relationship between baroreceptor and sympathetic activity. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Jan;53(1):23–32. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M., Spyer K. M. Participation of the anterior hypothalamus in the baroreceptor reflex. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):271–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illert M., Seller H. A descending sympathoinhibitory tract in the ventrolateral column of the cat. Pflugers Arch. 1969;313(4):343–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00593958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUVER H., BARRERA E. A method for the combined staining of cells and fibers in the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1953 Oct;12(4):400–403. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195312040-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn N., Mills E. Centrally evoked sympathetic discharge: a functional study of medullary vasomotor areas. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):339–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kezdi P., Geller E. Baroreceptor control of postganglionic sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):427–435. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner F., Sato A., Weidinger H. Bulbar inhibition of spinal and supraspinal sympathetic reflex discharges. Pflugers Arch. 1971;326(4):324–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00586996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. Termination and secondary projections of carotid sinus nerve in the cat brain stem. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):142–153. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. The role of the solitary and paramedian reticular nuclei in mediating cardiovascular reflex responses from carotid baro- and chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):525–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROUT B. J., COOTE J. H., DOWNMAN C. B. SUPRASPINAL INHIBITION OF A CUTANEOUS VASCULAR REFLEX IN THE CAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Aug;207:303–307. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Keck W., Seller H. The course of inhibition of sympathetic activity during various patterns of carotid sinus nerve stimulation. Pflugers Arch. 1970;317(2):110–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00592496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer H. Inhibition of sympathetic discharge by stimulation of the medulla oblongata in the rat. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 1966;29(1):56–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01226707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller H., Illert M. The localization of the first synapse in the carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex pathway and its alteration of the afferent input. Pflugers Arch. 1969;306(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00586608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


